BIO Lab Exam 2 Lab 12 Microscopy and Cell Diversity
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Microscope
A typical compound microscope is capable of extending the vision of the observer more than a thousand times. Other microscopes, such as the transmission electron microscope, can magnify objects up to 1 million times. Since its invention more than 300 years ago, the microscope has greatly improved our understanding of the cell, tissues, disease, and ecology.
Compound lights microscope
most commonly used microscope in the biology laboratory today
-two sets of lenses to magnify an object (occulars and objectives). Light microscopes are capable of magnification up to 2,000×× and a resolution of 300 nanometers.
simple light microscope
have a single lens similar to early microscope
Calculating Magnification
Total magnification is the multiplicative product of each lens in sequence. Compound light microscopes have an ocular lens and an objective lens.
The ocular lens is 10x on all the microscopes in our lab
The total magnification = ocular lens x objective lens.
Resolution
ability to see two images as separate distinct units. an image with more detail has a higher _____
Ocular lens (eyepiece)
uppermost lens or series of lenses through which a specimen is viewed.
-have magnification of 10x
-one _______= monocular microscope; two ______= binocular microscope
-Some oculars contain a pointer or a micrometer disk used to determine the size of an object. Never touch the ocular lens with your fingers.
Arm
serves as a handle
Nosepiece
Revolves and holds the objectives. When changing objectives always turn the _______ themselves. The objectives will click into place when properly aligned.
objective lenses
lower lenses attached to nosepieve. The magnification of each objective is stamped on the housing of the objective. The magnification may vary with different brands.
-NEVER touch
Stage
platform on which slides are placed. Some microscopes have a mechanical ____ to accurately control the movement of slides. Stage clips secure the slide.
Light source (illuminator)
serves as the source of illumination for the microscope
Iris Diaphragm
regulates light entering the microscope; usually is controlled by a mechanical lever or rotating disk that opens or closes the hole though which light travels
Condenser
Used to aim the light on the specimen from underneath the stage
Coarse-focus adjustment knob
used to adjust the microscope on scanning and low power only
Fine-focus adjustment knob
used to adjust the specimen into final focus
Base
the supportive portion of the microscope, which rests on the laboratory table
tips for using the microscope
The on button can be an obvious on/off switch or you may have to rotate the brightness dial until it clicks on/off.
If there are two ocular lenses, you may have to adjust them independently. You can also change the distance between your eyes.
ALWAYS start with the lowest objective lens to find your specimen, center it, then zoom in with higher magnification lenses.
First focus with the course-focus adjustment knob then the fine-focus adjustment knob.
ALWAYS return the microscope to the lowest objective lens or the blank "no" objective slot on the nosepiece if there is an empty one available.
Make sure you do not leave a slide on the stage when you are finished.
Do not rub any lenses with your sleeves, paper towels, nor Kimwipes. Only use lens paper!
A cell serves as the exclusive functional unit in unicellular organisms. In multicellular organisms ranging from the giant sequoia to a minute mushroom, however, cells differentiate to perform a variety of specialized functions. Multicellular organisms involve a division of labor, with certain groups of cells becoming highly specialized to perform duties that benefit the entire organism.
unicellular
Bacteria and many protists such as the green alga Spirogyra and the paramecium are composed of one cell
. Several species of protists exist as colonies, or loosely connected groups or aggregates of cells.
colonial organism
Ex: green alga Volvox
Colonial organisms are clonal colonies composed of many physically connected, interdependent individuals. The subunits of colonial organisms can be unicellular, as in the alga Volvox (a coenobium), or multicellular, as in the phylum Bryozoa.
Multicellular
Organisms composed of many cells, such as the azalea, the mushroom, and the walrus are examples of _________
-The biological levels of organization of these organisms exhibit a division of labor and have a variety of specialized tissues.
Prokaryotic
-more primitive and evolved first
-lack membrane-bound nucleus and organelles like mitochondria
-DNA in long loop that is loose in the cytoplasm
-smaller
-cytoplasm surrounded by plasma membrane and encased in protective cell wall
-In domains Bacteria and Archae
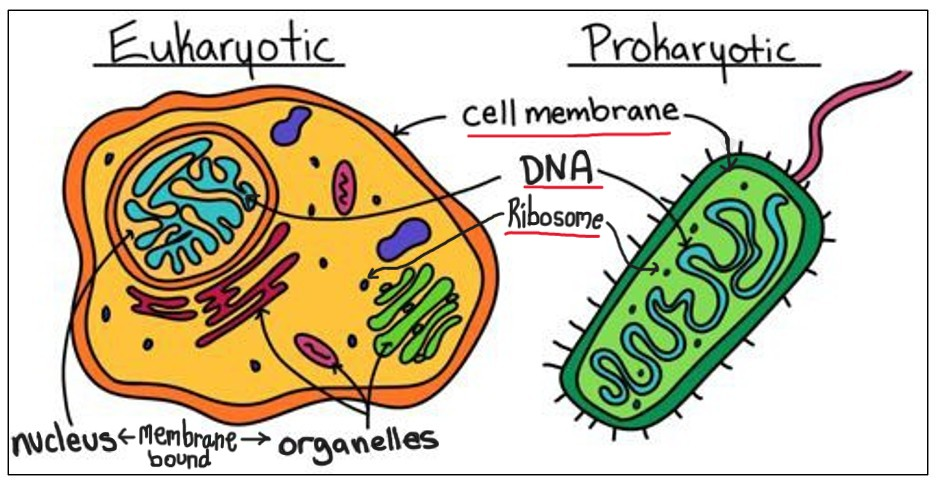
Eukaryotic cells
-evolved later after prokaryotes started living inside other prokaryotes
-membrane bound organelles
-structurally complex
-surrounded by plasma and a cell membrane
-larger
-DNA inside membrane bound nucleus
-In Domain Eukarya and Kingdoms Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, and Protista
Bacteria -Prokaryotic
Archae- Prokaryotic
Eukarya- Eukaryotic
Domains?
kingdom of Bacteria
Bacteria, the kingdom, is in the Bacteria Domain. Eubacteria" means true bacteria.
cocci
3 types of bacteria
-spherical in shape, such as Neisseria meningitidis (bacterial meningitis);
Bacilli
3 types of bacteria
-are generally rod-shaped, such as Escherichia coli (fecal contamination); and the
Spirilli
3 types of bacteria
-spiral in shape, such as Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease).
lthough the majority of eubacteria are harmless or helpful, such as Lactobacillus acidophilus in yogurt, there are several medically dangerous species. Examples of these organisms are Yersinia pestis (black plague), Clostridium perfringens (gangrene), Helicobacter pylori (ulcers), Vibrio cholerae (cholera), Staphylococcus aureus (boils), and Bacillus anthracis (anthrax).
Cyanbacteria
arephotosynthetic bacteria. They are not algae, but they used to be called "blue-green algae."
Archaebacteria
the kingdom, is in the Archae Domain. Live in extreme environments (e.g., very salty, very hot, etc.).
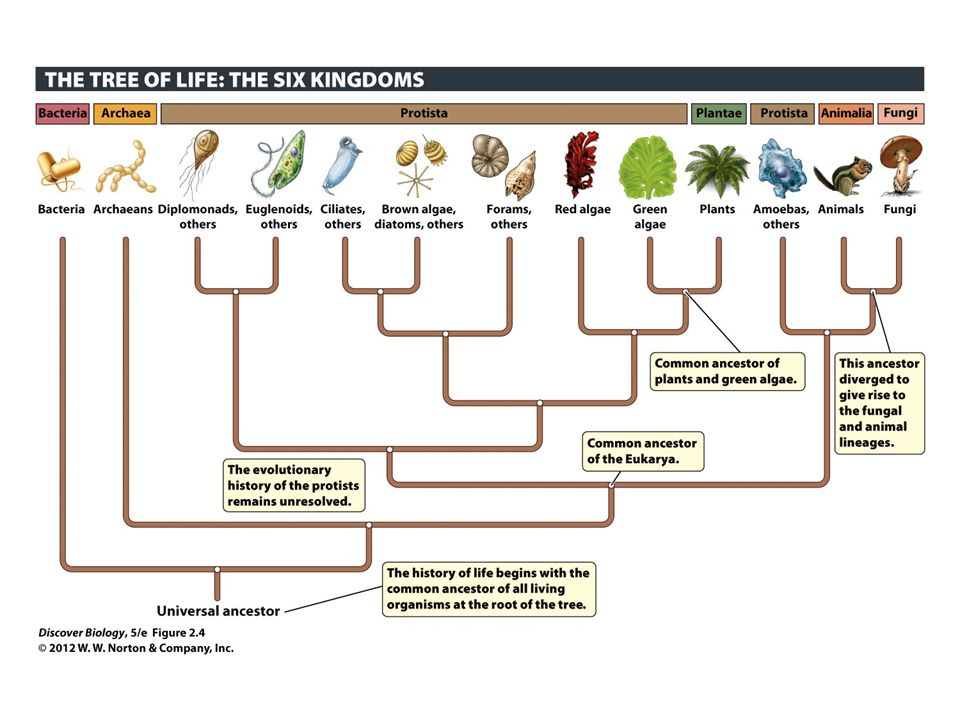
Plants, Animals, Fungi, and Protists
kingdoms in the Eukarya domain. Protists are a very diverse group and most are unicellular.
Animalia
-1.5 million species of multicellular heterotrophs
-members of the _____ kingdom vary tremendously, from simple sponges to humans. The cells lining your mouth along the inside of your cheeksare excellent examples of typical _____ cells.
-Epithelial cells
-contain some organelles that plant cells do not, including: lysosomes (vesicle containing digestive enzymes), centrioles (microtubules that form the spindle apparatus in cell division).
Epithelial
squamous ______ cells, are flat and thin and possess an obvious nucleus. ______ cells appear in regions of wear and tear and are constantly being sloughed away. In this specimen, only the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus will be easily observed.
Plantae
-includes some of the most conspicuous organisms on Earth
- contains approximately 280,000 species of multicellular, photosynthetic autotrophs. _____ vary in size and complexity from the minute duckweed to the giant redwood tree.
-contain some organelles that animals cells do not like vacuoles (large, fluid-filled sac to maintain the shape of the cell and store metabolites), chloroplasts (sites of photosynthesis and chlorophyll pigments), cell wall (a cellulose envelope that provides protection and shape).