U4: Chapter 37,38,39: Musculoskeletal Trauma, Degenerative Disorders, Infection, Inflammation
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Important aspects above Musculoskeletal system(Bones)
Structural Support and Framework for soft tissue
Storage of Minerals- Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium
Production of Red Blood Cells: “Red” Bone marrow
Protects Major Body organs and soft tissue
Provides leverage and movement
Name the bone that is described as Solid and Dense
Cortical Bone
Label the bone that is descried as a non-solid inner meshwork of the bone, making the bone porous. This bone is also called cancellous
The Trabecular Bone
Which type of bone is more susceptance to osteoporosis?
Trabecular bones such as femur, wrist, vertebrae
Name the term that is described as bone-forming cells. This starts bone mineralization by secreting Osteoid
Osteoblast
Name the term that is described as a mature osteoblast. This term maintains the metabolism including nutrient and waste exchange. This term does not divide
Osteocyte
Name the tern: This term is responsible for the bone reabsorption and degradation of existing bone, This term is the opposite of osteoblast
Osteoclast
Name the two terms that are the primary bone remodeling cells(also called the basic multicellular unit-BMU-.
Osteoblast and osteocytes
Name the term descried as bone growing and enlarging in the process termed modeling, where osteoblastic activity predominates
New bone growth
Name the term described as, once the bone reaches maturity, breakdown and renewal is caused by osteoclasts in a process called remodeling
Bone reabsorption
What determines skeletal mass and healing after an injury
The balance between bone formation and resorption occuring at the same time
at what point does osteoclast activity steady decrease in bone mass density
after the age of 30
What else other than calcium is needed for healthy bone production?
Parathyroid hormone, Vitamin D, Calcitonin
\Weight-bearing stress
Impacts the rate of bone remodeling and bone strength. Androgens and estrogens also affect bone health
What is dependent on the kidney and parathyroid function and slightlight exposure to be activated?
Vitamin D dependent
What facilitates Calcium absorption from GI tract?
Vitamin D
excess release of Ca from bone is blocked by
Calcitonin
Skeletal muscle is under _______ control of the somatic nervous system
voluntary
Musculoskeletal Trauma
Associated with sports injuries, or falls, overuse of tendons, strains in the muscles.
Sprain
overstretching of a ligament with possible tear due to twisting or pulling of muscle
Sx: pain, swelling bruising and pain with movement common
Strain
overstretching of tendons and muscle
Sx: pain, limited range of motion, muscle spasms
Fracture
any disruption complete or incomplete in the continuity of a bone
a break within the bone.
Open/compound fractures
bone protrudes outside the body, with risk of soft tissue injury and infection. This can be fixed with surgical repair, but must be done quickly as if the bone also snaps the artery or vein, patient may hemorrhage to death.
Closed/complete fracture
bone treatments separate completely, they are not displaced and remain beneath underling tissue. this can be fixed with a cast
Incomplete fracture
bone fragments remain partially joined
Compression fracture
crushing of cancellous bone
Stress fractures
bone damage from repetitive activity
Transverse fracture
Bone is separated but close

Comminuted
More than one fracture line with shattered/crushed bone

Greenstick fracture
incomplete break, bone is intact
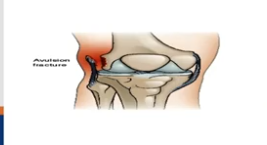
Avulsion fracture
Separation of a small part of bone at site of attachment ligament or tendon
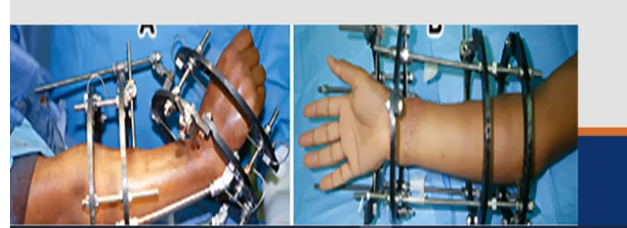
There are two ways to Fix a fracture, one of them is called reduction, what does it do?
This an alignment of the bone. an early stabilization of long bone fractures prevents fatty emboli
There are two ways to Fix a fracture, one of them is called Immobilization, what does it do?
Prevents further tissue damage by use of cast, and splints
In R.I.C.E what does the R mean?
REST. initial 24-48 hours
In R.I.C.E what does the I mean?
Ice per hour for 48 hours
In R.I.C.E what does the C mean?
Compression. by use of brace, splint, or ace
In R.I.C.E what does the E mean?
Elevate above the level of heart
In what case would we use a R.I.C.E treatment?
minor injuries such as sprains, soft tissue damage
Describe the first step to the healing process of a bone healing?
As soon as a fracture occurs, there will be bleeding between the edges of the fractures bone. a hematoma will form within the first few hour to days. The inflammatory response is triggered and this phase will also last 48 hours
Describe the 2nd step to the bone healing process?
fibroblast are attracted to the site of injury and there will be growth of vascular tissue
describe the 3rd phase of a bone healing process?
A callus will form. This callus is composed of osteoblast and chondroblast in the granulation tissue. The cells synthesize the extracellular organic matrix of bone producing new mineralized bone(within 6 weeks)
Describe the 4th phase of the bone healing process?
This is the strengthening phase where ossification begins. the mesh like callus is replaced with sheets of mineralized bone called lamellae. that are stronger than a callus. this will occur a week after callus forms.
Describe the 5th phase of the bone healing process?
at the site of healing, the bone remodeling by osteoclast. formation is sculpted and refined so that it can be properly used again?
strength is restored in 3- 6 months
how many complications of Musculoskeletal trauma are listed in our lecture?
5
Neuro Vascular injury and bleeding (complications of Musculoskeletal trauma)
damage of blood vessels, edema is compressing the nerves because of the swelling
Infection(complications of Musculoskeletal trauma)
Due to the open wound and surgical intervention, local or systemic infection may hurt the area of injury. this can result in serious affects. Use sterible practices!
Deep vein thrombus and PE(complications of Musculoskeletal trauma)
Due to a venous injury causing stasis of blood.
fat embolism(complications of Musculoskeletal trauma)
Fat globules from bone marrow enter circulation. this can occur after a pelvic and/or long bone fractures.
majority of fat emboli can go to the brain causing a stroke.
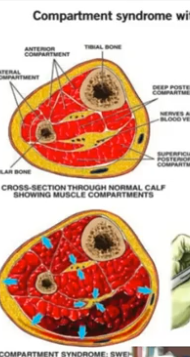
Compartment Syndrome(complications of Musculoskeletal trauma)
when swelling after an injury gets so bad that it squeezes everything inside too tightly, and it needs quick medical attention to fix it before it causes bigger problems. Doctor will go in and cut the skin(called a fascia) open to release the pressure that is within the area of injury
Symptoms:
- Edema
- parathesis in the affected area
- weak distal pulses
- pressures can be measures as greater than 30mmHm
- might feel cool to the touch
late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries. How many are mentioned in our lecture?
5
Delayed healing(late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries)
Bone taking abnormally long period to heal
Malunion(late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries)
Bone heals in an unacceptable position
non-union(late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries)
Permanent failure of bone to heal
Post traumatic arthritis(late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries)
inadequately reduced intra-arthricular joint fractures → chronic pain
Avascular necrosis(late complications of Musculoskeletal injuries)
Deterioration of bone due to lack of blood supply. This is common with fractures in the femoral head or humerus
List the two most common fractures
Hips, vertebral compression fracture
What are both hips and vertebral compression fractures most caused by?
Osteoporosis
If we were to have a femur fracture, what would happen?
This bone is the strongest bone in the body. This fracture will cause a lot of bleeding, we also cannot bear weight, stress fractures can occur with joggers.
If we were to have a Tibia or fibula fracture, what would happen?
Most common long bone fracture, usually the two bones are broken, result of a low energy fall, or athletic injury.
What is a lumbar strain or sprain?
L4-L5 bears the weight, so most motion happens here and can strain. the strain can be a partial or complete tear of muscles or tendons. Do a straight leg raise to find if patient has a herniated disc.
Rotator Cuff injuries
a tear of tendon or muscle
Sx: Weakness, limited ROM of shoulder, pain
Tx: rest, ice, steroids, surgical intervention may be needed
Brachial Plexus injury
happens because of trauma or birth injury. Overstretching of the arm. This term is also associated with injury to neck or head
Sx: shock like pain radiating down arm absent or diminished pulse in the arm
What is related to degenerative musculoskeletal disorders.
Aging
Osteoporosis
Low density and structural deterioration of bone tissue with actual breaks in bone matrix
There is increased risk of fractures due to the bone being so fragile
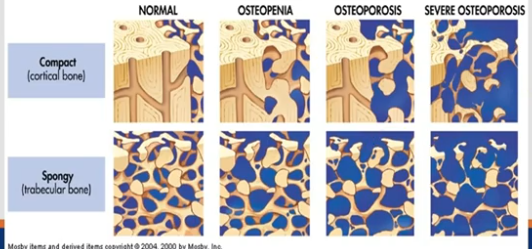
Osteopenia
Thinning of trabecular bone before osteoporosis develops
What is the patho for Osteoporosis?
Imbalance between osteoclast and osteoblast. specifically he osteoclast activity outpaces the osteoblast activity. resulting in bone destruction
Etiology of Primary osteoporosis
prolonged negative calcium balance due to a nutritional deficit of CA, lack of weight bearing activity, decline in sex hormones and lack of exposure to sunlight.
Etiology of secondary osteopororsis
Disorder affecting the bone: Hyperparathyroidism, corticosteroid medications, celiac disease, malabsorption conditions
Why is osteopororsis also called the “Silent disease”
First symptom of this disease is often a fracture of the hip or back. that’s how we know there is something more going on
Risk factors for osteoporosis
Aging, post-menopause, decreased mobility, hormone disorders, deficits in calcium or Vitamin D, cigarette smoking, excess caffeine
Osteoarthritis
Progressive degeneration and inflammation of joints that will gradually wear away the cartilage surface exposing bone. This will affect the weight bearing joints like the ankle, hip, knee
Risk factors of Osteoarthiris
Age, obesity, history of sports or previous joint injury
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
stiffness of joints, deep aching joint pain after exercising or weight bearing. pain will be released with rest
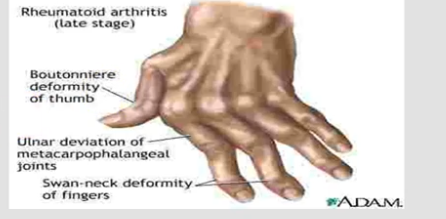
Rheumatoid Arthritis
a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disorder, causing permanent damage to joint. Immune system attacks synovial tissue stimulating an inflammatory process that destroy cartilage, bone, tendon and ligaments.
This disease will lead to permanent deformity of joints and destruction of joint through erosion.
Genetic factor 50% possible if a loved one has it.
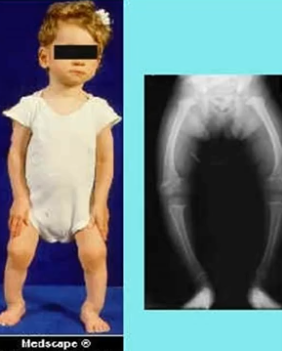
Rickets
failure to osteoid calcification resulting in soft bones. May be due to a malnutrition. can affect children ages 4-12. you can see on bones that the bones are not as straight as they need to be.
Only in children
Osteomalacia
Almost the same as rickets, except this occurs in adults, not children.
disorder of calcium absorption caused by vitamin D deficiency in adults.
Sx: pain in lumbar area, pain when sternum is palpated, muscle weakness or bone pain
Degenerative Disc disease
very common, intervertebral disc flatten in the cervical or lumbar spine, with age the disc becomes rigid and loose elasticity and can collapse. Disc may herniate out of the column putting pressure on nerves that may affect sensory and/or motor function
risk factors: heavy lifting, obesity, twisting of torso, poor physical condition and family history
Osteomyelitis
infection and inflammation of bone caused by a microorganism typically a bacteria. Bones and joints become infected through two ways. Contiguous spread- organisms invading via puncture or wound, or hematogenous spread- pathogens spread via blood stream from another site of infection
Chronic osteomyelitis- untreated, or undertreated. failed response to antibiotics and is a destructive disease. bones become necrotic
What can happen to a person when they have osteomyelitis?
Bacteria invades the bone and deprives the bone of oxygen. the bone tissue will die, become necrotic and from that will be susceptible to gangrene.
Label symptoms of Osteomyelitis
Fever, chills, Malaise the whole body is the response. Tenderness, edema and pain in localized area.
treatment for osteomyelitis
6-8 weeks of antibiotics, removal of prosthesis, therapy
Etiology of Osteomyelitis
Staph aureus most common organism
Reactive arthritis (reA)
an autoimmune reaction in one or more joints caused by bacteria infection in another part of the body.
What joints can be most affected by infection or inflammation?
Knee and hip
Where can there be an increased risk of joint infection
A joint replacement surgery
Inflammatory arthritis
an inflamed joint, where. CHat pgt this im not sure eaither
why is it difficult to treat the joint synovial?
there is limited exchange between the blood stream and synovial joint, the limitation hinders transport of therapeutic agents into inflamed joints.
Intra-articular injection is often needed for medication delivery
What is a huge risk when getting a prosthetic?
a susceptibility to infection, this is because the joint in vulnerable to infection during surgery. its important to note that prosthetic materials can act as a binding site for various bacteria
Septic Arthritis/ Infectious Arthritis
A direct invasion of a joint by pathogenic organisms entered by the blood stream. bacteria is most common. Joint will become inflammed
Etiology of a Septic Arthritis/ Infectious Arthritis
Invasion of a bacteria 40%. Prosthetic joint infections caused by contamination in the OR is in 60-80% of cases
Symptoms of Septic Arthritis/ Infectious Arthritis
inflammation, pain in joint, malaise, fever. can get red and swollen and there will be a decreased ROM.
Treatment of Septic Arthritis/ Infectious Arthritis
aggressive treatment with antimicrobial to prevent destruction of cartilage and fibrosis of joint.
Gouty Arthritis(Gout)
recurrent inflammation triggered by recurrent hyperuricemia, elevated uric acid in blood and high uric acid crystals in the synovial fluid.
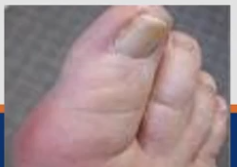
How can Gouty Arthritis(Gout) cause damage?
This disease will leave deposits of uric acid crystals in the joint leading to acute inflammatory response that will lead to damage to articular cartilage
Primary gout
metabolic cause, it is a defect in renal excretion of uric acid
Secondary gout
due to other conditions such as obesity, cancer, psoriasis, or medications
What would happen if Gouty Arthritis was there for a long time?
there will be crystal deposits in the joints and skin, this is very painful
the uric acid crystal forms in tissue by product if purine metabolism
Psoriatic Arthritis(PsA)
an autoimmune disorder. a chronic inflammatory disease of the joints and connective tissue that is linked to the skin disorder psoriasis. in 85% of this disease it will move on into a joint disease