Liberals vs. Conservatives Packet
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
liberalism
began under leadership of Jefferson and Jackson
favored less involved gov.
oppossed Bank and argued for power to the people
today's liberalism
racial equality, foreign aid, lower military spending
active gov.
lessen gap between rich and poor
conservatism
began under leadership of Hamilton, Adams (Federalists)
believed in right to rule for elected few
strong central gov.
today's conservatism
free enterprise and private property rights
less government involvement in economy
want to limit social welfare programs
want to conserve traditions
New Deal
offered major social welfare programs during the Great Depression
boost in gov. programs called for increased gov. role
very liberal
conservative attitudes
tradition, conformity, authority
liberal attitudes
individuality, experimentation, nonconformity
1960s liberals
sexual revolution, drug experimentation, rejection of materialism, civil rights, distrust of gov. and police, Vietnam War all shaped liberal leanings
1960s conservatives
sexual revolution, drug experimentation, rejection of materialism, civil rights, distrust of gov. and police, Vietnam War led to strong conter-reaction for traditional values, respect for authority, laissez-faire capitalism, patriotism
Gallop Poll
37% Moderate
25% Liberal
36% Conservative
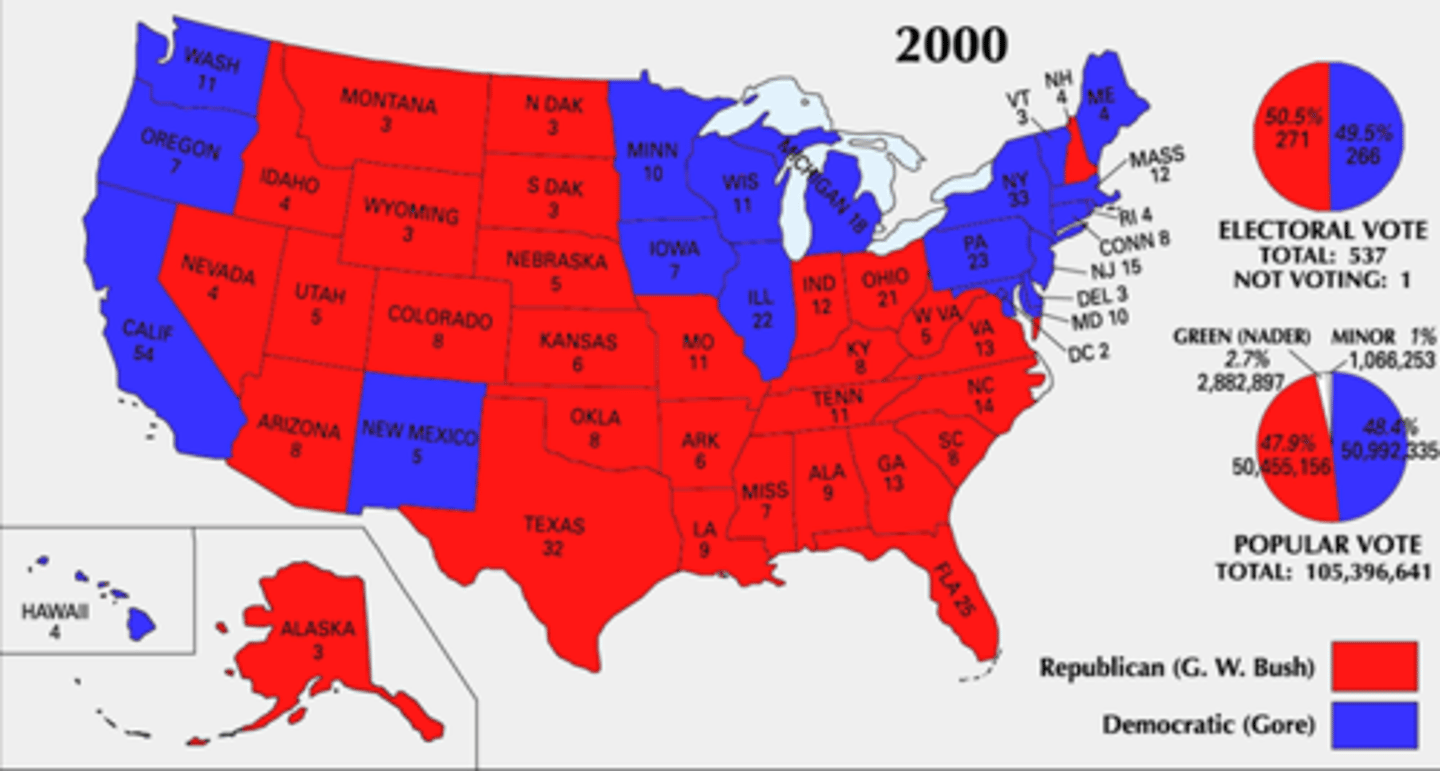
2000 election
red states (pro-Bush) were in heartland while blue states (pro-Gore) were on each coast
political ideology scale
communist -> socialist -> liberals -> moderate -> conservative -> reactionary -> fascists
political culture
america's shared beliefs, values, and norms concerning the ways political and economic life should be carried out
Tocqueville's 6 core values of american political culture
liberty, democracy, equality, civic duty, individual responsibility, rule of law
trust in government
steadily declined since the end of the 1950s
because of watergate and vietnam
political socialization
life long process through which an individual acquires their political opinions
family
#1 factor of political socialization
religion
factor of political socialization
catholics are more liberal on economic issues than social ones
protestant families are more conservative and Jewish families are more liberal
cafeteria catholics
put one single issue over the whole party
history of religion in politics
poor jewish and catholic immigrants sided with democrats but as status improved, their support decreased
Jews have always put a bigger emphasis on social justice and Protestants have on personal morals
Christian Coalition
grassroots organization with leader Pat Robertson
Republican and very conservative right
gender gap
since the 60s, men have become more republican and women have become more democrat
education
teachers teach children to be good citizens
college has a liberalizing affect
opinion leaders
any person who has an influence on what others think
mass media
Television, radio, newspapers, magazines, the Internet, and other means of popular communication
influence political opinion
cleavages in public opinions
factors that cause division
religion
income
race
gender
rust belt
Great Lake states with many factory workers and unions
tend to be liberal
solid south
when south was fully democrat
up until Civil Rights movement
elections
when a candidate wins an election they win a mandate
public has permitted them to act on their promises
interest groups
private organizations whose members share certain views and work to change public opinion
polls
survey to get information or opinions by asking people questions
polsters
people who take polls
push polls
polls that ask leading questions
straw vote
when questions are asked to a large number of people
exit polls
when people are asked questions as they leave from voting
scientific polls
first used in 1930s
examples are Gallop Poll and Harris Survey
bandwagon effect
voters vote for leaders in polls in order to support a winner
negative of polls
franchise
right to vote
electorate
those eligible to vote
over 210 million
setting suffrage requirements
reserved power but states can't withhold suffrage from voters protected in the Constitution
1789
suffrage expanded to white male property owners
1850
suffrage expanded to all adult white males
1870
suffrage expanded to all adult males
15th amendment
1920
suffrage expanded to all men and women over 21
20th amendment
1960s
Civil rights movement strengthened voting rights of African Americans
23rd Amendment gave DC 3 electoral votes
1971
suffrage expanded to everyone over 18
26th amendment
requirements to vote
must be citizen, must be a resident of the state (most require 28-30 days), 18 years old, registration
Motor Voter Law
register to vote when you update your license (1995) to make registration easier
Literacy
Voting Rights Acts prohibited it being a requirement to vote
24th amendment
outlawed poll taxes
mental institution patients
if deemend not competent, may not vote
incarcerated felons
have limited voting rights
most likely to vote
old
rich
churchgoers
suburban
marries
long-term residents
women
educated
white-collar
Ballot Fatigue
people go to polls but don't mark the entire ballot
further down ballot, less likely a vote is cast
reasons people don't vote
Ballot Fatigue, bad weather, west coast residents hear early returns and think their votes don't matter, lack of interest, not registered
factors for people who do vote
place in society (income, job, gender, ethnicity, religion, education, town, family)
loyalty to a party
if voters like candidates
how much voters care about the issues
straight ticket voters
voting for candidates of the same party
split ticket voters
voting for candidates of different parties for various offices in the same election
same day registration
result in increased voter participation
one-party systems
one party controls the government my law
voter fraud and patronage often keep the dominant power in change
(Russia, China, Iran, Mexico)
Two-Party systems
2 major parties compete for control
one right wing and one left wing party
political parties are usually broad
no minor parties can truly expect to win
(USA)
multi-party systems
many contending parties
cause coalitions to forms
Proportionate Representation: each party wims seats in the legislative proportionate to votes
(UK, Canada)
First Past the Post
An electoral system in which individual candidates compete in single member districts; voters choose between candidates and the candidate with the largest share of the vote wins the seat.
split ticket
when more than one candidate from the same party runs
1796- Jefferson and Burr split Dem-Rep
1820- JQAdams and Monroe split Rep
1860- Breckinridge and Douglas split Dem
splinter party
party split off from a major party usually from a disagreement
Progressive (Bull Moose) in 1912 and 1924
Dixiecrats in 1948
ideological party
party based on a particular set of beliefs
Libertarian, socialist, communist
economic protests party
Greenback party, populists party
single-issue party
Prohibition Party, Free Soil Party, Know-Nothings Party, Right to Life
Retrospective voting
voting for a candidate because you like his or her past actions in office
elections of 1980, 1984, 1988, 1992, 1996 based on incumbent's record
usually helps unless economy is down
midterm elections voters tend to turn against president's party
prospective voting
voting for a candidate because you favor his or her ideas for handling issues
coalitions
Alliances of various parties
base of loyal constituents
democrat coalitions
black people are most loyal
most hispanics (not cubans), catholics, unionists
republican coalitions
businesses and professional people, farmers
party realignments
when a new issue becomes so important that is causes voters to cut party division and replace old issues
slavery and economy
most likely to vote