1.2 biology
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
matter is made up of
atoms
atoms can be combined in various ways to form
matter, such as solids, liquids, and gases and makes up elements
compounds
can be broken down further by chemical reactions because they are made up of two or more elements that are in a fixed ratio to each other. for example, bc there is a fixed ratio of hydrogen to oxygens water is a fixed compound
living organisms require…
constant exchanges of energy and macromolecules. exchanging matter allows an organism to grow and reproduce
radioactive isotopes
are used for processes that include fossil dating and medical imaging and carbon - 14 is used for dating sites, fossils, and artifacts
radiocarbon
atomic nucleus with six protons and eight neutrons, 6 electrons
energy level or electron shell
is the location/strucutre. called electron’s potential energy
when electrons absorb energy energy…
they move up or jump an energy level farther away from the nucleus. when they release energy, they move closer to the nucleus
what is carbon?
building block of all the major macromolecules/organic molecules: carbs, lipids, proteins and nucleus acids. it is a major component of compounds and helps form cells in organisms
why is carbon unique?
it can from four covalent bonds, known as tetra valence. stable element and readily bods with a variety of other elements
octet rule
carbon must find eight electrons to fill its outer shell.
states that atoms will lose, gain, or share electrons to achieve an electron configuration of eight valence electrons
nitrogen
building block of nucleic acids, amino acids, and enzymes. these molecules play crucial roles in many bio processes and include metabolism, cell division, and DNA replication.
what is nitrogen a component of?
of many hormones, like adrenaline and insulin
why is nitrogen important?
important for the environment, key element in the nitrogen cycle, and plays a crucial role in balancing nutrients in ecosystems. even tho it is primarily in the atmosphere, some microgansims can convert atmospheric nitrogen into a usable form for other organisms through nitorgen fixation, which is essential for overall functioning of ecosystems
phosphorous
key component of nucleic acids, protiens, and lipids. plays a role in DNA and RNA, which are essential components of the genetic material in all living organisms. also involved in biological processes like energy production, and helps balance nutrients in ecosystems
functional groups
accessory elements that give molecules a different structure, therefore a different function. either hydrophilic or hydrophobic depending based on their charge and polarity charactersistics.
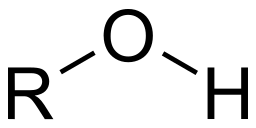
hydroxyl group
hydrogen bonded to Oxygen (oh) attached to the carbon skeleton (present in alcohols such as methanol, polar).
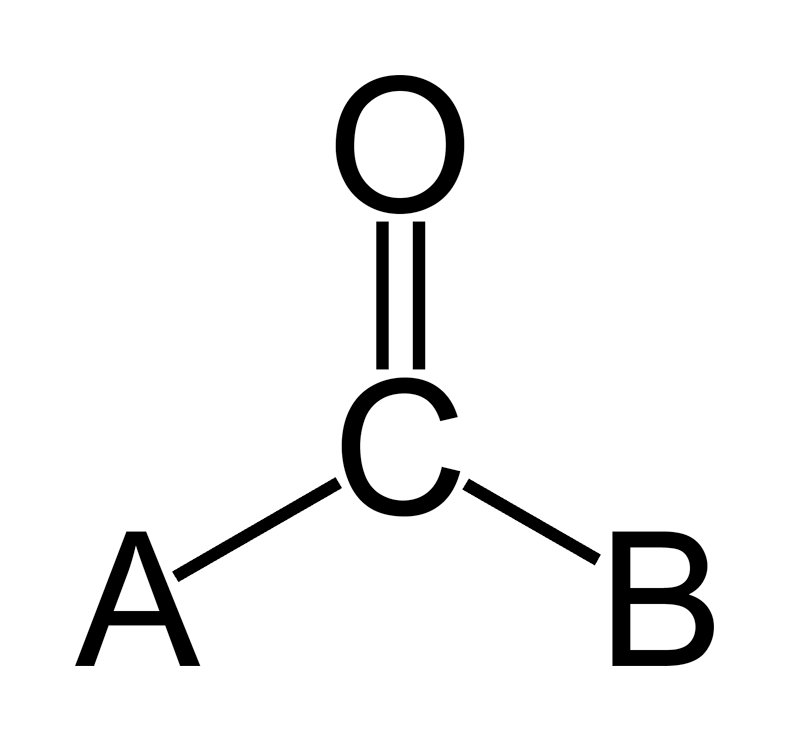
carbonyl group
double bond (shares two pairs of valence electrons) between carbon and oxygen. If the carbonyl groups is on the end of the carbon skeleton, it is called aldehyde. if not, then it is a ketone (polar).
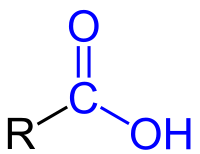
carboxyl group
a combination of carbonyl and hydroxyl where carbon is double-bonded to an oxygen and a hydroxyl (release H+ into solutions, acidic).
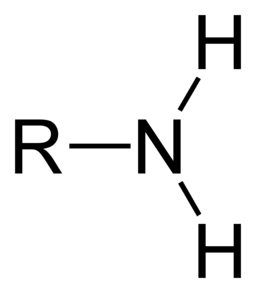
amino group
nitrogen bonded to two hydrogens and one carbon atom. amines are organic molecules that have an amino group (remove H+ from solutions, therefore, basic). Nitrogen is used to build proteins and nucleic acids
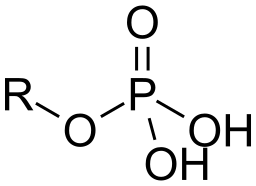
phosphate group
phosphate ion covalently attached to the carbon skeleton. (lots of energy is used to make nucleic acids and phospholipids, acidic because they release H+ into solutions).
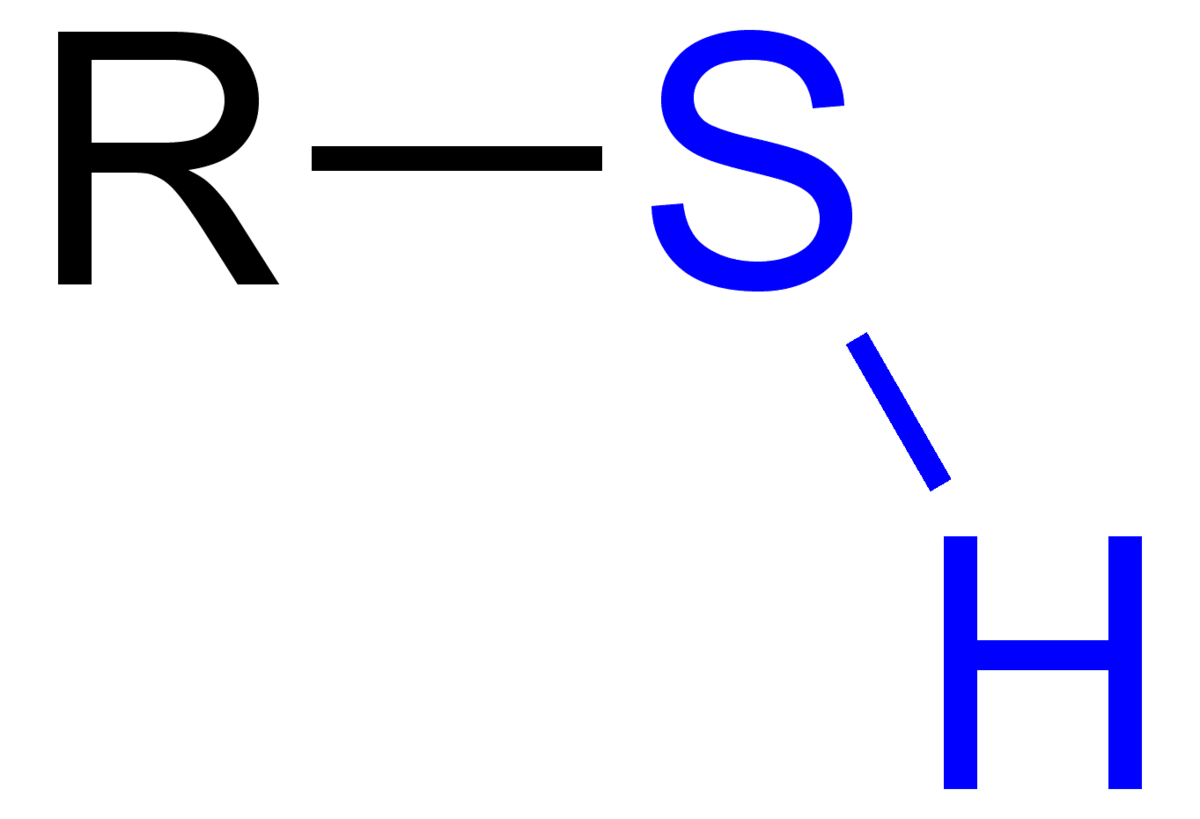
sulfhydryl group
sulfure bonded to a hydrogen atom (polar)
adrenaline
produced by adrenal glands during high stress or physically exhilarating situation, triggers the body’s fight or flight response
aldehyde
organic compounds that have a carbonyl group located at the end of the carbon skeleton. R-CHO
amines
organic compounds and a type of functional group that contain nitrogen atoms with a lone pair. They play a significant role in the formation of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
amino acids
form Proteins, building blocks for life
calcium ca
is an essential chemical element for living organisms, which includes humans. most abundant mineral in the body and plays a crucial role in body functions like bone formation, blood clotting, muscle contraction, nerve transmission
carbon
atomic number 6, nonmetallic and tetravalent - four electrons available to form covalent bonds
chlorine ci
chemical element with an atomic number of 17 and essential mineral for humans in the process of making protiens and DNA
compound
is a substance formed when two or more chemical elements are chemically bonded together
DNA and RNA
are nucleic acids that carry genetic information in cells. DNA provides instructions for growth, development, functioning, and reproduction while RNA translates those instructions into proteins
electron shells
energy levels where electrons reside around a nucleus. each shell can hold a certain number of electrons
energy level
In quantum mechanics, an it is a quantized state of an atom or molecule where it can exist. It represents the potential energy of the particle and determines how likely it is to transition between different states
enzymes
biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed
functional groups
are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties, regardless of the other atoms present in a molecule. They determine how organic molecules participate in chemical reaction
hydrogen
has a atomic number of one, standard atomic weight of 1/008, lightest element in the periodic table
insulin
hormone produced by the pancreas that emulated the amount of glucose in the blood. it allows cells to take in glucose from the bloodstream and use it an energy
ketone
carbonyl group
macromolecules
large, complex molecules that make up living organisms, they include carbs, protiens, lipids, fats, and nucleic acids
nitrogen
atomic number of 7
nitrogen cycle
is a series of processes by which nitrogen and its compounds are interconverted in the environment and in living organisms, including nitrogen fixation and decomposition
nitrogen fixation
is a process where N2 (atmospheric nitrogen) is converted into NH3 (ammonia). This process makes atmospheric nitrogen accessible to living organisms.
nucleic acids
Nucleic acids are large biomolecules essential for all known forms of life. They include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), which carry genetic information.
octet roe
chemical rule of thumb that states that atoms tend to combine in a way that they each have eight electrons in there valence shells, giving them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas
organic molecules
Carbohydrates provide quick fuel for cells. Lipids store long-term energy and insulate bodies. Proteins perform most cell functions including catalyzing reactions. Nucleic Acids store genetic information
oxygen
is a chemical element with symbol O and atomic number 8. It's essential for life on Earth because it's part of water molecules and used by cells for respiration process.
phosphate group
is a molecule in the chemical form PO4 that is part of many important biological structures such as DNA, RNA, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and phospholipids.
phospholipid
These are a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. They're made up of two fatty acid chains and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone.
phosphorous
is a chemical element that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of living organisms. It's an essential component of DNA, RNA, ATP (adenosine triphosphate), and phospholipids. It impacts how our body uses carbs and fats and is needed for building strong bones along with calcium
potassium
chemical element that is crucial for the proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs in the bud. it helps maintain fluid balance, nerve transmission, and muscle contractions
radioactive isotopes
also known as radioisotopes, are unstable forms of elements that decay over time, releasing radiation in the process.
radiocarbon
or carbon - 14, is radioactive isotope of carbon that has six protons and eight neutrons in its nucleus. It occurs naturally in small amounts in the atmosphere and gets absorbed by living organisms.
sodium (NA)
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin "natrium") and atomic number 11. It's vital for nerve impulse transmission and muscle contraction.
sulfur
atomic number 16, it is an essential element for all life, and is an component of certain amino acids and vitamins
tetra valence
refers to the ability of certain atoms, like carbon, to form four bonds with other atoms