Prenatal Development: From Blastocyst to Baby
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Gestation (Fertizilation to Parturition)
Average Duration 266 Days (38 Weeks)
Parturition
Process of giving birth

Pregnancy
Expected Date of Birth 40 weeks after Last Menstrual Period (LMP)Approximately 9 months divided into 3 TRIMESTERS
Calculation
Expected Date of Birth
(D.O.B. = First day of Last Menstrual Period + 9 Months + 7 Days)
3 Periods of Prenatal Development
1.) Pre-embryo: First 2 weeks after fertilization
2.) Embryonic Period: 3rd week to end of 8th week
3.) Fetal Period: 9th week to end of 38th week (or Birth)
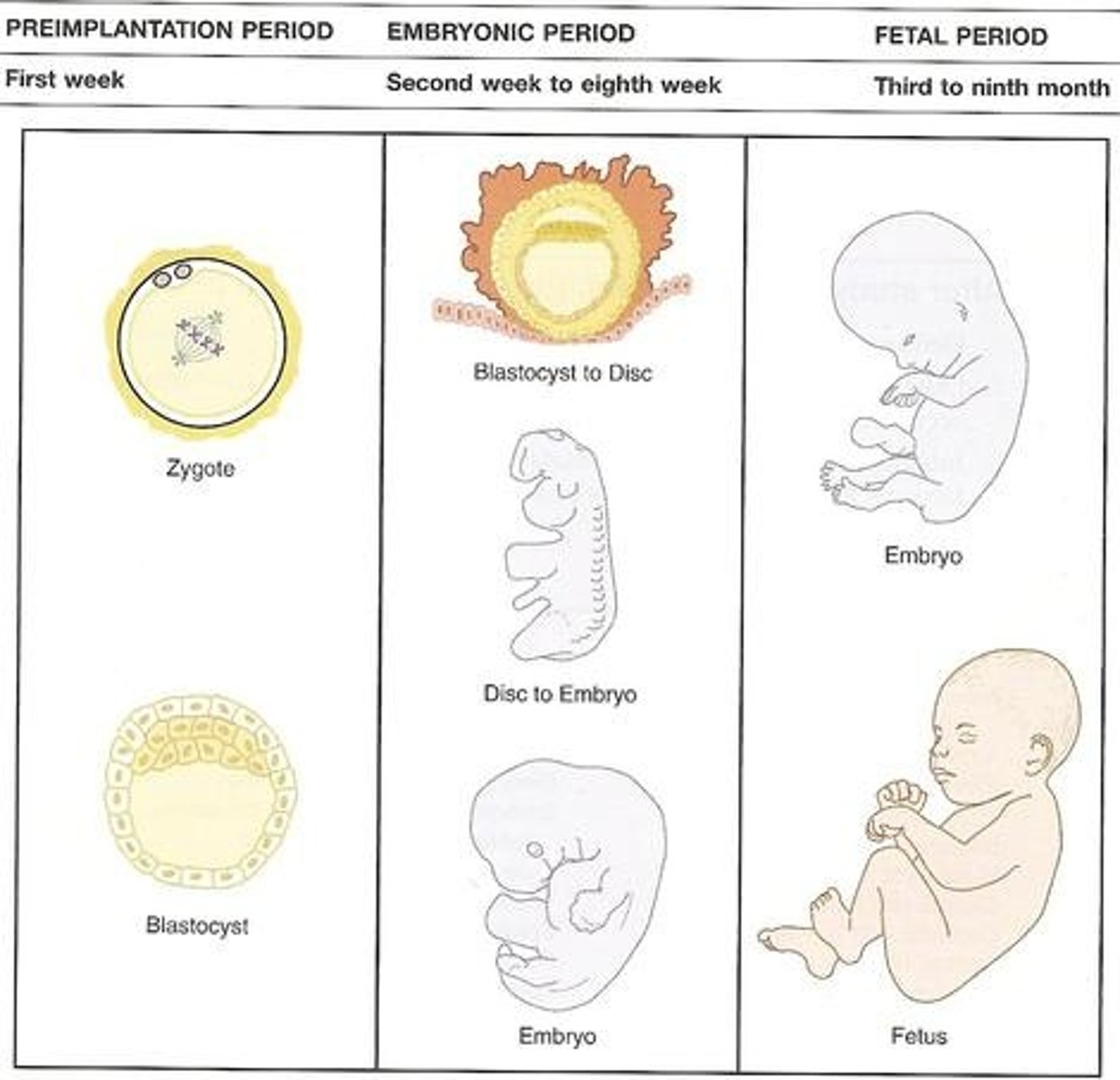
Pre-Embryonic Period
First 2 weeks after fertilization
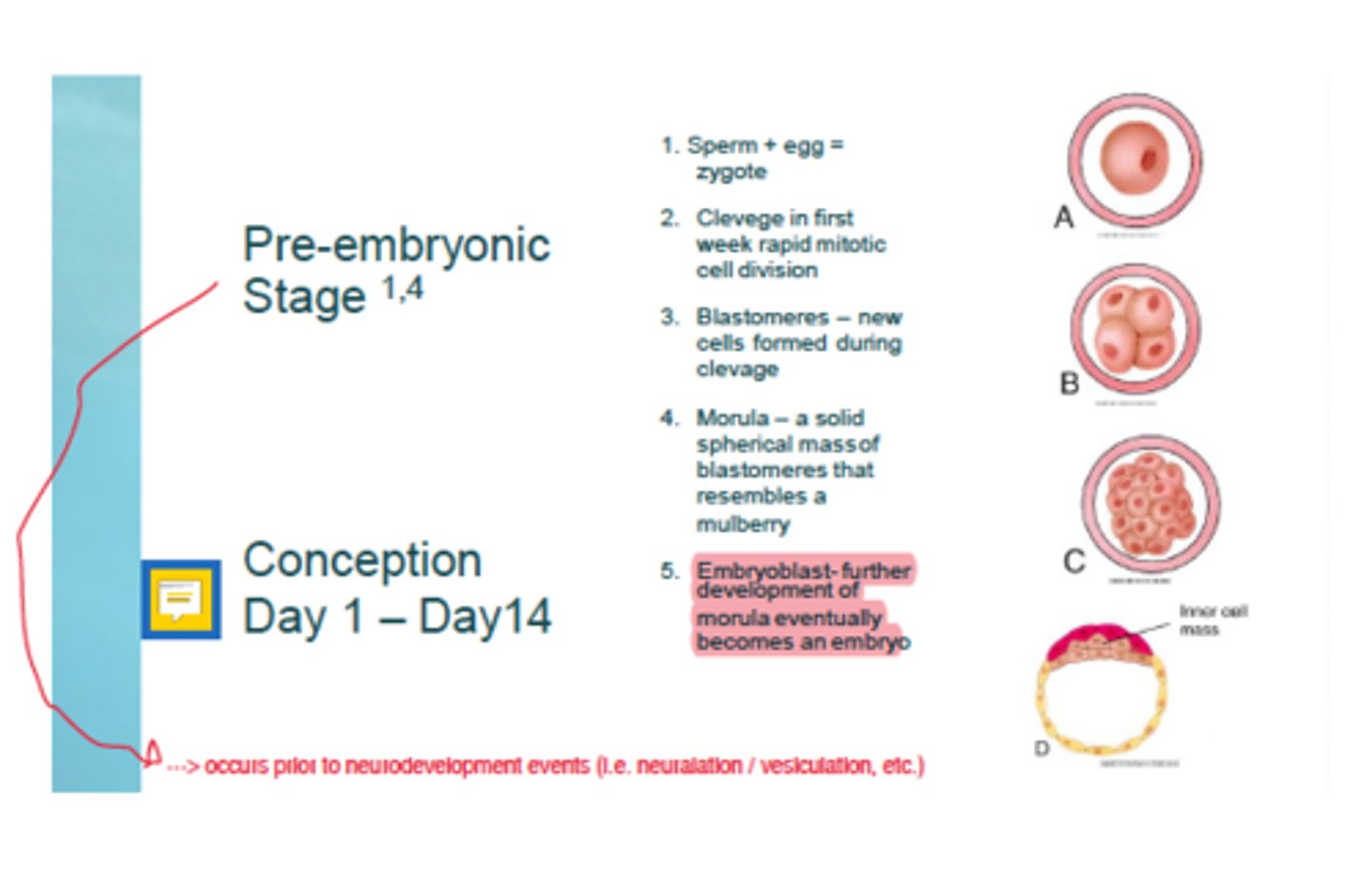
Embryonic Period
3rd week to end of 8th week
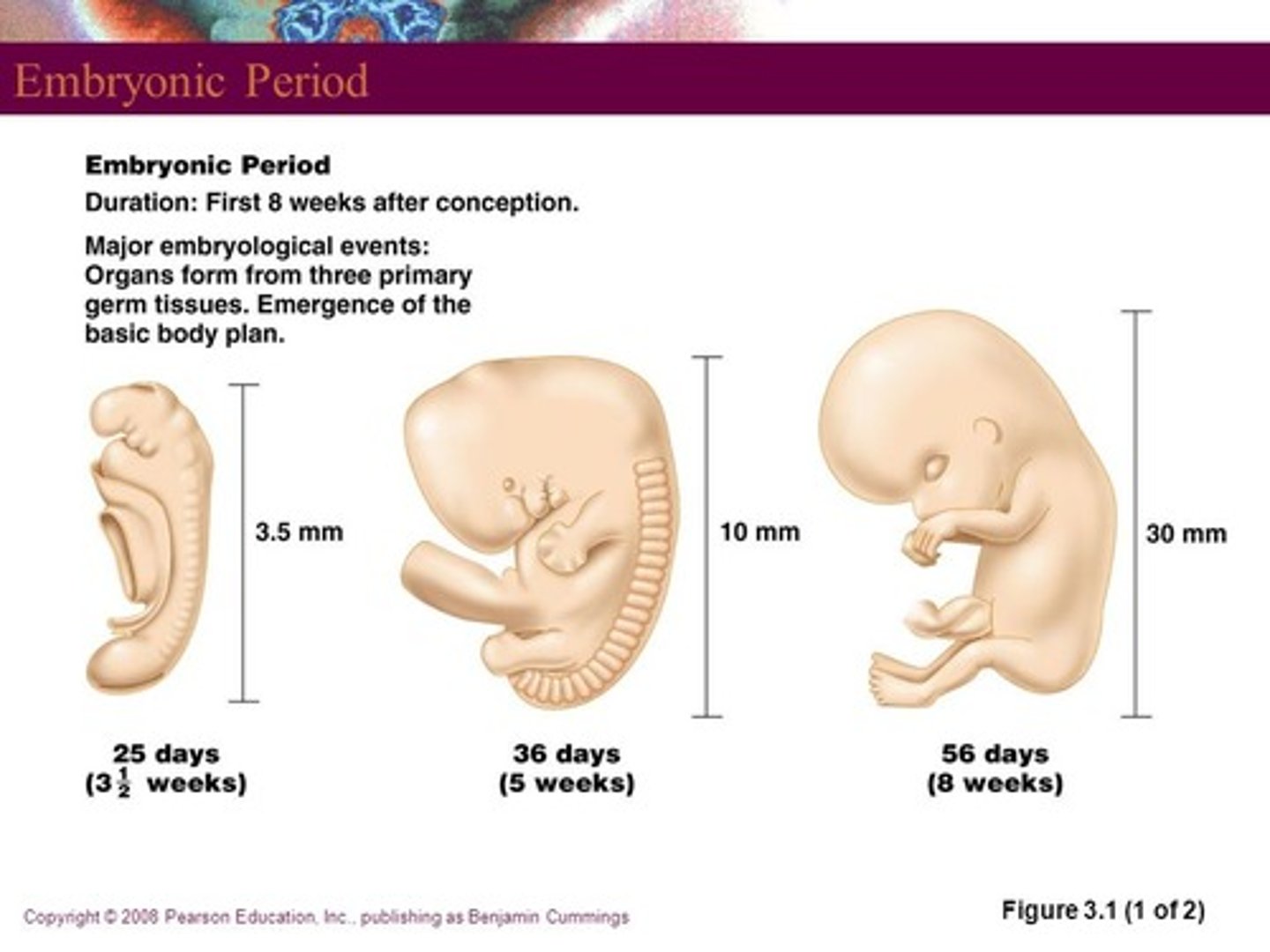
Fetal Period (Fetus)
9th week to end of 38th week (or Birth)
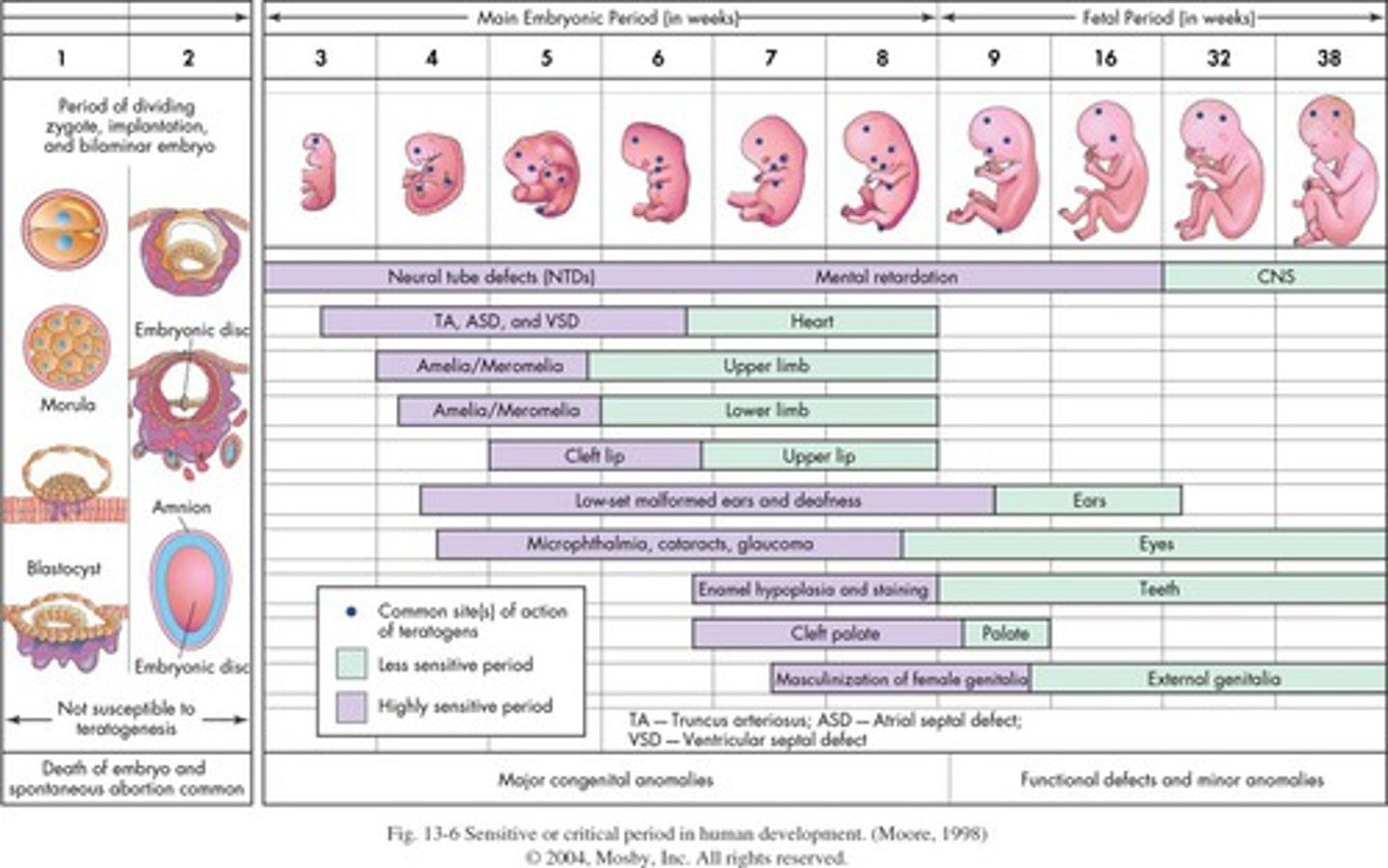
Teratogenesis
The process by which congenital malformations are produced in an embryo or fetus by exogenous factors
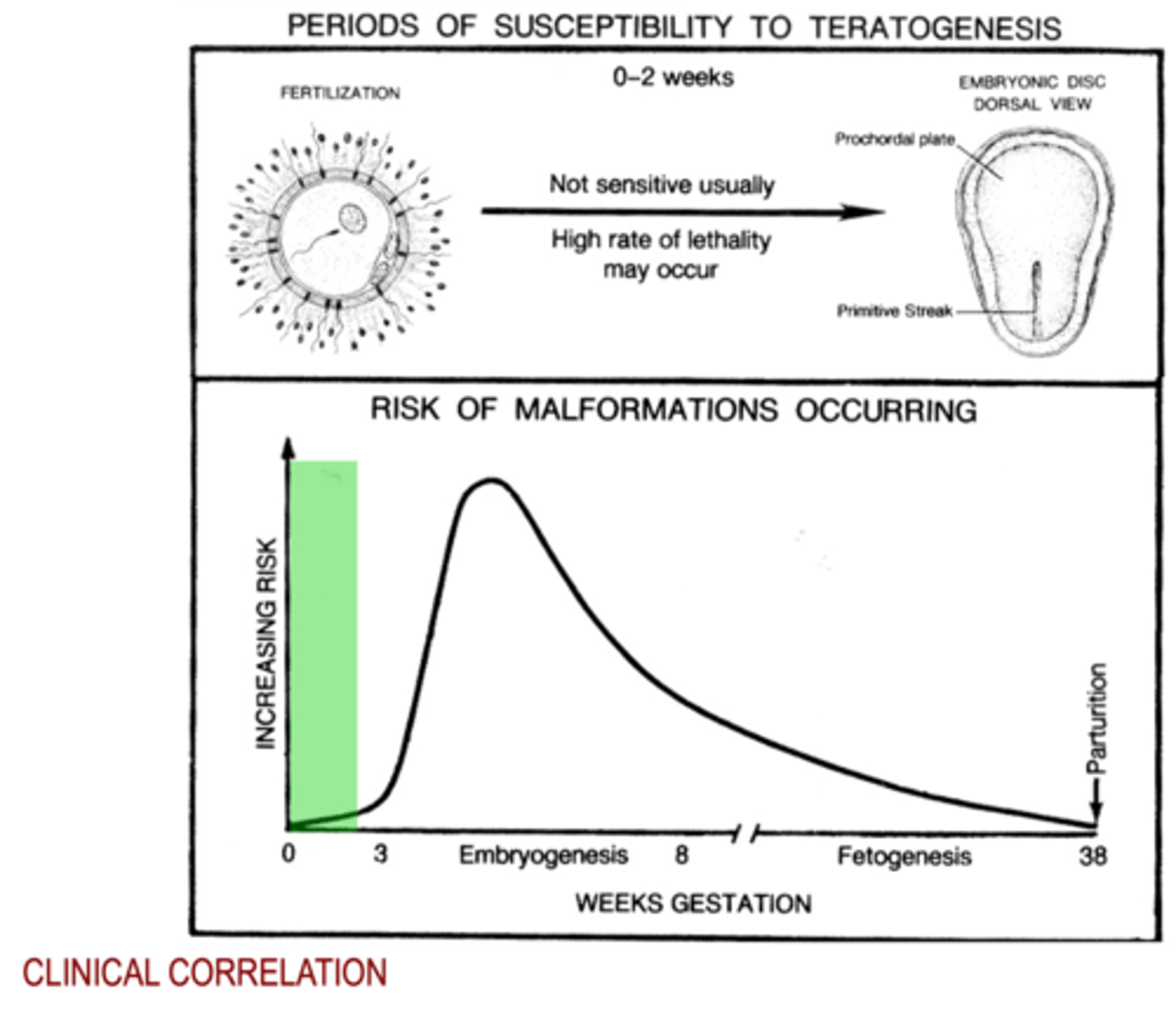
Periods of Susceptibility to Teratogenesis (Fertilization to Embryonic Disc - Dorsal View)
Early= 0-2 weeks (not usually sensitive but high rate of lethality)
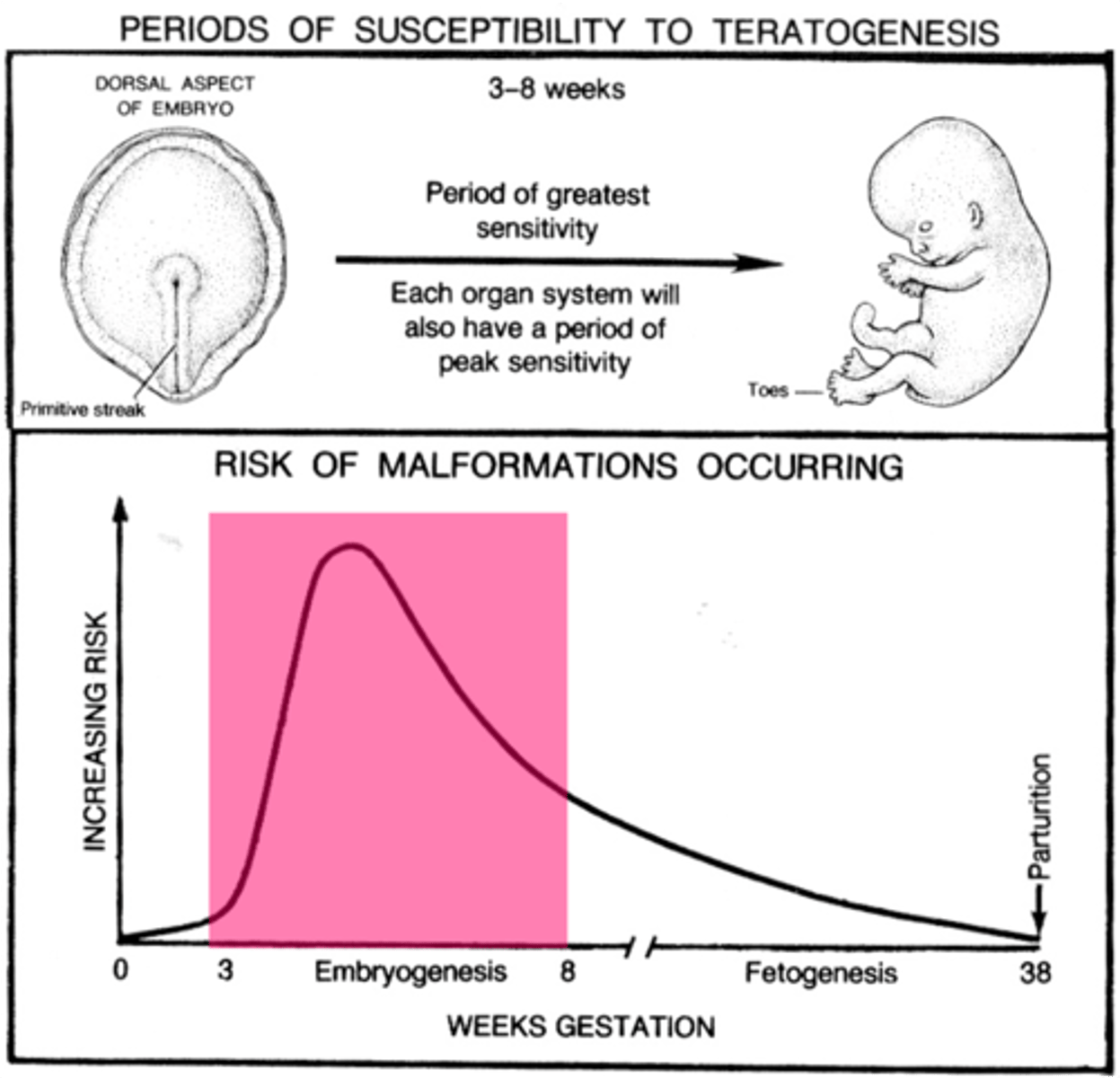
Periods of Susceptibility to Teratogenesis (Dorsal Aspect of Embryo to Fetal Formulation)
Embryonic= 3-8 weeks (period of greatest sensitivity and each organ will have a peak sensitivity)
*Primitive Streak is present
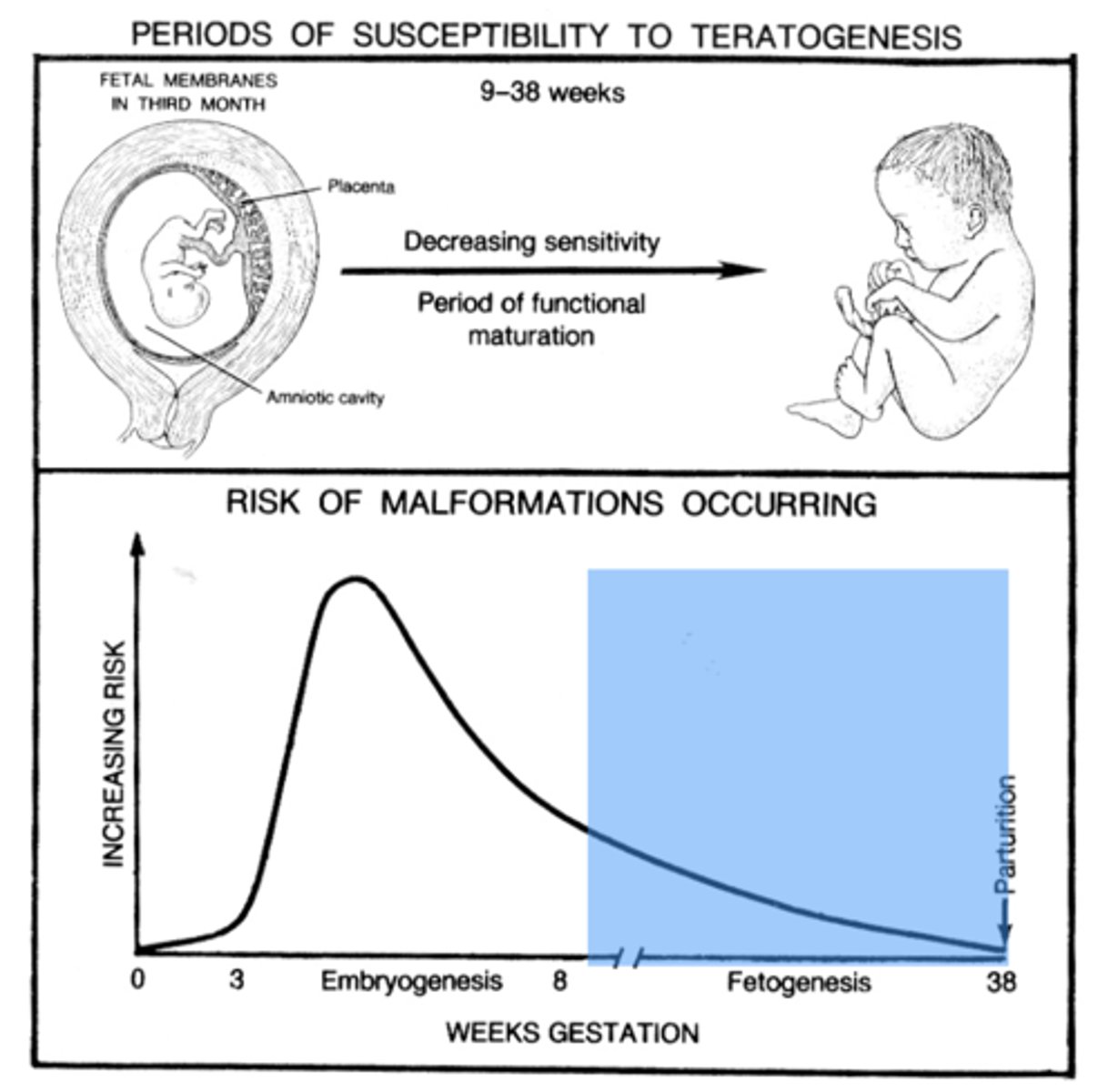
Periods of Susceptibility to Teratogenesis (Fetal Membrane in 3rd Month to Term)
Fetal= 9-38 weeks (decreasing sensitivity and periods of functional maturation)
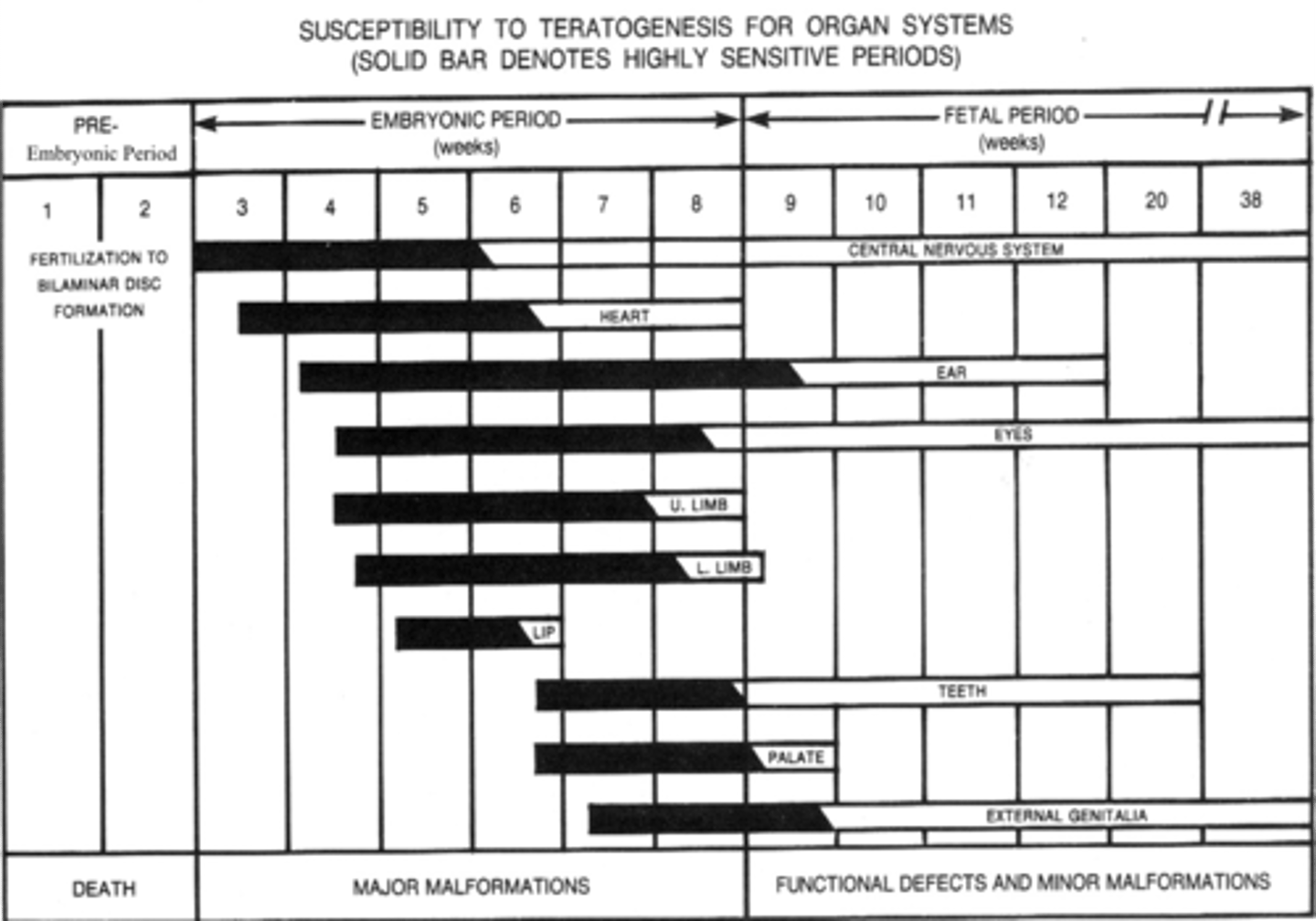
Susceptibility to Teratogenesis for Organ Systems
Propensity for Major Malformations & Functional Defects and Minor Malformations
*Indicated by Solid Bars Correlates to Highly Sensitive Periods
Male Orgasm
Results in the
ejaculation of SEMEN containing approx 300,000,000 SPERMATAZOA
Female Orgasm
Results in the elevation of the CERVIX and UTERUS, and slight opening of the cervical canal and lumen of the uterus
Fertilization
Occurs when a sperm fuses with an egg to form a diploid zygote. This usually occurs in the upper reaches of the fallopian tube.
(Fertilization -> 4-Cell Stage -> Morula -> Blastocyst -> Blastocyst Implantation)
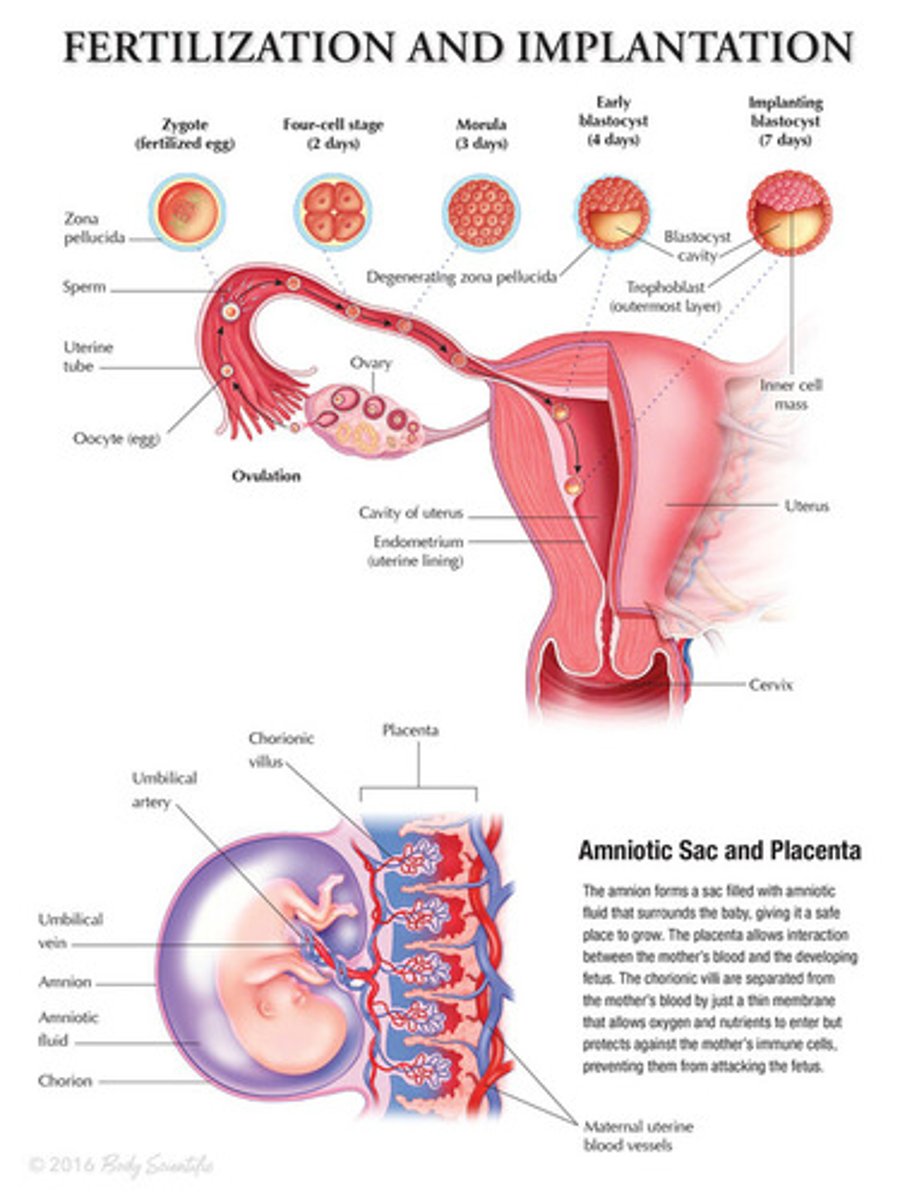
Cleavage
The process of early mitotic cell divisons, which progressively reduce cell size.
During cleavage, the total embryonic mass remains relatively constant.
2-Celled to 8-Celled
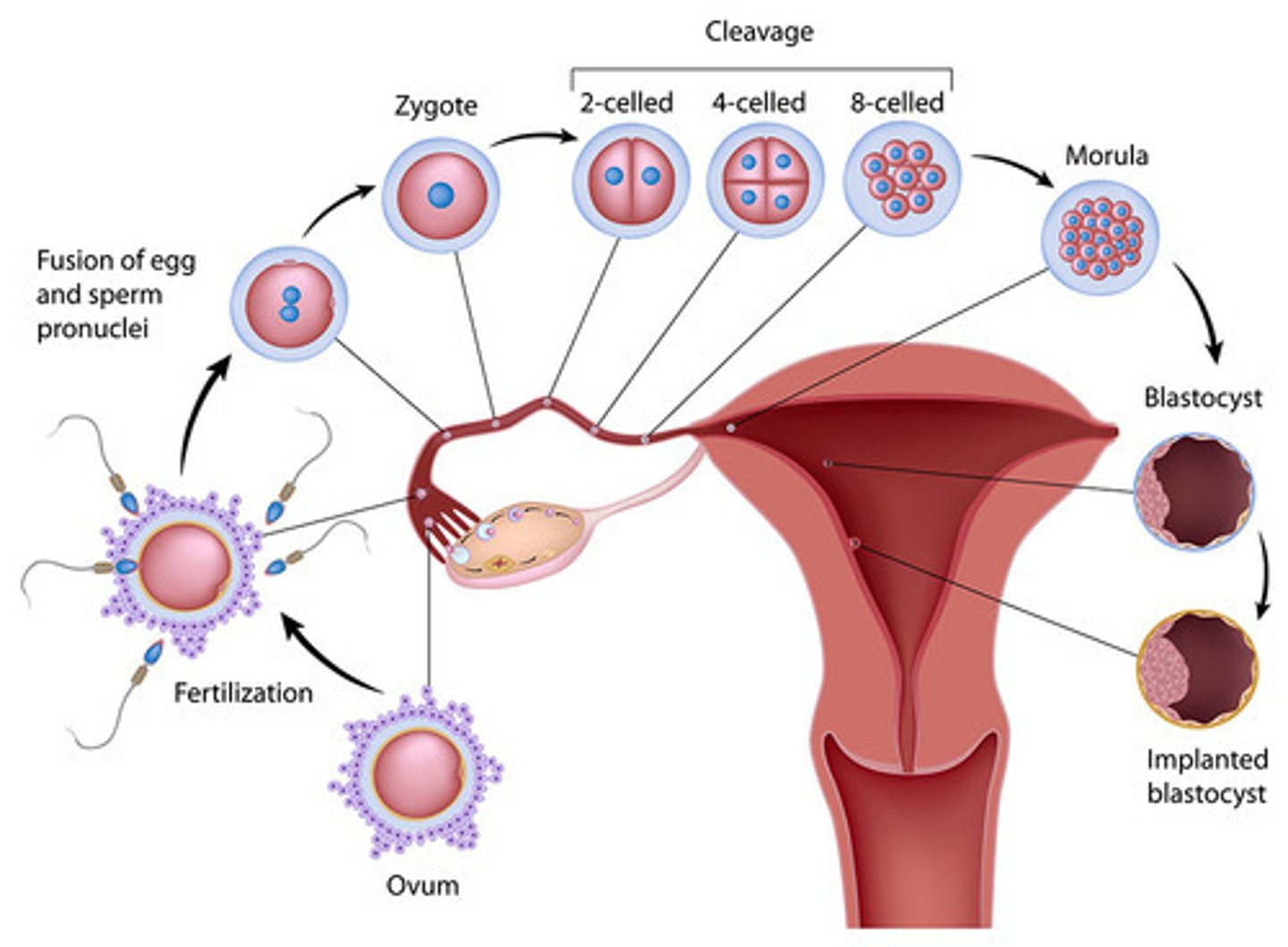
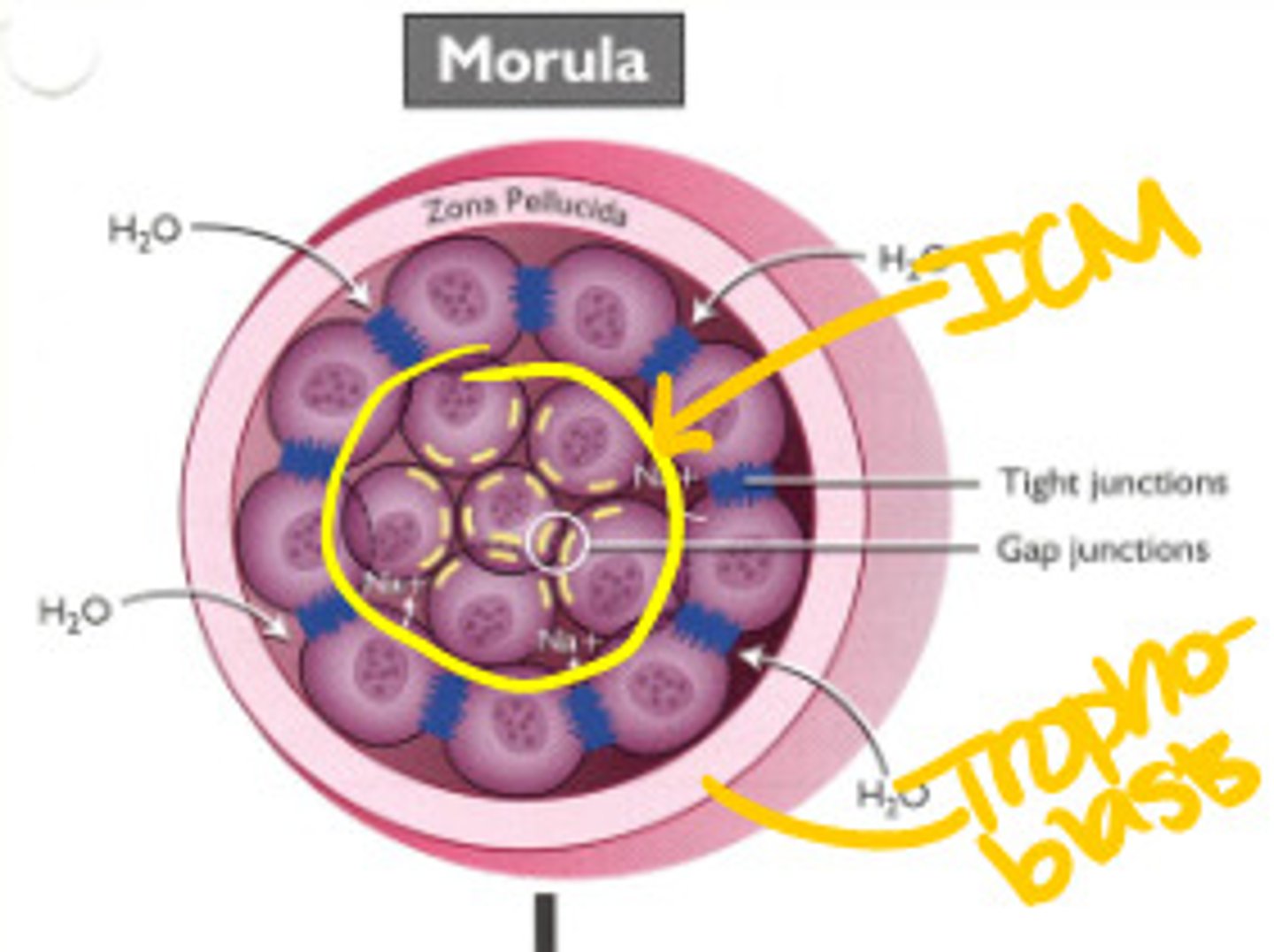
Morula ("Mulberry")
When the embryo has about 16 cells, its individual cells begin to adhere to one another, and it coalesces. Approximately 3-Days Post-Fertilization
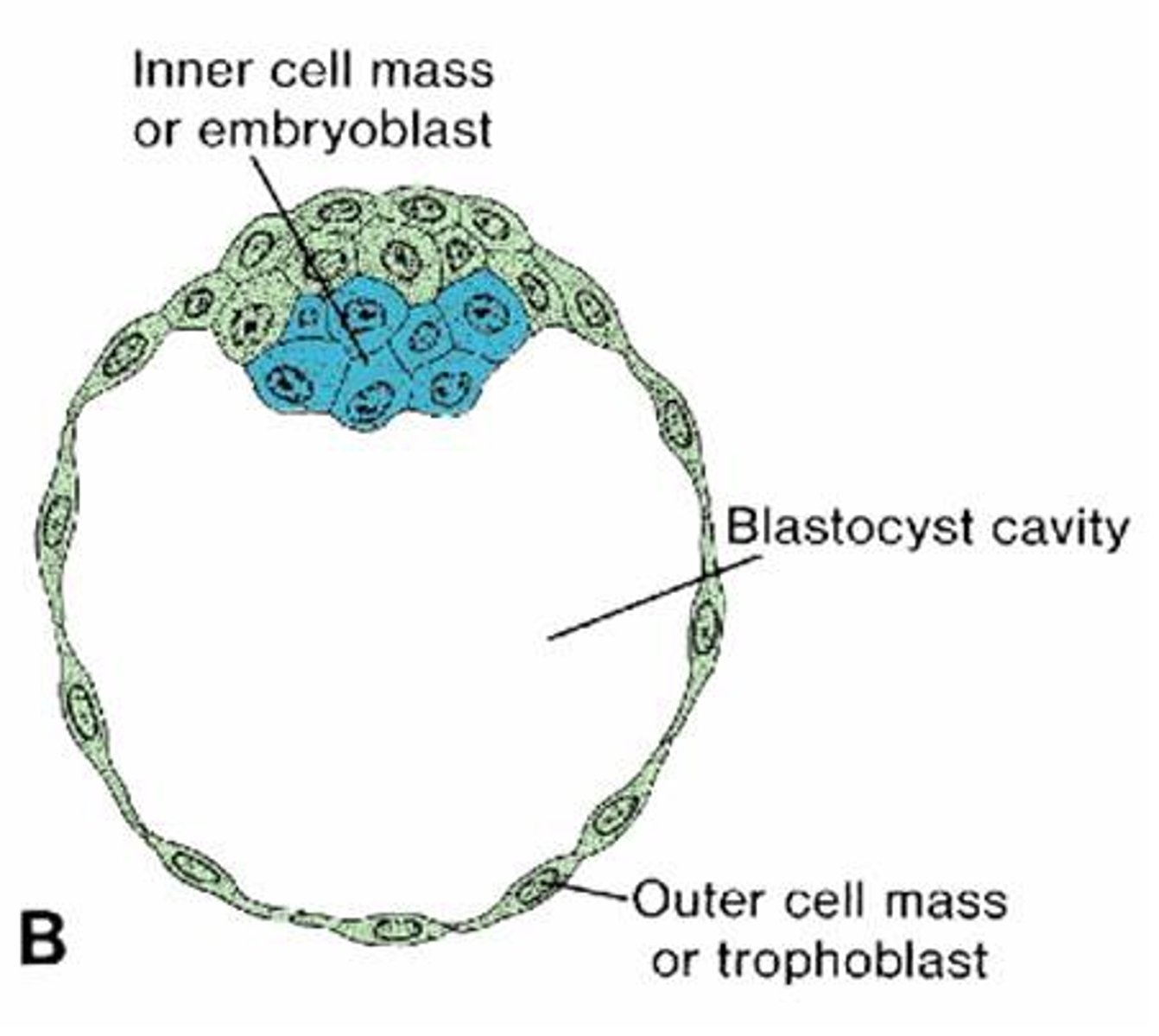
Blastocyst
A fluid-filled sphere formed about 4-5 days after fertilization of an ovum that is made up of an outer ring of cells and inner cell mass. This is the structure that implants in the endometrium of the uterus.
Implantation of Blastocyst
Starts around 5-7 days post-fertilization and takes about a week.
+ Blastocyst adheres to endometrium
+ Trophoblasts differentiate, invade the endometrium and initiate implantation
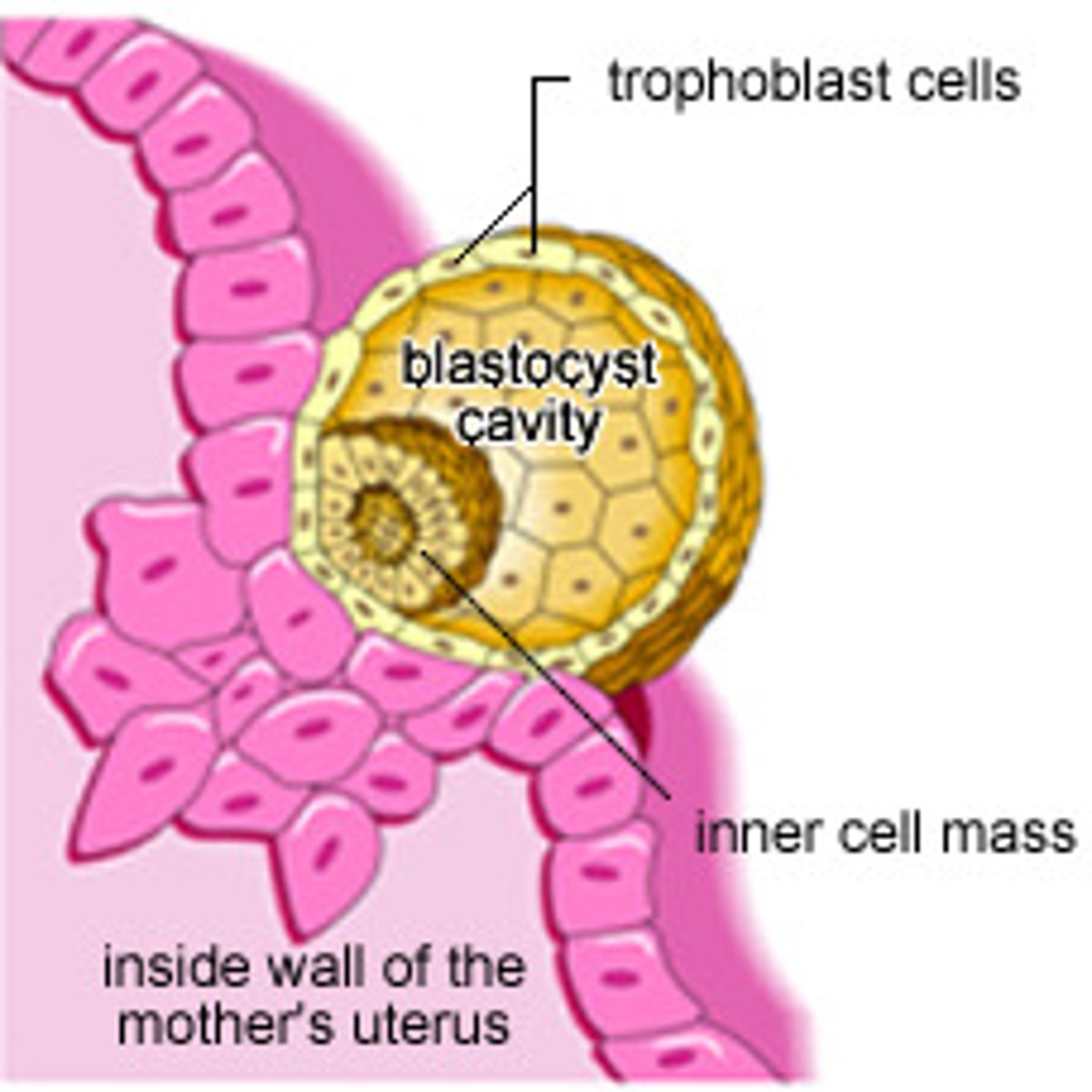
Sites of Ectopic Implantation
2-5% of All Pregnancies
1. Into the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity, usually within the Pouch of Douglas
2. Ampullary/Infundibular Region of the Uterine Tube
3. Uterine Tube (Tubal Pregnancy) - Most Common
4. Interstitual Implantation within the narrow region where the tube joins the uterus
5. Internal Os of the Uterus
6. Ovary
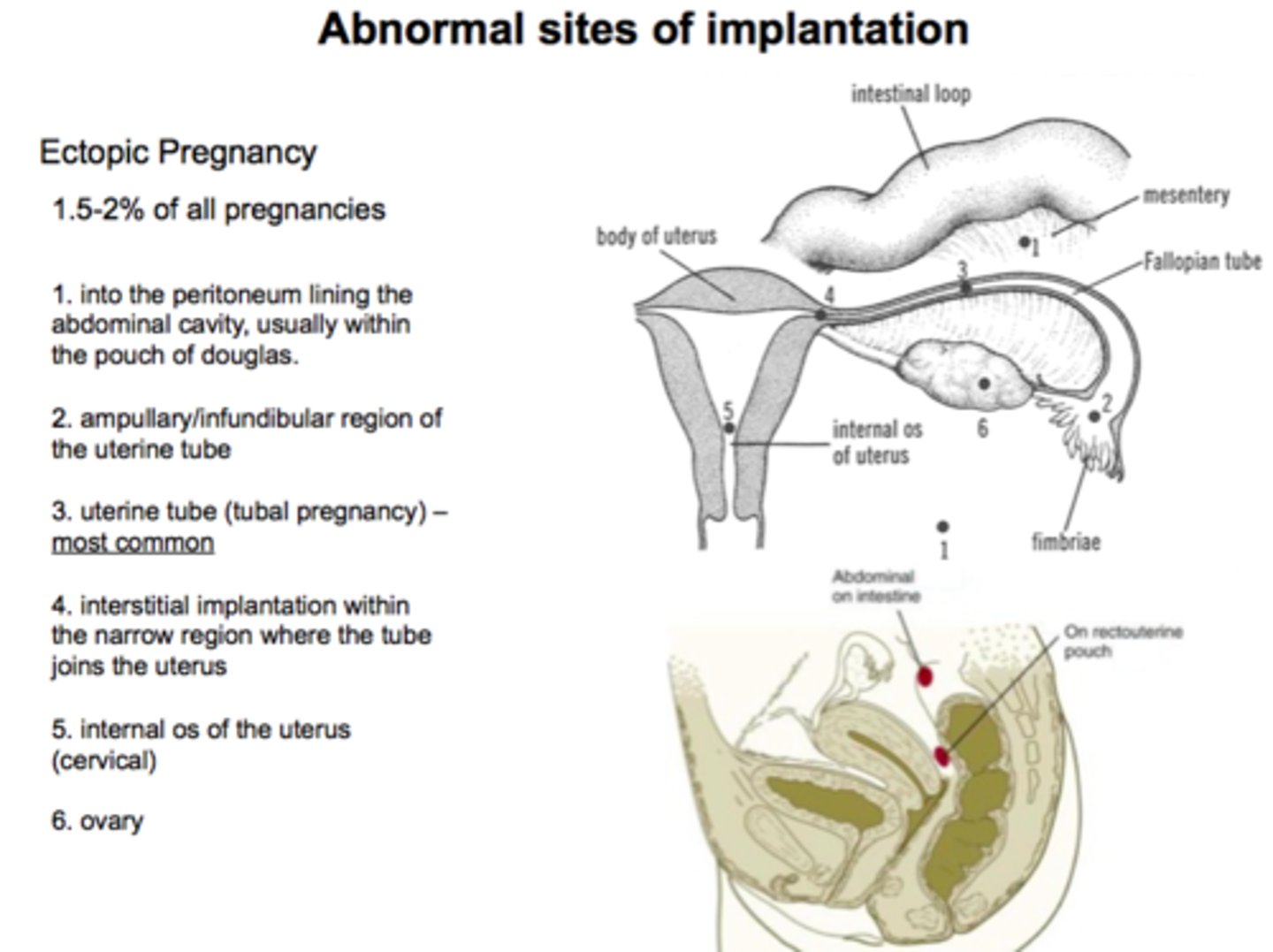
(1) Germ Layer Formation: 9-day Human Blastocyte
- Hypoblast: lines blastocyte cavity
- Blood circulation from mother
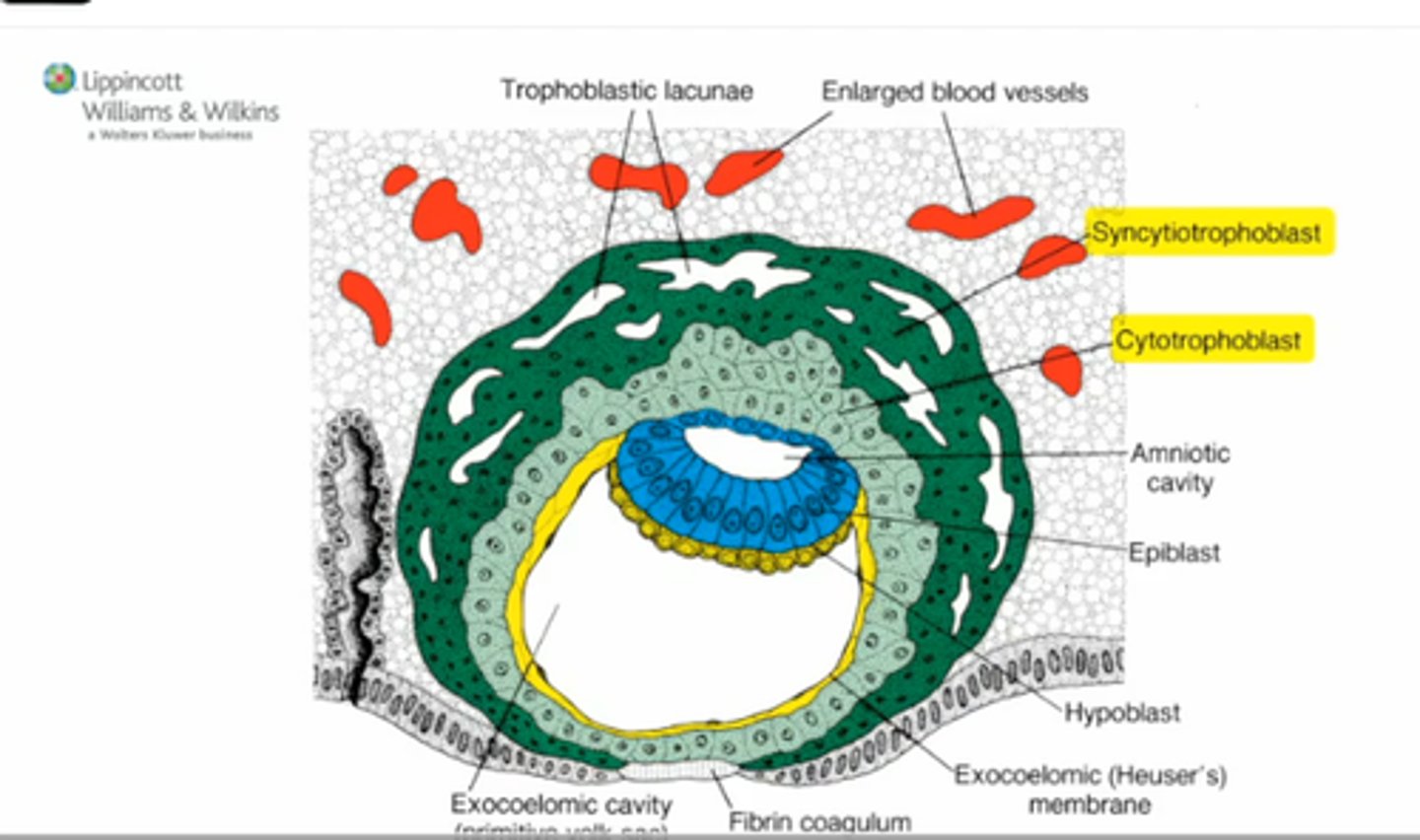
(2) Presomite Embryo
Occurs 14-17 days post fertilization
(Bilaminar Disc)
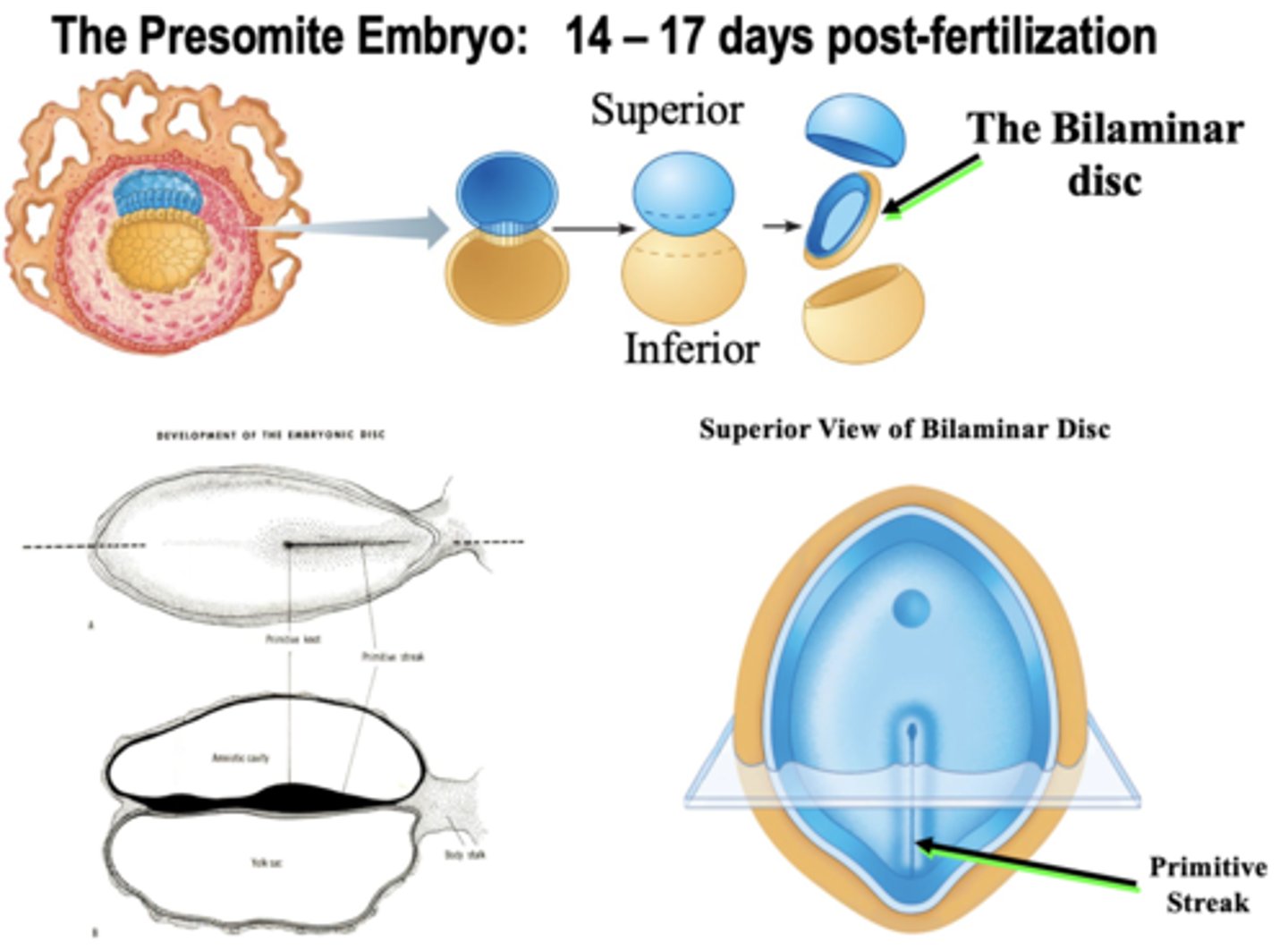
Bilaminar Disc
Two-layered disc (epiblasts and hypoblasts) that forms from the inner cell mass at the beginning of the second week
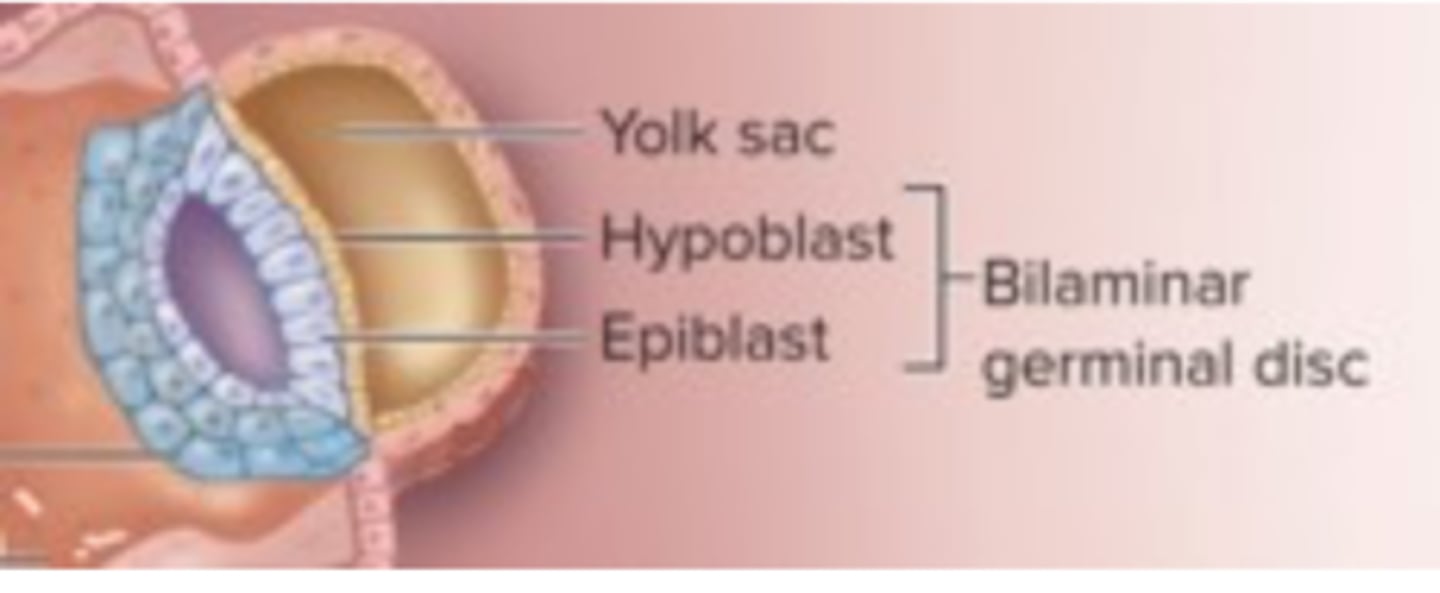
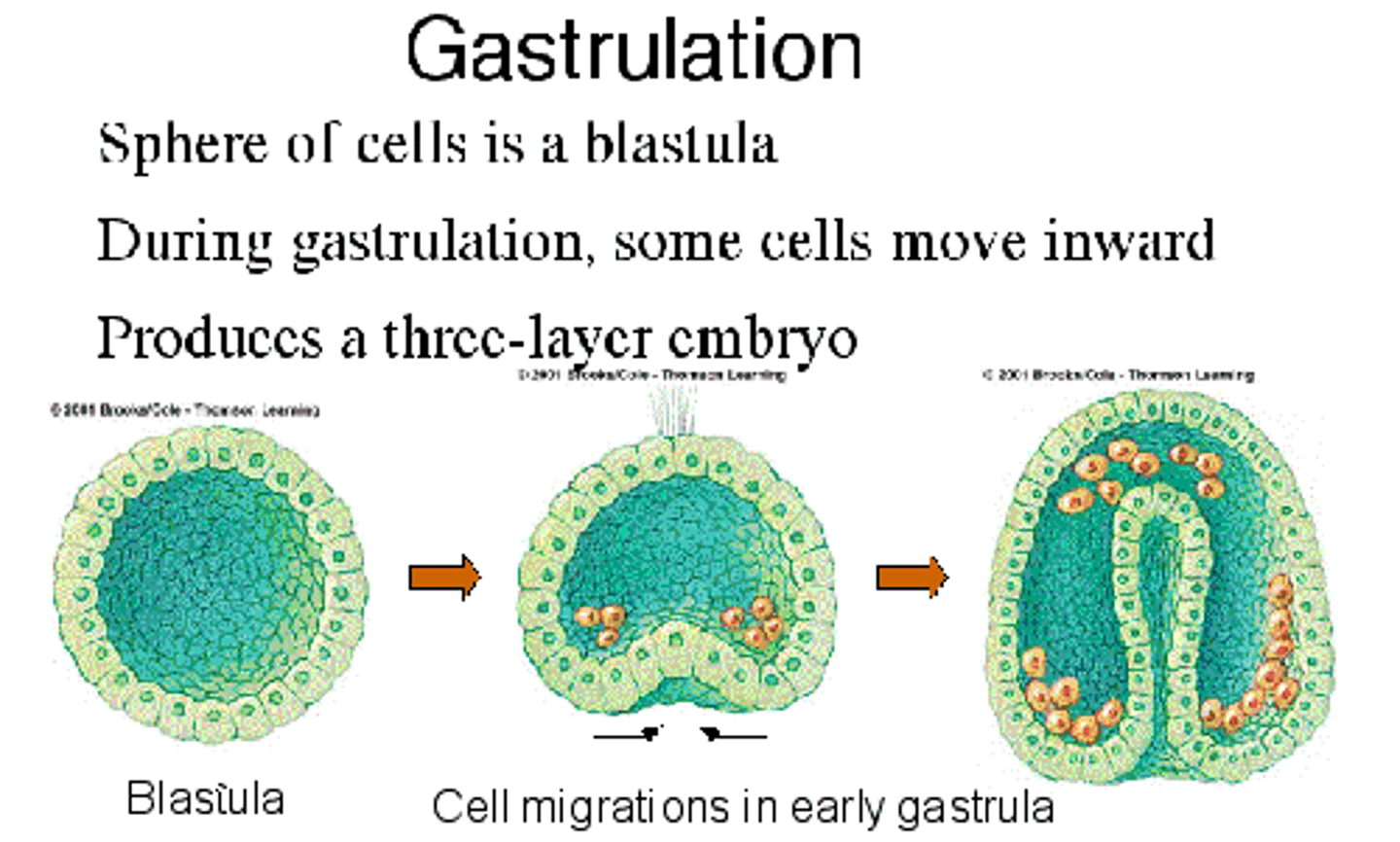
(3) Gastrulation
Formation of the mesoderm; The process by which a blastula develops into a gastrula with the formation of three embryonic layers
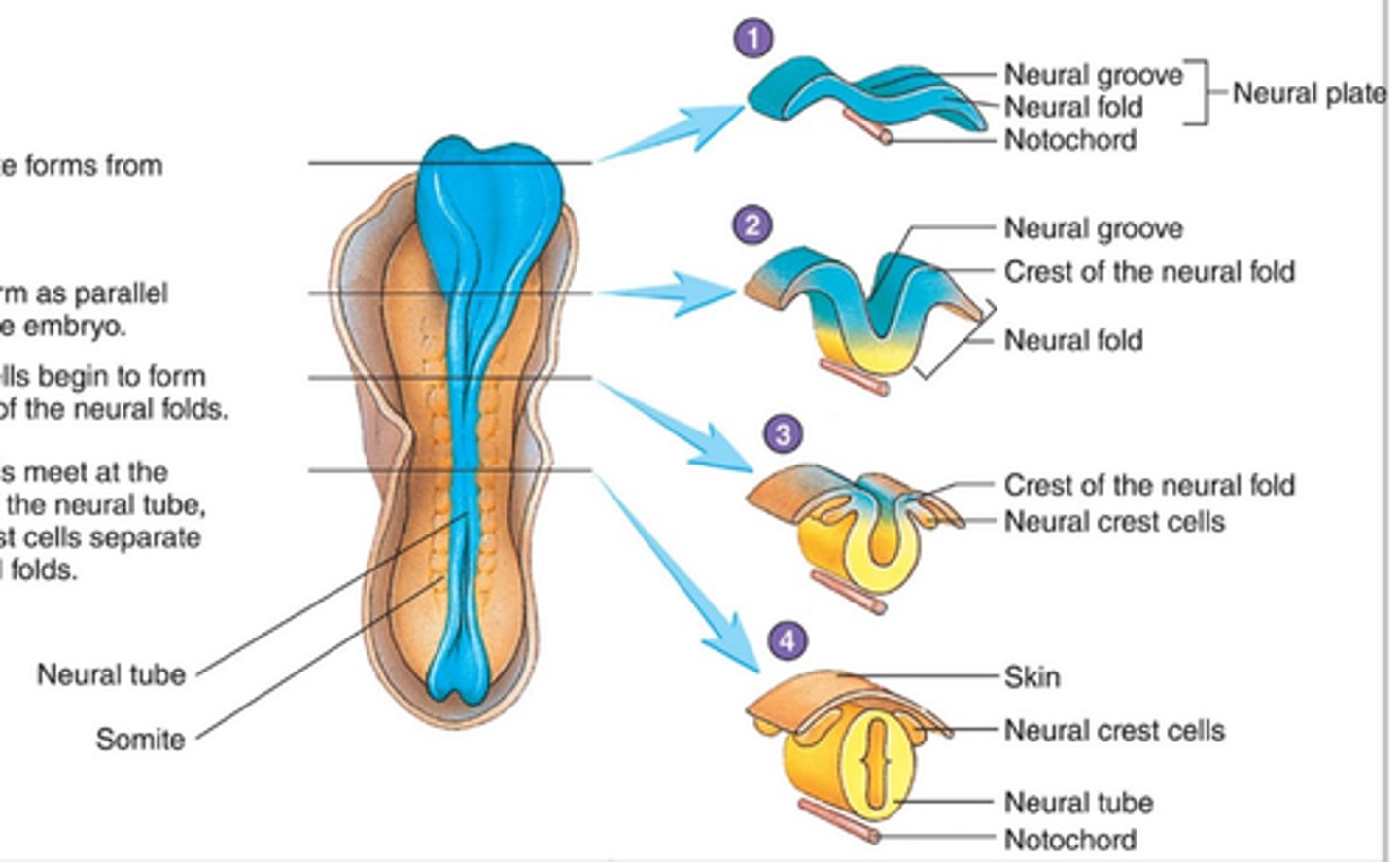
(4) Neural Tube Formation
As the Mesoderm forms it condenses along the midline to form the NOTOCHORD (Days 15-21); Signals from the notochord trigger reorganization of the dorsal ectodermal cells leading the neural tube formation
* the neural tube is the precursor to the brain and spinal cord
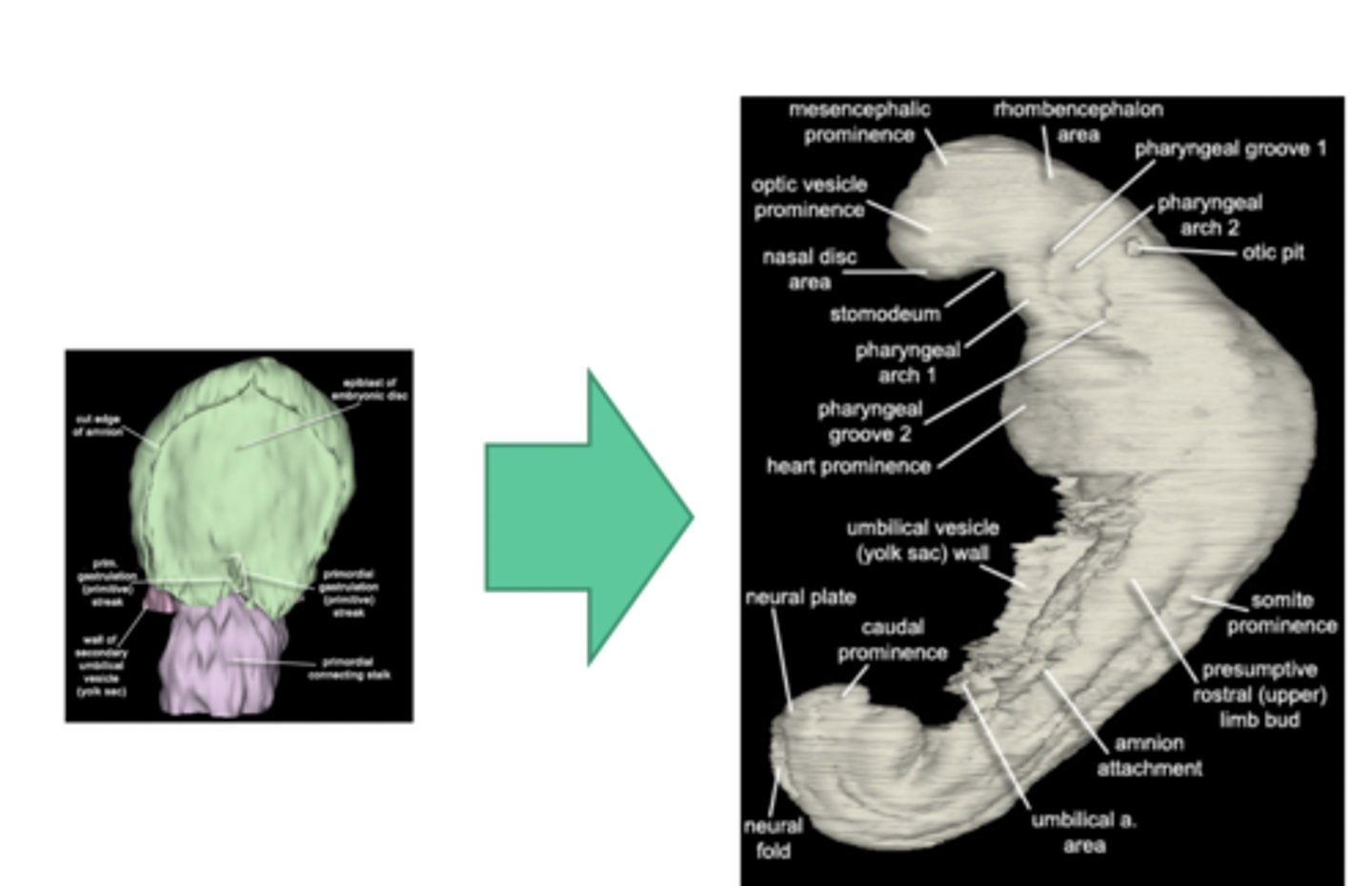
(5) Formation of Body Shape
Part of process where the embryo begins to take shape after the Developing Brain and Spinal Cord
(6) Ectodermal Development Neurulation
Grows rapidly and curls under the head and tail ends of the embryo
The Head and Tail ‘folds’ give rise to the foregut and hindgut, push the early heart to its central location, and bring the amnion to enclose all of the embryo except the umbilical cord
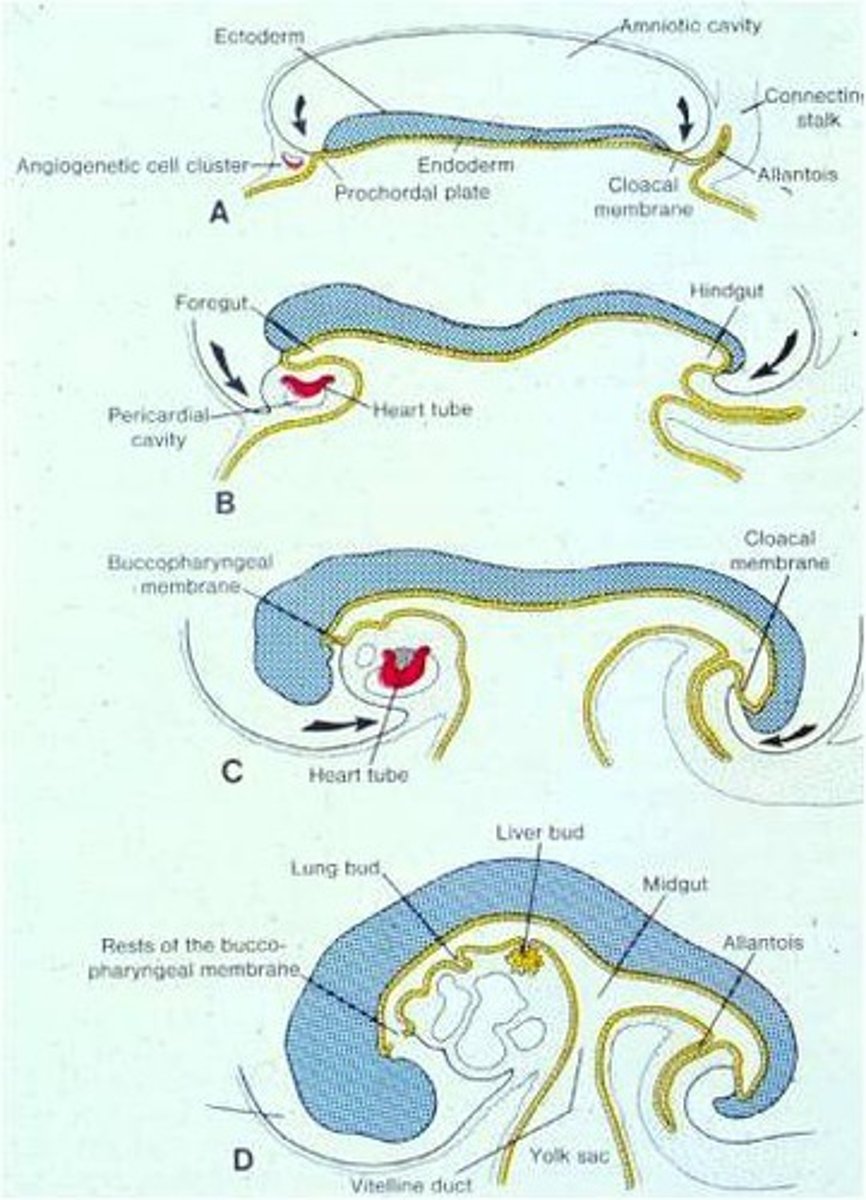
(7) Formation of Tissues and Organs
When prominent tissue formations begin to separate and sub-level
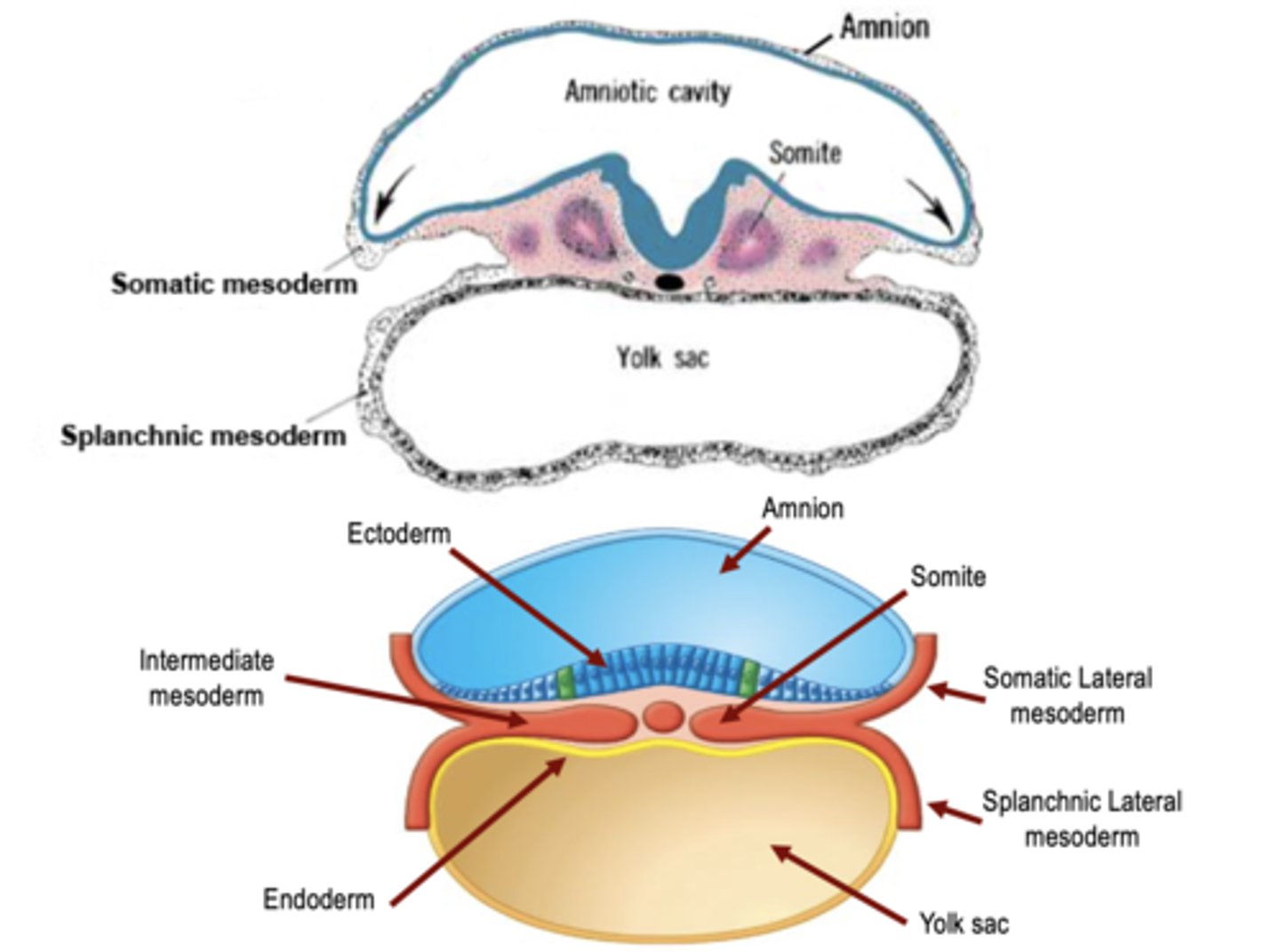
Embryo Tissue Layers
+ Ectoderm (Superficial)
+ Mesoderm (Middle)
+ Endoderm (Deep)
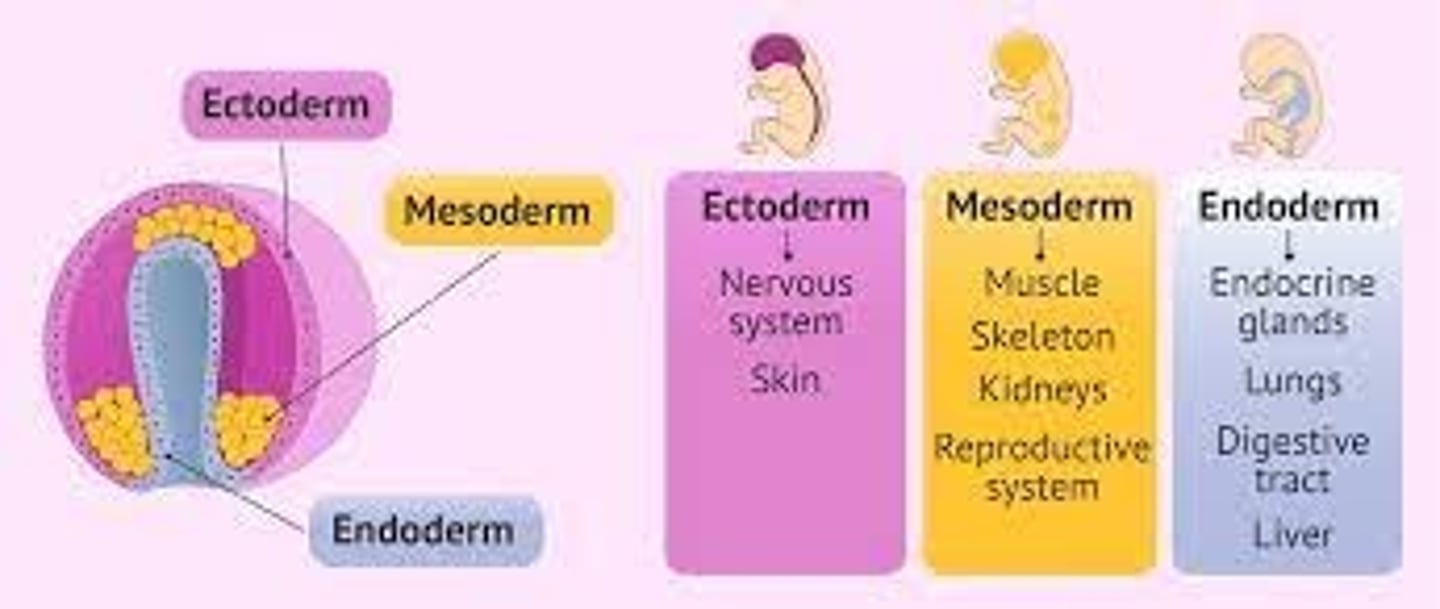
Major Derivates of Embryonic Germ Layers
Step by step process of Germ Layer Development
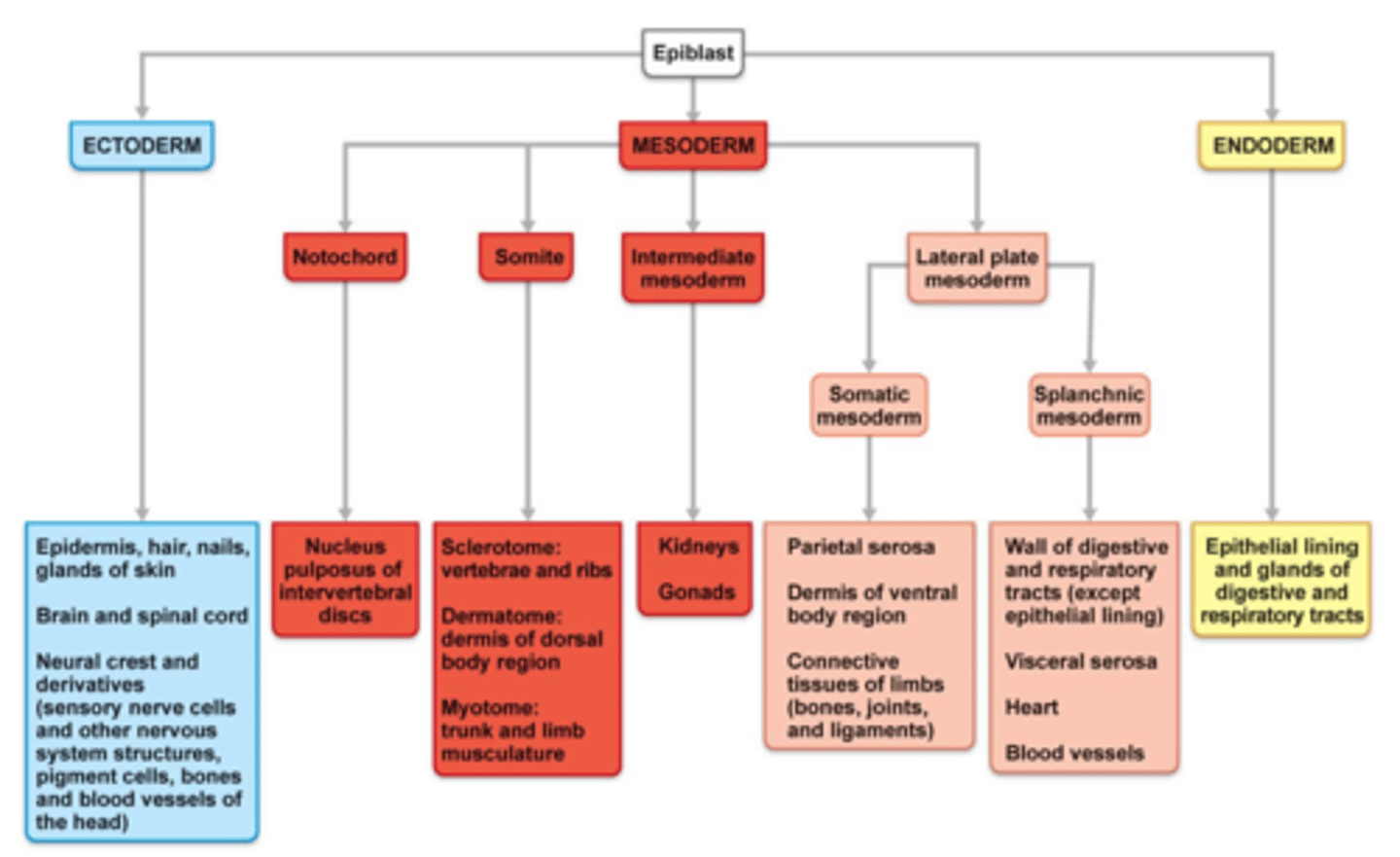
Ectoderm
Responsible for formulating:
+ Epidermis, hair, nails, glands of skin
+ Brain & spinal cord
+ Neural Crest and derivatives (sensory nerve cells & other nervous system structures, pigment cells, bones and blood vessels of the head
*Starts from EPIBLAST
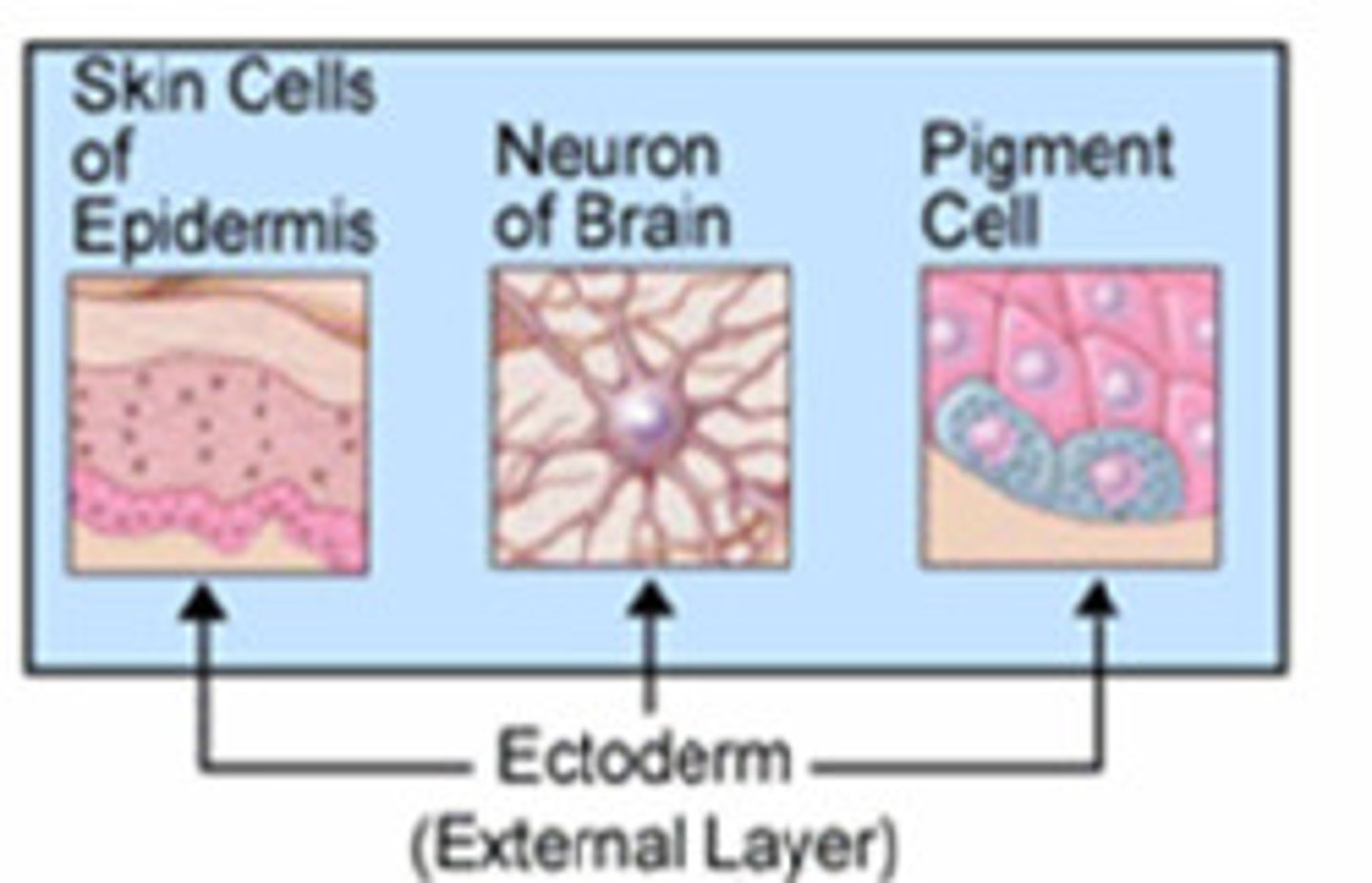
Mesoderm
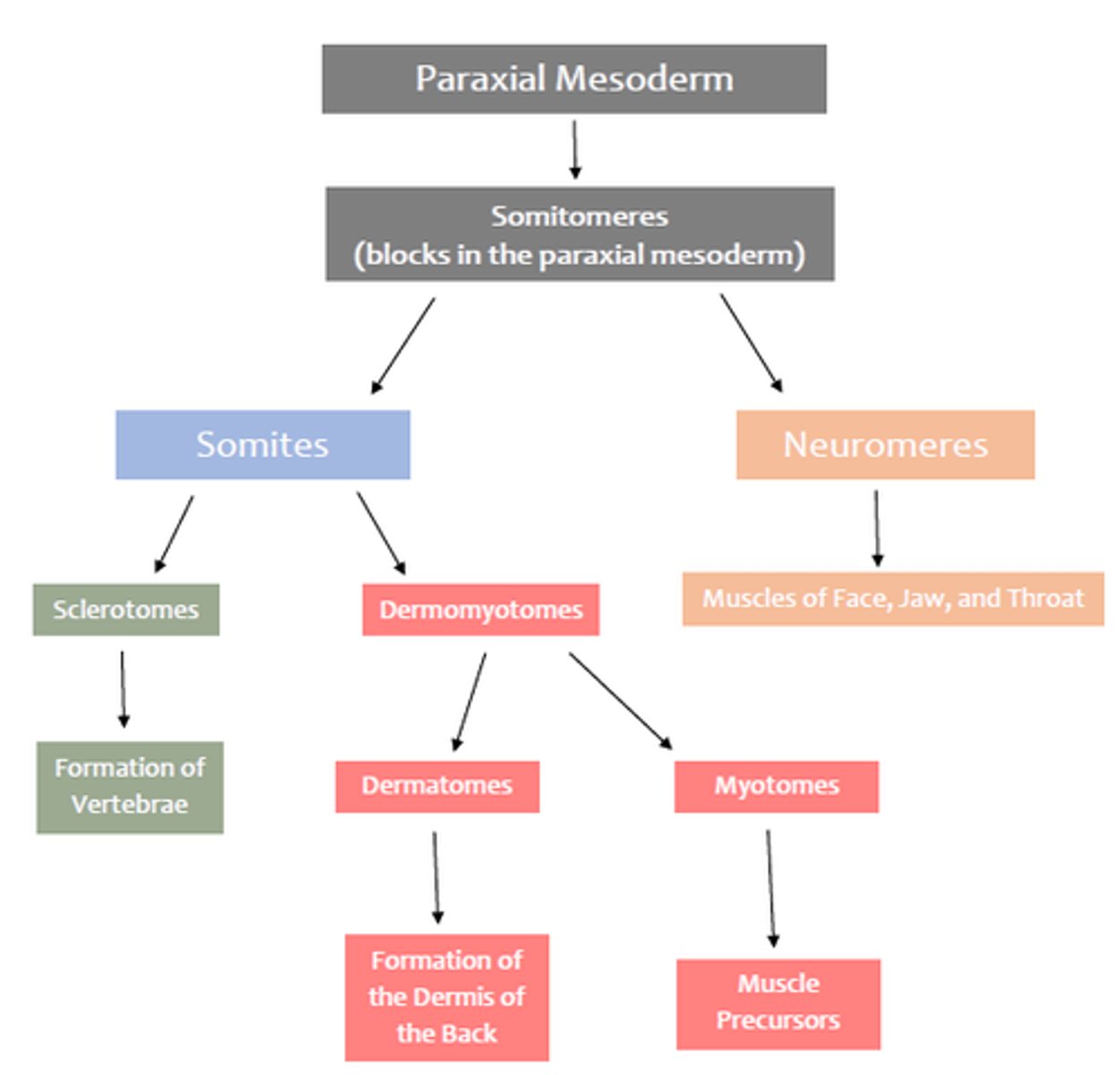
Responsible for Formulating:
A.) Notochord - Nucleus pulposus of intervertebral discs
B.) Somite
B1: Scierotome: vertebrae and ribs; B2: Dermatome: dermis of dorsal body region, B3; Myotome: trunk and limb musculature
C.) Intermediate Mesoderm - Kidneys & Gonads
Endoderm
Epithelial lining and glands of digestive and respiratory tracts
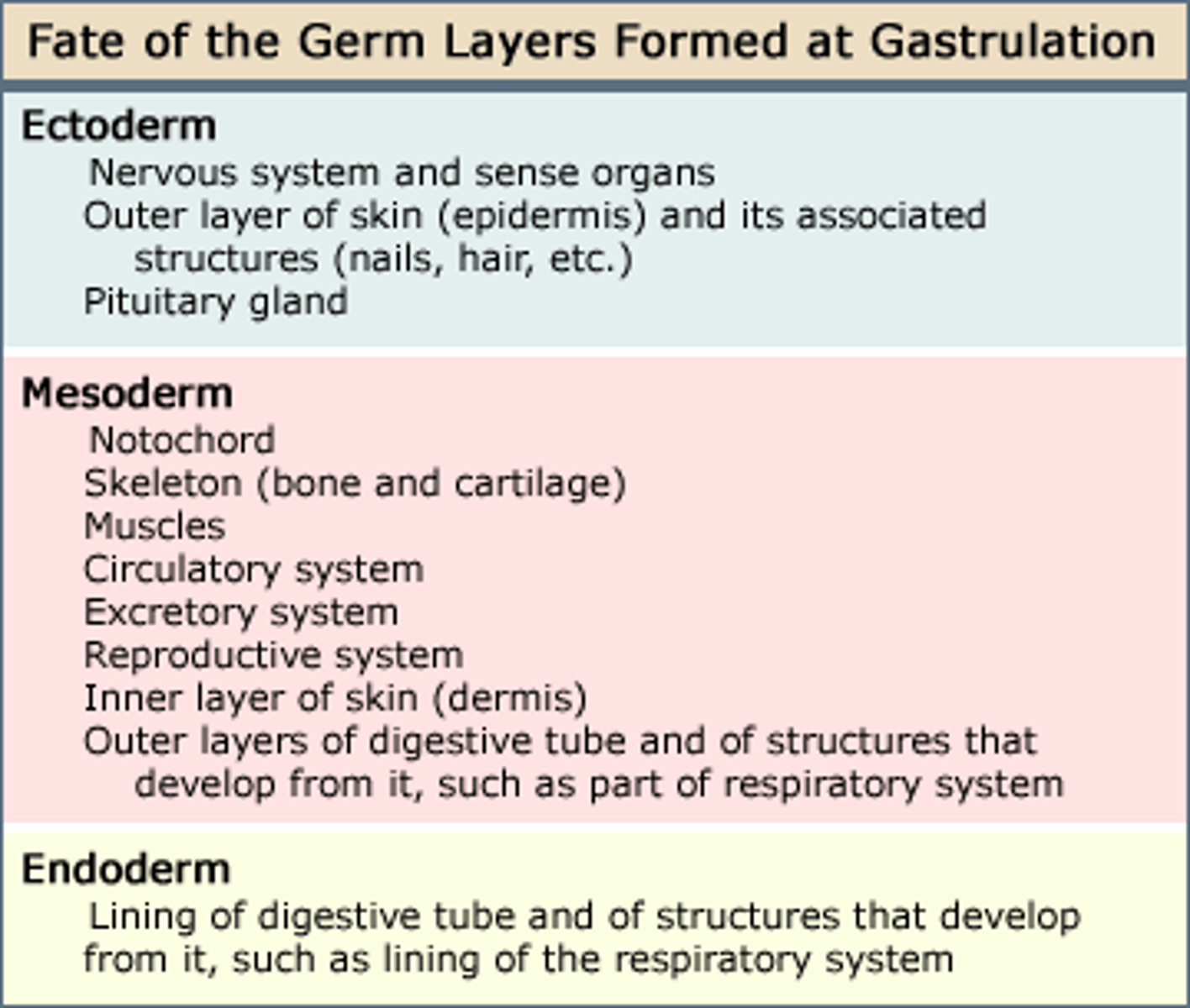
Myotomes
Sometimes give rise to Myotome, Myotomes Give rise to Axial Skeletal Muscles (Muscle Percursors)
Embryonic Cardiovascular System
The first red blood cells and primordial blood vessels from in the wall of the yolk sac
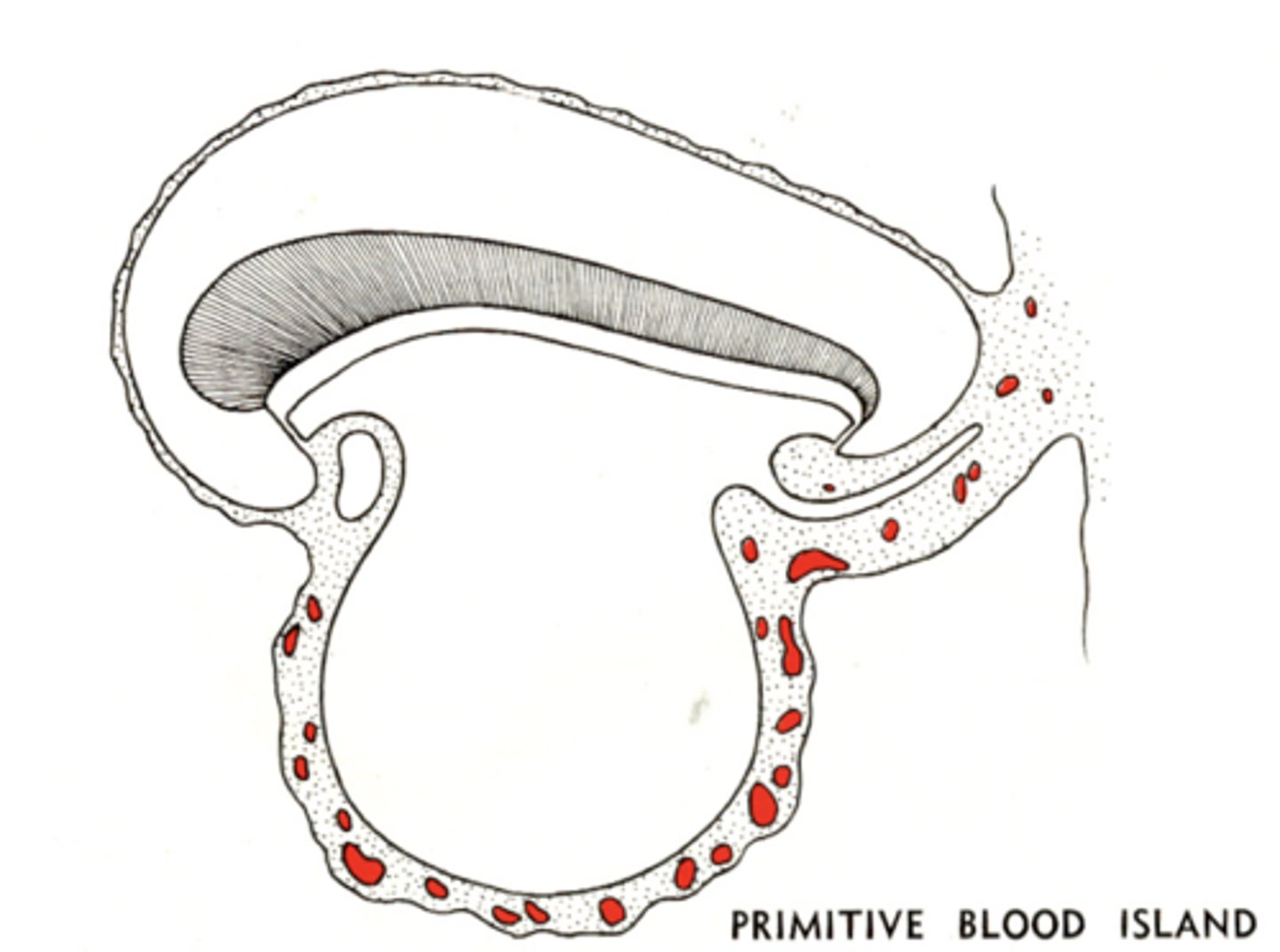
During Cardiovascular Development of the Fetus, the Brain begins to.....?
Grow over the cardiogenic area and pushes the developing heart into its thoracic location
During Cardiovascular Development of the Fetus, blood vessels at the head-end of the yolk sac/embryo boundary begins to....?
Form a Heart Tube
Fetal Growth and Development
Fetal Growth Begins at Stage 23 (Average Size at 47 Days is 29mm)
Marked changes in shape and form
• Early in prenatal period, head is larger than body
• Order of tissue growth determined by physiological importance (CNS first)
• Largest increases in weight of fetus occur during the last trimester of pregnancy
Average Fetal Size (2 Weeks)
1.5 mm
Average Fetal Size (3 Weeks)
2.5 mm
Average Fetal Size (4 Weeks)
5 mm
Average Fetal Size (5 Weeks)
8.5 mm
Average Fetal Size (7 Weeks)
20 mm
Average Fetal Size (2 Months)
33 mm
Average Fetal Size (3 Months)
95 mm
Average Fetal Size (4 Months)
135 mm
Average Fetal Size (6 Months)
230 mm
Average Fetal Size (9 Months)
335 mm
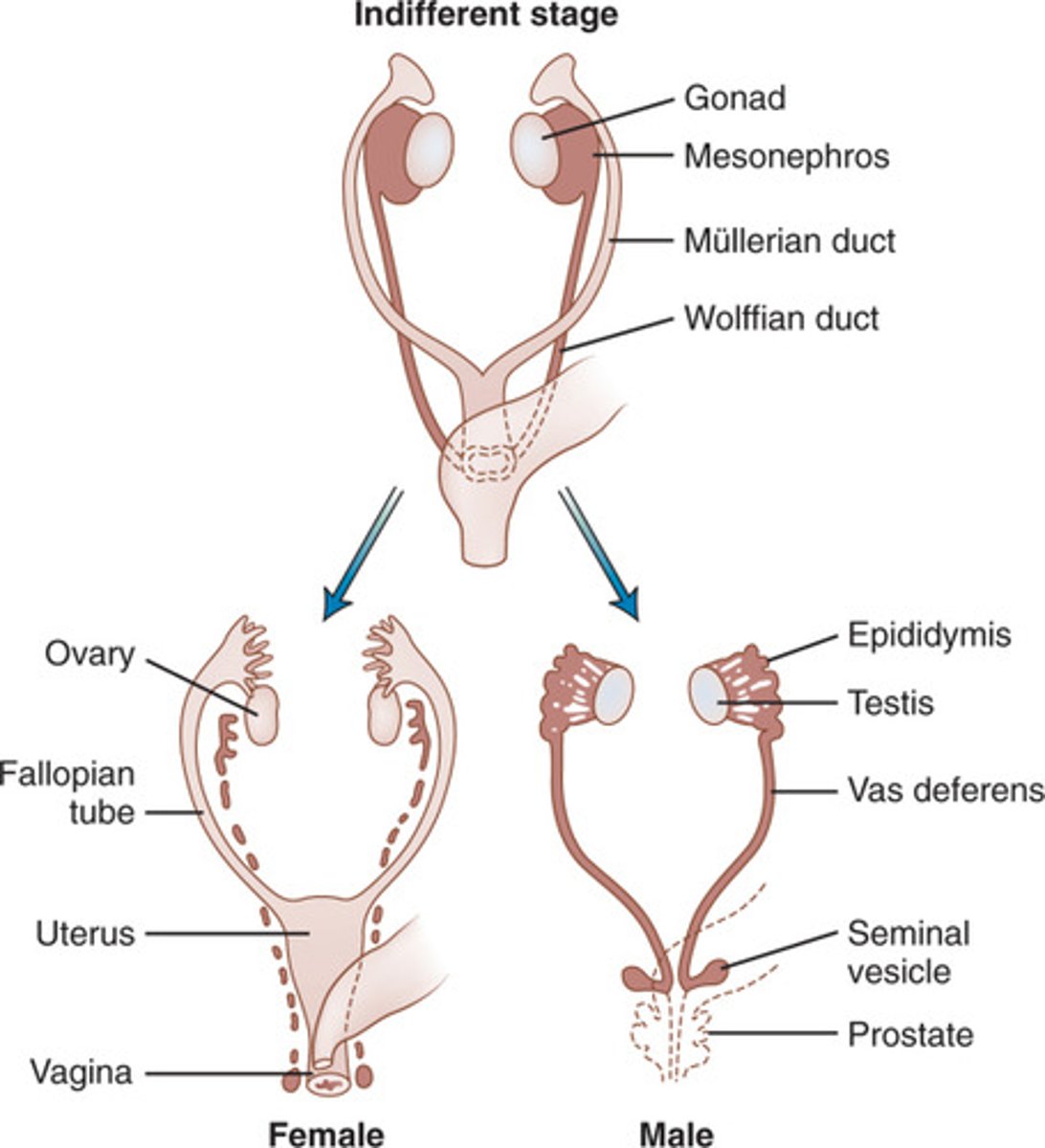
Sexual Differentiation
Up until 9 weeks post/after fertilization is the same for males and females
+ Gene products from the SRY gene convert the Gonads to Tests
+ Testosterone from the testes then promotes the development of male characteristics
What hormone promotes the development of males characteristics?
Testosterone
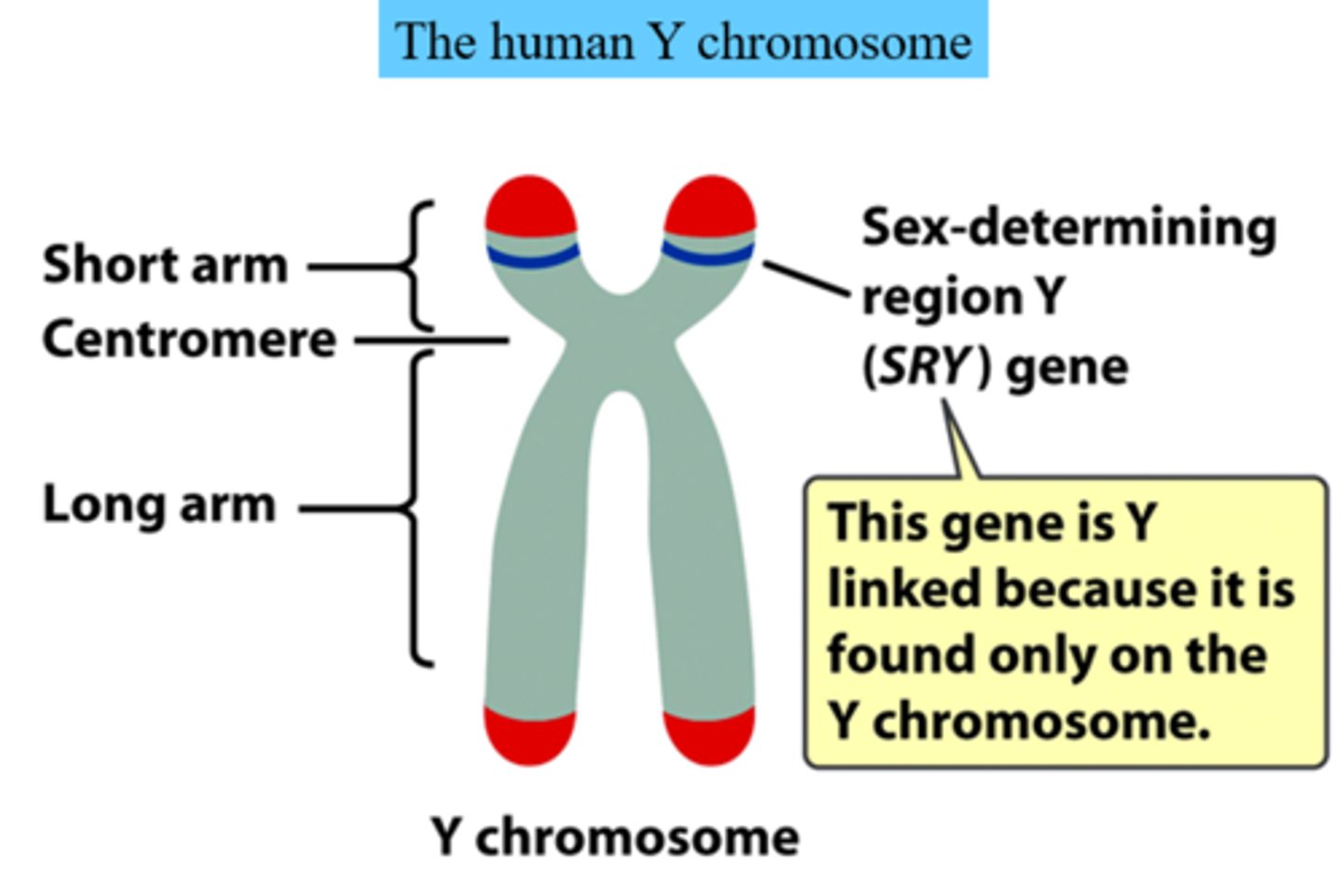
SRY (Sex Determining Region Y) Gene
Gene on Y chromosome that codes for transcription factor that initiates testis differentiation & formation of male gonads
* Found only on the Y chromosome
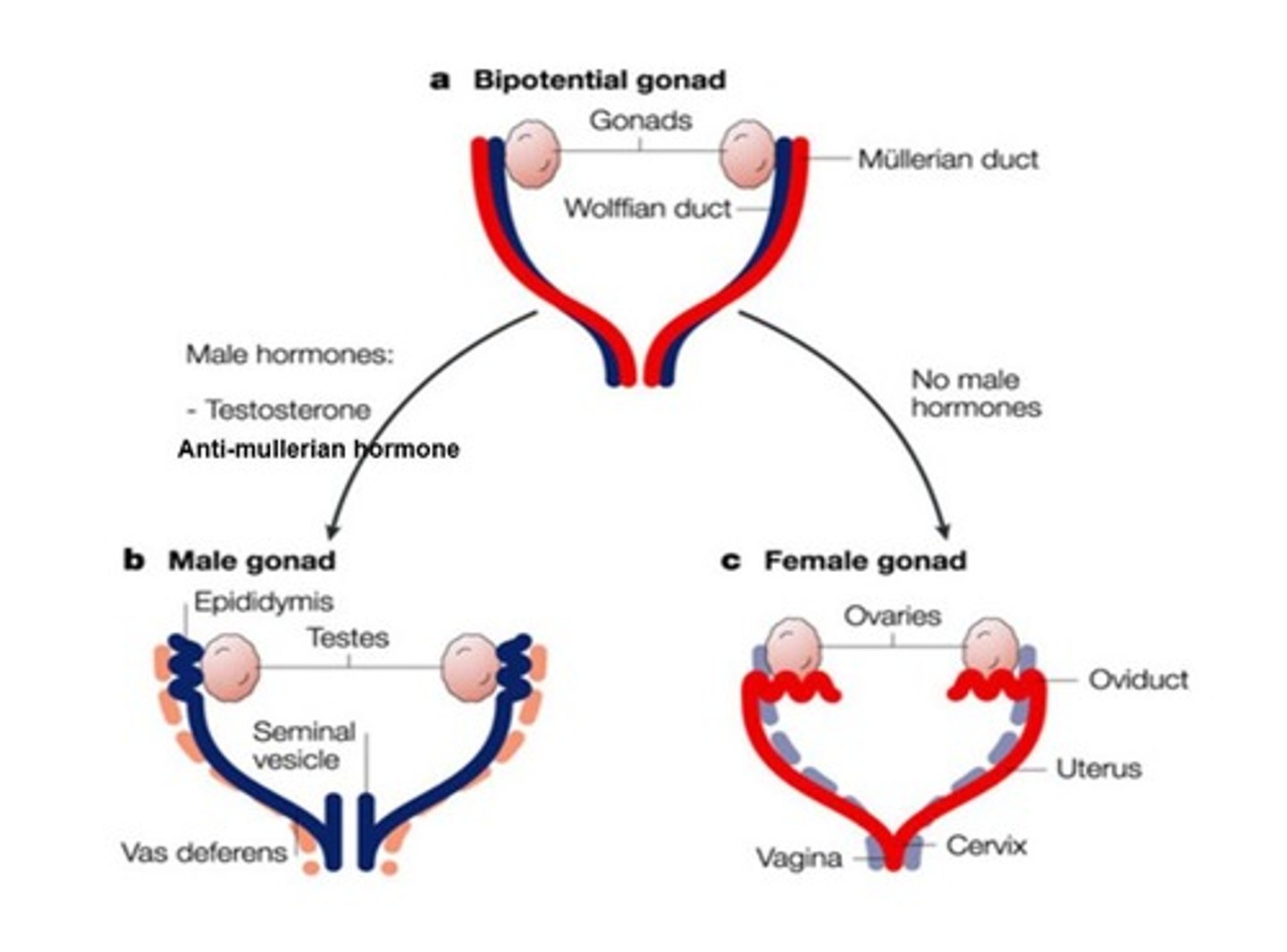
Bipotential Gonad
The gonad of the developing embryo that is capable of differentiating along two developmental pathways toward the development of either a testis or the ovary
External Genitalia Development
Functional similarities btwn sexes
structures develop from same tissues
penis and clitoris
scrotum and labia majora

Hormone that determines gender identity, sexual behavior and external genitalia
Testosterone
Male (XY)
+ SRY is Present = Gonad (Testis)
+ Mullerian ducts degenerate
+ Wolffian Duct Development
- Epididymis
- Vas Deferens
- Seminal Vesicle
- Ejaculatory Duct
Female (XX)
+ NO SRY Present = Gonad (Ovary)
+ Wolffian Ducts Degenerate
+ Mullerian Duct Development
- Fallopian Tubes
- Uterus
- Upper part of Vagina
Intersexuality
Discordance between genitor gender and genital anatomy (Ambiguous Genitalia)
+ Can be Genetic or Endocrine
+ Affects between 1-5 in 2,000 Children
+ Distinct from TRANSGENDER
+ Discordance between gender identity and genital anatomy
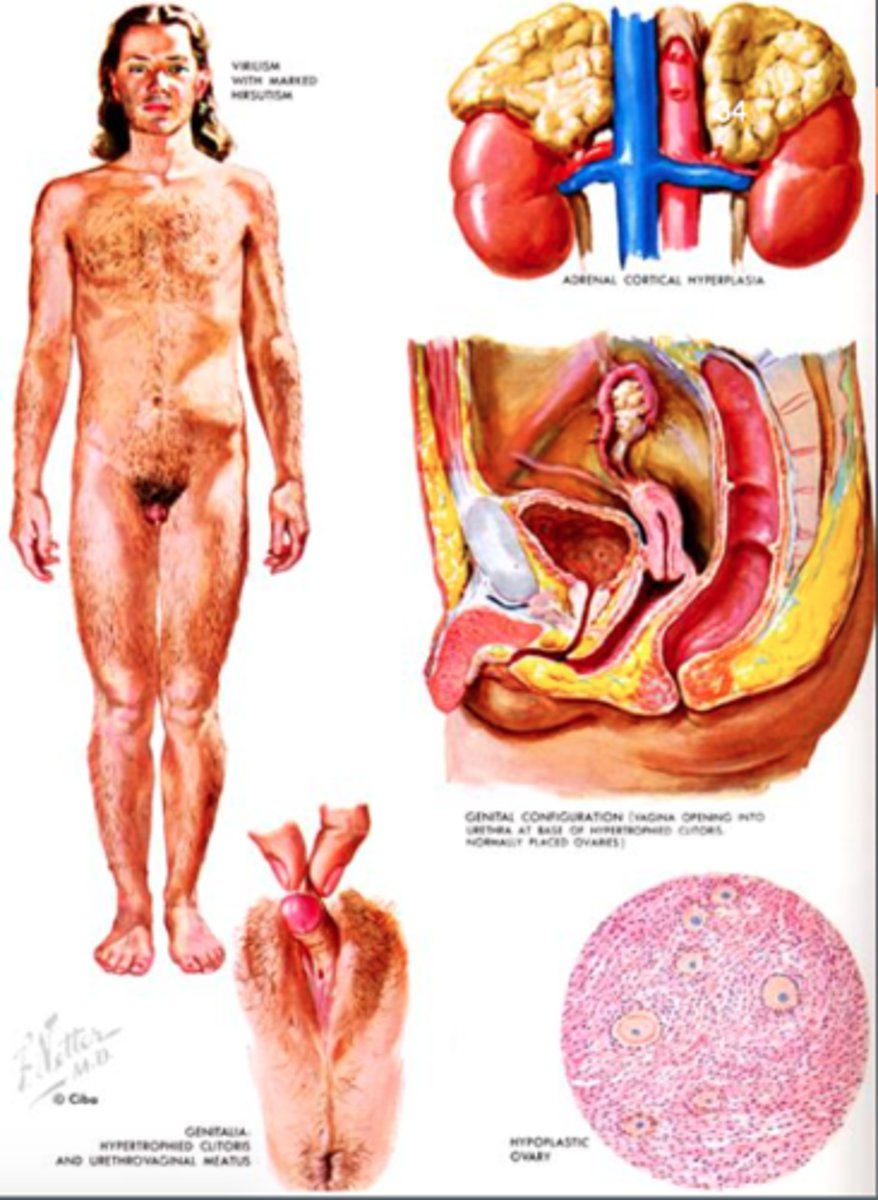
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (AIS)
Body cells of genetic males are unable to respond normally to testosterone (Genetically Male - XY; 46XY Chromosome Complement)
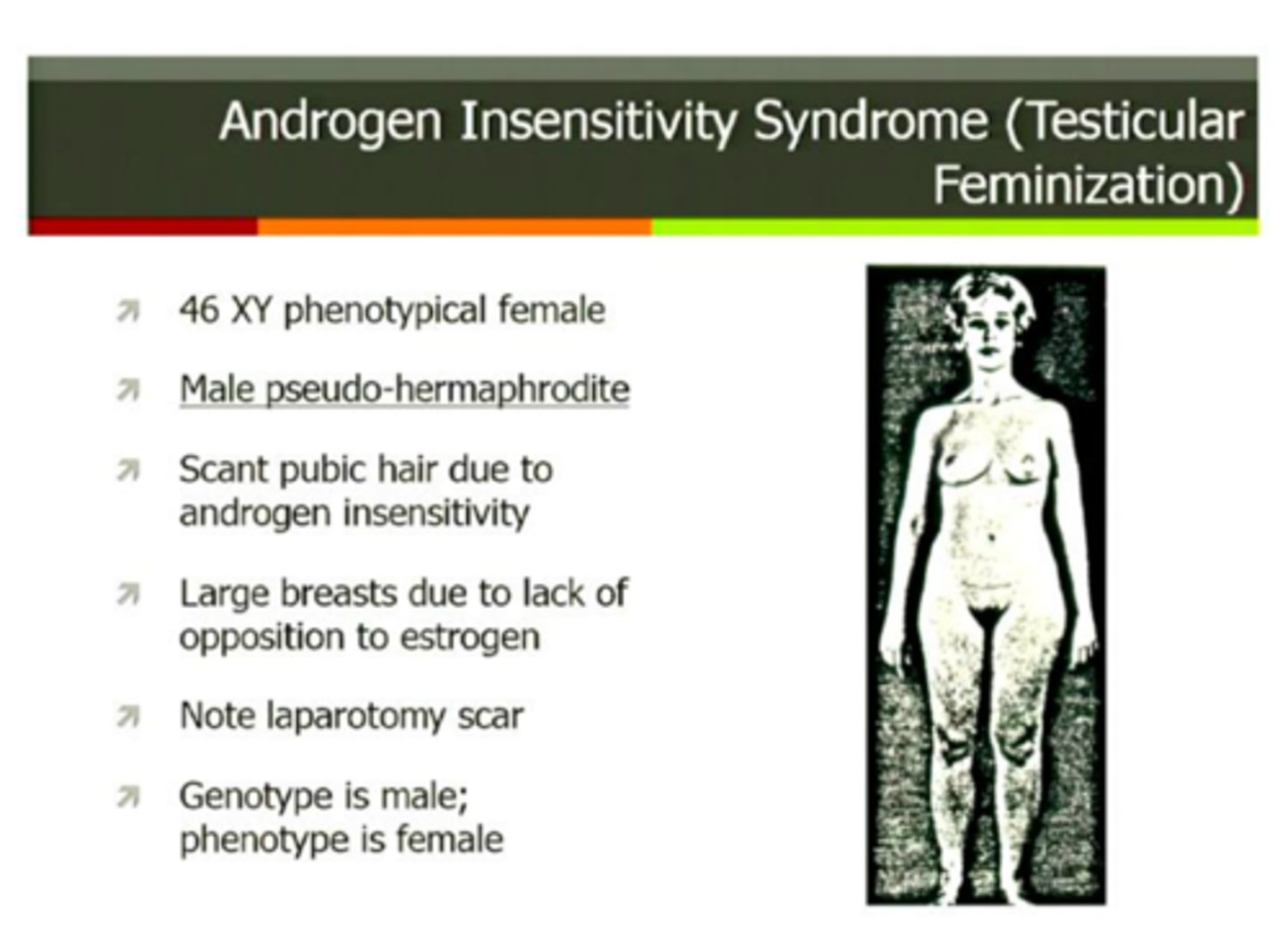
Typical Characteristics of AIS
Genetic males (XY) are born with normal appearing female genitals, and are usually raised as girls.
+ At puberty, they developed breasts but cannot menstruate. Tend to behave in feminine ways
Predominant Gender Identity of AIS
Female (Feminine)
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Genital disorder in which androgens accumulate in the body (Genetically Female - XX)
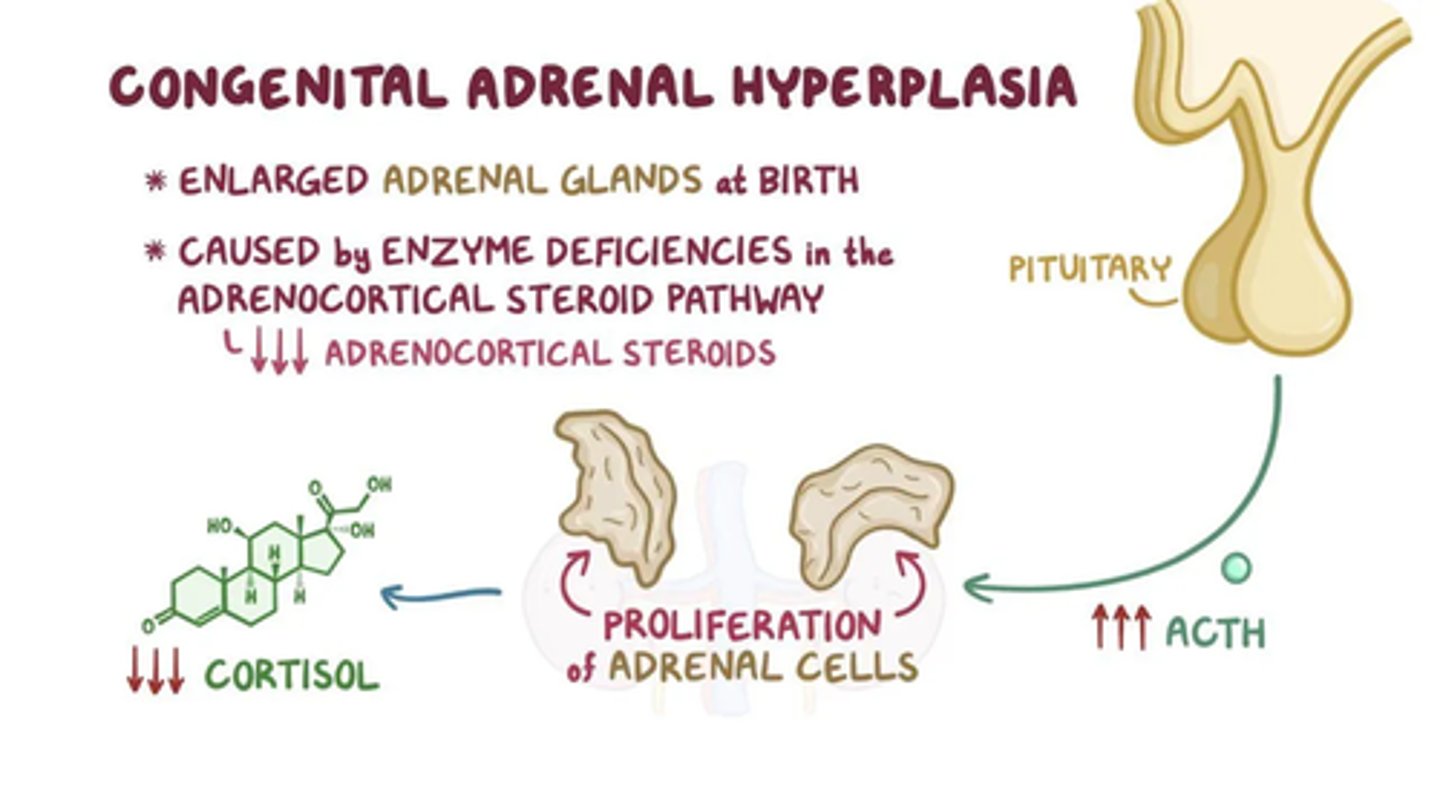
Typical Characteristics of CAH
Masculinization of genitals in genetic females (XX). Even after surgical correction and being raised as female, these girls tend to prefer boy's toys and behavioral patterns, and have higher spatial abilities
Predominant Gender Identity of CAH
(Either), with a tendency towards some masculine traits
Klinefelter Syndrome (XXY)
Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic condition that results when a boy is born with an extra copy of the X chromosome. Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic condition affecting males, and it often isn't diagnosed until adulthood.
Klinefelter syndrome may adversely affect testicular growth, resulting in smaller than normal testicles, which can lead to lower production of testosterone. The syndrome may also cause reduced muscle mass, reduced body and facial hair, and enlarged breast tissue. The effects of Klinefelter syndrome vary, and not everyone has the same signs and symptoms.
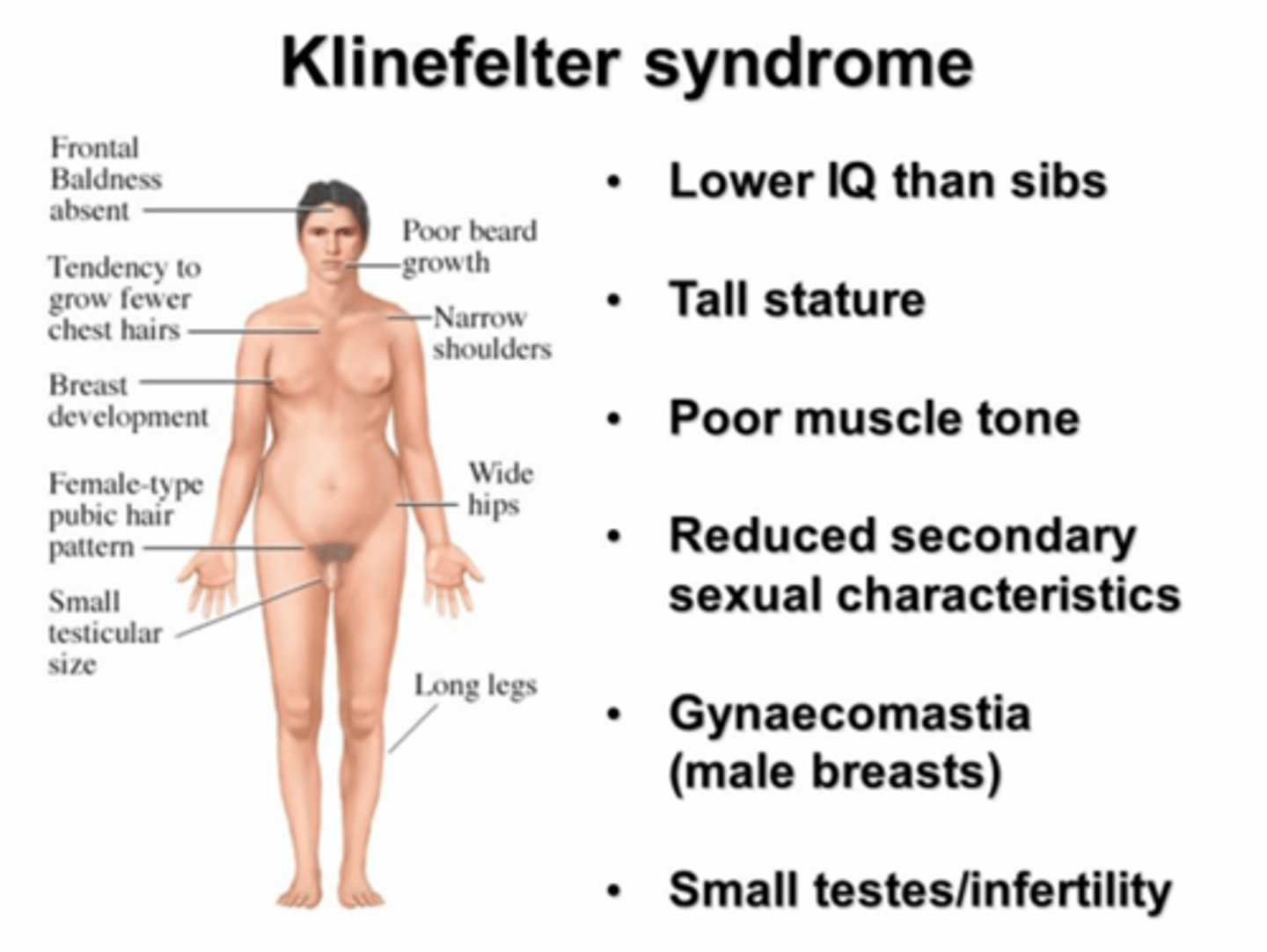
Characteristics of Klinefelter Syndrome
+ Karyotype: 47 (XXY)
+Phenotype: Tall Male
+ Sexual Development: Infertile; Hypogonadism
+ Intelligence: Learning Difficulties (some patients)
+ Behavioral Problem: May have poor psychosocial skills
XYY Syndrome and XXX Syndrome (Trisomy X)
XYY or XXX
May be normal male (XYY) or normal female (XXX)
May have slight intellectual disability and/or fertility problems
Characteristics of XYY/XXX
+ Karyotype: 47 XYY Syndrome (Jacobs Syndrome)/47 XXX (Trisomy X)
+ Phenotype: Tall Male, Female Usually Tall
+ Sexual Development: Normal/Usually Normal
+ Intelligence: Normal Learning/Difficulties in some patients
+ Behavioral Problem: Frequent/Occasional
Turner Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder in females in which either an X chromosome is missing, making the person XO instead of XX, or part of one X chromosome is deleted.
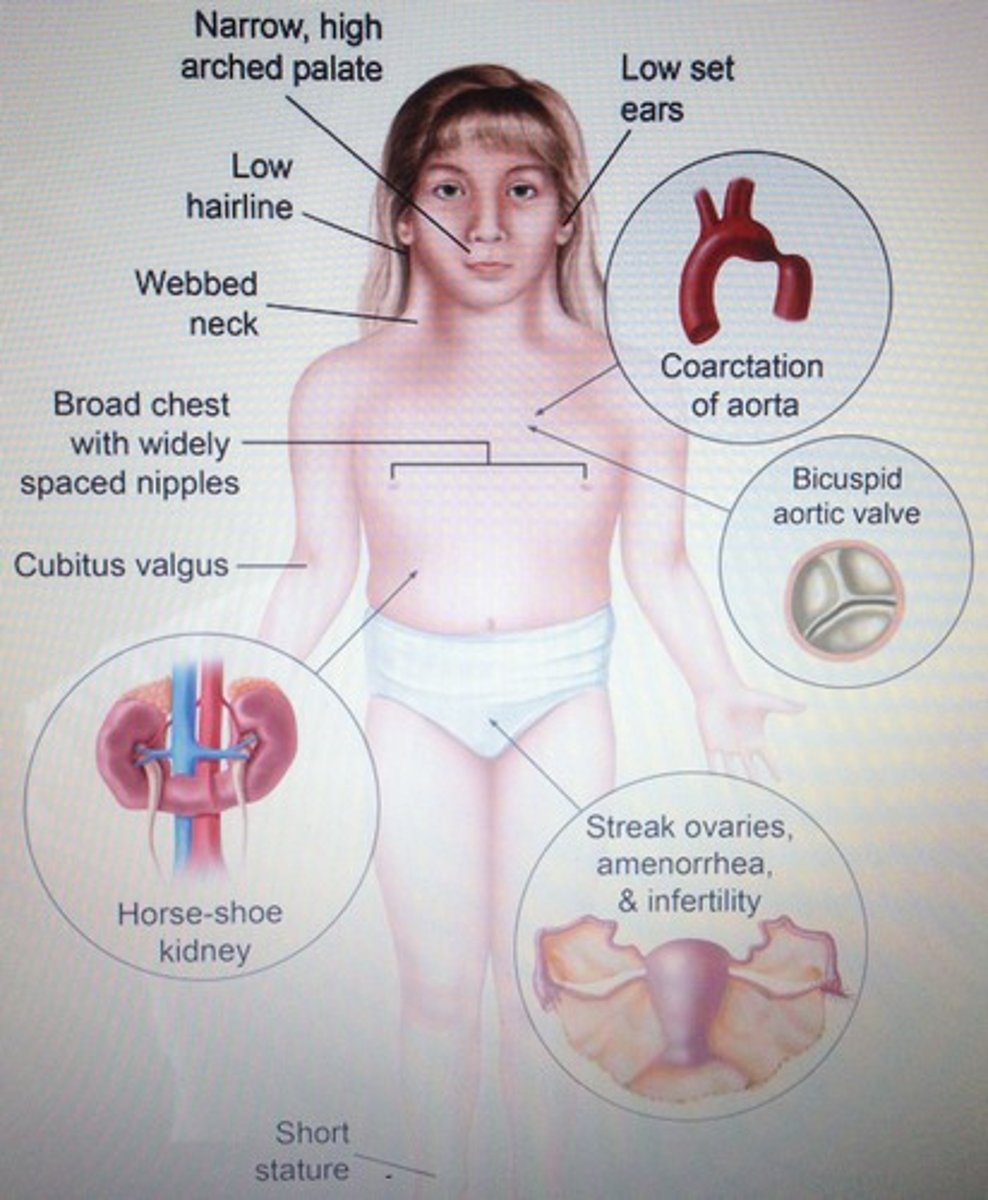
Characteristics of Turn Syndrome
+ Karyotype: 45 XO
+ Phenotype: Short female, distinctive features
+ Sexual Development: Infertile; Streak gonads
+ Intelligence: Normal
+ Behavioral Problem: Rare