Geosystems Chapter 4: Global Temperatures
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
What are greenhouse gases?
They absorb infrared waves as they reradiate from Earth’s surface and try to leave the atmosphere
What are the four things that impact global temperatures?
Latitude, Altitude and Elevation, Cloud cover, and Land-water heating differences
Does temperature decrease with an increase or decrease of altitude?
Increase of altitude
Air density decreases with an increase or decrease of altitude?
Increasing altitude
Thin air absorbs?
Less heat
True OR False: Do clouds impact temperature?
True
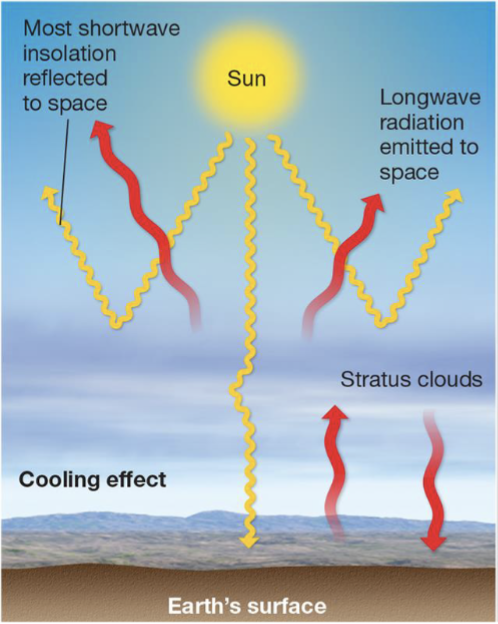
Low thick clouds do what?
Block light and cause cooling in temperature
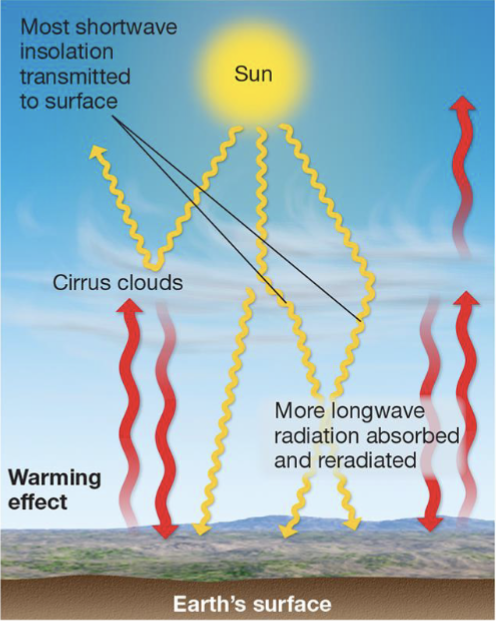
High, ice-crystal clouds do what?
Allows light to reach the surface and warms the temperature
What are some characteristics of an Urban Heat Island?
Conduct more energy (metal,glass, asphalt, concrete)
Have lows albedos so they absorb heat
Their homes, vehicles, and factories generate heat
What are Urban Heat Islands?
Places that have higher temperatures then their surroundings
What is an Urban Canyon?
Buildings block winds, insolation reflected on urban surfaces
What is an Urban Desert Effect?
Lower evaporation and plant transpiration is reduced
Land-Water Heating Differences
Continental: Temperature conditions are more extreme (land warms and cools rapidly)
Less evaporation
Surface is opaque
Land has a lower specific heat
Land has no mixing between layer
Marine: Temperature conditions more moderate (water warms and cools slowly)
More evaporation
Surface is transparent
Water has a higher specific heat
Water has mobility and mizes in vast ocean current
What is specific heat?
The heat required to raise the temperature of the unit mass (usually one degree)
Higher pressure =
More molecules
Lower pressure =
Less molecules
Air pressure will always move…
High to low pressure
What is air pressure?
Force per unit area exerted against a surface by the weigh of the air above it
Wind is causes by a change in…
Air pressure
What is a pressure gradient force?
Air flows from high pressure to low pressure
What are Isobars?
Are equal pressure lines that help indicate pressure gradients
Closer isobars show..
A higher the pressure gradient and stronger wind speeds
What is a Coriolis Force?
Deflects moving objects due to Earth’s rotation
Northern Hemisphere~ To the right
Southern Hemisphere~ To the left
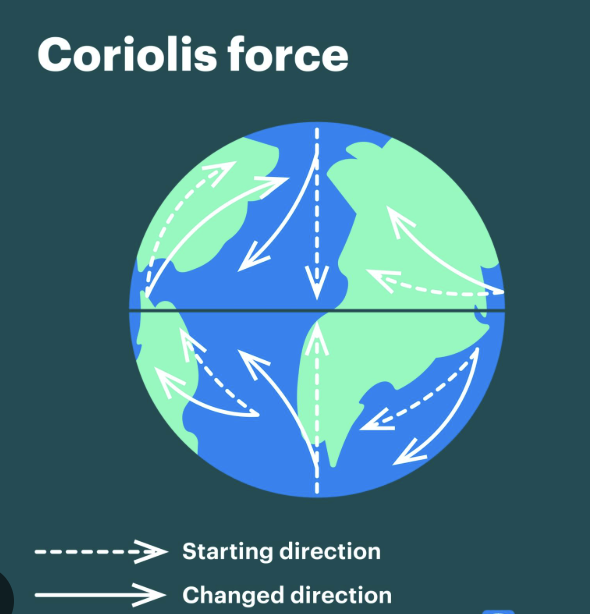
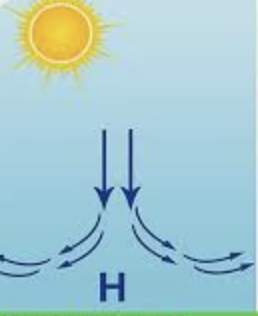
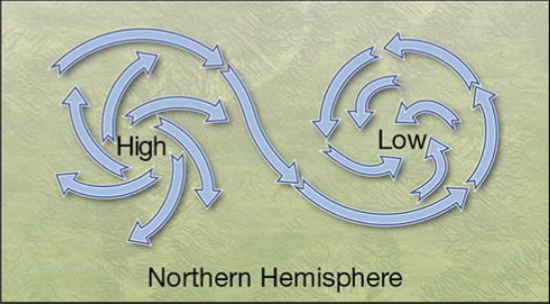
High pressure does what to air..
Air descends and diverges

Low pressure does what to air?
Air ascends and converges
The pressure gradient force acting by itself on a nonrotating Earth causes..
winds to move form high to low pressure across isobars
Pressure Gradient Force+Coriolis Force=
Geostrophic Wind
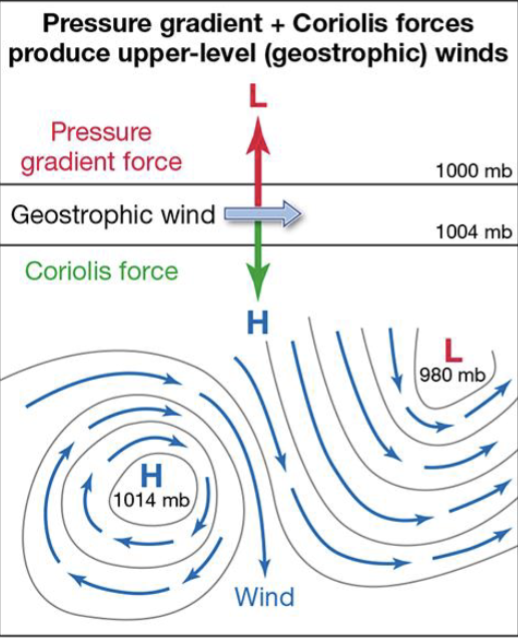
Earth’s rotation adds the Coriolis forces, which
gives a “twist” to air movements, so high-pressure and low-pressure areas develop a rotary motion
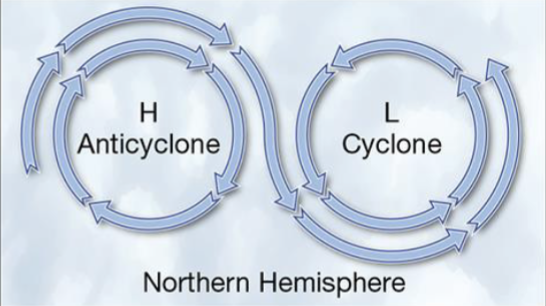
High pressure air spirals intro
low pressure systems
Pressure Gradient Force + Coriolis Force + Friction =
Surface Winds
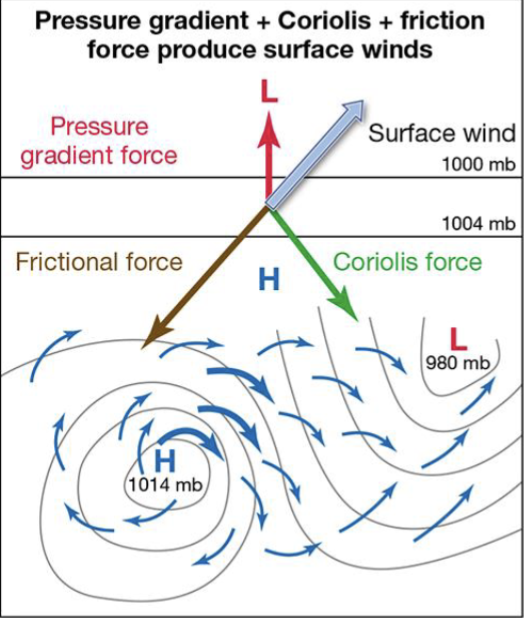
Friction adds a countering force to..
Coriolis, producing winds that spiral out of high areas into low areas
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
Lies along the equator, a trough of low pressure and light or calm winds
Has high precipitation year-round
At the equator there is the..
Equatorial Low Pressure Trough
ITCZ
Trade Winds
High Precipitation
Hadley cells are
large atmospheric circulation patterns move energy and air from the tropics to the subtropics.
30 degrees North and 30 degrees South are
high pressure areas (subtropical high-pressure cells)
Are dry and hot
Westerlies
Bermuda High
Pacific High
Sub-Polar Low Pressure Cells are areas that are
Cool and moist
Aleutian low
Icelandic low
Polar front
Sub-Polar High-Pressure Cells areas are
Frigid and dry
Descend and diverges
Polar easterlies
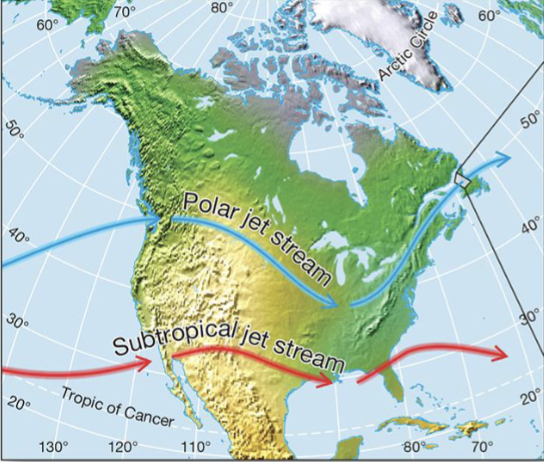
What are jet streams?
High-altitude river of high-speed air
Caused by Earth’s rotation and atmospheric heating
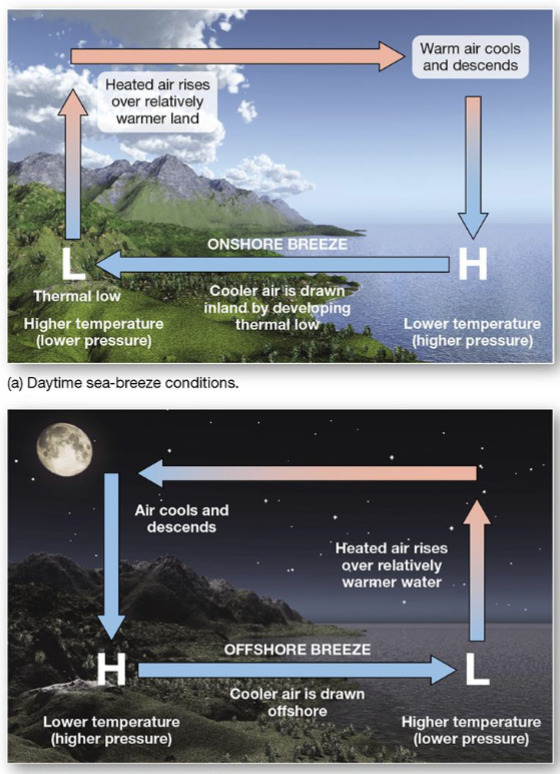
Local and Regional Breezes are affected by..
The time of day (higher and lower temperatures)
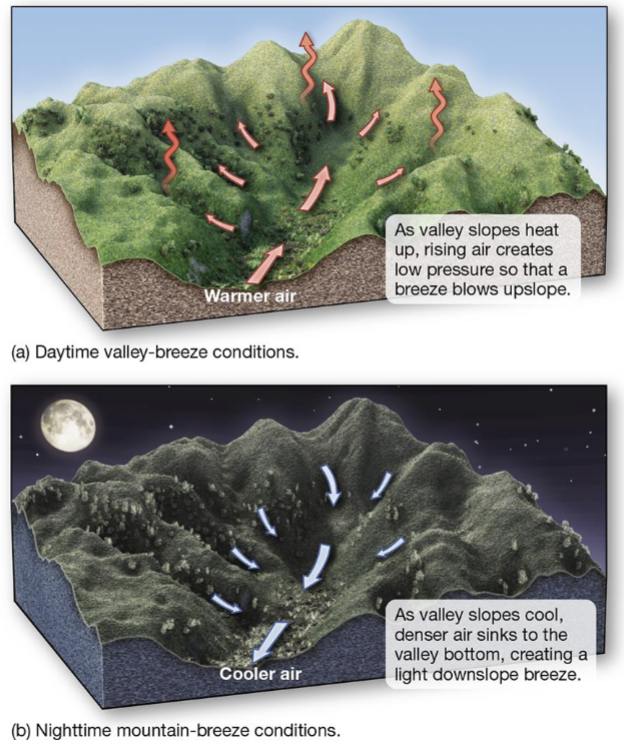
Mountain and Valley Breezes are affected by…
The time of day (warmer and cooler air)
Surface currents are caused by..
Surface Winds
What is thermohaline circulation?
Deep currents caused by density differences in temperature and salinity
What are the two different types of ocean currents?
Surface currents and thermohaline circulation
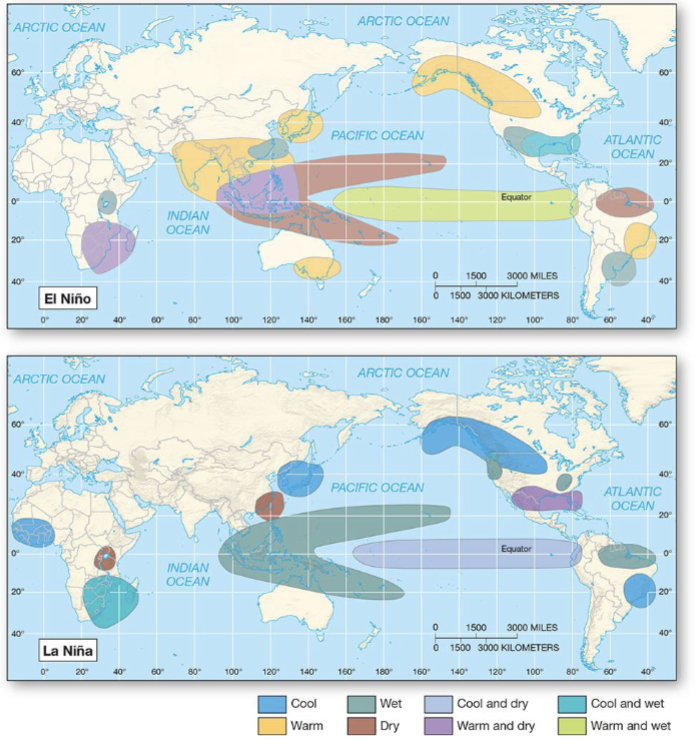
What is an el niño southern oscillation?
A natural climate pattern in the Pacific Ocean where the sea surface temperatures fluctuate between warm phases (El Niño) and cool phases (La Niña)