CS 2810 Exam 1 Weber State
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
A computer that runs the same programs day in and day out has a particular workload. If the computer can be improved to speed up this particular workload, then which of the Seven Great Ideas would be addressed?
Group of answer choices
Performance via parallelism
Performance via prediction
Hierarchy of memories
Make the common case fast
Make the common case fast
Throughput is a measure of:
The time it takes to establish a network connection
The number of instructions a CPU can execute per second
The number of tasks that can be processed in a unit of time
How quickly a single task is completed
The number of tasks that can be processed in a unit of time
A word processor software has sophisticated software libraries that implement complex functions to support the application. The hardware in a computer can only execute simple low-level instructions. To go from a complex application to simple instructions involves several layers of software that interpret the high-level commands into simple computer instructions. This is an example of which of the Seven Great Ideas?
Abstraction to simplify design
Dependability vs Redundancy
Make the common case faster
Hierarchy of Memories
Abstraction to simplify design
What is the purpose of the SPECs?
Evaluate the performance of the CPU
A type of software programming language
Specialized computer hardware
A type of software programming language
Evaluate the performance of the CPU
When evaluating two computer systems, what is a workload?
The amount of storage capacity a computer system can handle
The amount of power the program uses
A set of programs run on a computer.
A single program selected for using in comparing computer performance
A set of programs run on a computer
There are several types of memory. SRAM is faster but less dense than DRAM, however, it is more expensive. SRAM and DRAM are two layers of which of the Seven Great Ideas?
Use abstraction to simplify design
Dependability via redundancy
Performance via prediction
Hierarchy of memories
Hierarchy of memories

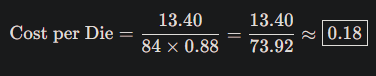

A computer that runs the same programs day in and day out has a particular workload. If the computer can be improved to speed up this particular workload, then which of the Seven Great Ideas would be addressed?
Make the common case fast
What is the clock rate?
The clock rate refers to the time it takes for a clock to complete one full rotation.
The clock rate is the number of hours a clock can run on a single battery.
The clock rate is the frequency of chimes produced by a clock.
The clock rate is the speed at which a microprocessor executes instructions, typically measured in hertz (Hz).
The clock rate is the speed at which a microprocessor executes instructions, typically measured in hertz (Hz).
A car has simple items like a steering wheel, gas pedal, and brake pedal. Behind the scenes, they are actually complex parts of the car. The simple items keep operating the vehicle an easier more efficient task. This is an example of which of the Seven Great Ideas?
Performance via Pipelining
Hierarchy of Memories
Abstraction to simplify design
Performance via Parallelism
Abstraction to simplify design
A computer that runs the same programs day in and day out has a particular workload. If the computer can be improved to speed up this particular workload, then which of the Seven Great Ideas would be addressed?
Hierarchy of memories
Performance via prediction
Make the common case fast
Performance via parallelism
Make the common case fast
When evaluating two computer systems, what is a workload?
A single program selected for using in comparing computer performance
The amount of power the program uses
A set of programs run on a computer.
The amount of storage capacity a computer system can handle
A set of programs run on a computer.
Select the three underlying principles of hardware design:
Simplicity favors regularity.
Smaller is faster.
Good design demands good compromises.
Don't compromise on good design.
Smaller is slower.
Reguarity requires complexity.
Simplicity favors regularity.
Smaller is faster.
Good design demands good compromises.
What would happen If many more registers are added.
The system would get slower.
The system would get faster.
It would make no change to the speed of the system.
The system would get slower.
In the MIPS architecture, there are _____ registers.
32
64
16
128
32

add $t2, $t1, $t0
add $t0, $t1, $t2
addi $t0, $t1, $t2
addi $t2, $t1, $t0
More than one of these will do that calculation.
add $t0, $t1, $t2

addi $t3, $t1, 27
addi $t1, 27, $t3
add $t3,$t1, 27
add $t1, 27, $t3
More than one of these will do the calculation
addi $t3, $t1, 27
When printing an integer, what do you put in register $a0 before making the syscall?
The integer to print.
The address of the integer.
The service number for the syscall function you are requesting (1 for print integer).
The integer to print.
To maintain regularity, all MIPS machine language instructions use the same field layout.
Group of answer choices
True
False
False
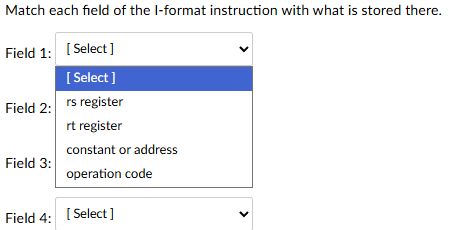
Field 1: operation code
Field 2: rs register
Field 3: rt register
Field 4: constant or address
When printing a string, what do you put in register $a0 before making the syscall?
The address of the string.
The string surrounded with quotes.
The register number that contains the actual string.
The service number for the syscall function you are requesting (4 for print string).
The address of the string.
To maintain regularity, all MIPS machine language instructions are all the same length.
Group of answer choices
True
False
True
Program instructions are stored in the computer as a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
Group of answer choices
True
False
False
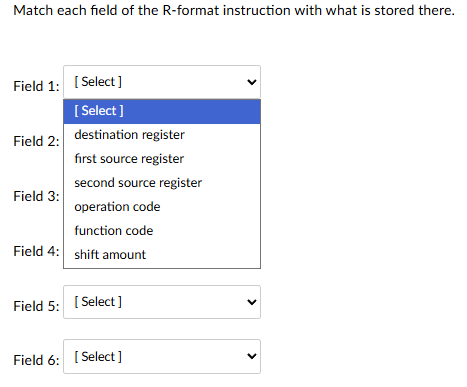
Field 1: operation code
Field 2: first source register
Field 3: second source register
Field 4: destination register
Field 5: shift amount
Field 6: function code
When coding a system service using syscall, in which register do you put the service number for the syscall function you are requesting ( 4 for print string, 1 for print integer, 10 for exit, etc.)?
Group of answer choices
$v0
$a0
$t1
It does not matter, any register will do.
$v0
To maintain regularity, all MIPS machine language instructions use the same field layout.
True
False
False
MIPS is an example of __________ architecture.
CISC
RISC
RISC
Select the four items from the list below that describe CISC architecture.
Focuses on hardware.
Some instructions take multiple clock cycles.
Has more registers.
Has fewer registers.
Instructions are a fixed size.
Instructions are variable length.
Focuses on software.
Each instruction takes one clock cycle.
Focuses on hardware.
Some instructions take multiple clock cycles.
Has fewer registers.
Instructions are variable length
When a shift happens, the emptied bits are
filled with 1s
filled with 0s
left empty
filled with 0s
Shifting changes the value. What is the effect of shifting left 1?
Adds 4 to the value
Multiplies the value by 4
Adds 2 to the value
Multiplies the value by 2
Multiplies the value by 2
What is the result of using the AND operation on the following 8-bit numbers?
0011 1101
1001 1001
1011 1101
0100 0010
0001 1001
1100 0010
0001 1001
What is the assembly condition to implement the following C-style if statement?
if (index != 12) {
...
}
the value of index is stored in $t2
the value 12 is stored in $t3
exit_code is the label for where the code after the if statement starts
if_code is the label where the code in the if section starts
If more than one of the conditions would work, pick the one that is more efficient.
beq $t2, $t3, exit_code
beq $t2, $t3, if_code
bne $t2, $t3, exit_code
bne $t2, $t3, if_code
beq $t2, $t3, exit_code
Which branch instruction works to implement the following for loop?
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
....
}
i is in $s0
k is in $s1
1 is in $s2
Loop: slt $t1, $s0, $s1
___________ # branch instruction
# Loop body
Exit:
beq $t1, $s2, Exit
bne $t1, $zero, Exit
bne $t1, $s0, Exit
beq $t1, $zero, Exit
beq $t1, $zero, Exit
Consider the following if/else statement.
If: # if condition and branch
# code when true
___________ # branch instruction
Else: # code when false
Exit: # code after if/else statement
Which branch instruction fits after the the code in the if portion?
j Else
j Exit
j If
More than one of these will work.
j Exit
Assume memory at the indicated addresses have the given decimal values:
4216: 82
4217: 65
4218: 67
4219: 69
4220: 115
If $t3 initially holds 4216, what is $t2 (in decimal) after:addi $t3, $t3, 1lb $t2, 0($t3)
82
115
65
656769115
65
Consider a program that loops through an array of integers.
the array is stored at label my_array
$t1 contains the address of the current location in the array (a pointer)
$t5 contains the value to be stored
What code will store the value in the array at the current location and then update the pointer to the next element?
More than one of these will work.
sll $t4, $t1, 2
sw $t5, my_array($t4)
addi, $t1, $t1, 1
sll $t4, $t1, 2
sw $t5, my_array($t4)
addi, $t1, $t1, 4
sw $t5, 0($t1)
addi, $t1, $t1, 4
sw $t5, 0($t1)
addi, $t1, $t1, 4
What is stored in $t0 in the following instruction:
la $t0, my_label
address
instruction is incorrect
value to be stored in memory
value from memory
address
Shifting changes the value. What is the effect of shifting left 2?
Group of answer choices
Adds 2 to the value
Multiplies the value by 4
Multiplies the value by 2
Adds 4 to the value
Multiplies the value by 4
Assume memory at the indicated addresses have the given decimal values:
2800: 84
2801: 114
2802: 105
2803: 112
If $t3 initially holds 2800, what is $t3 (in decimal) after:addi $t3, $t3, 1
2801
114
2804
84
2801
What is the correct relationship between the stack and registers in MIPS assembly language?
The stack is a region in memory, and register $sp points to the top of the stack in memory.
The stack is a region in the set of registers.
The stack and registers are unrelated.
The stack is a subset of registers.
The stack is a region in memory, and register $sp points to the top of the stack in memory.
If a procedure is going to update registers $s0, $s1, $s2, and $s3, how does it make space on the stack for these values?
Subtract 12 from $sp.
Subtract 16 from $sp
Add 12 to $sp.
Add 16 to $sp.
Subtract 16 from $sp
What is the purpose of the $a0 to $a3 registers in MIPS when calling a function?
Destination operand
An argument or value to be used by the function
The return value of the function
The return address of the function
An argument or value to be used by the function
A procedure is going to use registers $s0 and $s1 and has saved the previous values on the stack. The function has made the proper calculations. What is to be done to the stack before the return jr call?
Pop the values from the stack into $s0 and $s1.
Subtract 8 to the $sp
Push the current values of $s0 and $s1 onto the stack
Add 8 to the $sp
Pop the values from the stack into $s0 and $s1.
Add 8 to the $sp
No action is required on the stack.
Pop the values from the stack into $s0 and $s1.
Add 8 to the $sp
What is an Exception (or interrupt)?
Scheduled event that keeps the programming running despite irregularities in the system
Unscheduled event that keeps the programming running despite irregularities in the system
Scheduled event that disrupts program execution.
Unscheduled event that disrupts program execution.
Unscheduled event that disrupts program execution
Which of the following operations have the possibility of resulting in an exception?
subu
addu
add
addiu
add
What is the Inverse Law for the And and Or form? Group of answer choices
And Form: 1x = x Or Form: 0 + x = x
And Form: x + x' = 1 Or Form: xx' = 0
And Form: xx' = 0 Or Form: x + x' = 1
And Form: 1 + x = 1 Or Form: x' + 0 = x
And Form: xx' = 0 Or Form: x + x' = 1

Boolean Product
Boolean Sum
AND - product
OR - SUM
What is the Inverse Law for the And and Or form?
And Form: 1x = x
Or Form: 0 + x = x
And Form: x + x' = 1
Or Form: xx' = 0
And Form: xx' = 0
Or Form: x + x' = 1
And Form: 1 + x = 1
Or Form: x' + 0 = x
And Form: xx' = 0
Or Form: x + x' = 1

Assertive
Deasserted
Sequential
Combinational
Assertive
Deasserted
Which register is used to return a value from a function call?
$s0
$t0
$v0
$a0
$v0
What is the purpose of the $ra register in MIPS procedures?
Group of answer choices
Registers an address
Allows the return type to accumulate a value
Allows the program to return from a function call
Allows the argument to accumulate a value
Allows the program to return from a function call