Biology 20A - Midterm 1 - John Tamkun UCSC
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
126 Terms
Most Common Elements in Cells
CHONPS
Strength of Bonds (Weakest to Strongest)
Hydrogen bonding < Ionic Bonding < Covalent Bonding (Non-polar < Polar
When pH decreases (becomes more acidic
Concentration of H+ goes up
5 Special Properties of Water
Cohesive, High Heat Capacity, High Heat of Vaporization, denser as a liquid, good solvent for polar molecules
1 m
10^-6 µm, 10^-9 nm, 10^-12 pm
How does perspiration keep our bodies cool?
Water has high heat of vaporization due to H-bonding, thus sweating (evaporation of water) has cooling effect on human body.
What is a buffer?
prevents changes in pH, usually weak acid with corresponding base. Can accept/release protons to maintain constant pH
Cells are mainly composed of...
Water and carbon-based molecules
Hydrocarbons
Molecules that contain only C and H
Linked by nonpolar covalent bonds
hydrophobic (not soluble in water)
Importance of Carbon chemistry
Unique in ability to form long chains, branched molecules, rings
Versatile building block for wide variety of complex molecules
Diversity of Hydrocarbon Skeletons
Vary in length
can be linear or branched
may contain one or more multiple bonds/rings
Common functional groups
Hydroxyl, Carbonyl, Carboxyl, Amino, Sulfhydral, Phosphate
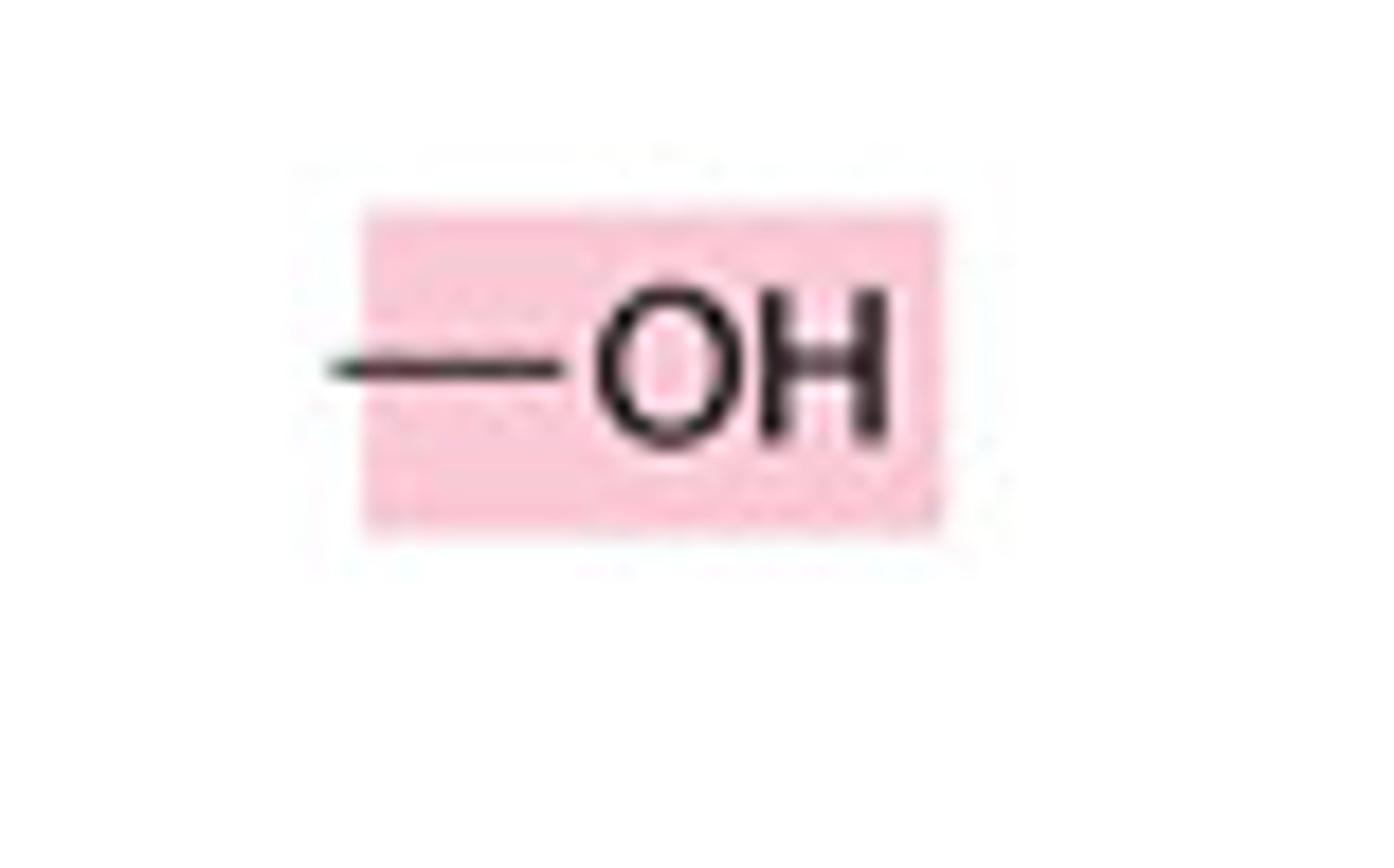
Hydroxyl Group
founds in alcohols, sugars, and other organic molecules
Carbonyl Group (Ketone)
middle of carbon chain=keytone
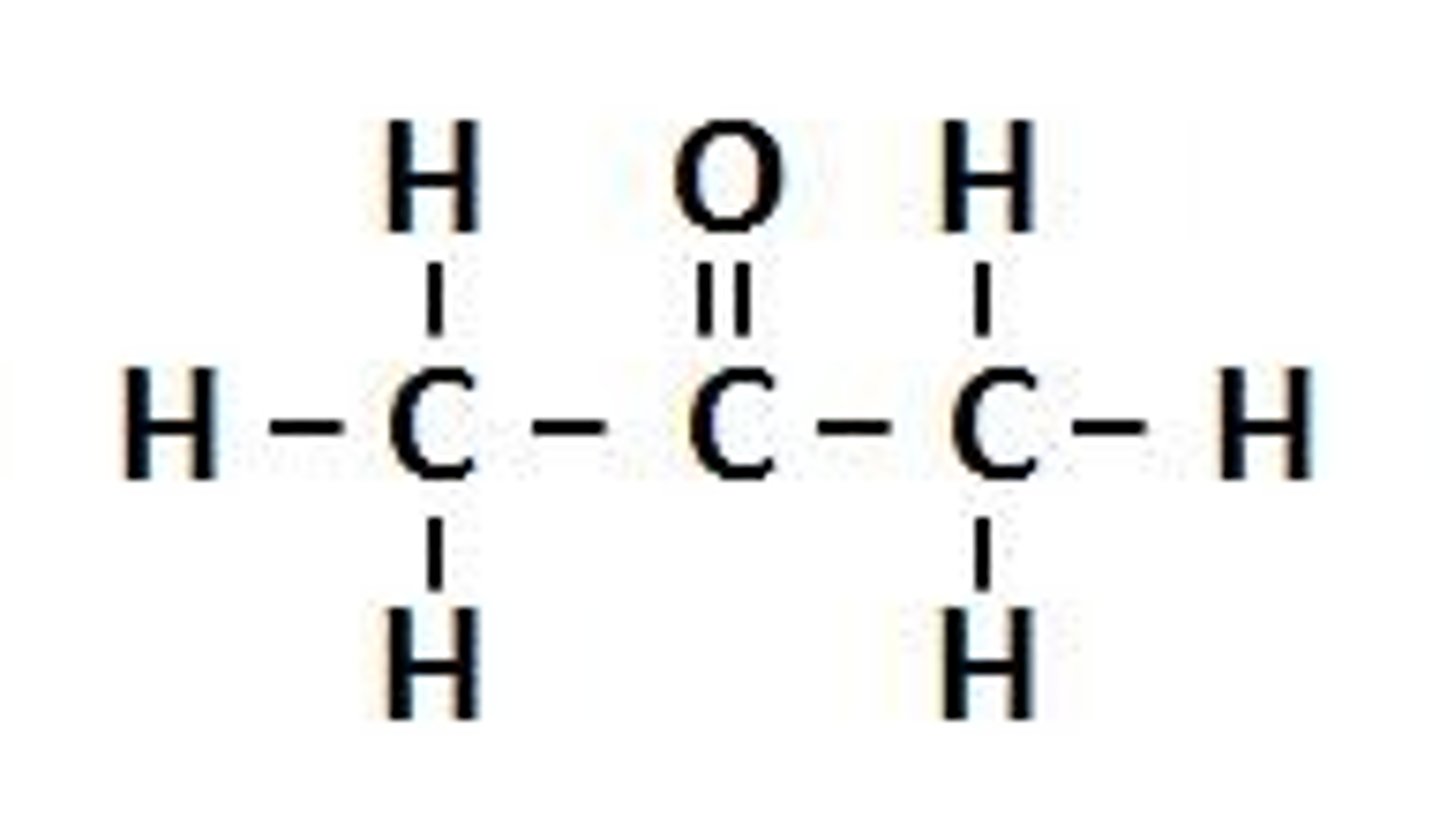
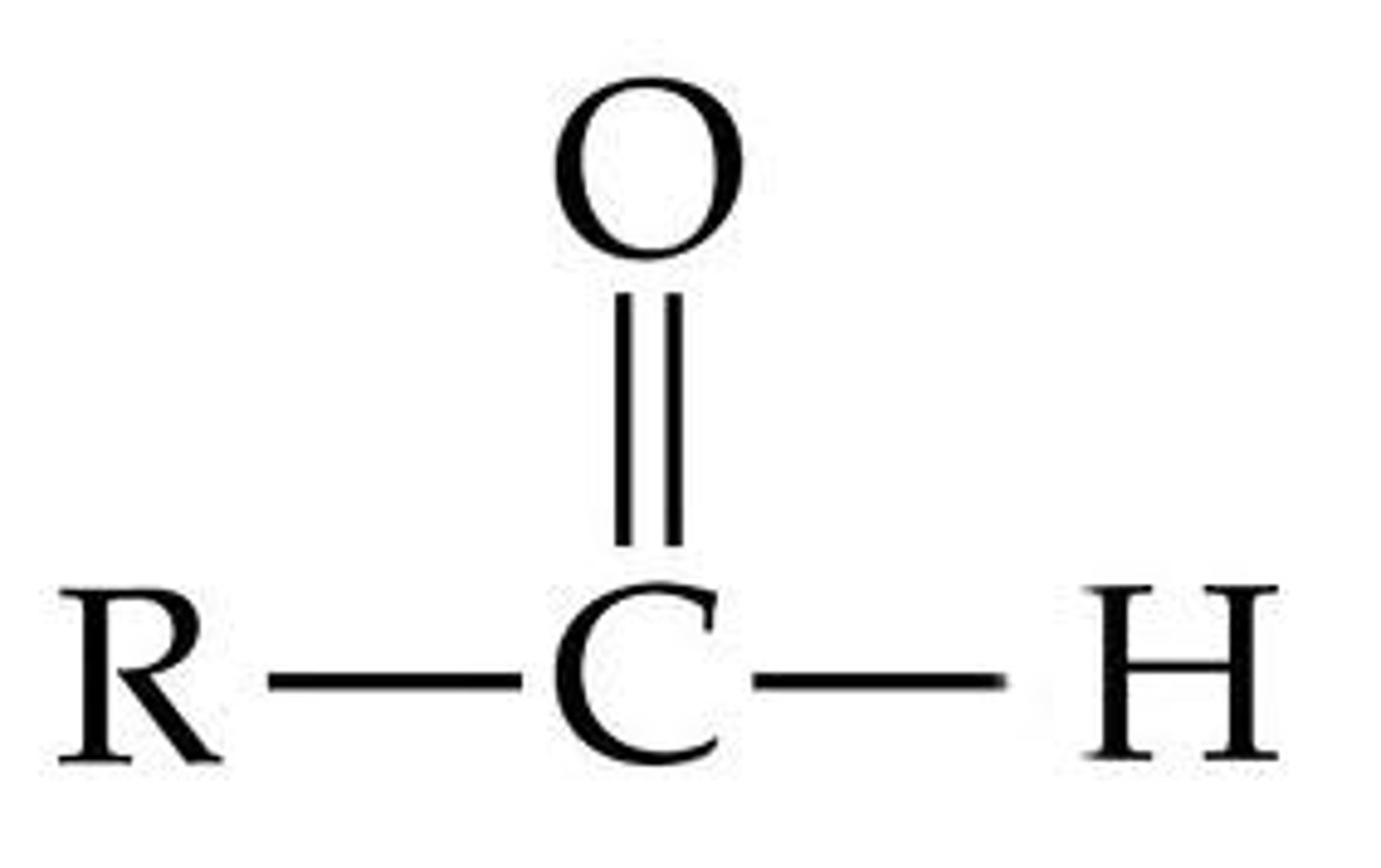
Carbonyl Group (Aldehyde)
end of carbon chain=aldehyde
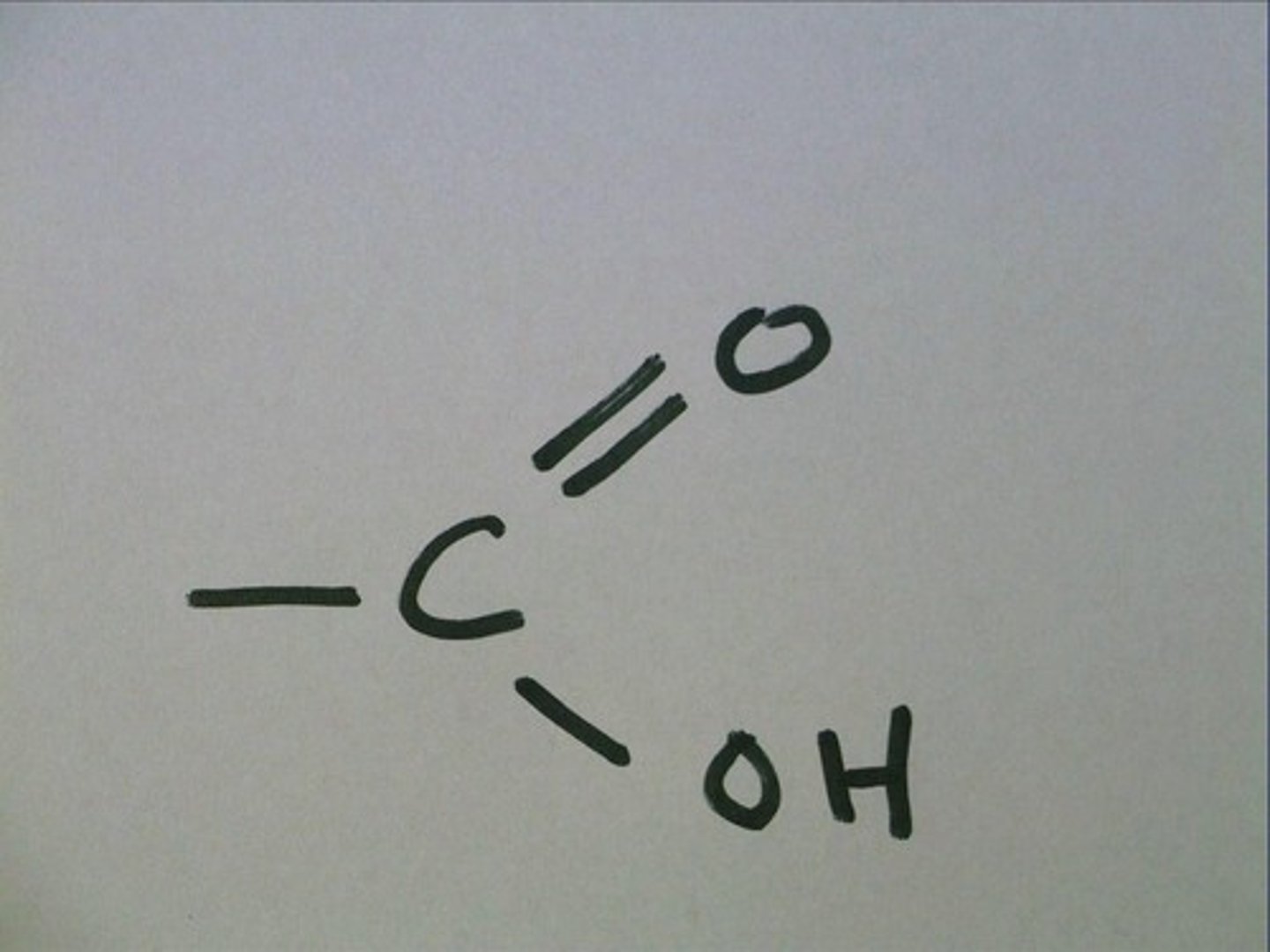
Carboxyl Group
organic acid, exists in non ionized and non-ionized for(means O loses a H)
Amino Group
basic group, accepts protons
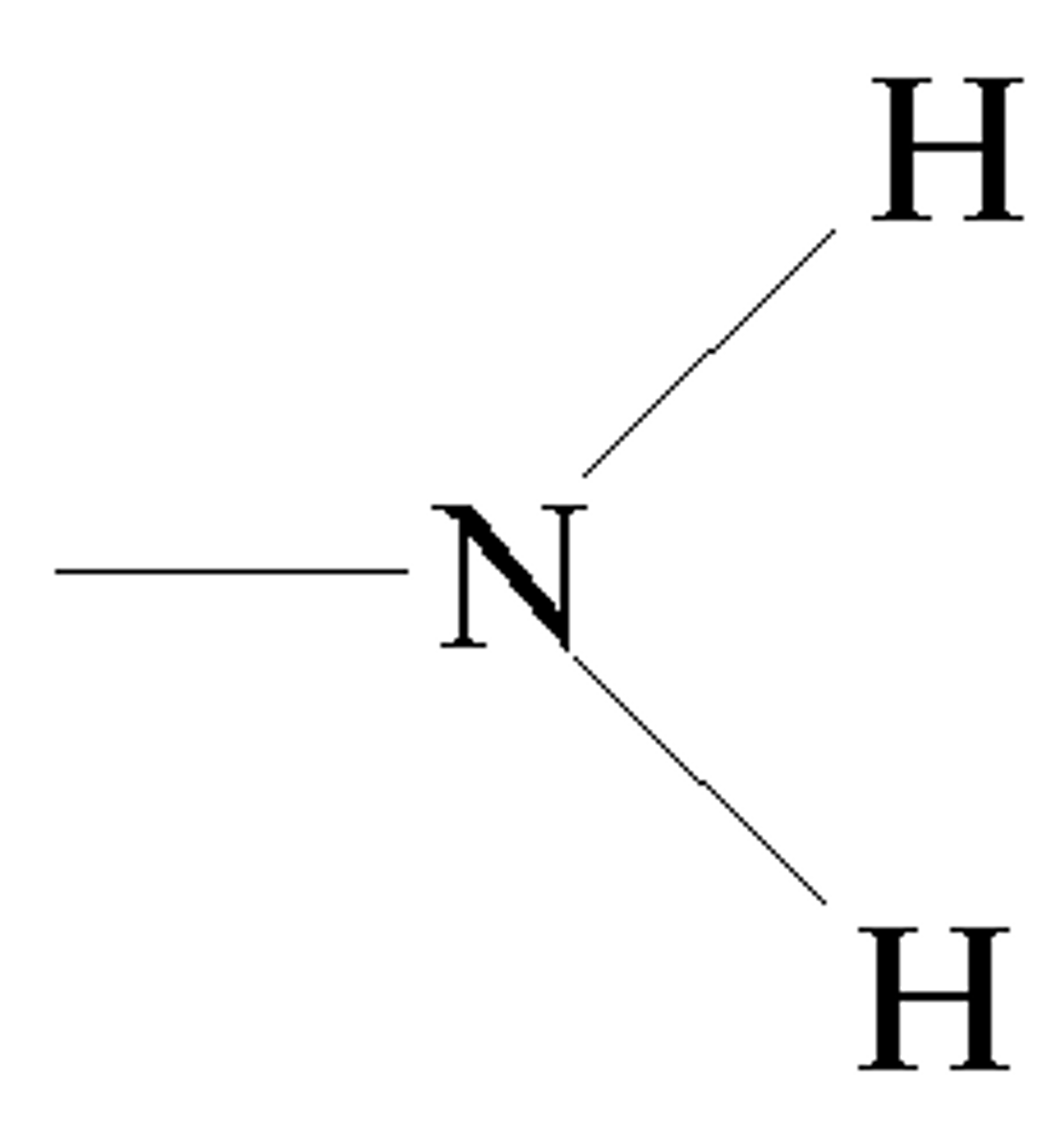
Sulfhydral Group
found on thials (??)

Phosphate Group
-Po4 (-2). Acidic group found on the 5' carbon in deoxyribose and ribose [DRAW THIS!]
![<p>-Po4 (-2). Acidic group found on the 5' carbon in deoxyribose and ribose [DRAW THIS!]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/22cfcb01-9087-4786-8f53-9d84bb7ebb2c.jpg)
4 Major Groups of Macromolecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Lipids
Bonds are often made/broken by...
Dehydration reactions/Hydrolysis Reactions
Proteins (monomer/polymer)
Monomer: Amino Acids
Polymer: Polypeptide
Functions of Proteins
Structure, Regulation, Signaling, Movement, Metabolism, Transport
Amino Acid
[DRAW THIS!] Label amino group, alpha carbon, r-group, and carboxyl group!
![<p>[DRAW THIS!] Label amino group, alpha carbon, r-group, and carboxyl group!</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ee082ac6-b596-4fdf-865b-d7ae1a803196.jpg)
How do R groups affect amino acids
It affects their structure/shape. Determines how they fold.
Alanine
A, Ala Nonpolar
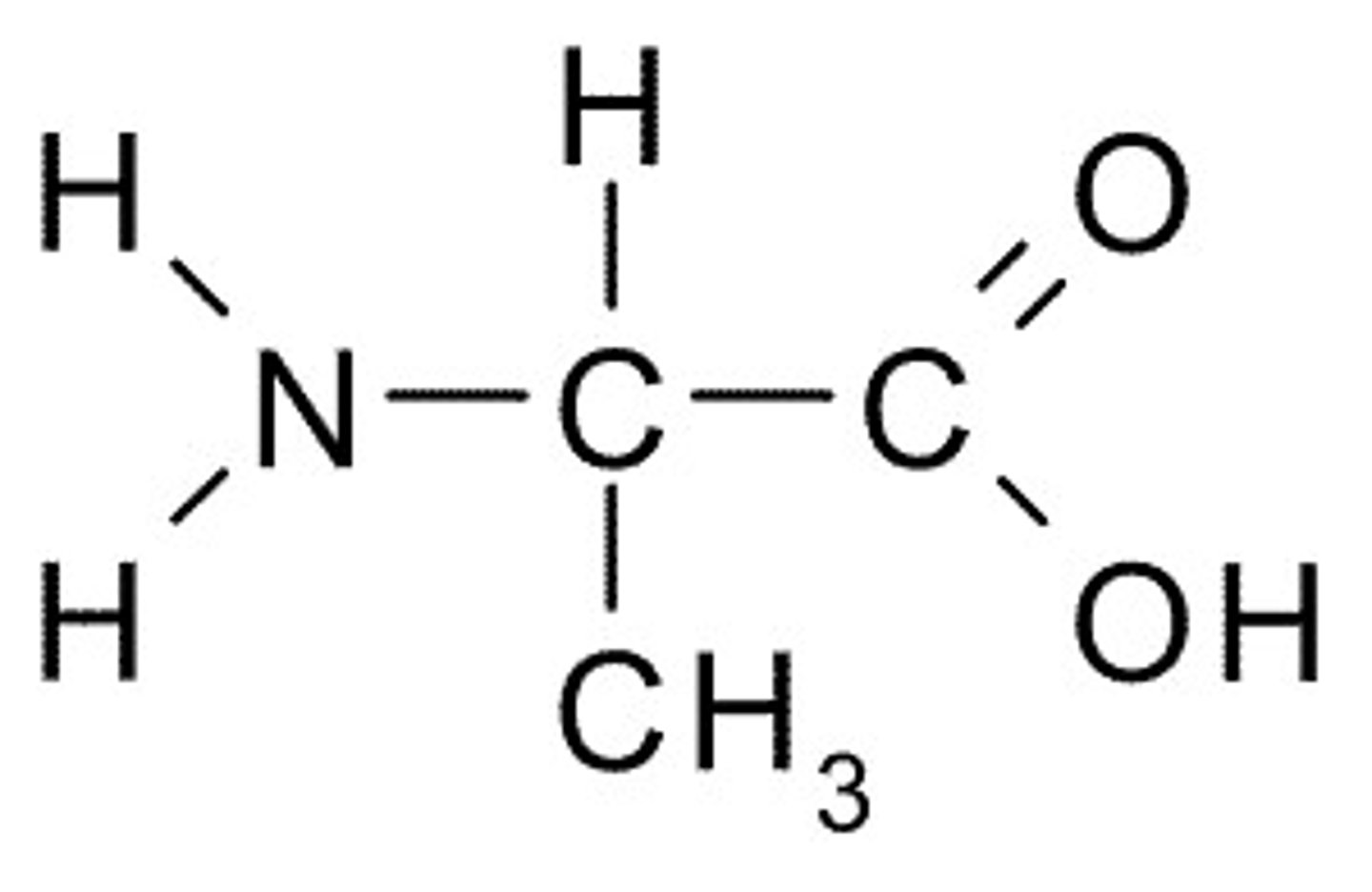
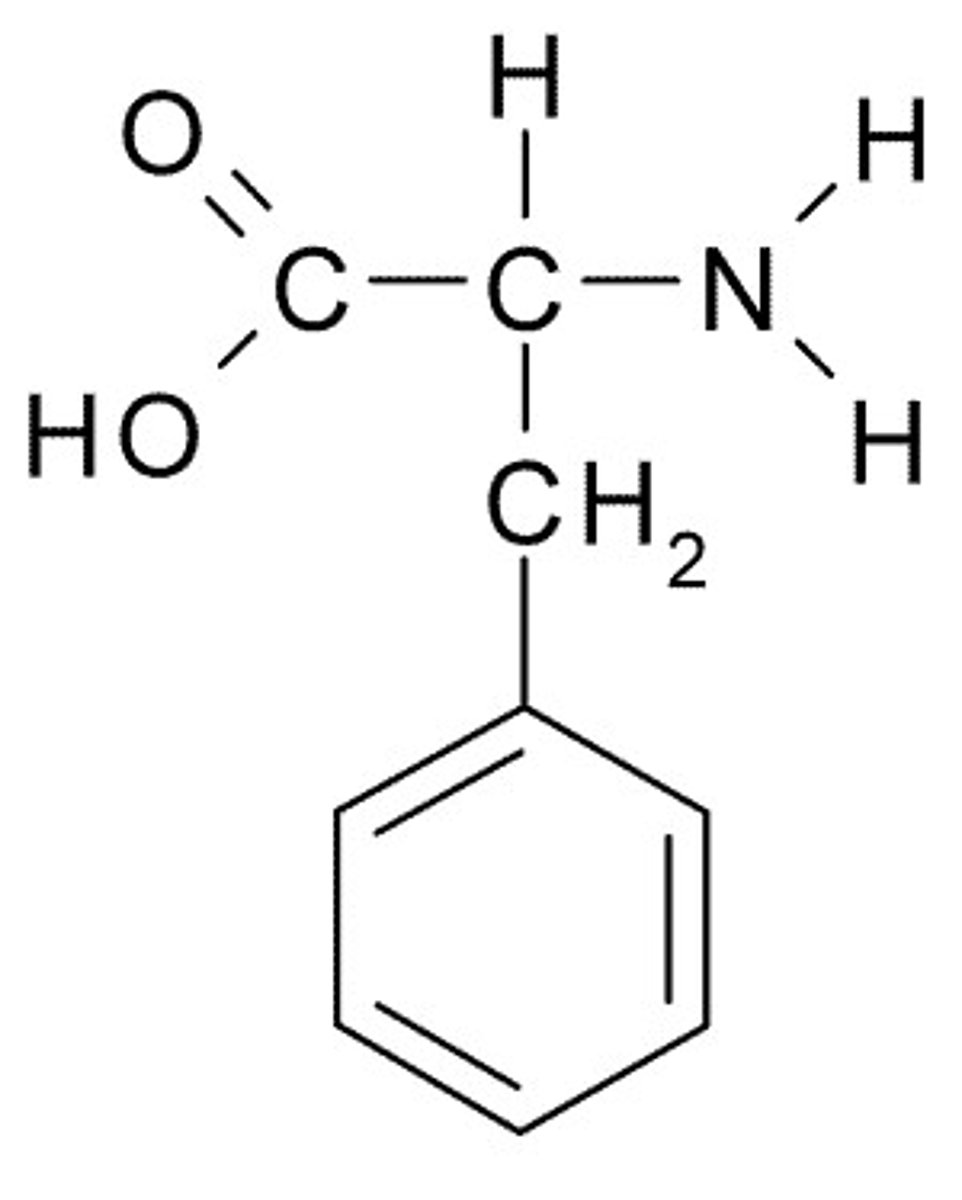
Phenylalanine
F, Phe, Nonpolar
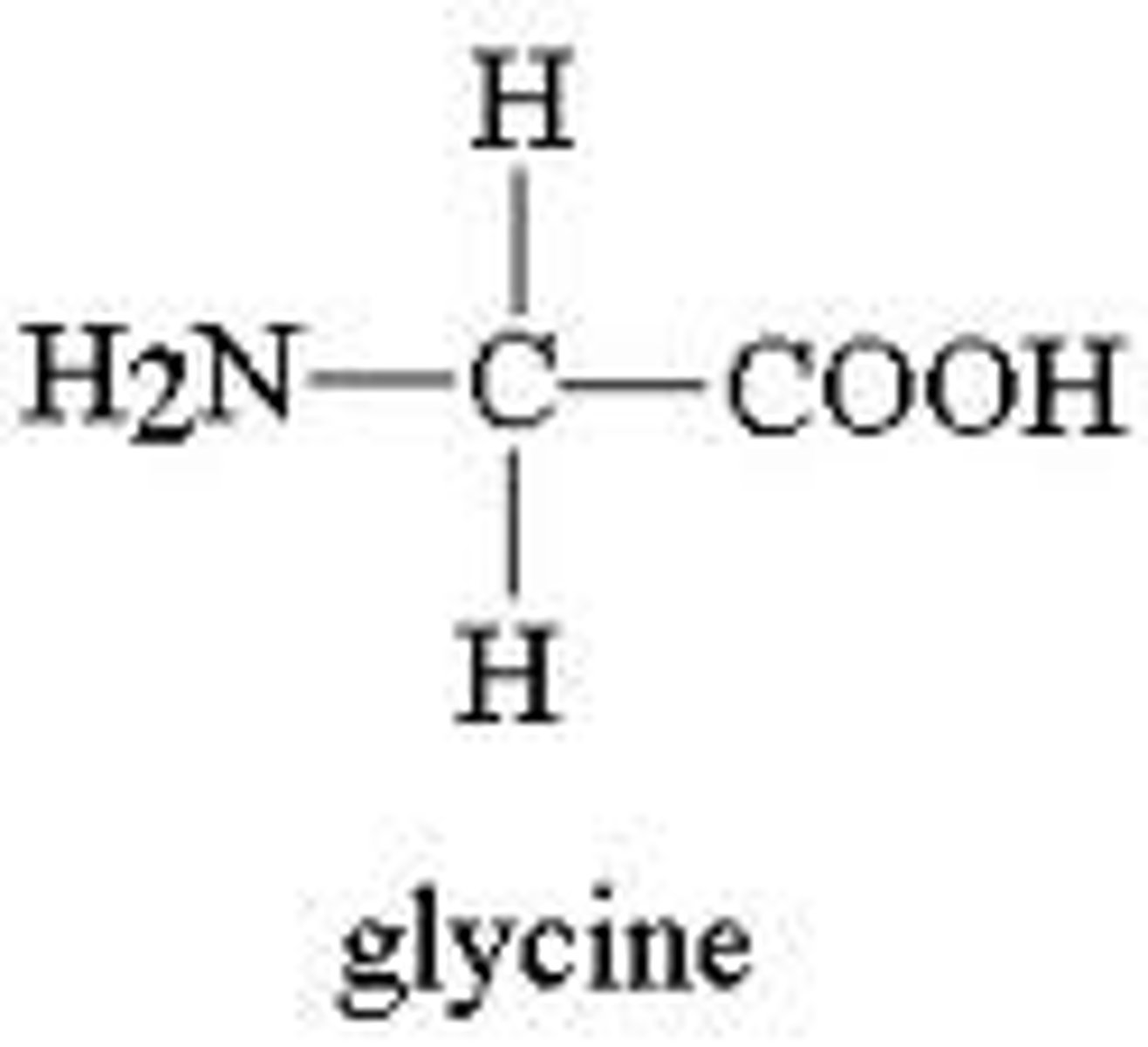
Glycine
G, Gly, Nonpolar
Isoleucine
I, Ile, Nonpolar
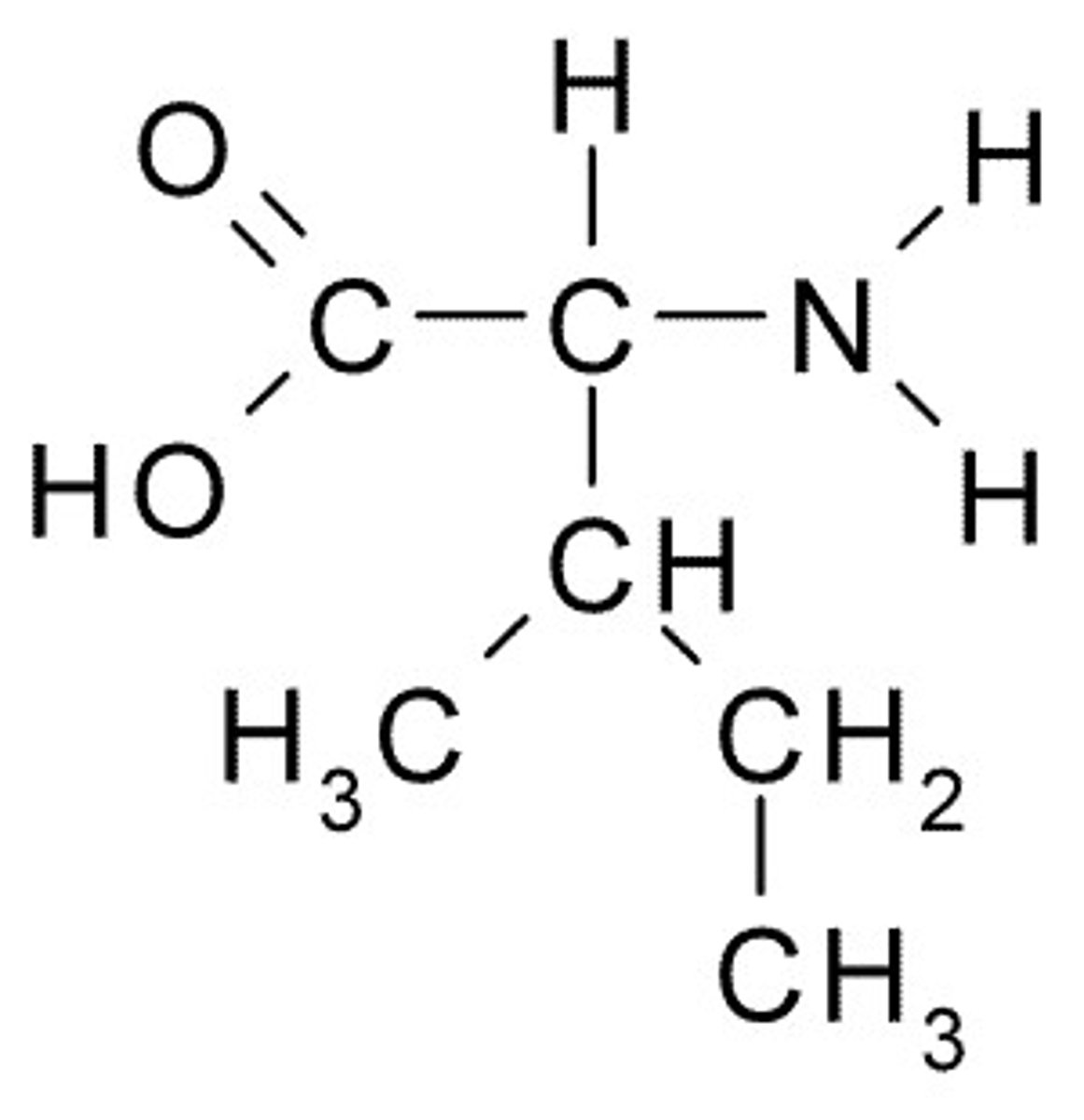
Leucine
L, Leu, Nonpolar
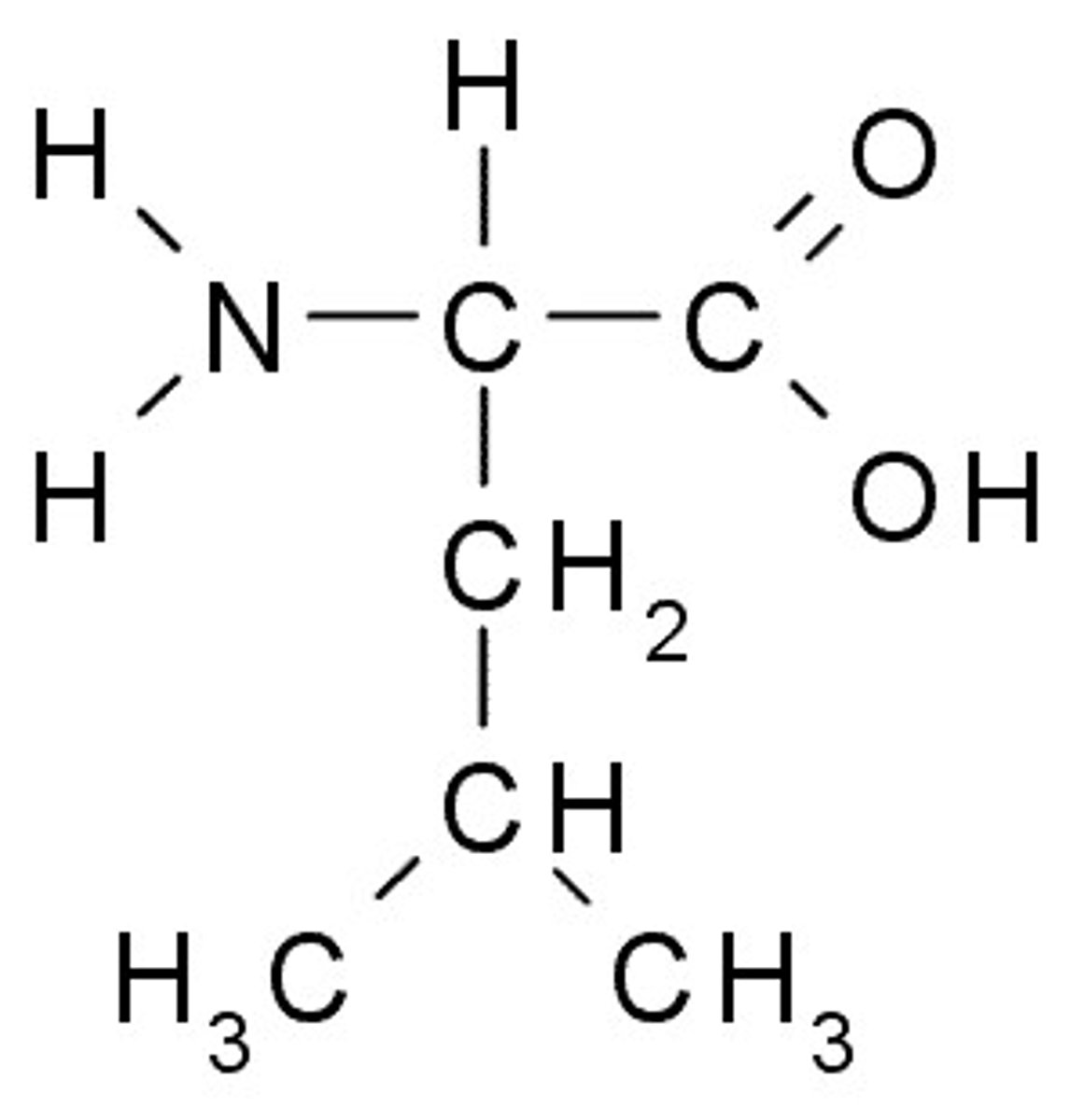
Methionine
M, Met, Nonpolar
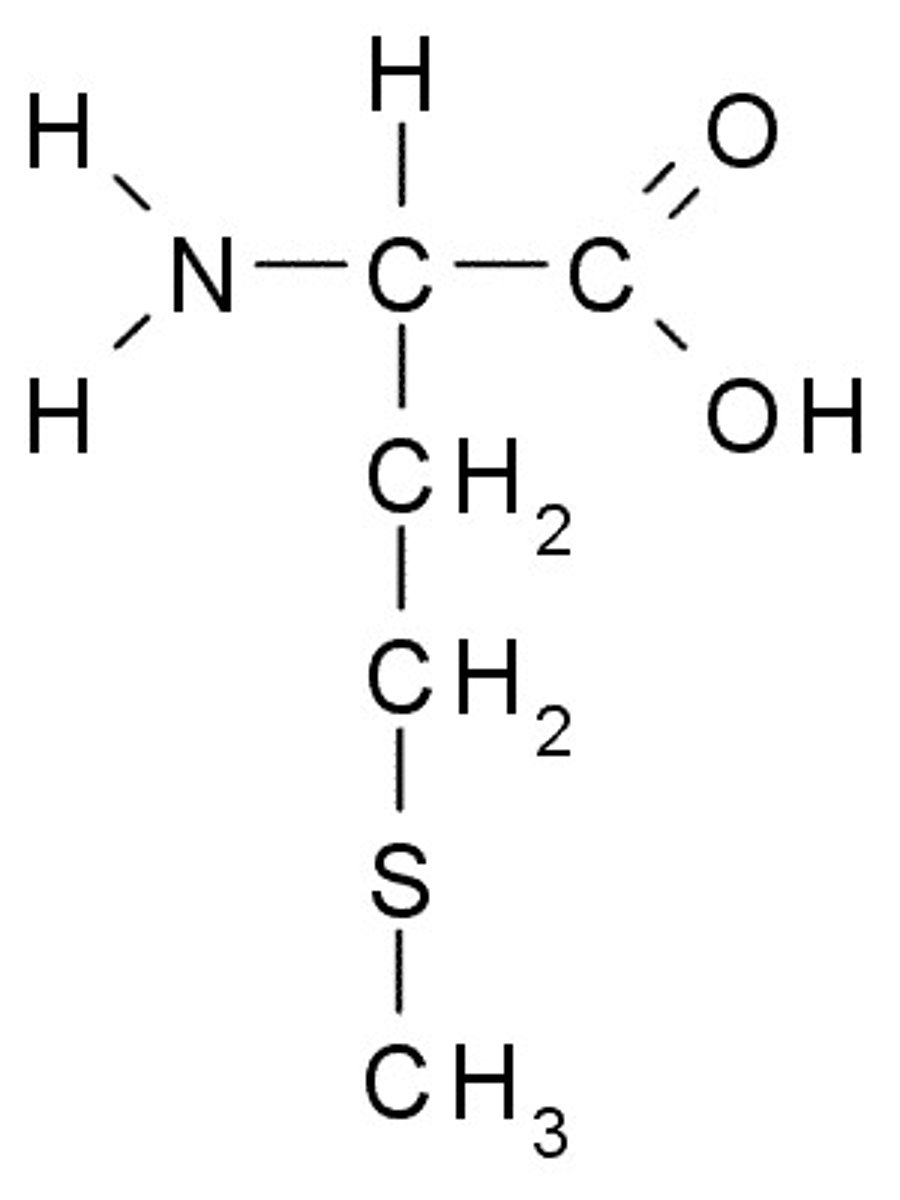
Proline
P, Pro, Nonpolar
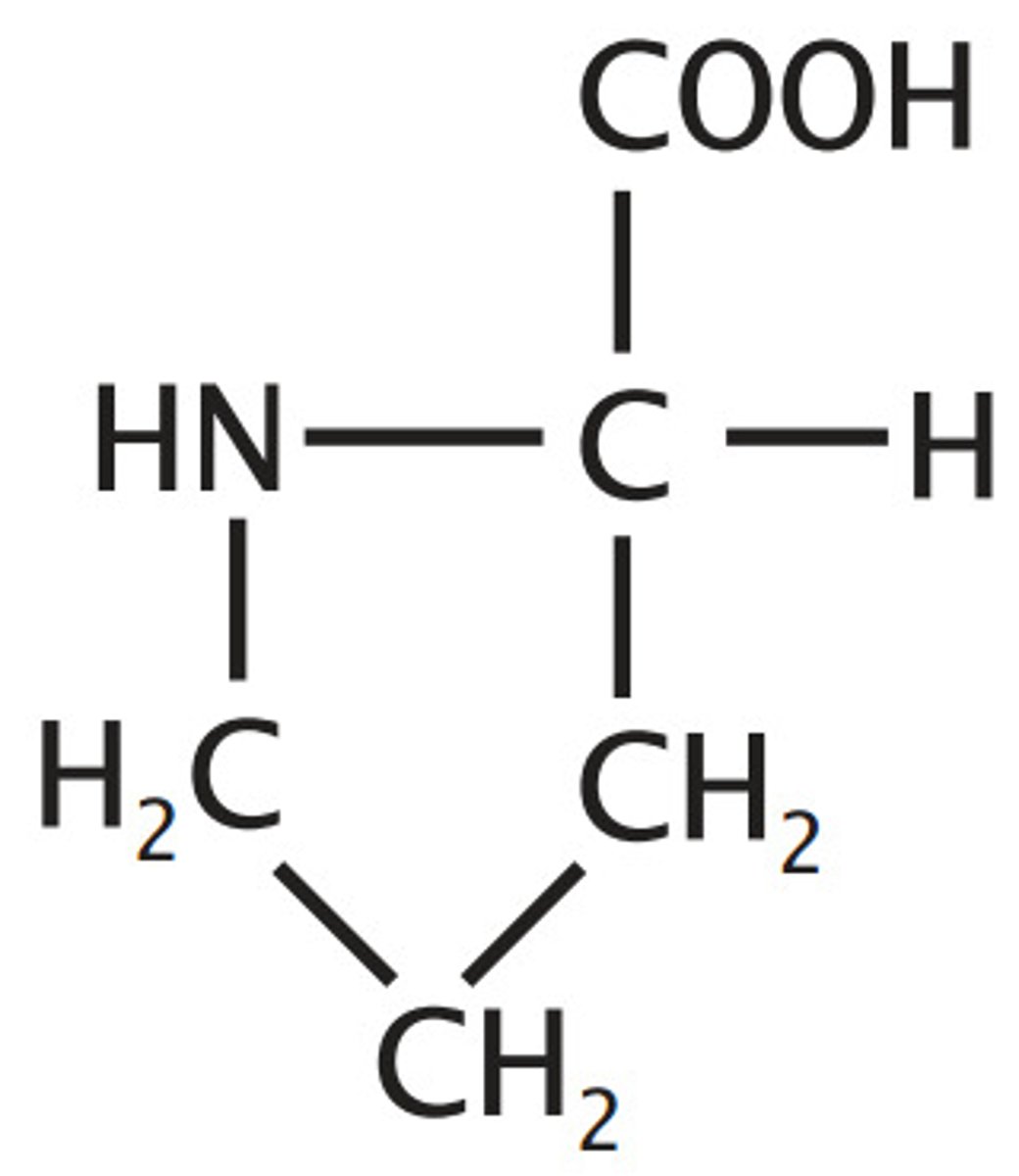
Valine
V, Val, Nonpolar
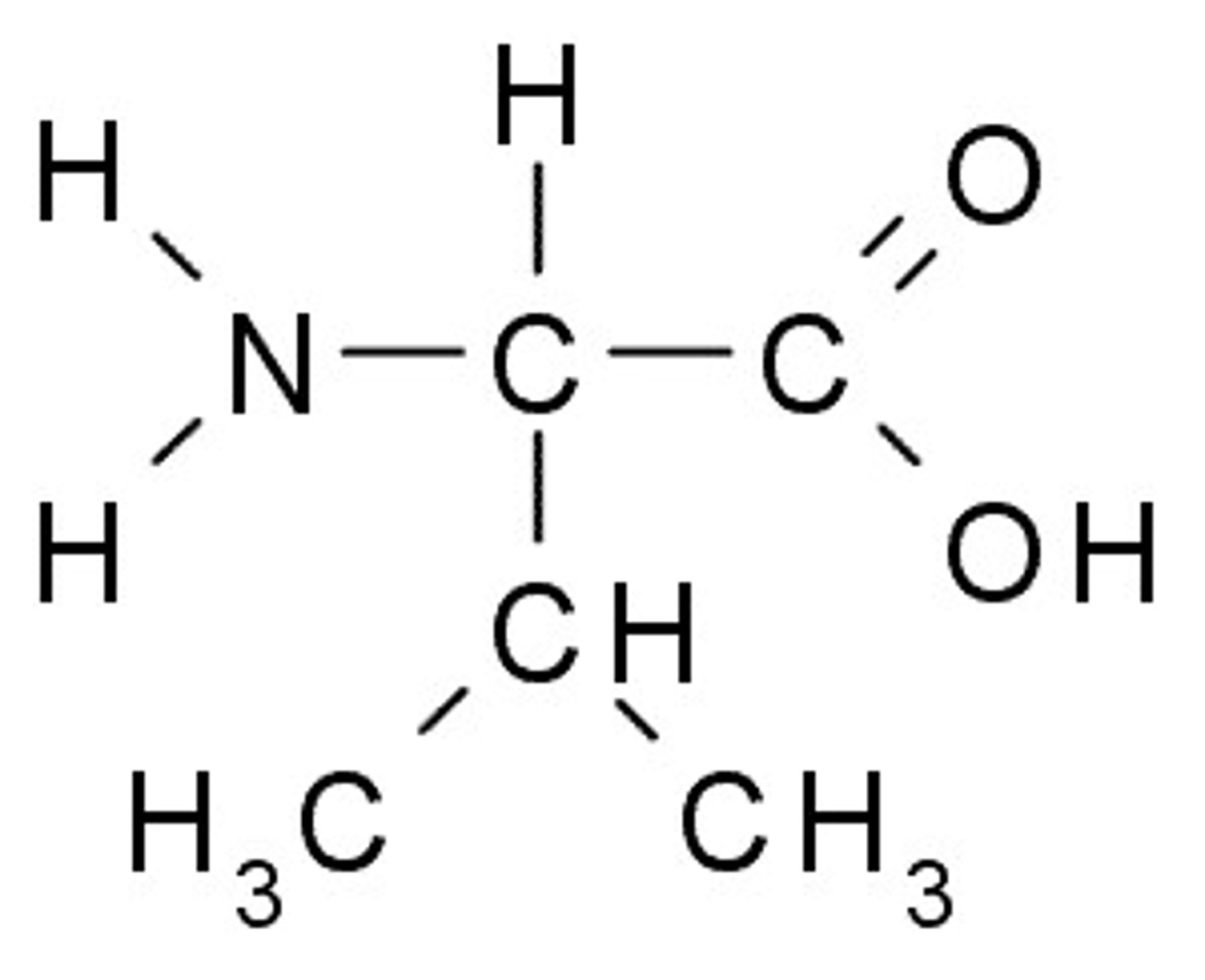
Tryptophan
W, Trp, Nonpolar
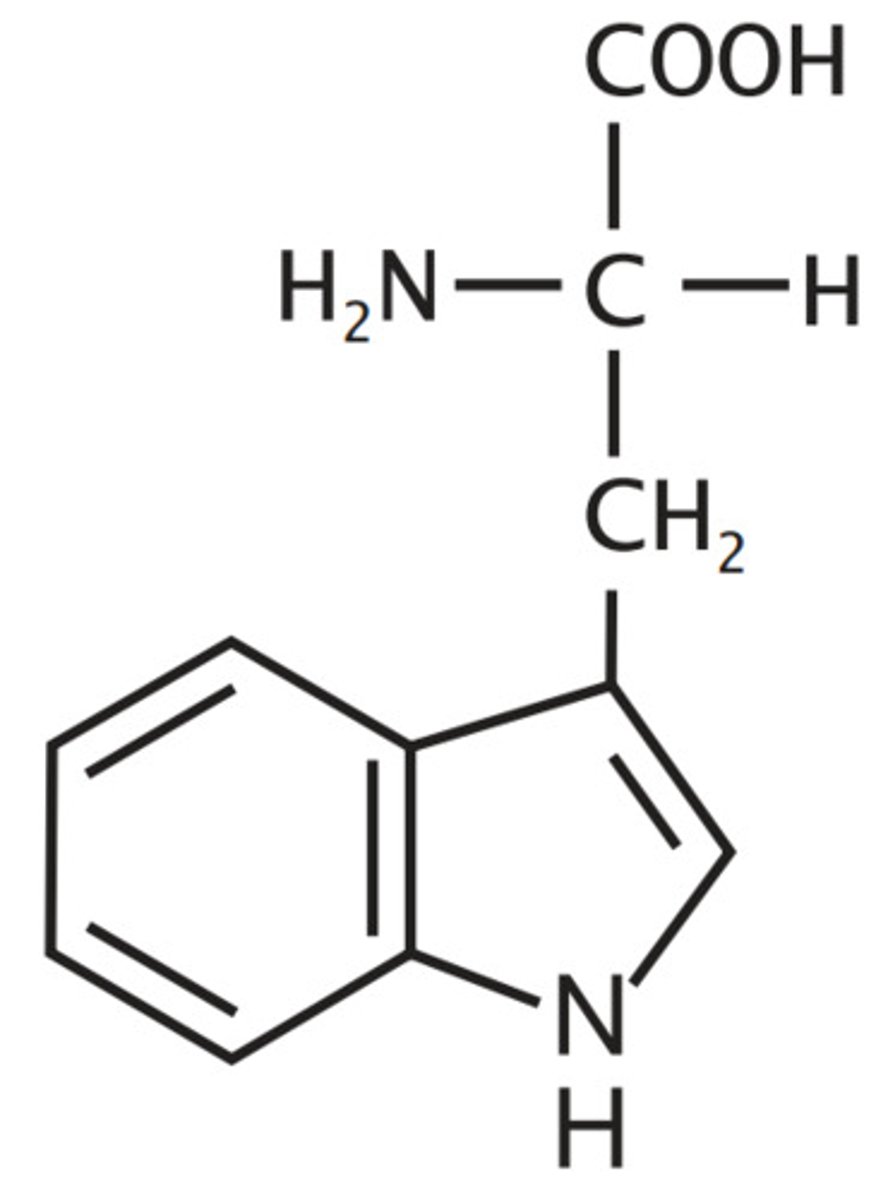
Cysteine
C, Cys, Polar
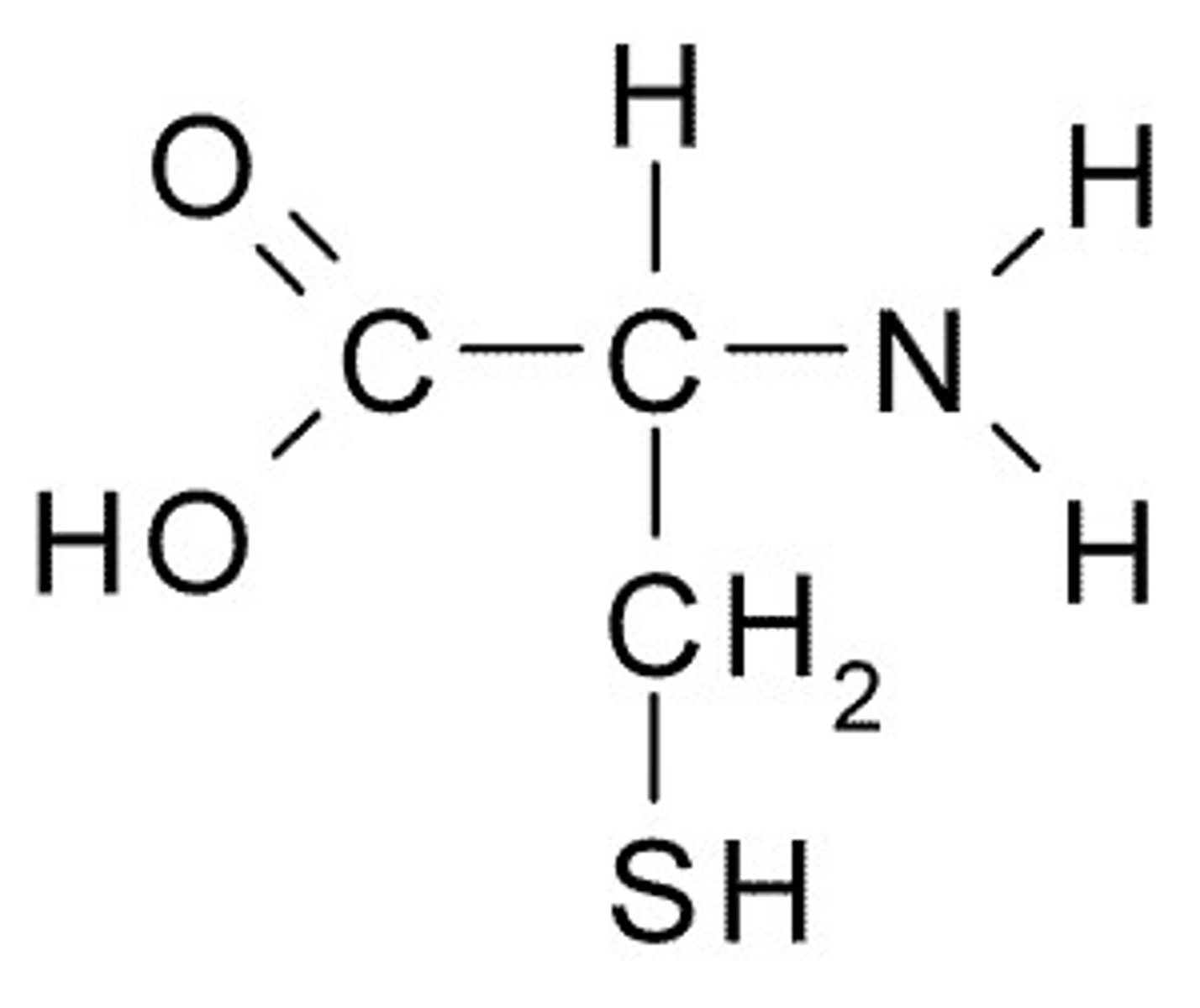
Asparagine
N, Asn, Polar
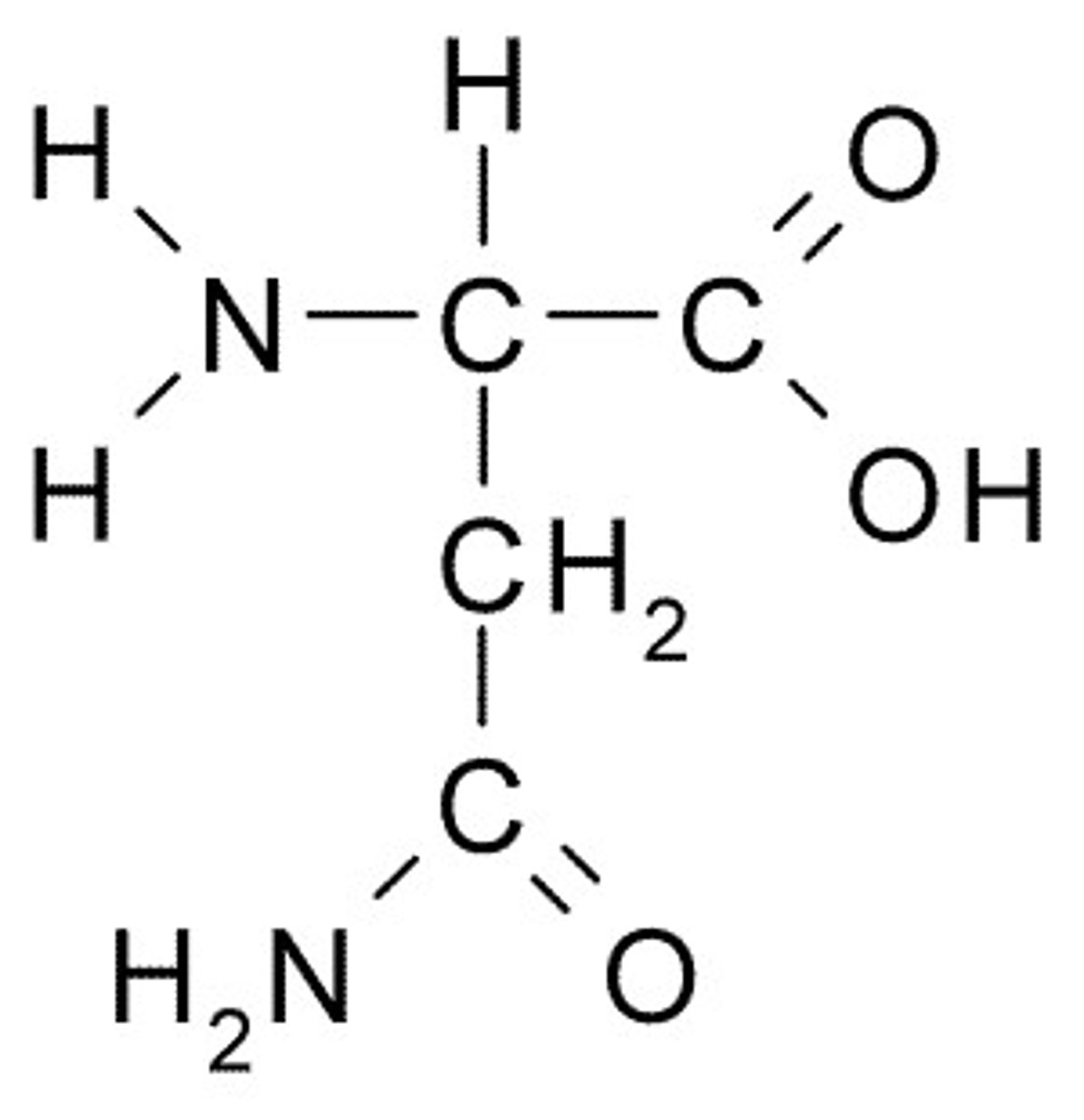
Glutamine
Q, Gin, Polar
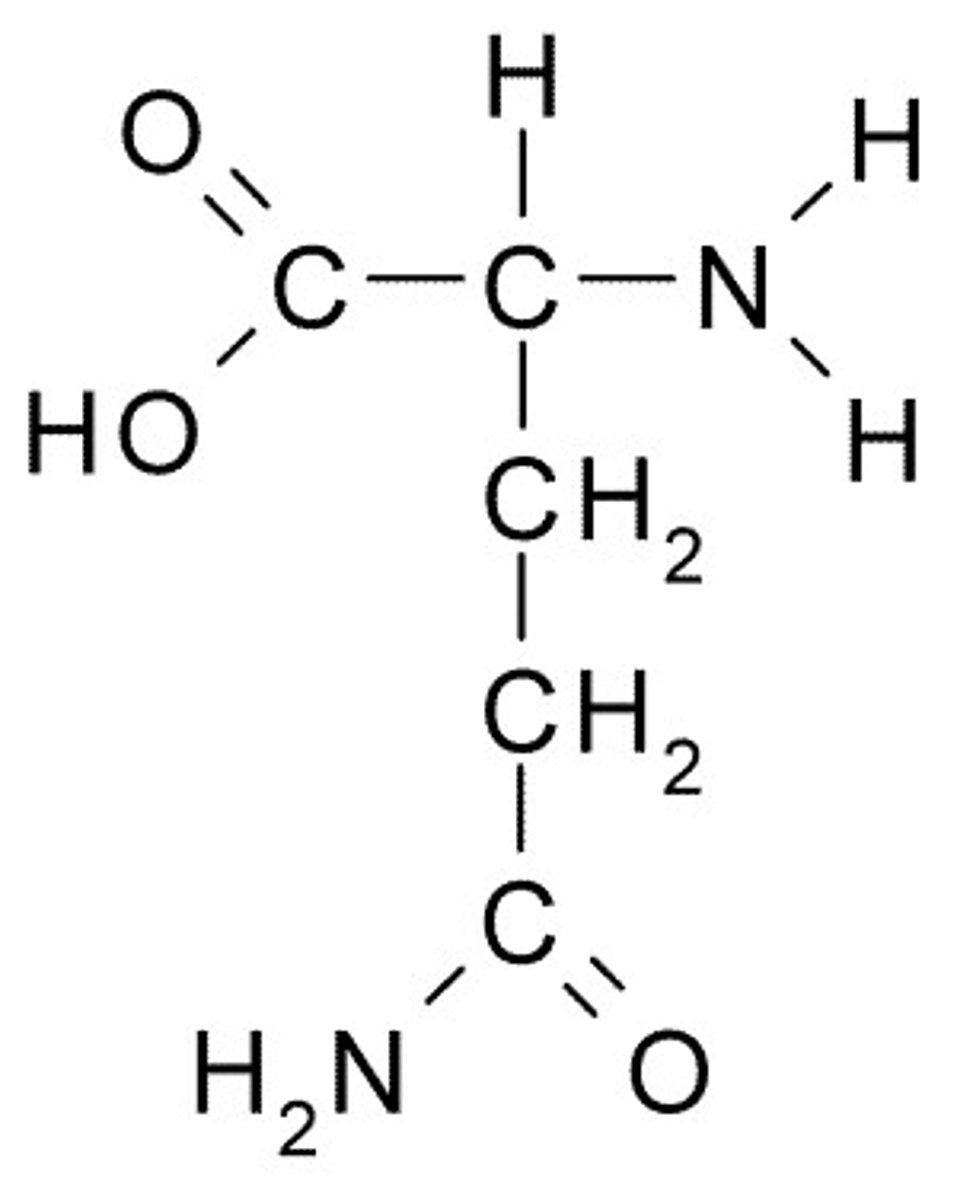
Serine
S, Ser, Polar
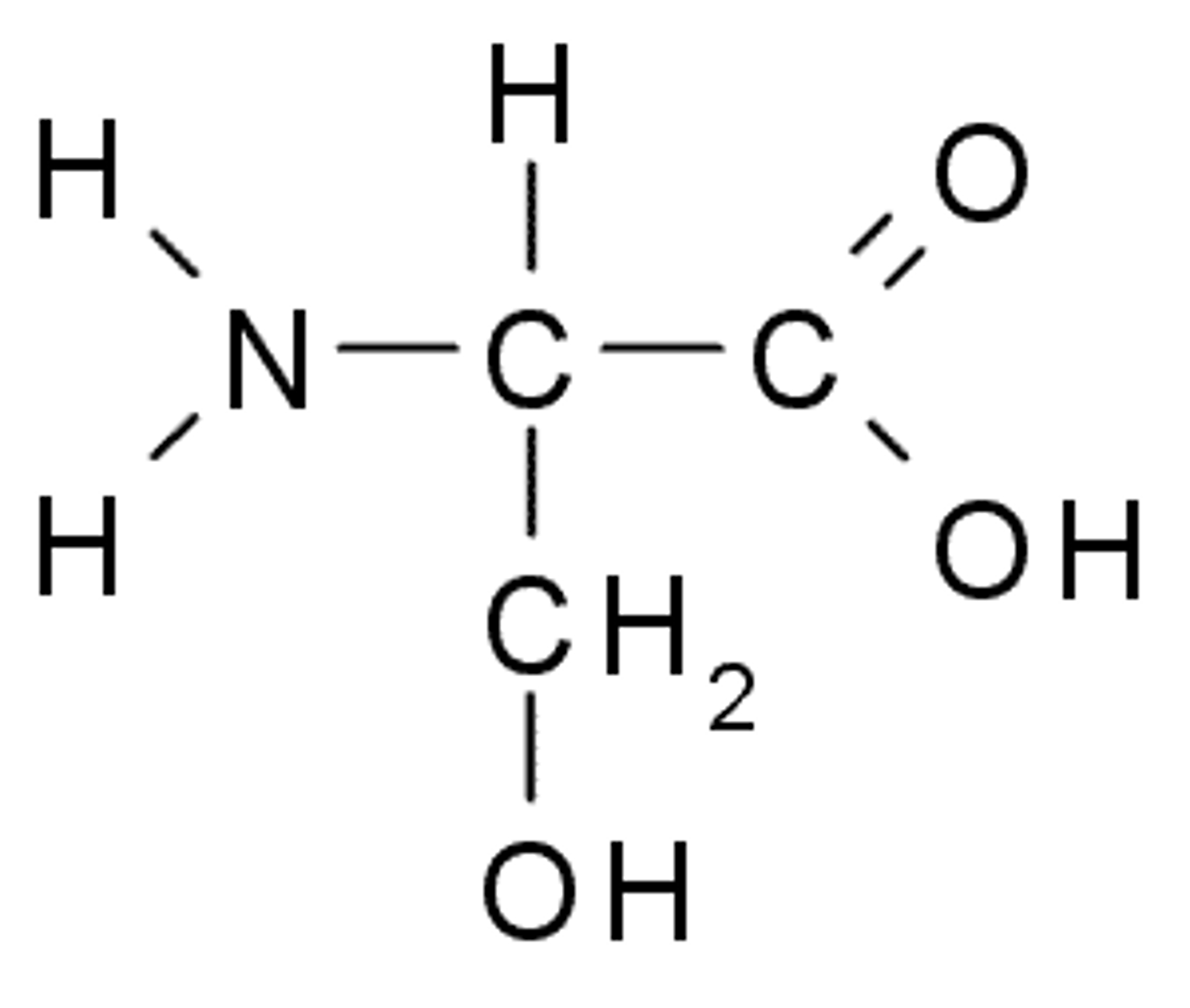
Threonine
T, Thr, Polar
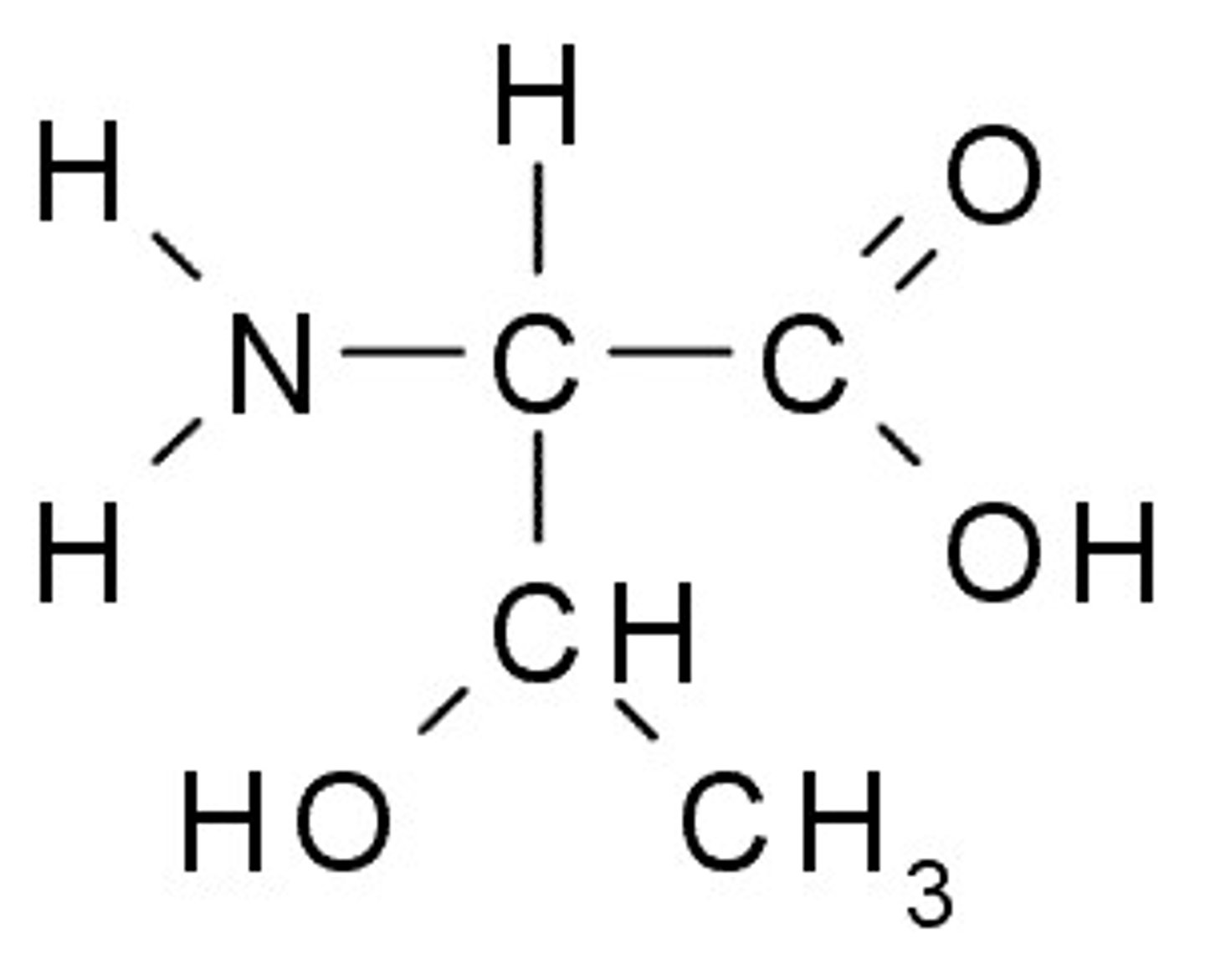
Tyrosine
Y, Tyr, Polar
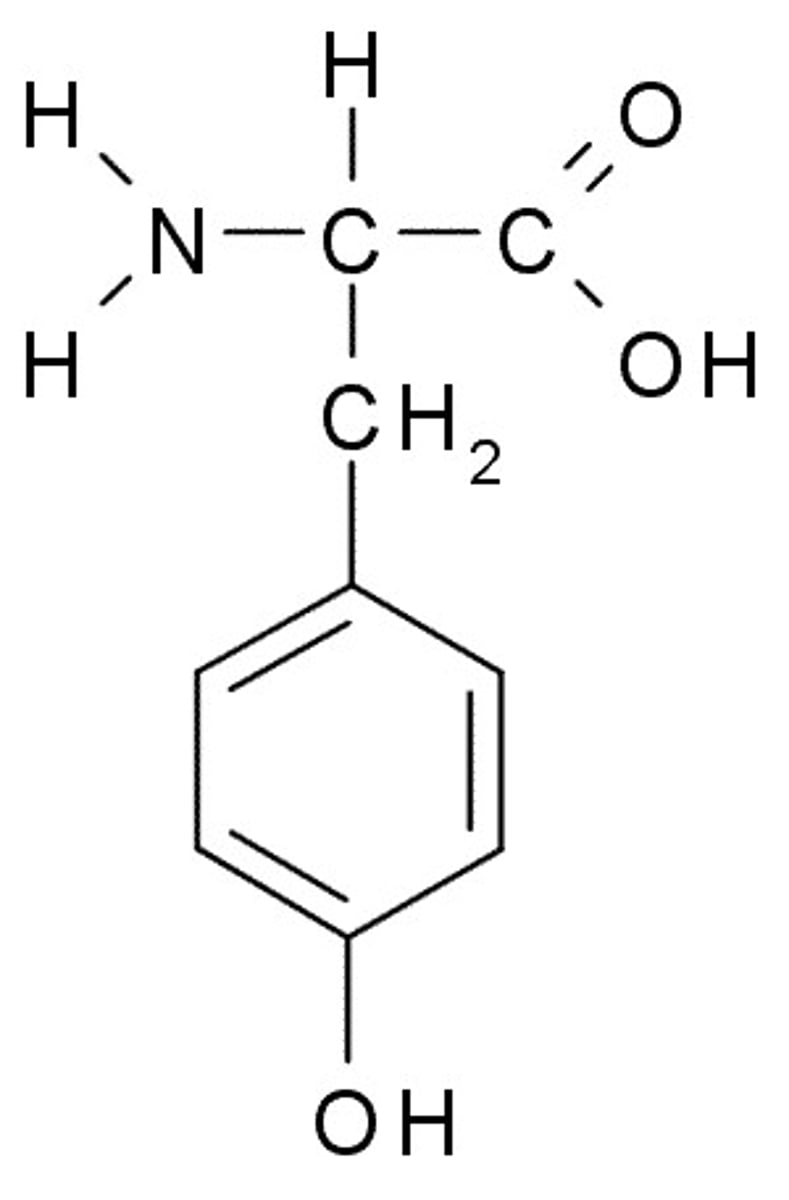
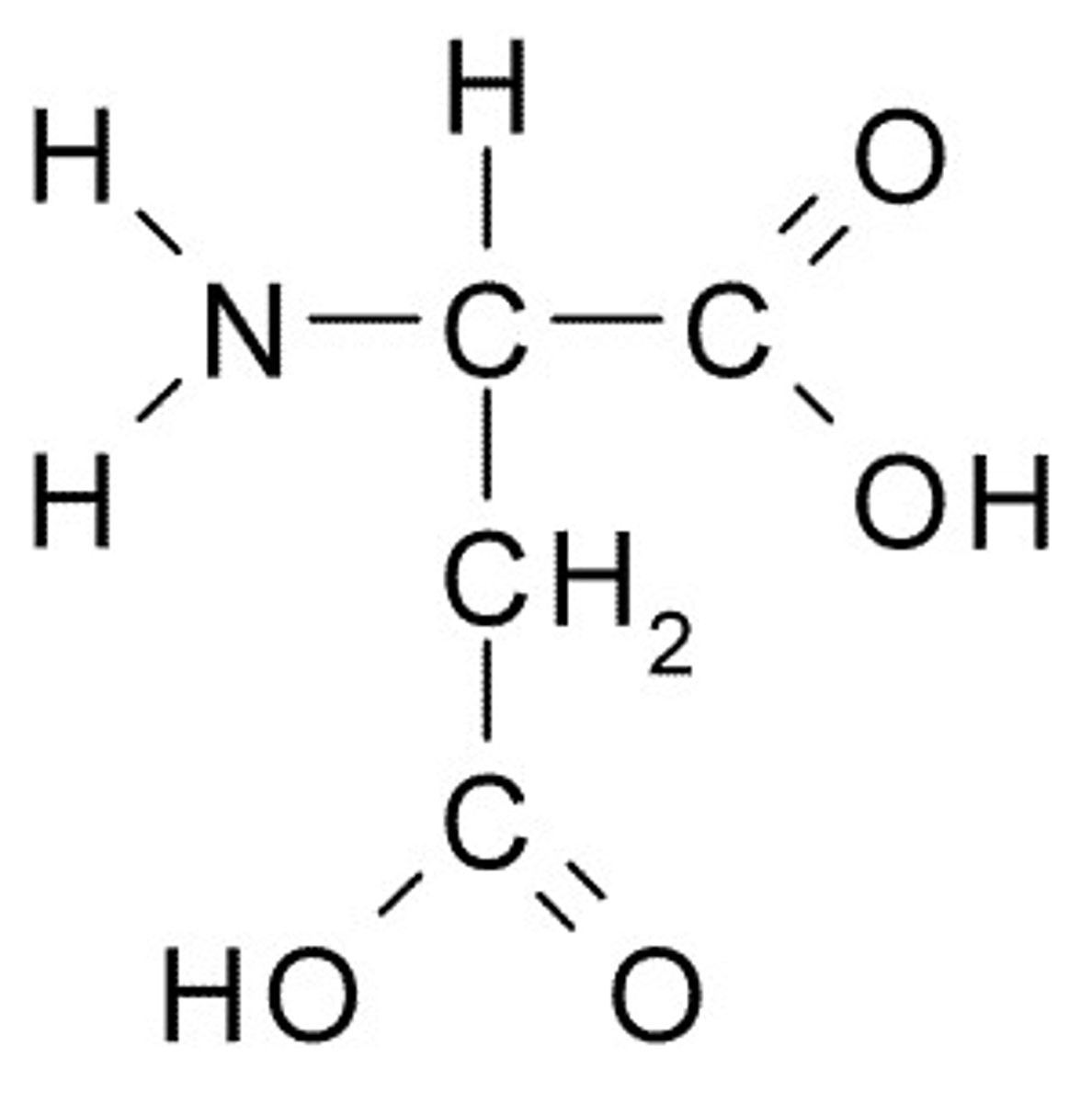
Aspartate
D, Asp, Charged (Acidic)
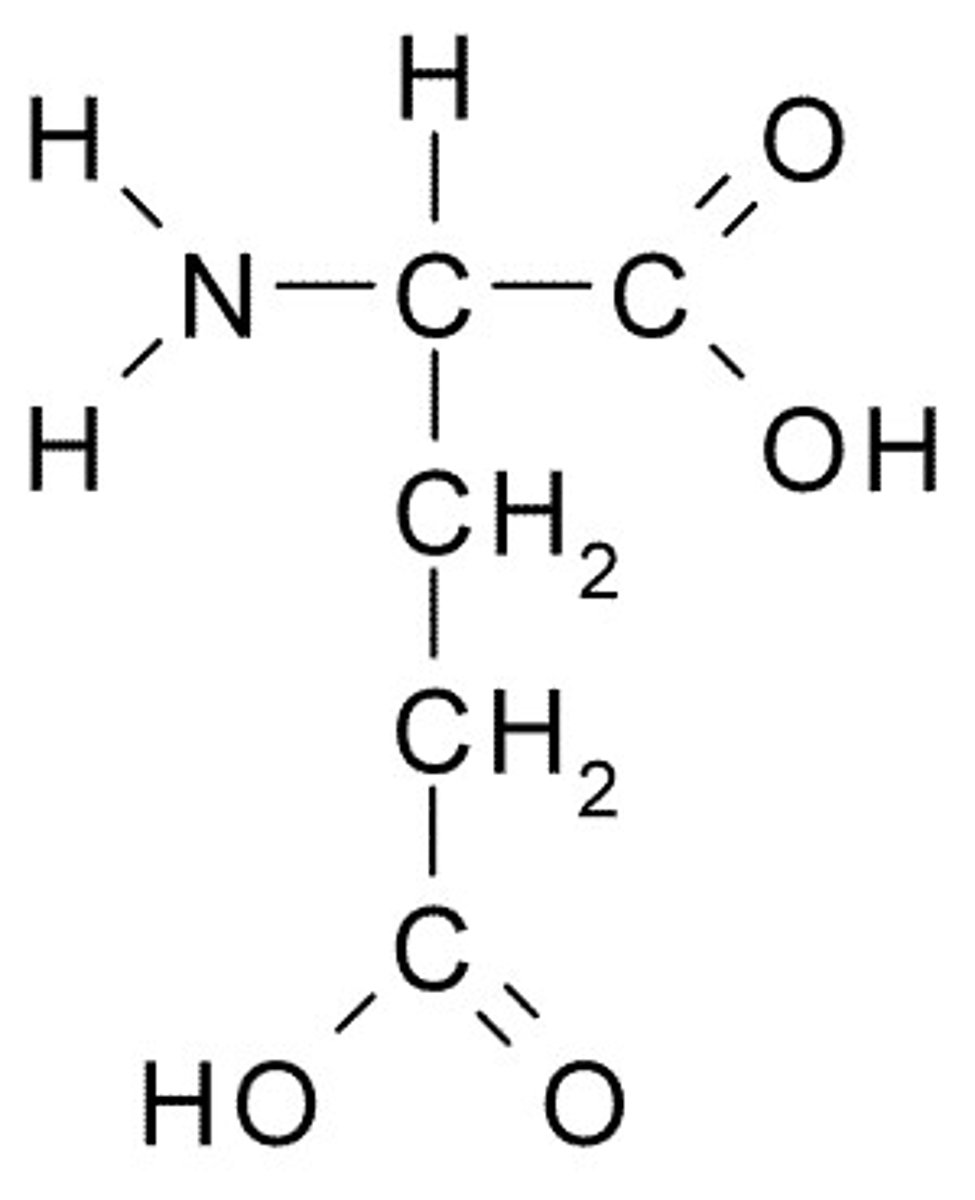
Glutamate
E, Glu, Charged (Acidic)
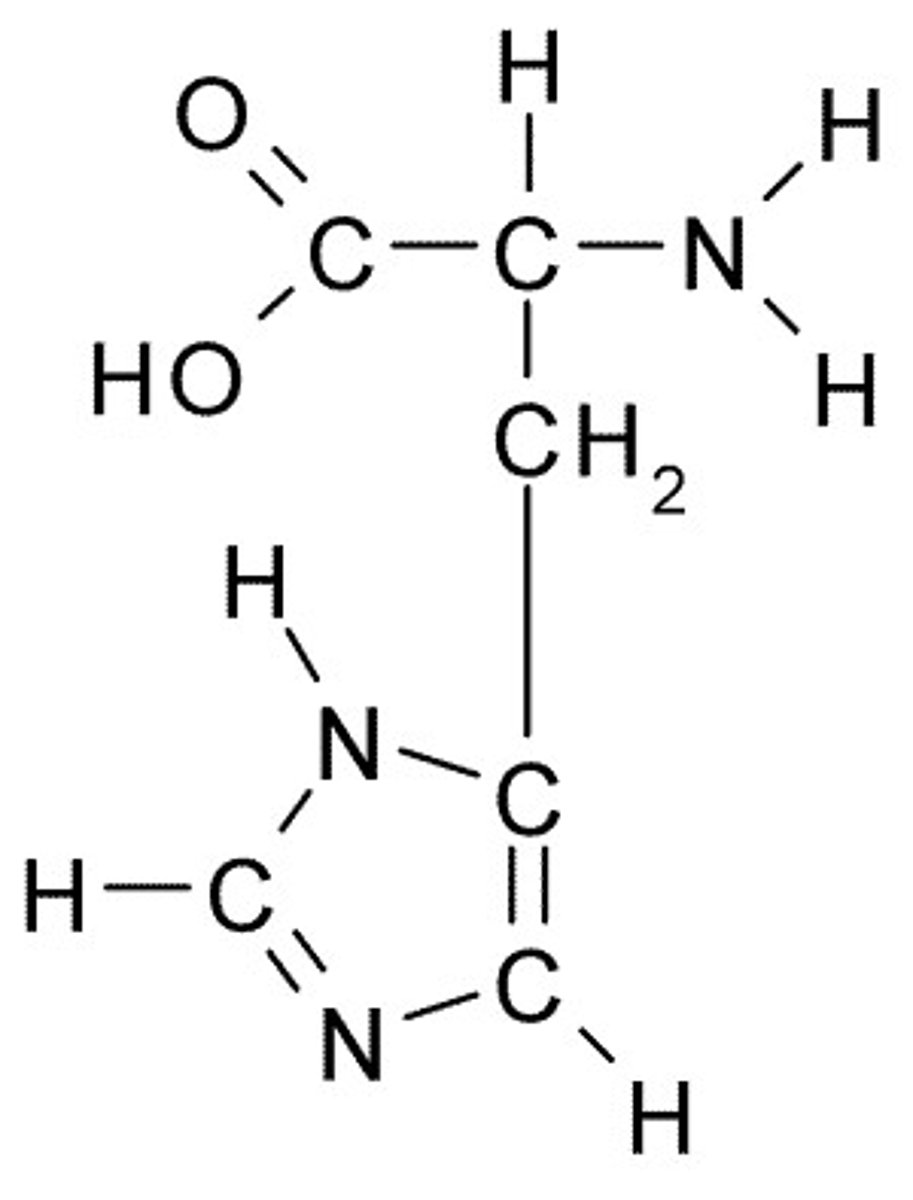
Histidine
H, His, Charged (Basic)
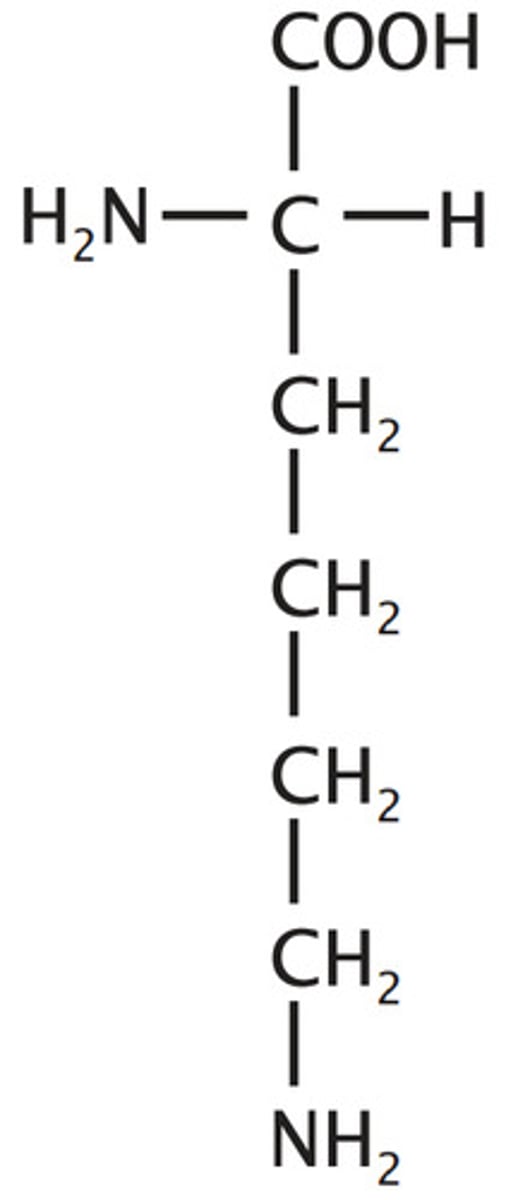
Lysine
K, Lys, Charged (Basic)
Arginine
R, Arg, Charged (Basic)
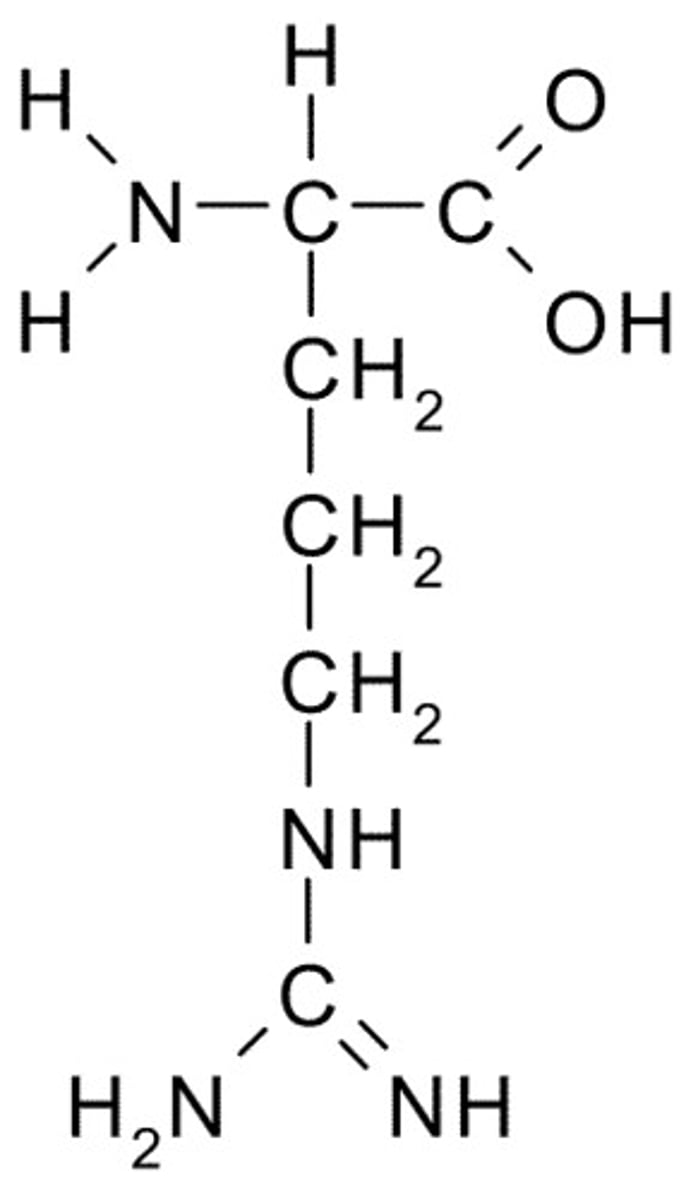
All NON-POLAR Amino acid R-Groups
Mnemonic: GLAM VIP, WF (Glam vip, winner forever)
G (Gly) glycine
L (Leu) Leucine
A (Ala) Alanine
M (Met) Methionine
V (Val) Valine
I (Ile) Isoleucine
P (Pro) Proline
W (Trp) Tryptophan
F (Phe) Phenylalanine
All POLAR Amino acid R Groups
Mnemonic: QSCNTY ( Queen, So, CuNTY)
Q (Gln) glutamine
S (Ser) serine
N (Asn) asparaine
T (Thr) threonine
Y (tyr) tyrosine
All CHARGED ACIDIC Amino acid R-Groups
Mnemonic: DE (Diva, Endorser)
D (Asp) Aspartate
E (Glu) Glutamate
All CHARED BASIC Amino acid R-Groups
Mnemonic: HKR (Hawkeye Kissed Roy)
H (His) Histidine
K (Lys) Lysine
R (Arg) Arginine
Deoxyribose Structure
[DRAW THIS!] Mark where the nitrogenous base goes and where the phosphate group goes. Number the carbons and show ALL bonds
![<p>[DRAW THIS!] Mark where the nitrogenous base goes and where the phosphate group goes. Number the carbons and show ALL bonds</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd69cd8b-e1be-4507-8600-0da4a973926e.jpg)
Ribose Structure
[DRAW THIS!] Mark where the nitrogenous base goes and where the phosphate group goes. Number the carbons and show ALL bonds
![<p>[DRAW THIS!] Mark where the nitrogenous base goes and where the phosphate group goes. Number the carbons and show ALL bonds</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/03495dfc-1e1a-4a3e-a74c-bf5e7784c2c2.jpg)
How do amino acids join together?
Peptide Bonds to form proteins
Written from N -> C Terminus
4 Levels of Protein Structure
Primary - sequence of amino acids
Secondary - short regions of folding on polypeptide backbone (due to polarity)
Tertiary - 3D structure of entire polypeptide
Quarternary - Structure of protein complexes
Proteins can be denatured by...
heat temperature, pH changes, salt concentration or solvent polarity
Carbohydrates (monomer/polymer)
Monosaccharides: Single sugars, eg glucose, fructose
(-ose ending)
General Formula: CnH2nOn
How are carbohydrates formed?
Two monosaccharides are joined via dehydration reaction
Oligosaccharides
Few monosaccharides bonded together (>3)
Carbohydrates (Polysaccharides)
Store chemical energy
Structural roles
Cellulose/plant starch are glucose polymers
arranged differently, animals can only digest one not the other
Lipids
hydrophobic
energy storage (fats and oils)
Major component of cell membranes
steroid hormones and signalling molecules
3 major classes of lipids
fats
phospholipids
steroids
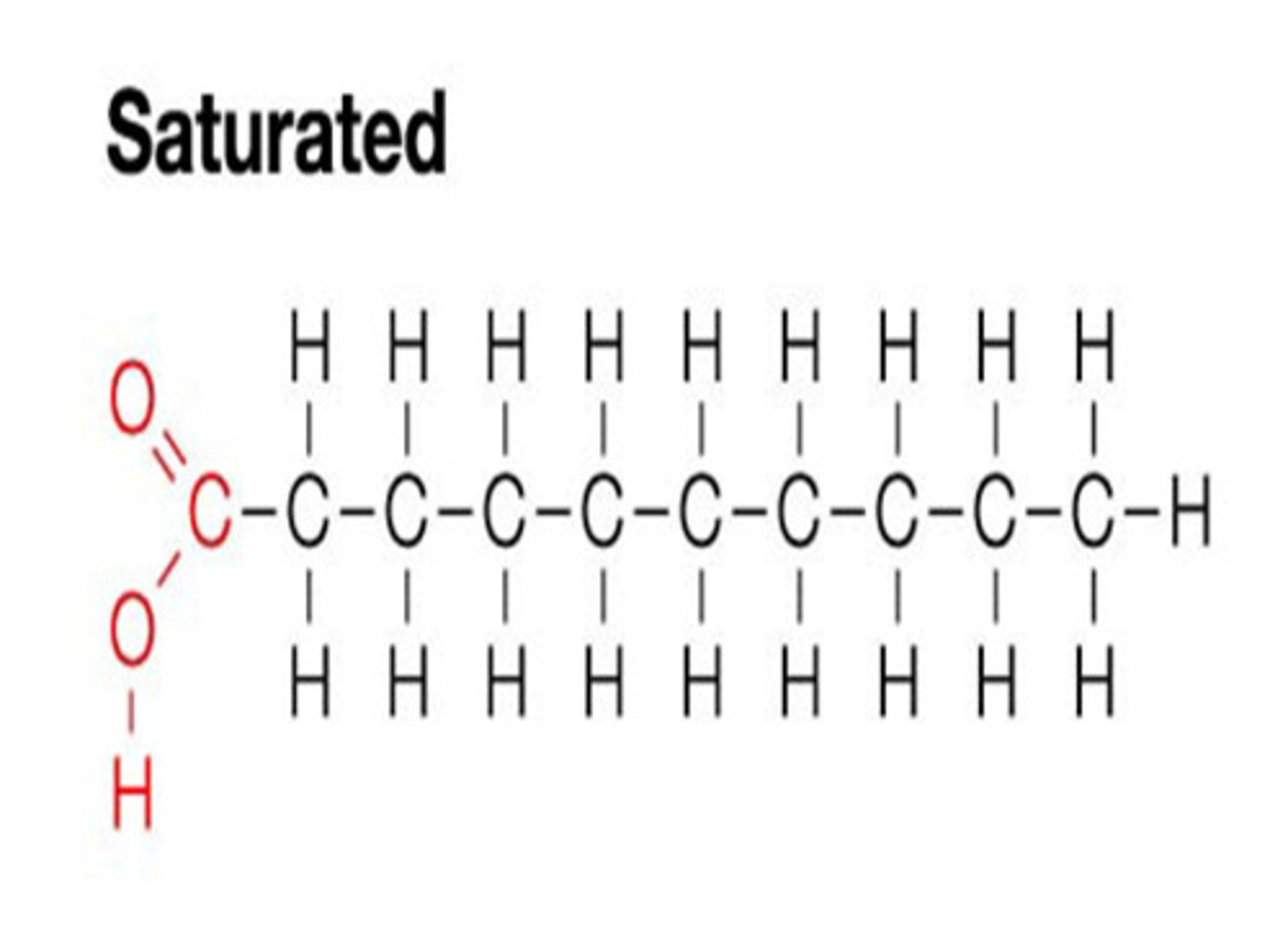
Fats
Triglycerides
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
fatty acid (pictured)long hydrocarbon with carboxyl group at end
added through dehydration
Phospholipids
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate-containing head group
hydrophillic head
hydrophobic tails
Amphipathic
form bilayers
structural basis for membranes
Saturated fatty acids vs Unsaturated fatty acids
Saturated contain no double bonds (more viscous)
unsaturated contain one or more double bonds (more fluid)
Saturation can influence the fluidity of...
...fats, oils and phospholipid bilayers
Nucleic Acids
Monomer: Nucleotides
Polymers: Nucleic Acids (eg DNA, RNA)
Dehydration builds polymers, hydrolysis breaks them down
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA
ribonucleic acid
Central Dogma of Molecular Bio
DNA (gene) encodes RNA (which encodes protein)
-->DNA contains genetic blueprint of cell
-->Transcription of DNA yields RNA
-->Translation of mRNA yields protein
-->tRNA and rRNAs involved in translation
Nucleotides
Composed of Nitrogenous Base, Sugar, Phosphate
Purines
Adenine, Guanine
Have double ring structure
Pyrimidines
Thymine, Uracil, Cytosine
Have single rings
Nucleoside
base + sugar
How are the nucleotides added to each other
Dehydration reaction of the 5' phosphate to the 3' OH of another
DNA (coupling of nucleotides)
A ----- T
G ----- C
RNA (coupling of nucleotides)
A ---- U
G ---- C
Two Major Classes of Metabolic Pathways
Catabolic
Anabolic
Catabolic
breakdown of molecules,
releases energy stored in chemical bonds
does not require energy
Anabolic
biosynthetic
creation of molecules
require energy
1st Law of Thermodynamics
energy neither created nor destroyed, only converted from one form to another
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer increases the entropy (randomness) of the universe
if free energy is negative...
...reaction is exergonic, energy released can be used for work, spontaneous
if free energy is positive...
...reaction is endergonic, energy absorbed
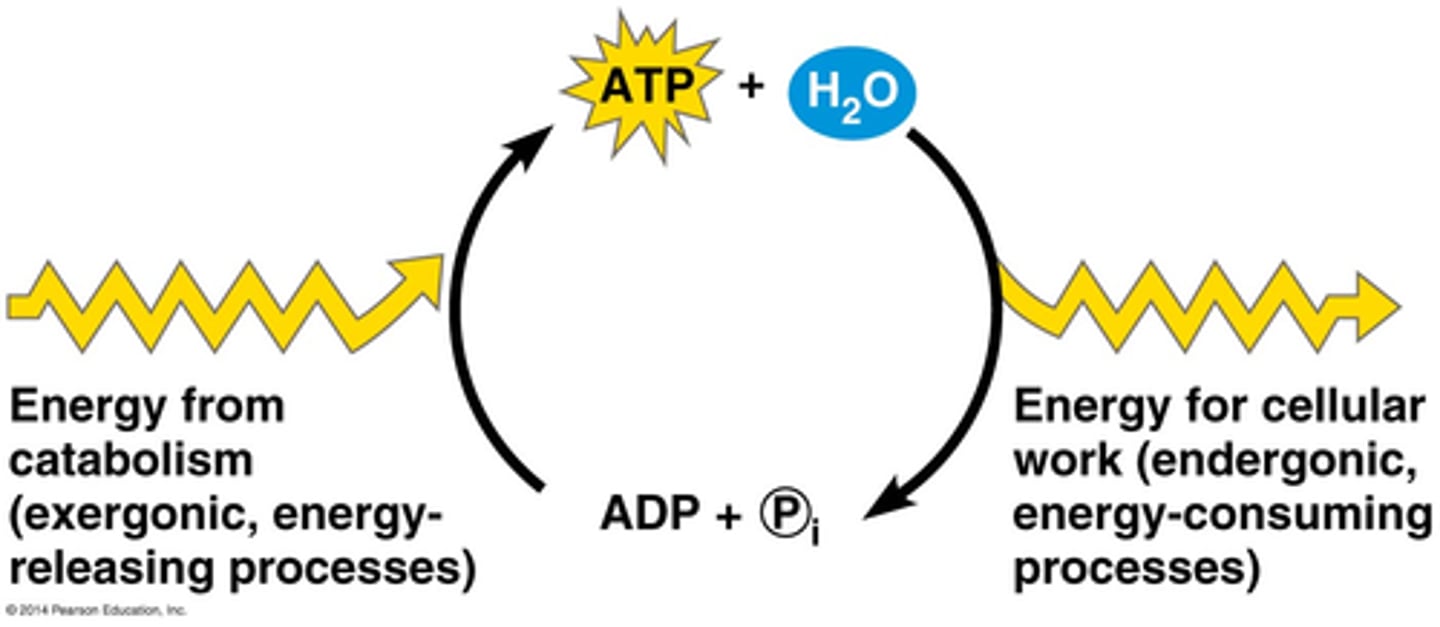
ATP
Adenosine Tri Phosphate. Universal "currency" of the cell. Stores energy.
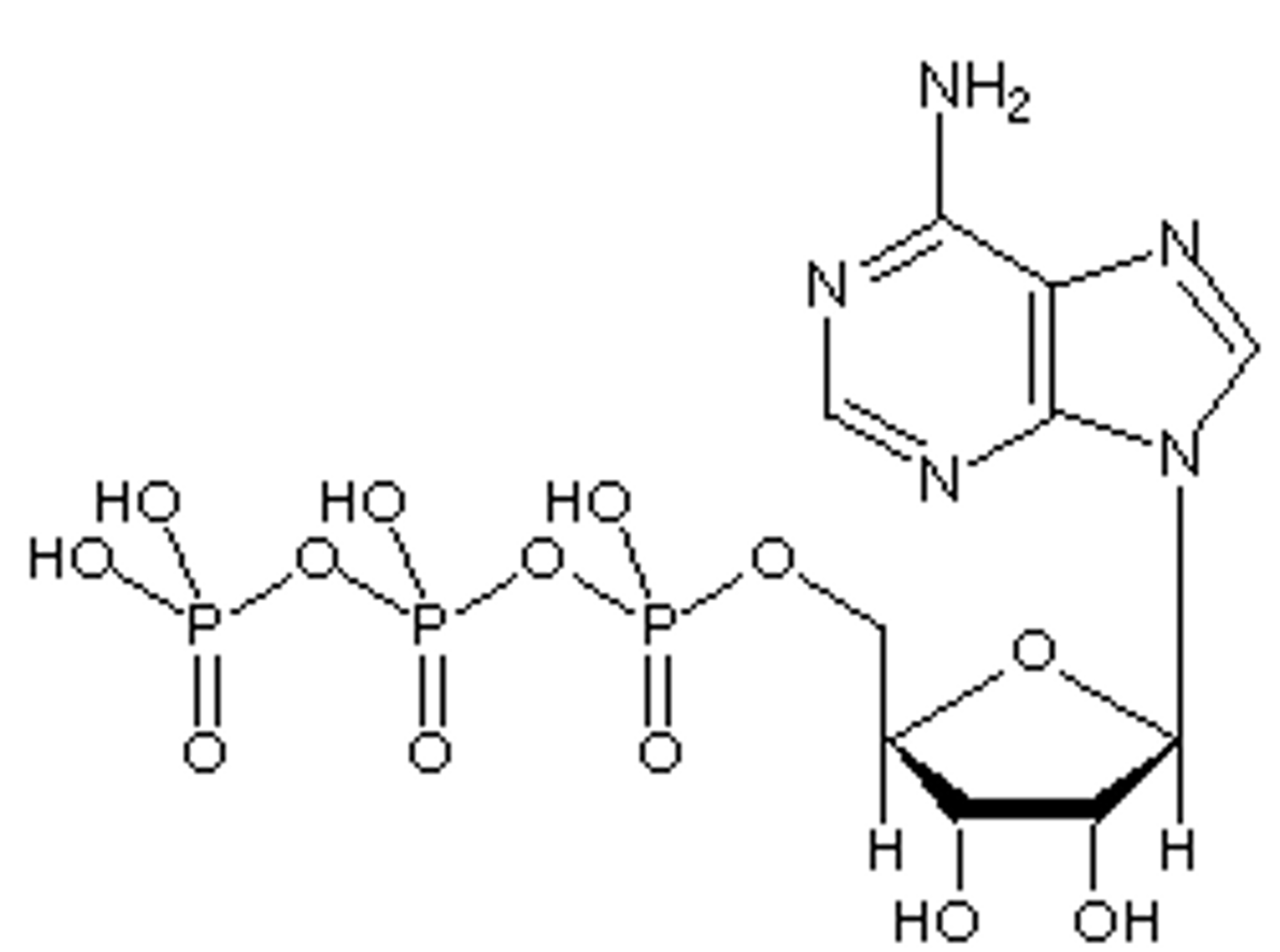
ATP to ADP reversible reaction
ATP hydrolysis releases energy by breaking the high-energy phosphate bonds. The reverse reaction combines ADP + Pi to regenerate ATP from ADP
Important Facts about Enzymes
Enzymes reduce activation energy, do not affect free energy
cant force reactions to occur
enzymes are specific
Cells contain thousand of different enzymes
How do cells regulate metabolic pathways?
By regulating activity of enzymes
What factors regulate enzyme activity?
Amount of enzymes in cell
phosphorylation of STY residues
Binding of small molecules
competitive inhibitors bind active site
compete with substrates
noncompetitive inhibitors/activators
aka allosteric effectors
alter structure and activity by
binding away from active site
How does changing a single amino acid in beta globin cause sickle cell disease?
changes secondary and tertiary structure leading to defective quarternary structures
What ends do the 5' and 3' ends have in nucleic acids?
5' end has a phosphate group. 3' end has a hydroxyl group. (next nucleotide monomer added to 3' end of polymer)
Bond that connect nucleotides
Phosphodiester bonds.
2 Major cell types
prokaryotes (ex. bacteria, archaebacteria) and eukaryotes (ex. protists, fungi, plants, animals)
Prokaryotic cell structure
Very simple. "Sack of enzymes plus DNA". Diameter about 1 micrometer
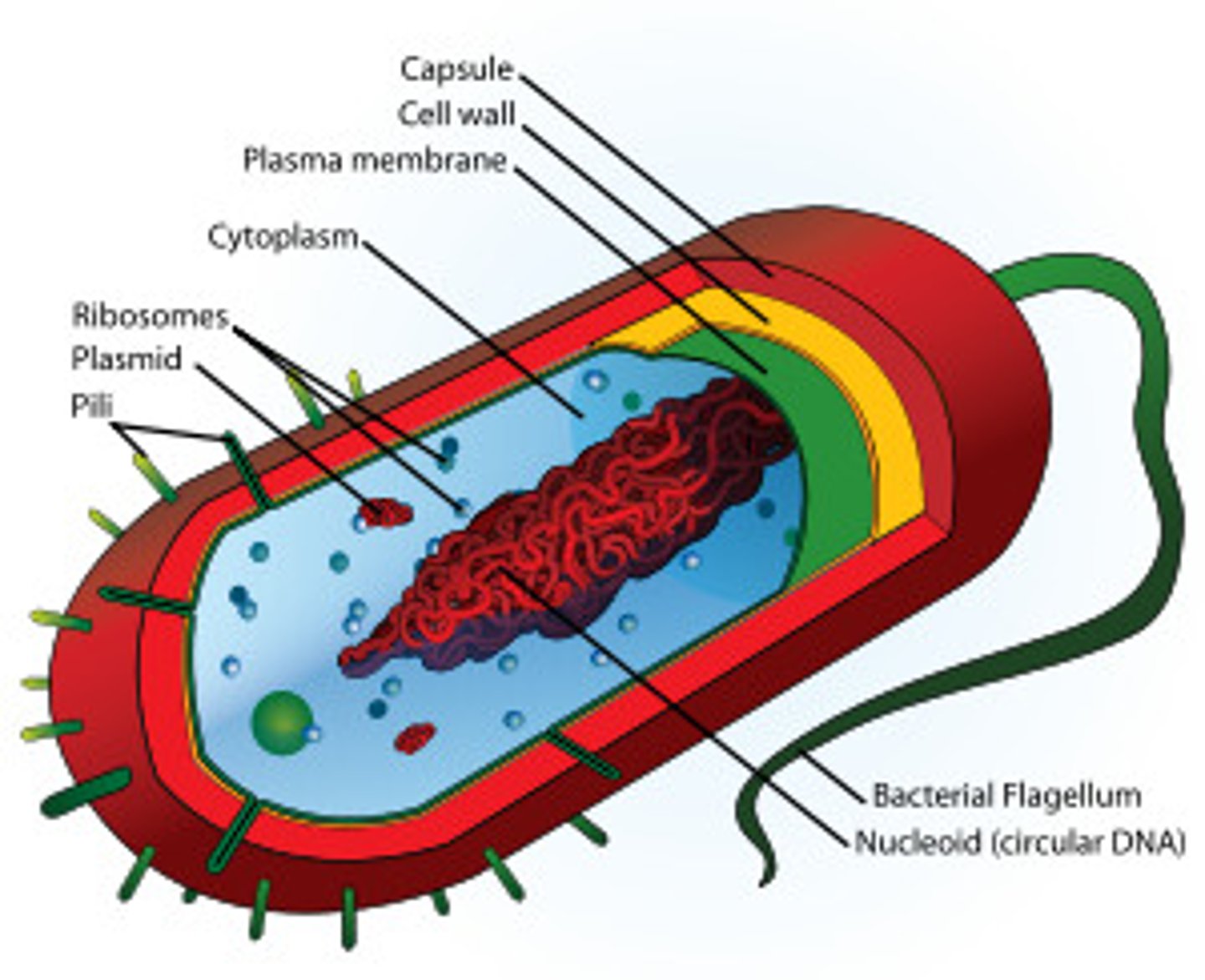
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Highly organized and complex. Has a nucleus, cytoplasm, plasma membrane, and organelles. Complicated reproduction cycle. Diameter of typically 10 to 100 micrometers
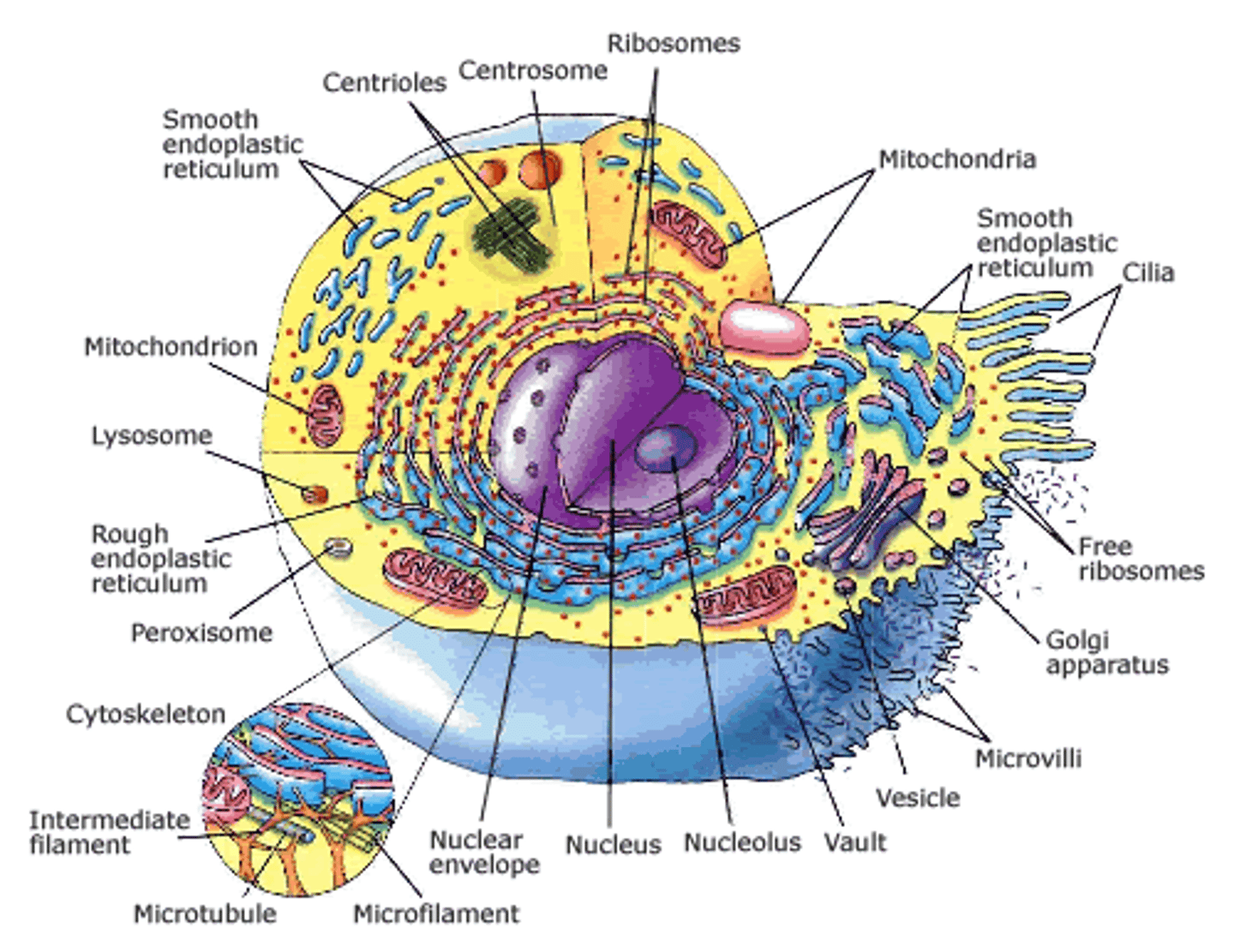
Eukaryotic cell organelles:
Mitochondria: "powerhouse: of the cell, site of ATP synthesis
Chloroplasts: unique to plant cells, site of photosynthesis
Lysosomes: "trash can" of cell, has enzymes that digest macromolecules
Vacuoles: store nutrients and wastes
Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Apparatus: lipid synthesis, processing and sorting of membrane, secreted and lysosomal proteins (?)
Plasma membrane
seperate cells from external walls
internal membrane
subdivide eukaryotic cells into separate "compartments"
Microtubules
Made of tubulin, hollow tubes, and "straw-like. Promote cell movement, vesicle transport, and chromosome segregation
Microfilaments
Made of actin, are like filaments. Support cell shape and movement, muscle contraction, and cell division,
Intermediate filaments
Made of intermediate filaments, are "rope-like" cables . Promote structural integrity of cells and tissues.
Organization of microtubules
Have polarity (- and + ends), grow out of "microtubule organizing center" (ex. centrosome). Microtubules used like "rail-road" tracks to support vesicle transport along spinal cord.