Functional Organization Of Nervous Tissue
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
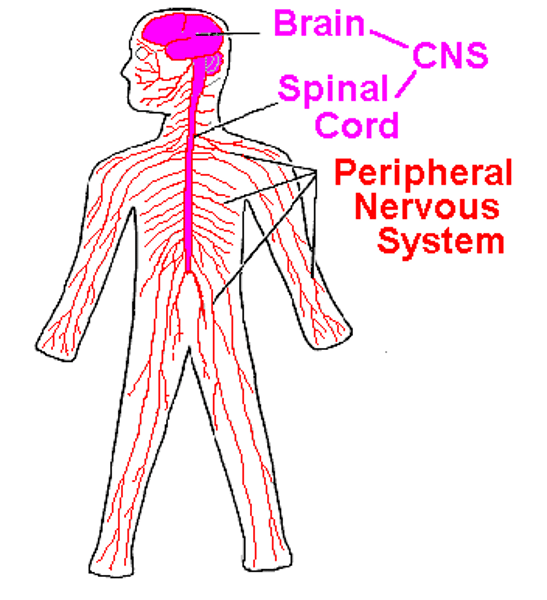
Functions of the Nervous System
Maintaining homeostasis
Receiving sensory input
Integrating information
Controlling muscles and glands
Establishing and maintaining mental activity
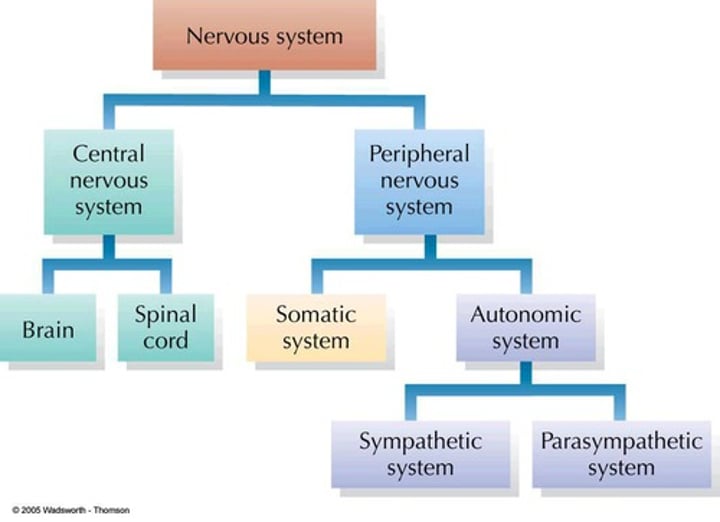
Nervous System Organization
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
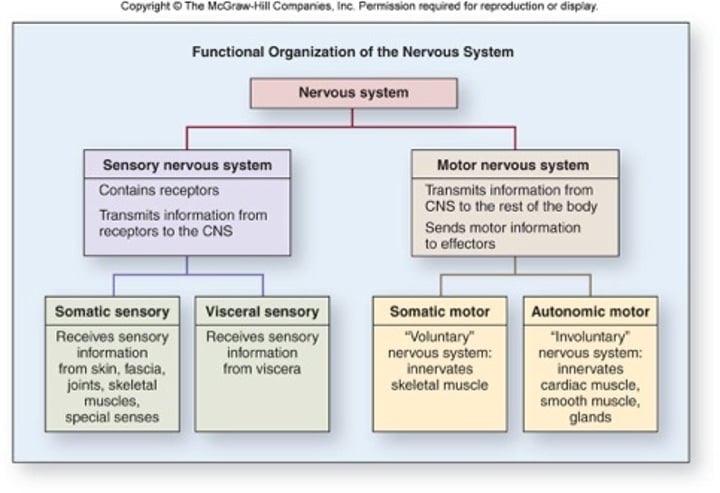
Functional Organization of the Nervous System
Sensory (Input)
Motor(Output)
Motor Nervous System
Initiates and transmits information from the CNS to effectors
Somatic Motor
Motor output that is consciously or voluntarily controlled
Ex. Effector is skeletal muscle
Autonomic Motor
Motor output that is not consciously or is involuntarily controlled
Ex. Effectors are cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, and glands
Sensory Nervous System
Detects stimuli we consciously perceive
Somatic Sensory
Sensory input that is consciously perceived from receptors
Ex. Ears, Eyes, Skin
Visceral Sensory
Sensory input that is not consciously perceived from receptors of blood vessels and internal organs
Ex. Heart
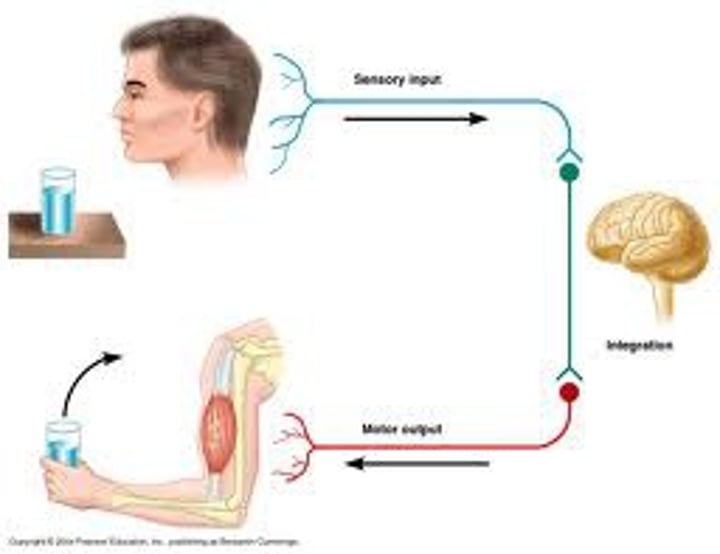
Sensory
Afferent- Transmits action potentials from receptors toward the CNS.
Sensory Receptors
Sensory nerve endings that respond to stimuli
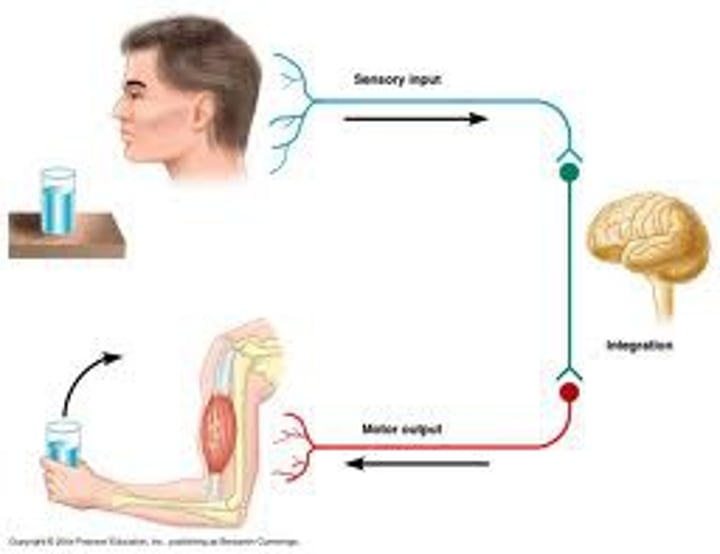
Motor
Efferent- Transmits action potentials from CNS to effectors.
SAME
Sensory (afferent)
Motor (efferent)
Somatic
Autonomic
Divisions of the Nervous System
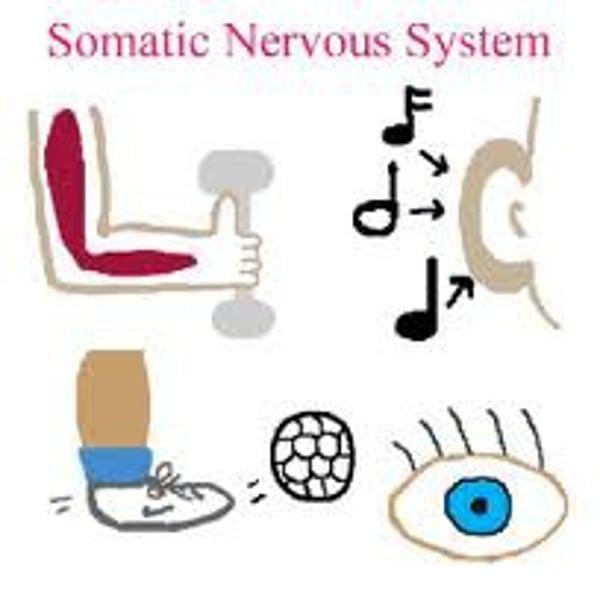
Somatic Nervous System
From CNS to skeleton muscles. (Voluntary)
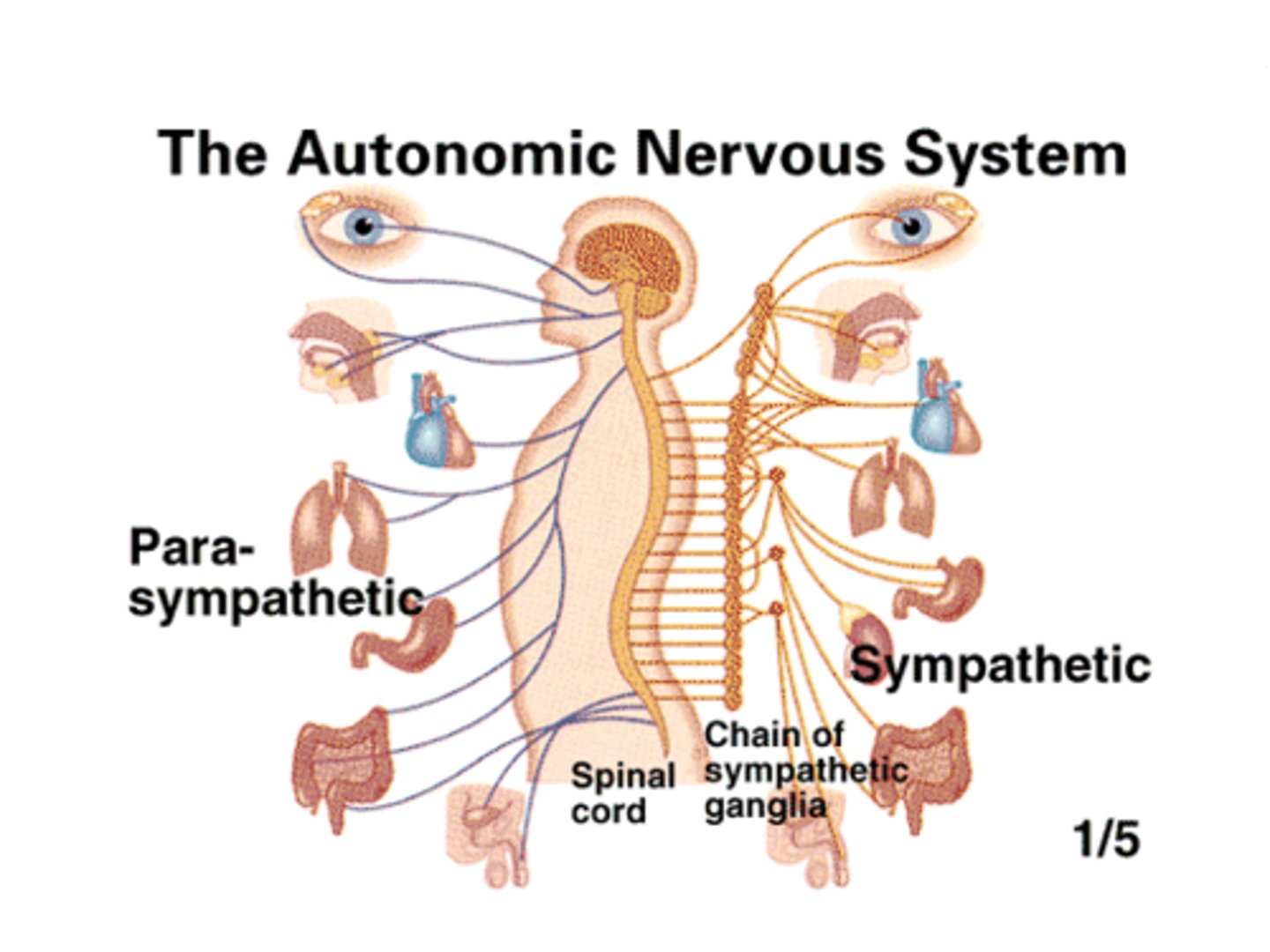
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
From CN to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and certain glands
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) Divisions
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic

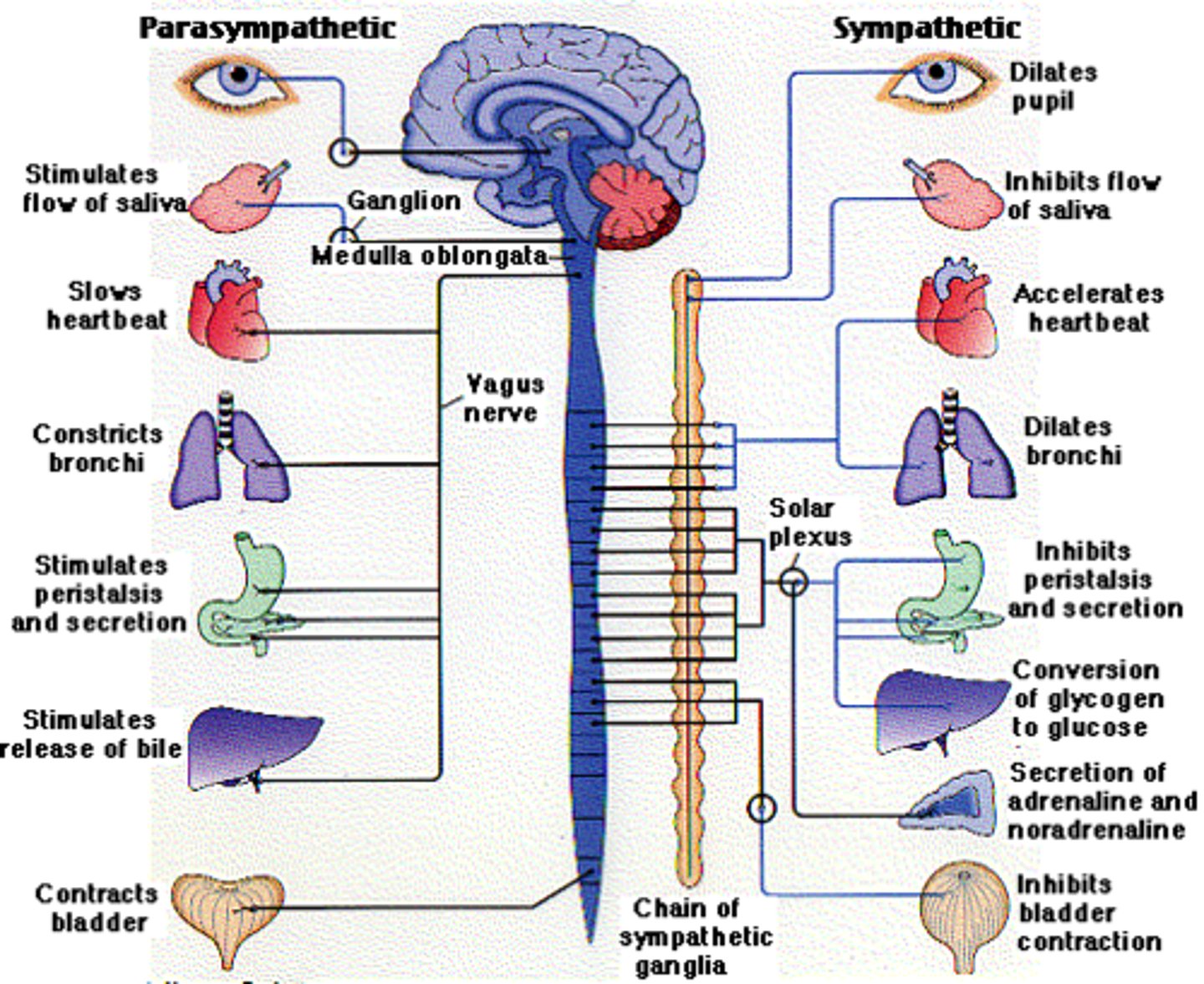
Sympathetic (ANS)
Prepares body for physical activity (Fight or Flight)
Parasympathetic (ANS)
Regulates resting such as digesting food or emptying of the urinary bladder
Enteric (ANS)
Plexuses within the wall of the digestive tract (Gut Function)
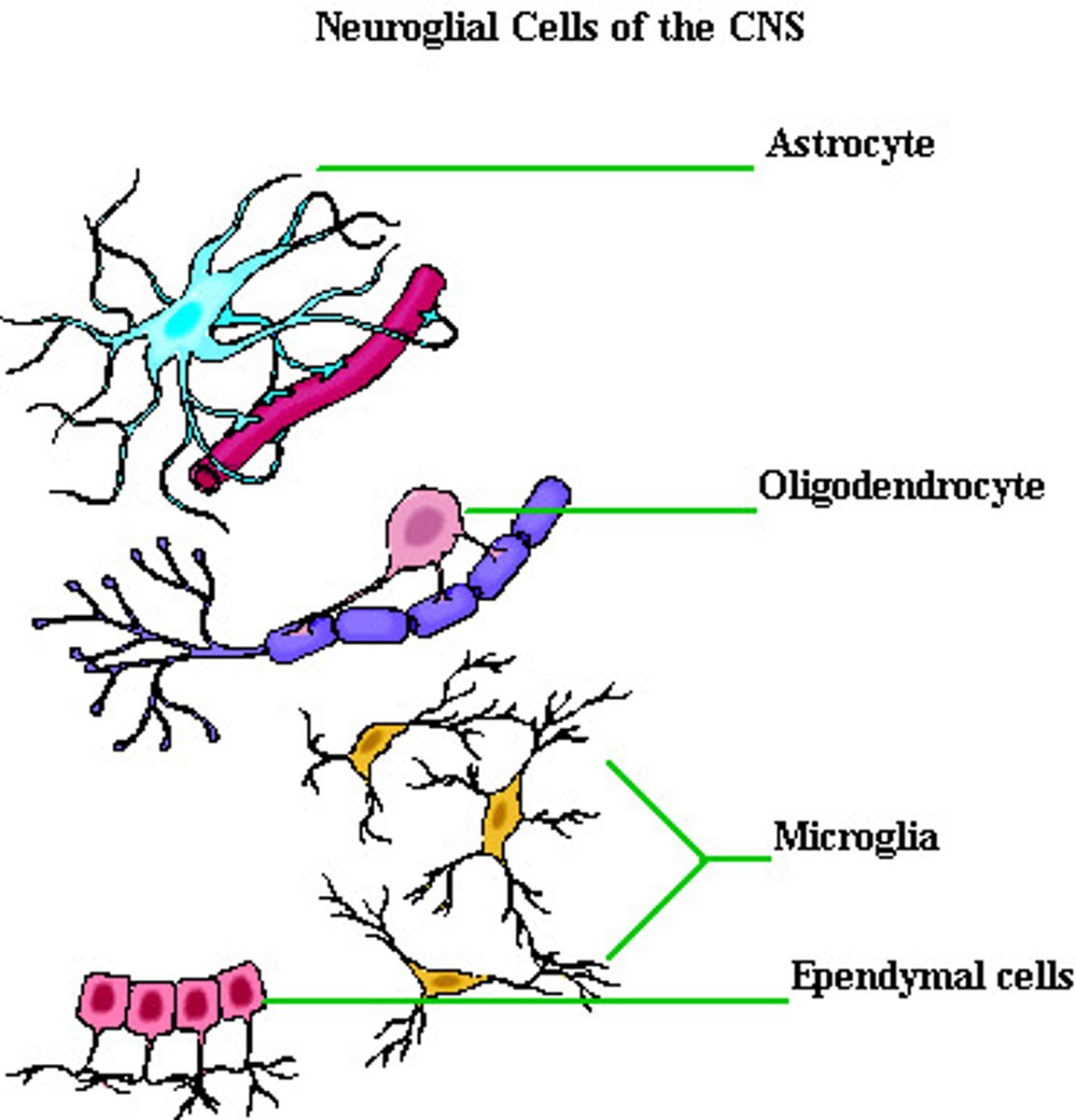
Glial Cells of the CNS
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal cells
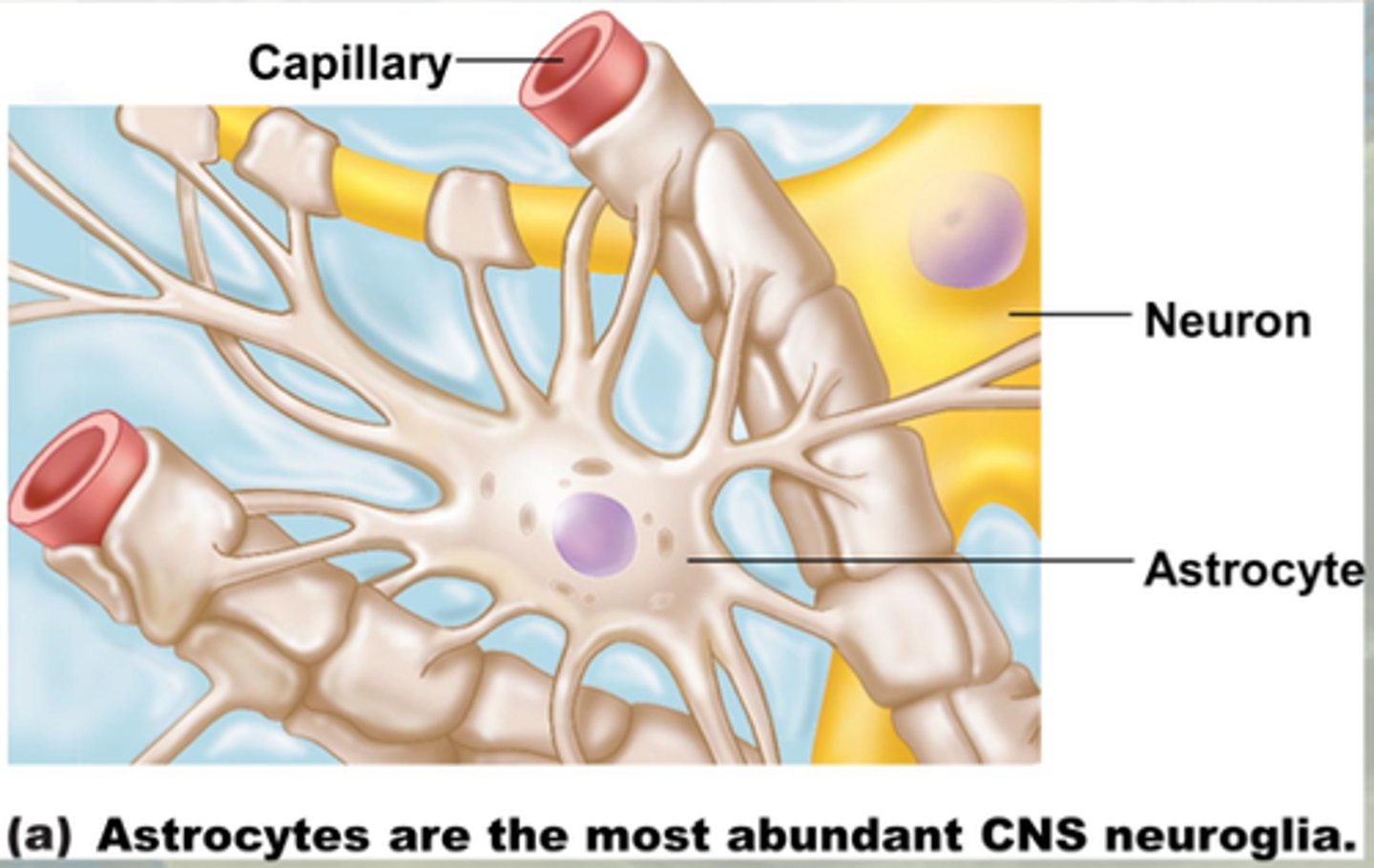
Astrocytes
Blood brain barrier (CNS)
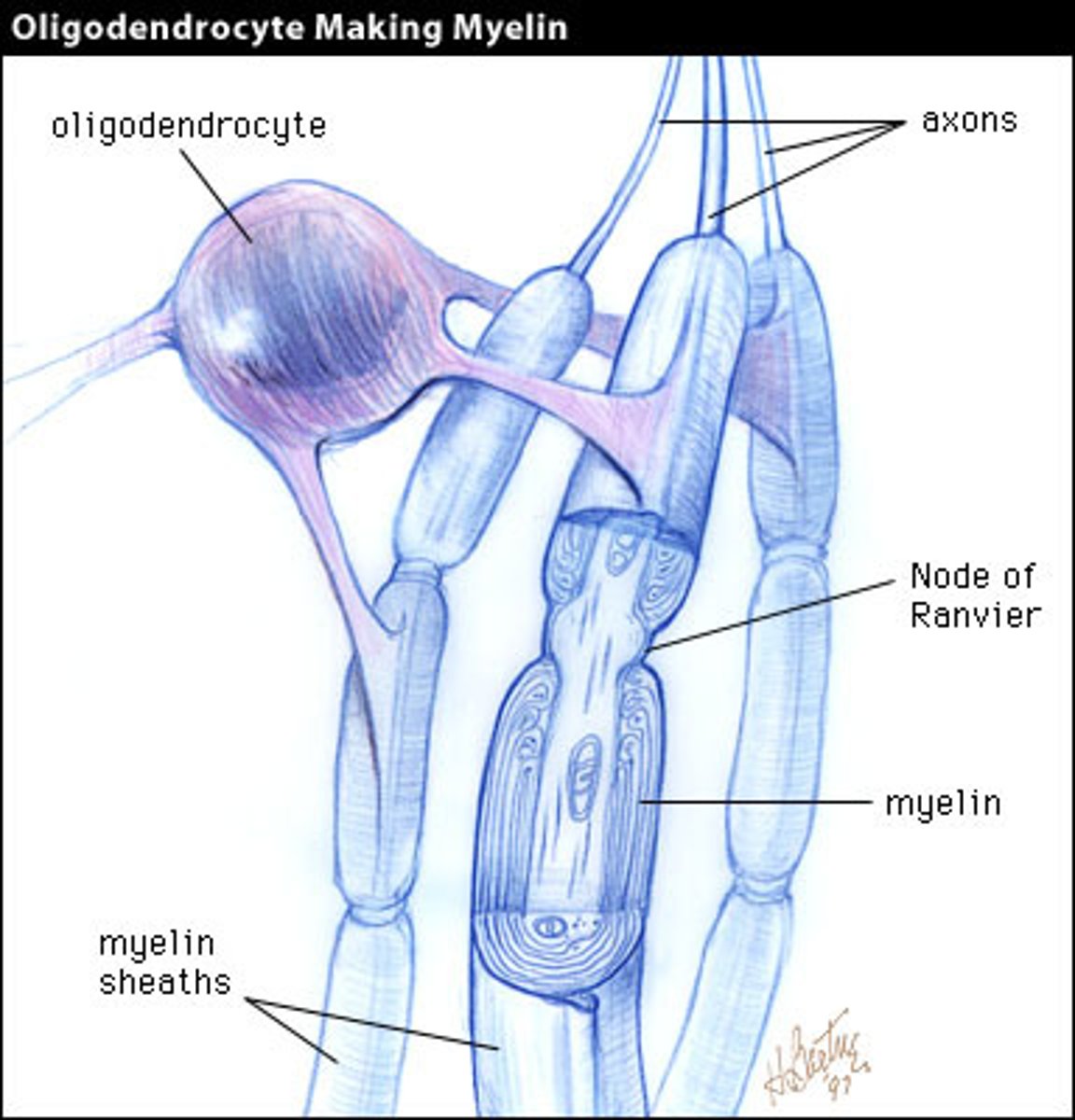
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin sheath in CNS
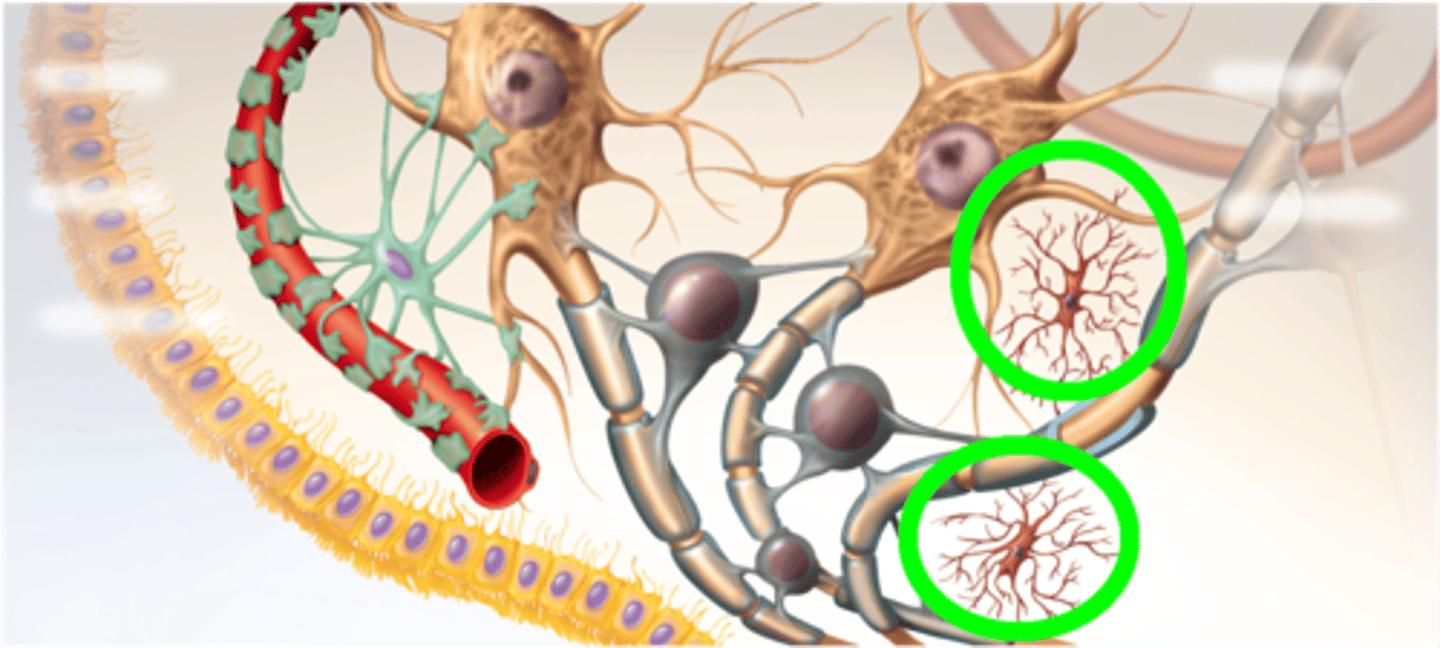
Microglia
Phagocytic cells that ingest and break down waste products and pathogens in the CNS
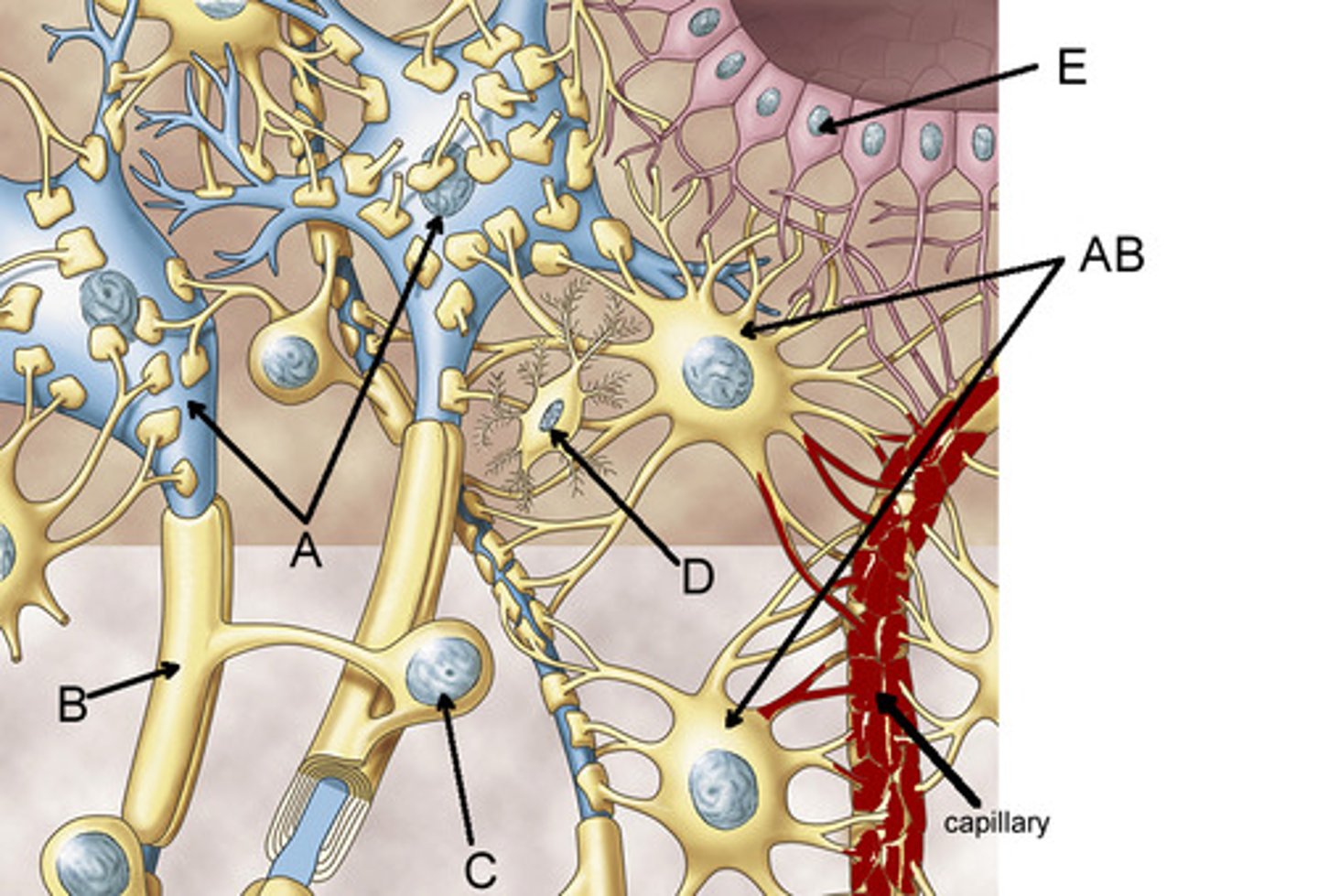
Ependymal cells
Produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Glial Cells of the PNS
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
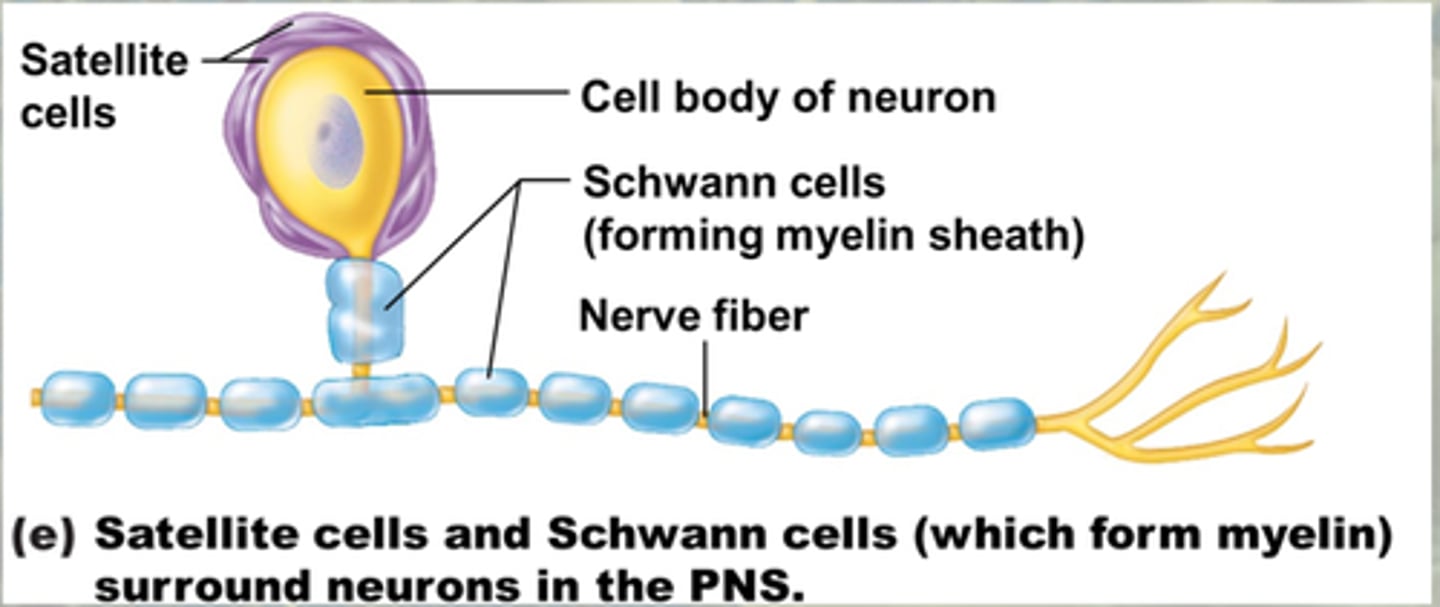
Schwann cells
Produce myelin in PNS
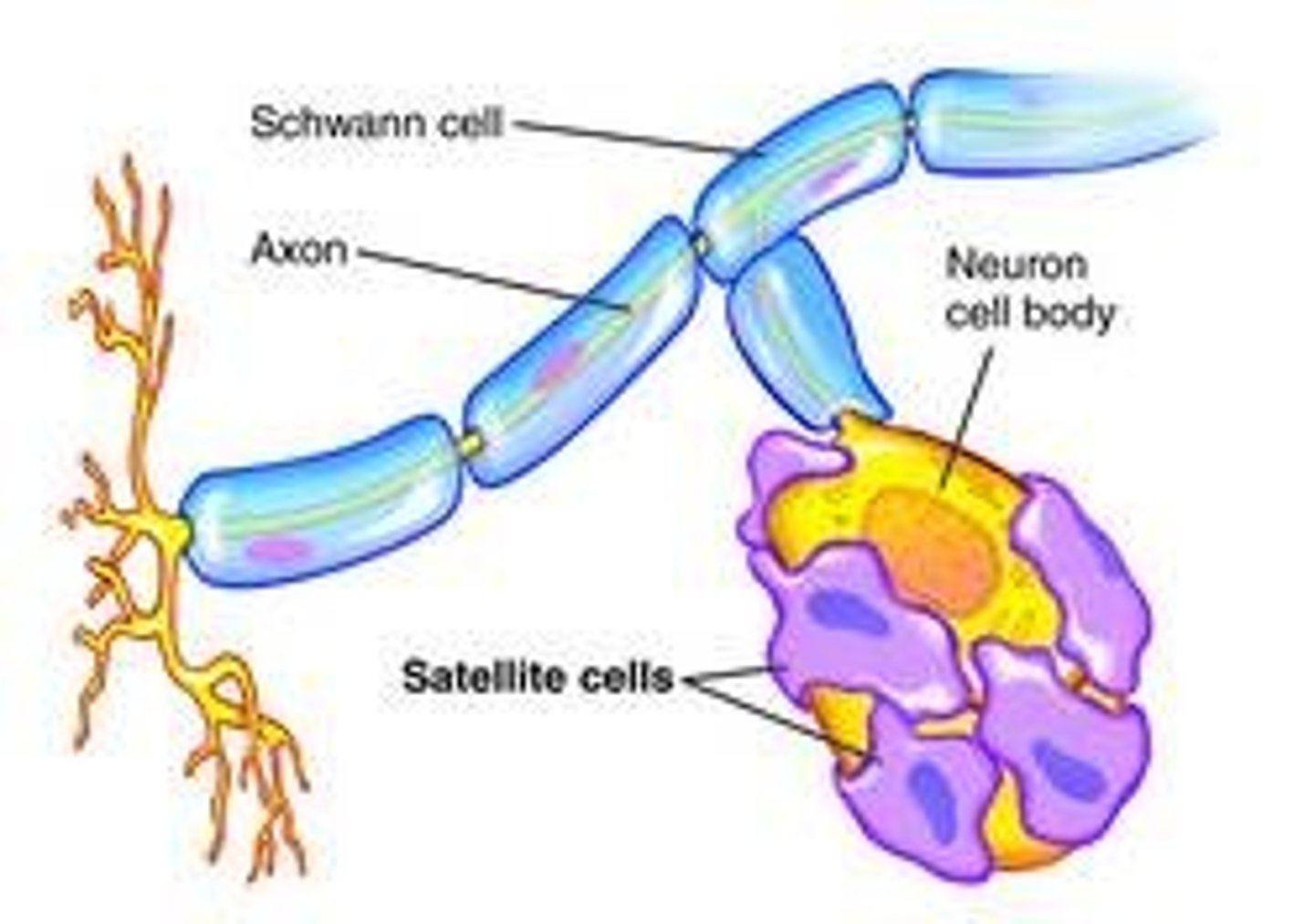
Satellite Cells
Surround neuron cell bodies in PNS
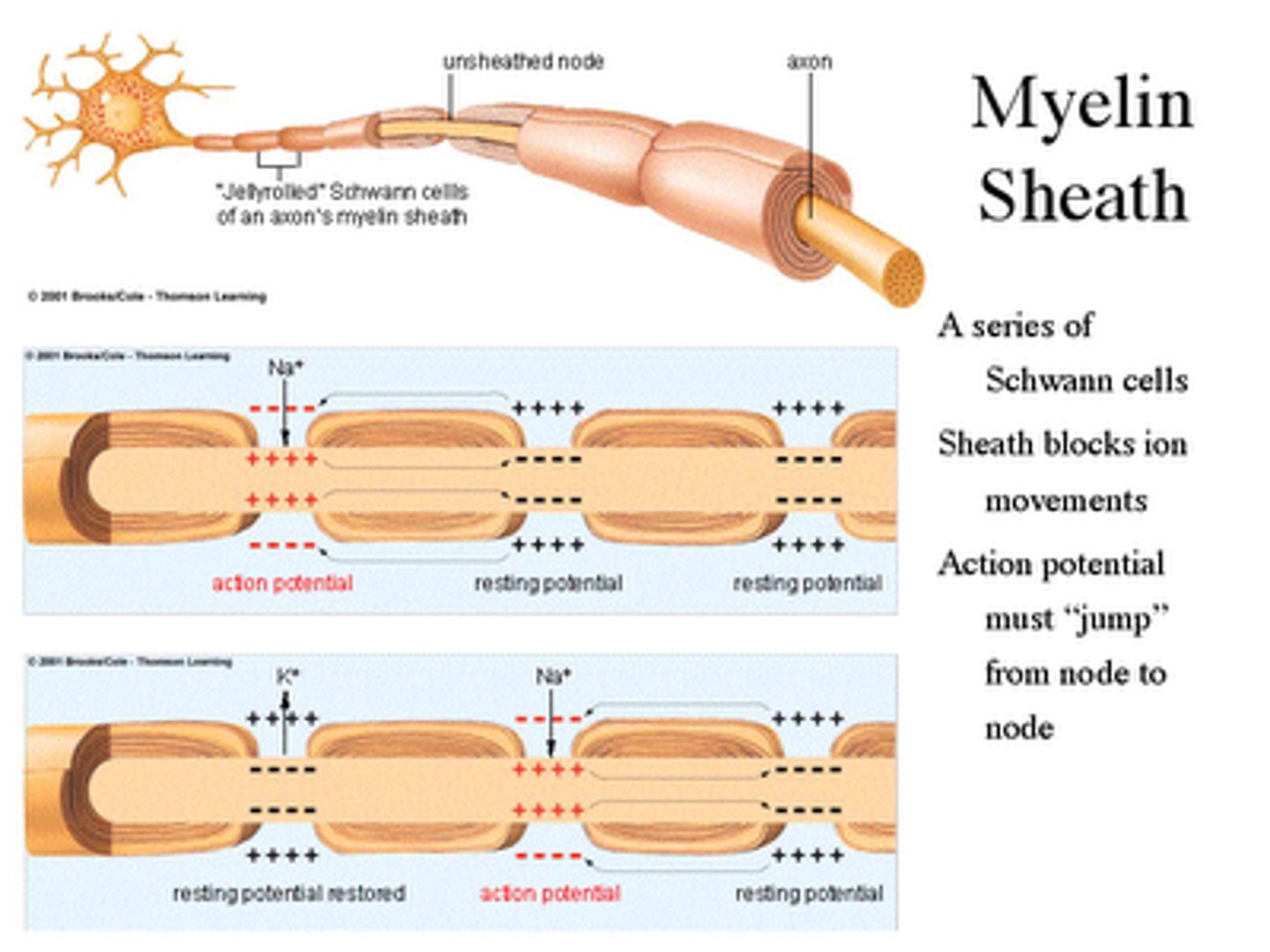
Myelinated Axons
Axons covered with myelin sheaths
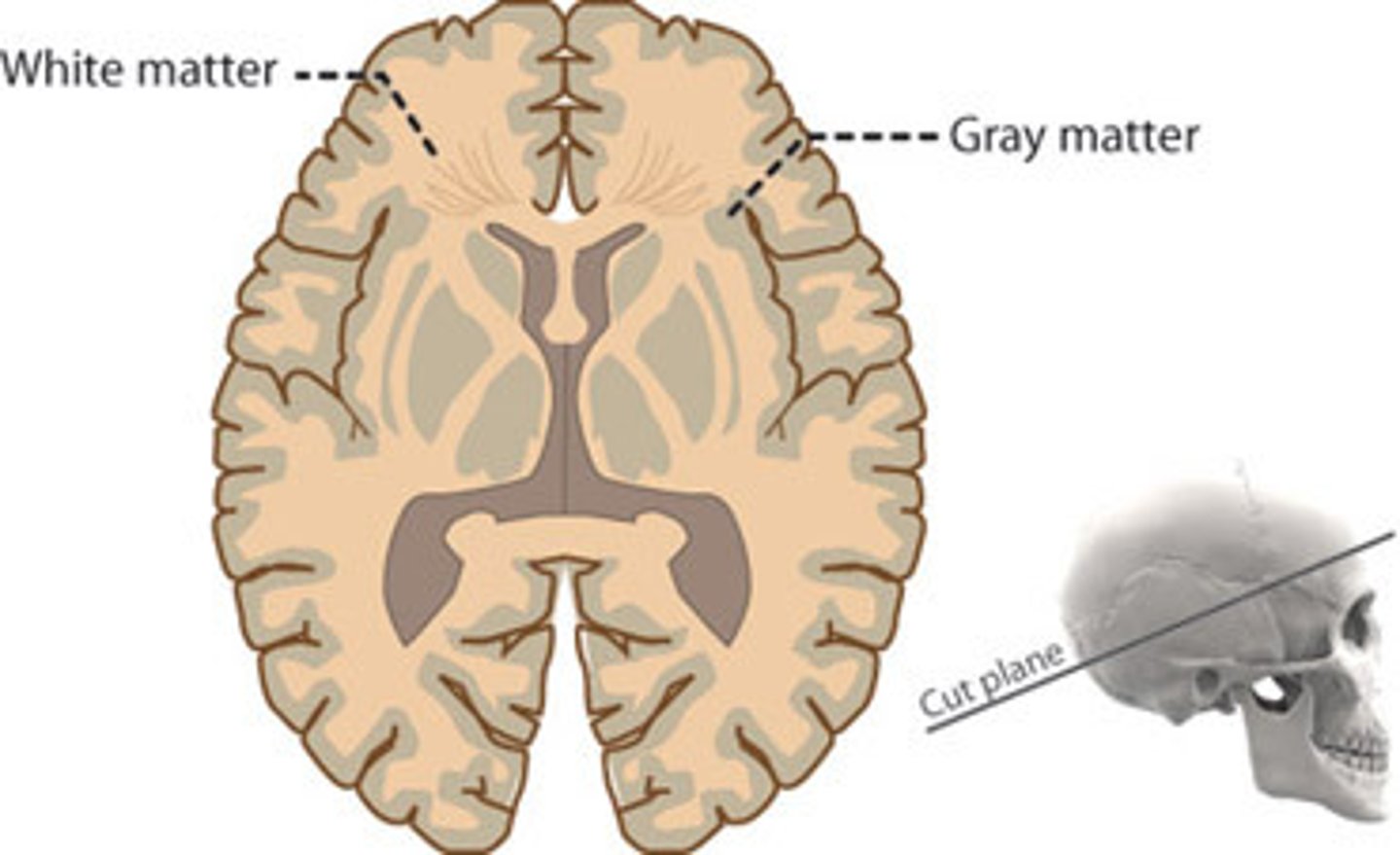
Organization Of Nervous Tissue
Gray matter
White matter
Gray Matter
Unmyelinated axons
Cell bodies
Dendrites
Integrative functions
The cortex of the brain
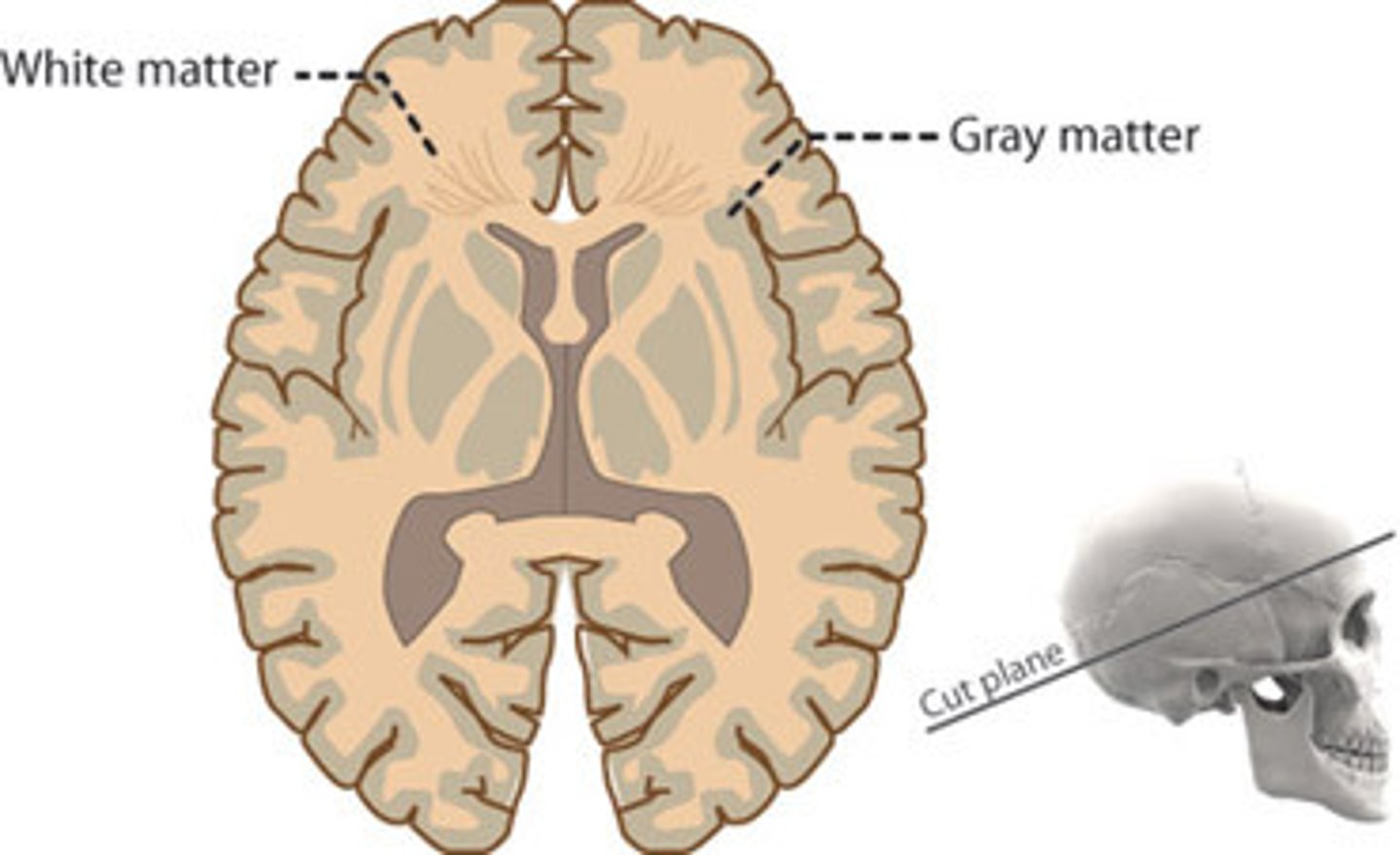
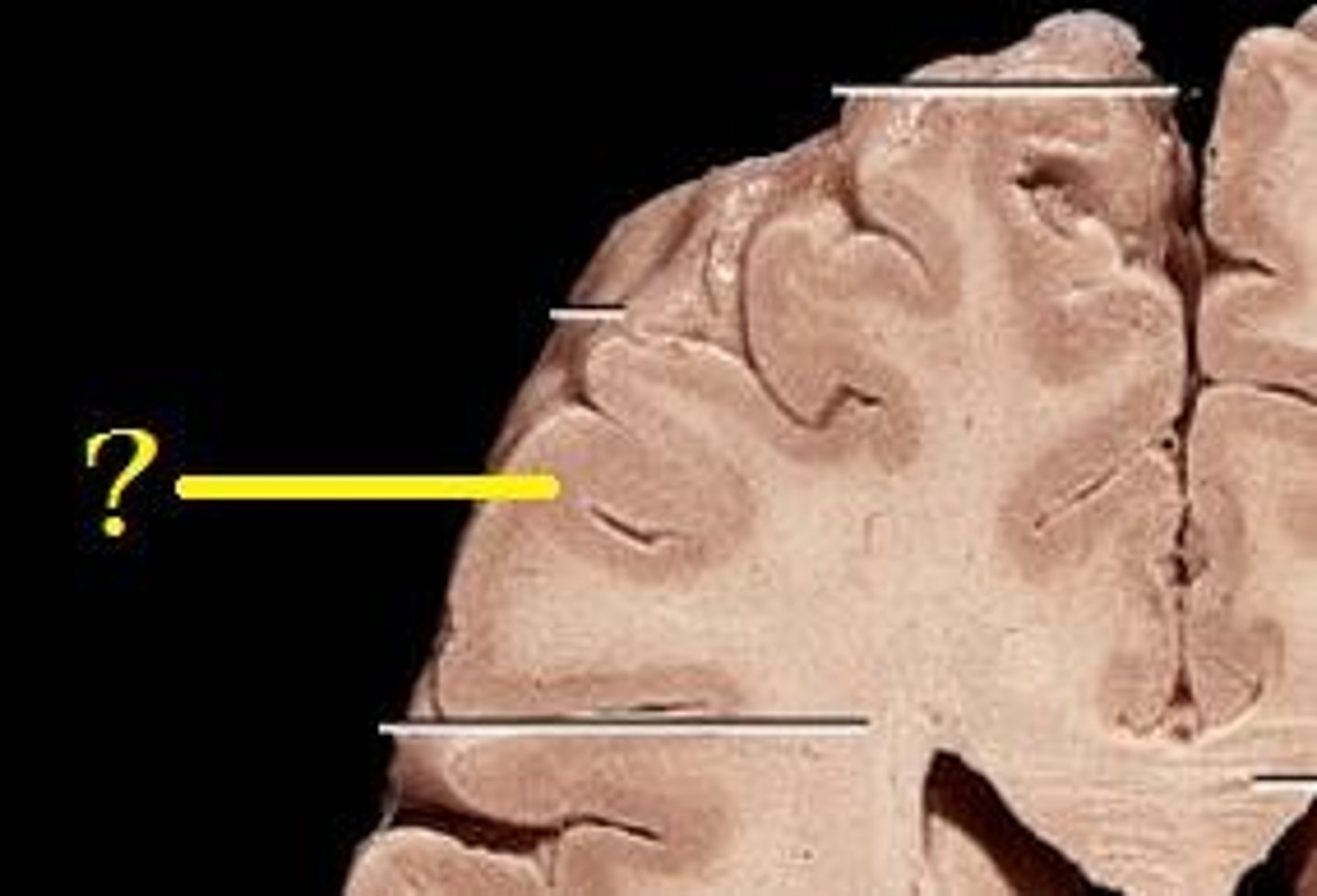
White Matter
Myelinated axons
Propagate action potentials
Cluster of neuron cell bodies in the PNS
ganglia
Bundles of axons with CT sheaths in PNS
Nerves
Clusters of neuron cell bodies in CNS
Nuclei
Tracts
Bundles of myelinated axons in CNS
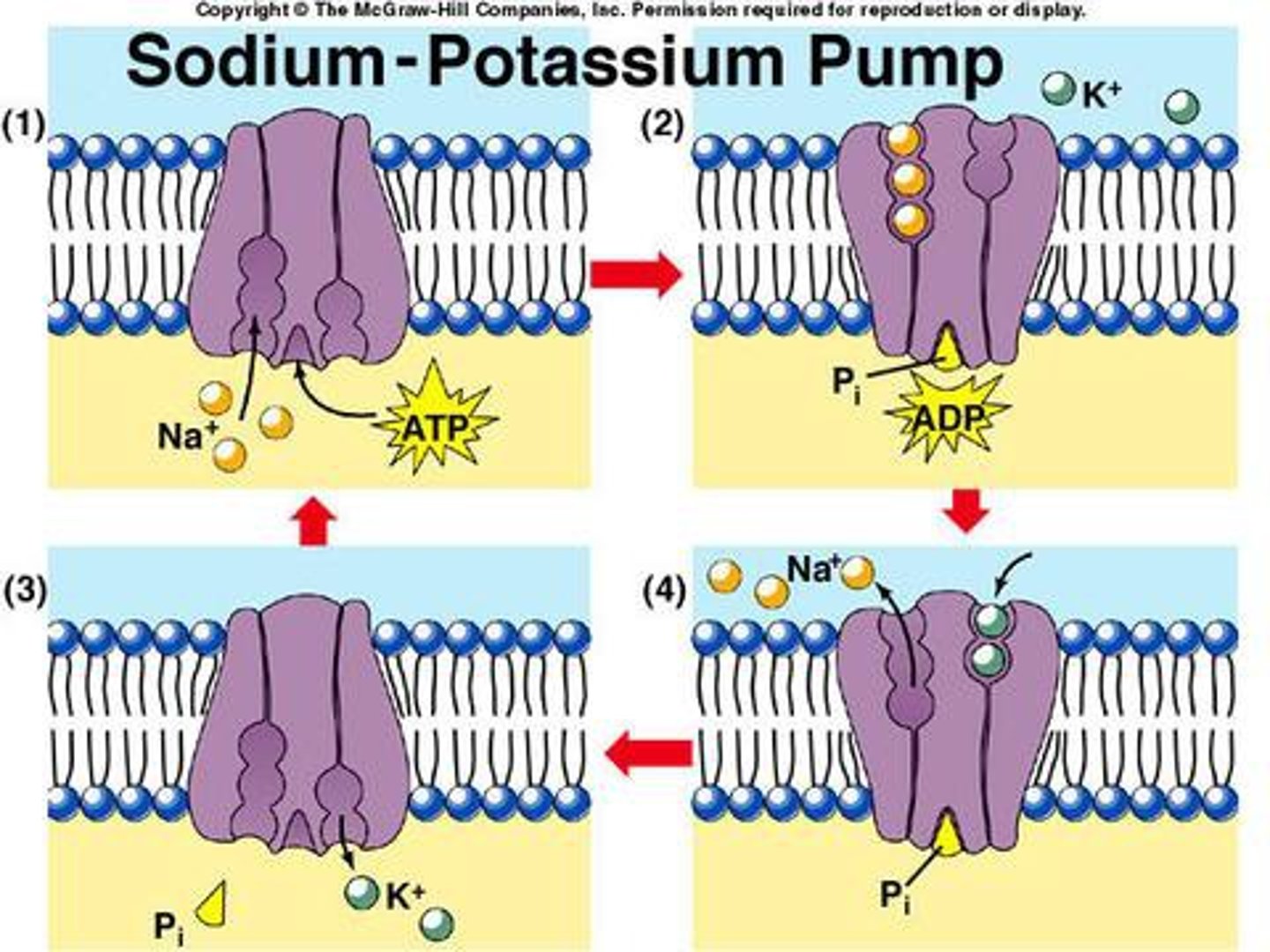
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Sodium is pumped outside the cell but wants to come in.
Potassium is pumped inside the cell and wants to go out.
Ligand-gated ion channel
Open or close in response to ligand such as neurotransmitter or hormone binding to receptor protein
Voltage-gated ion channel
Open or close in response to voltage changes
Other gated ion channels
Touch receptors: respond to mechanical stimulation of the skin
Temperature receptors: respond to temperature changes in the skin
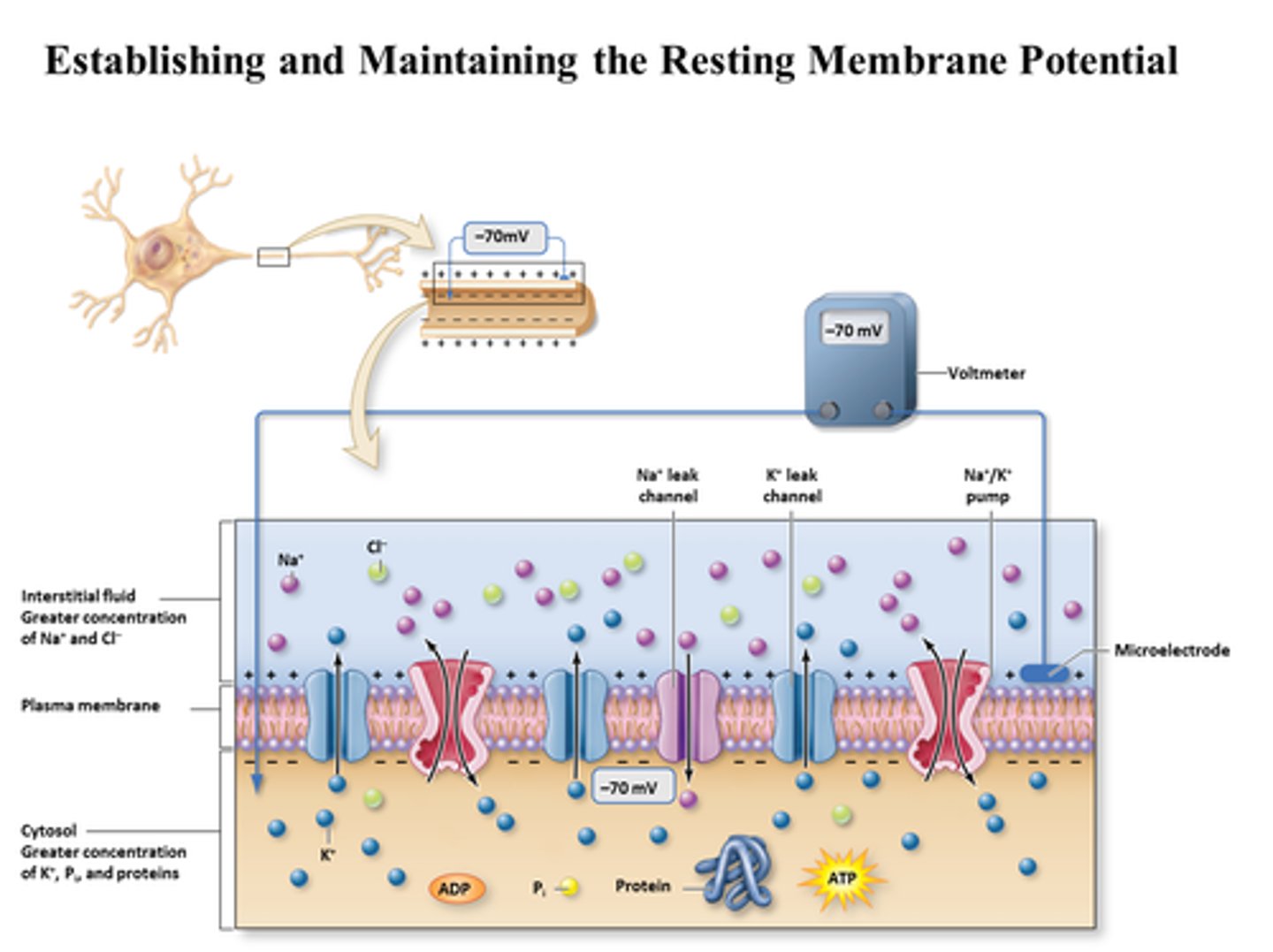
Establishing the Resting Membrane Potential
Higher potassium inside
Higher sodium outside
Proteins stuck inside
Depolarization
Inside of cell becomes more positive
Hyperpolarization
Inside of cell becomes more negative
Two major ways to hyperpolarize
Potassium Ions- Making cell more negative (Most common)
Chloride Ions- Ligand- gated chloride channels causes chloride to enter cell adding negative charges hyperpolarizes the cell
Graded Potential
A shift in the electrical charge in a tiny localized area of a neuron
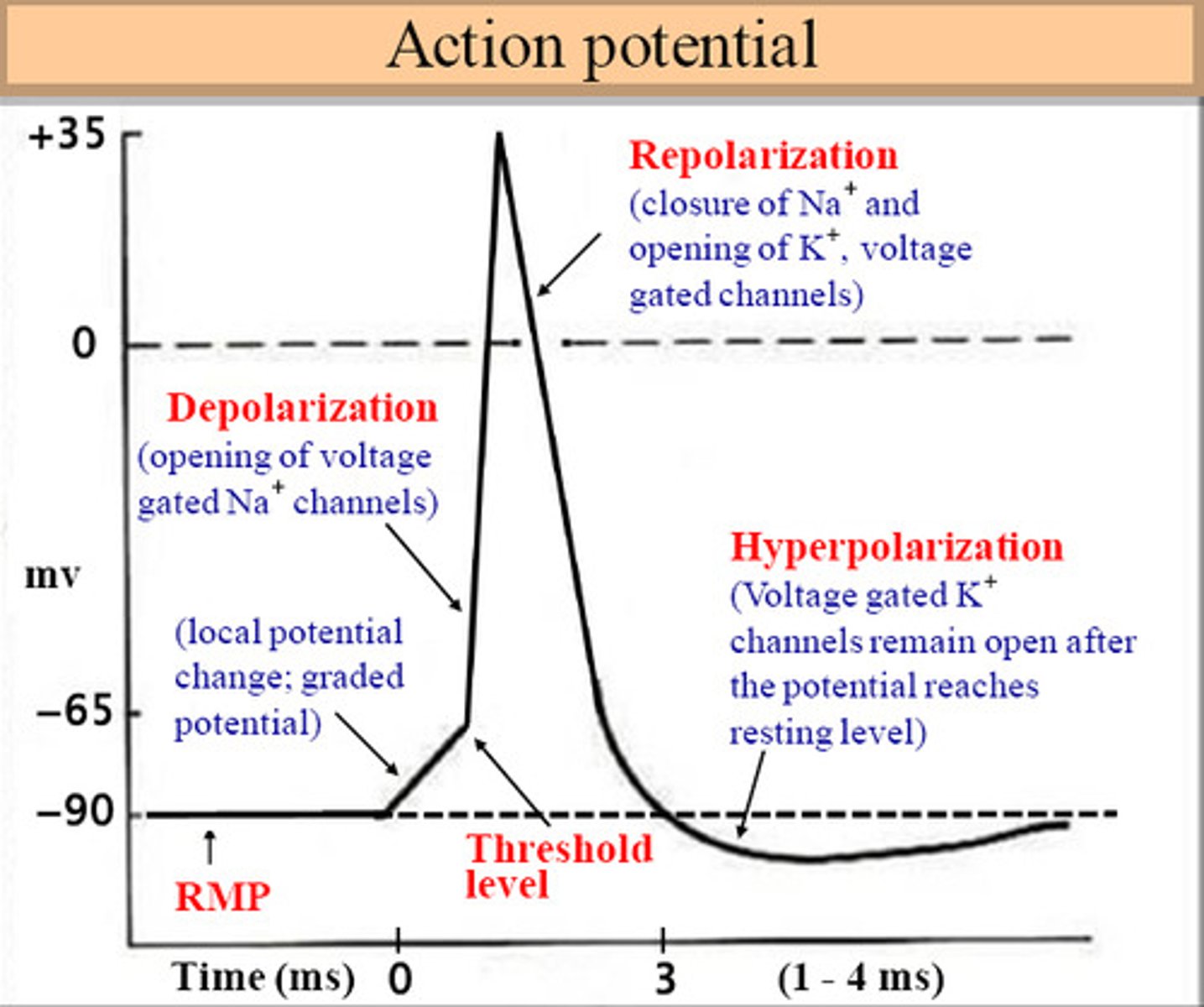
Action Potential- How neurons communicate
Graded potentials summate reaching threshold
All or none principle
No matter how strong the stimulus
As long as it is greater than threshold an action potential will occur
Depolarization
Sodium channels open
Incoming Sodium makes the inside of membrane more positive
As voltage changes more and more voltage-gated sodium channels open
Repolarization
As the membrane potential reaches its maximum depolarization voltage-gated sodium channels close and potassium open
Action Potential Frequency
Number of action potentials produced per unit of time to a stimulus
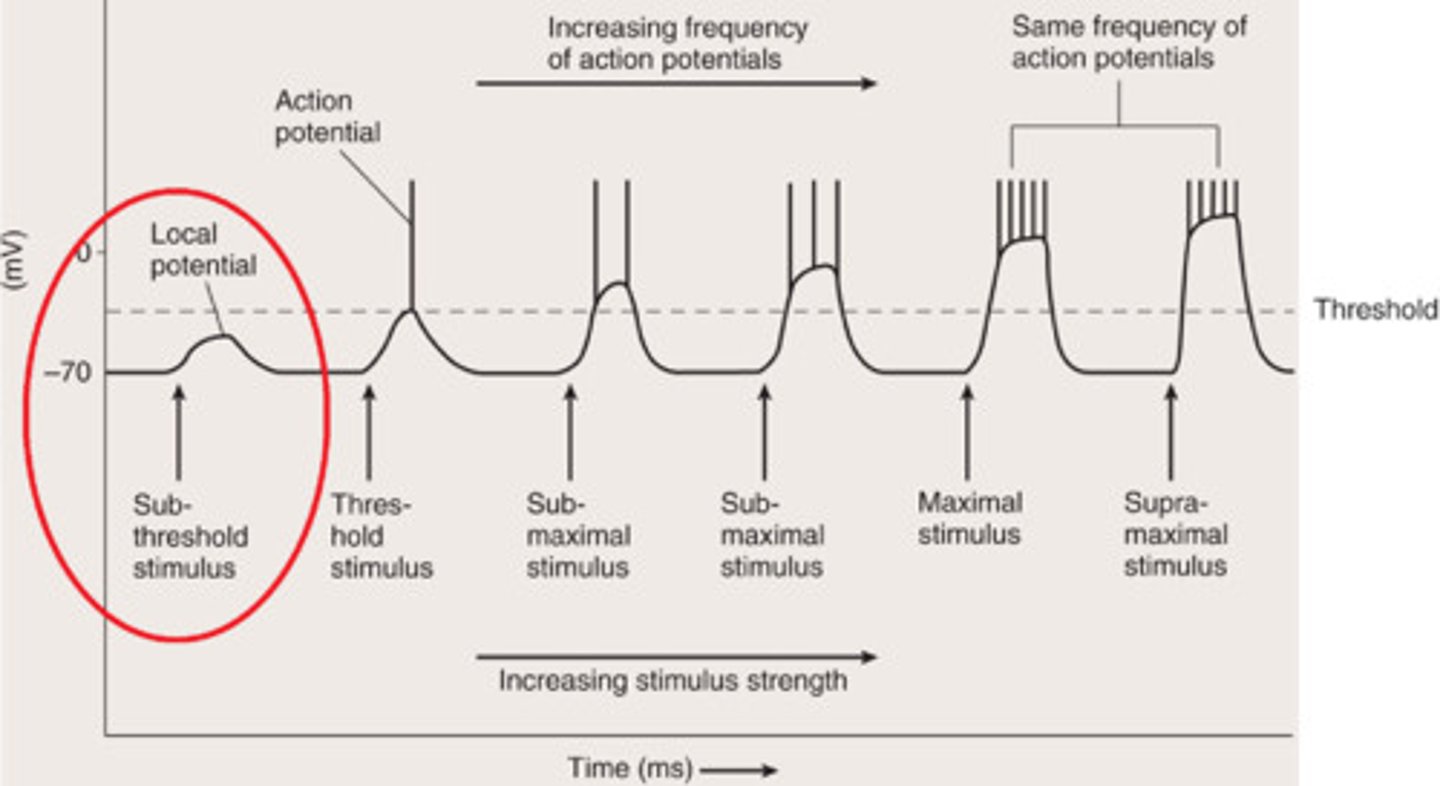
Subthreshold Stimulus
Stimulus not strong enough, so no contractions seen
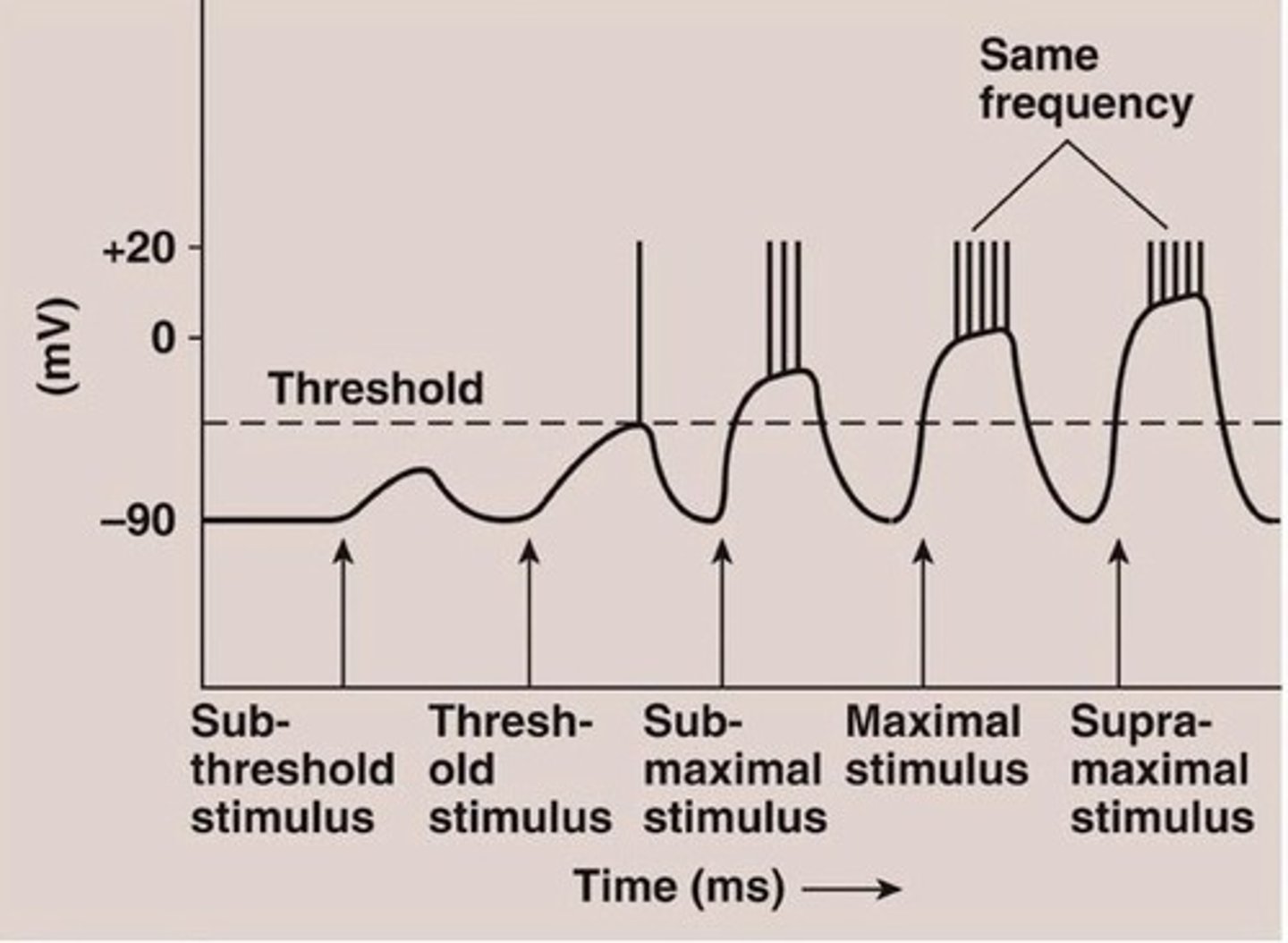
Threshold Stimulus
Graded potential initiates an action potential
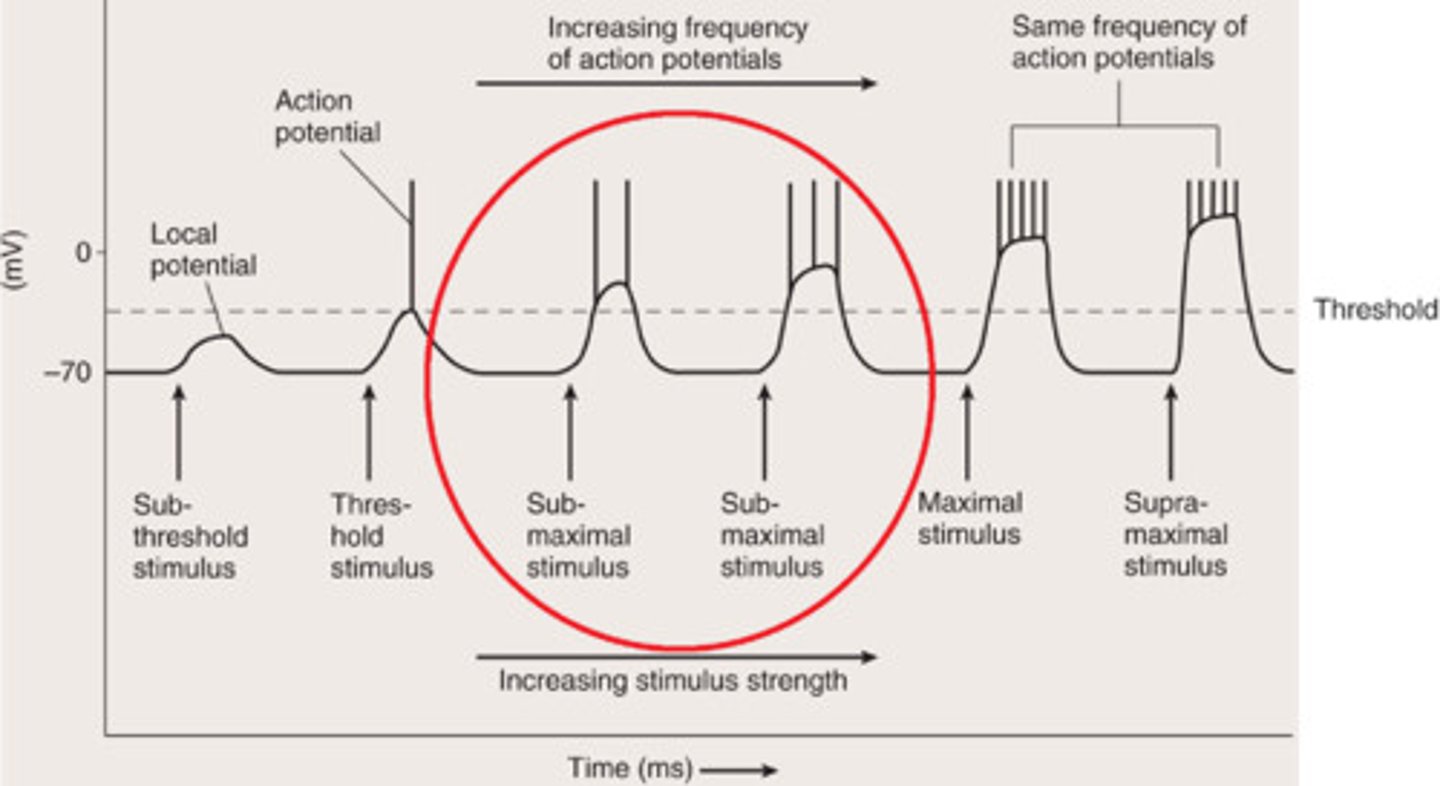
Submaximal Stimulus
Between threshold and maximal stimulus strength
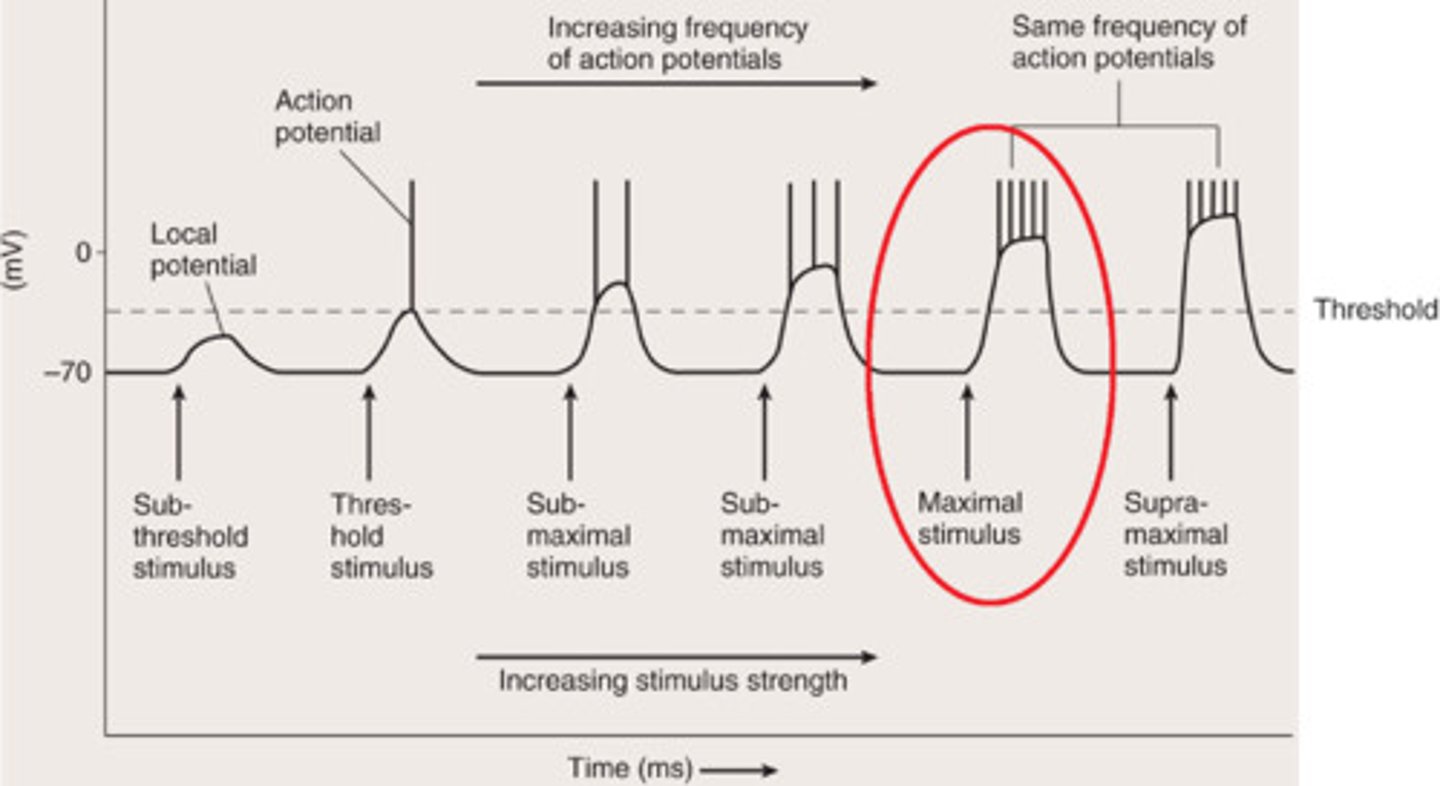
Maximal Stimulus
Strong enough to produce a maximum frequency of action potentials
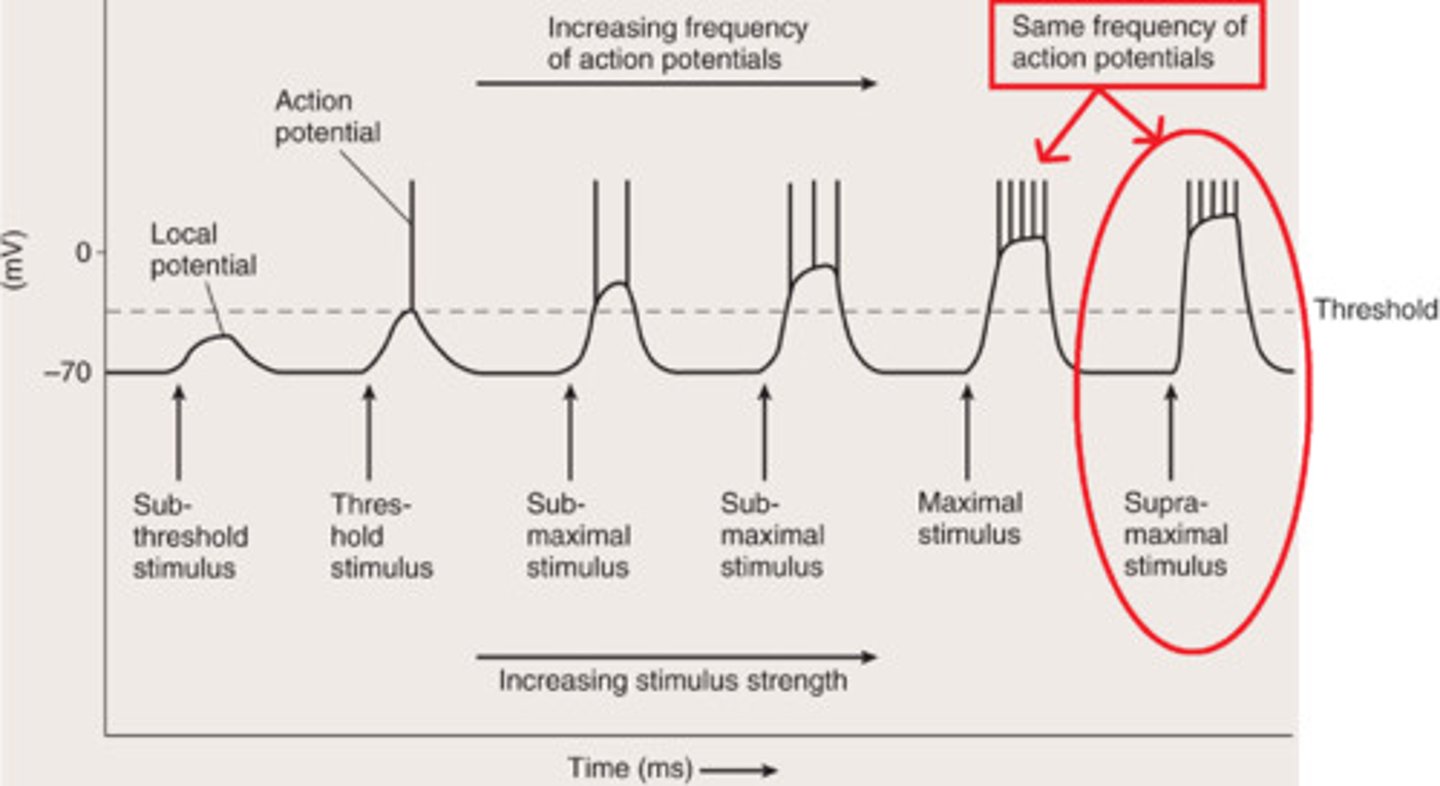
Supramaximal Stimulus
Any stimulus greater than maximal stimulus
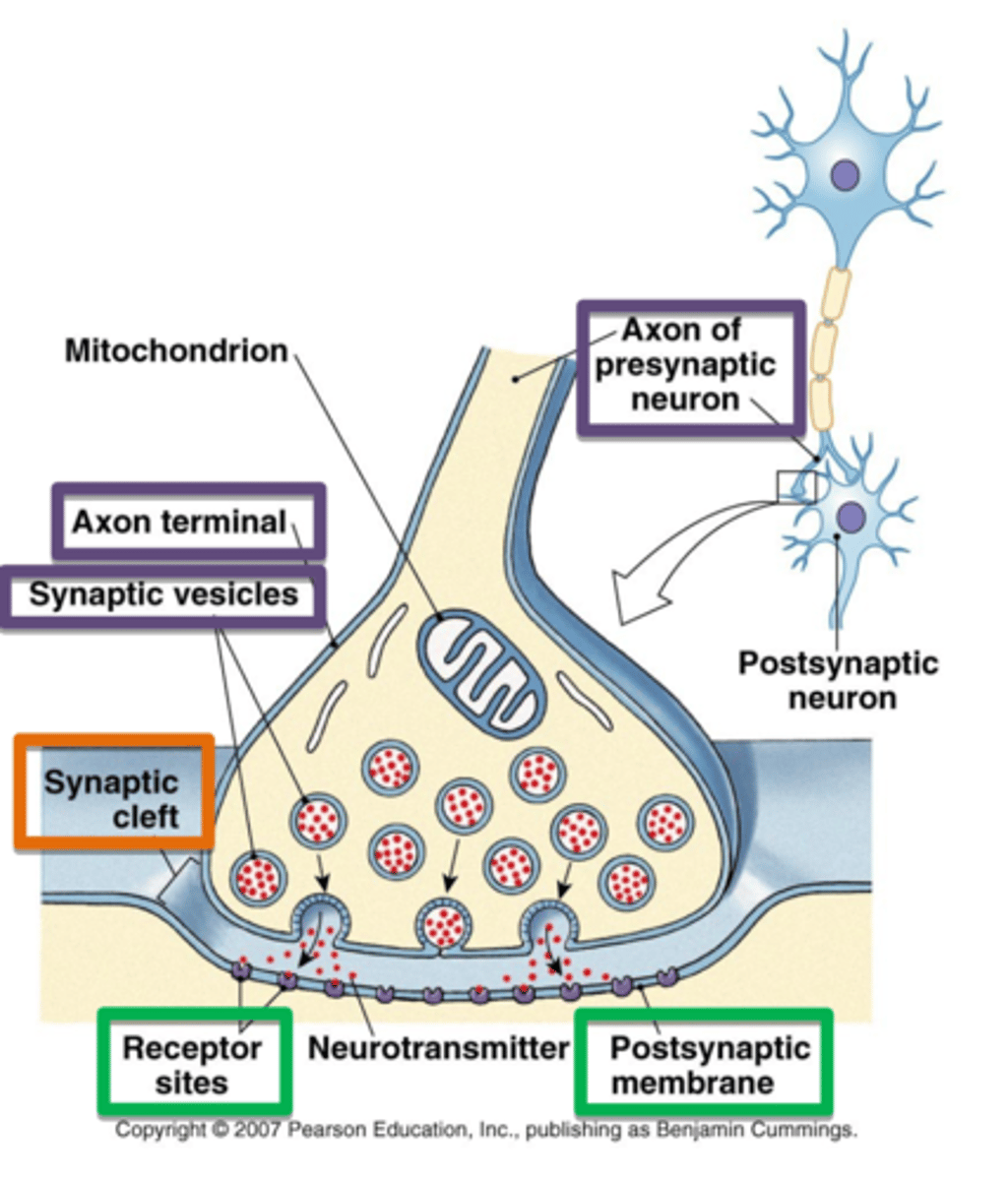
Chemical Synapse Components
Presynaptic terminal
Synaptic cleft
Postsynaptic membrane
Receptors
Chemical Synapse Steps
1. Action potentials arriving at the presynaptic terminal
2. Voltage-gated Calcium channels open
3. Calcium enter cells causing synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter molecules
4. Neurotransmitter diffuse across the synaptic cleft
5. Neurotransmitter bind receptors in postsynaptic cell
6. Binding of neurotransmitter to ligand-gated sodium channels causes sodium to enter postsynaptic cell
7. If the resulting depolarization graded potential reaches threshold an action potential is produced
8. Neurotransmitter is cleared
(Potassium or Chloride would hyperpolarize)
Removal of Neurotransmitter from Synaptic Cleft
1. Enzymes can break down the neurotransmitter.
2. Neurotransmitter can be taken up presynaptic terminal and recycled
3. Neurotransmitter can diffuse away
Two Types Of Summation
Temporal
Spatial