4 - How Mechanical Ventilators Work
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
major components of MV
power source/input power
electric or pneumatic
positive/negative pressure generator
control systems and circuits
open-/closed-loop systems to control ventilator function
control panel
pneumatic circuit (internal/external)
power transmission and conversion system
volume displacement, pneumatic designs
flow-control valves
output
pressure, volume, and flow waveforms
pneumatic circuit
tubes that allow gas to flow inside ventilator and between ventilator and patient
internal pneumatic circuit
pneumatic circuits that can be single (common in ICU vents) or double
external pneumatic circuit
pneumatic circuit that connects vent to patient’s airway
power transmission and conversion system
system that enables ventilator to perform mechanical/pneumatic operation
hardware:
drive mechanism for gas flow
output control mechanism that regulates gas flow
compressors
MV components that reduce internal volumes to make positive pressure
types:
piston
blades
diaphragms
bellows
volume displacement designs
bellows (out of production)
pistons (linear/rotary drive)
concertina bags
“bag-in-a-chamber” systems
output control
MV components that control pressure, volume, flow, and time
types:
mechanical
pressure reducing valves
solenoid valves
needle valves
volume flow-controlled valves
valves that regulate flow
open and close completely or in increments
types
solenoid valves
digital valves
classification of mechanical breaths
control
pressure, volume
trigger
patient and/or time
limit
pressure, volume, flow
cycling
time, volume, flow
volume control
pressure waveform

volume control
volume waveform
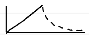
volume control
flow waveform

pressure control
pressure waveform
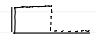
pressure control
volume waveform

pressure control
flow waveform
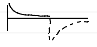
trigger variables
time or patient
patient can trigger breaths between timed breaths
trigger sensitivity
pressure
inspiration starts due to loss of circuit pressure (NIF)
usually -2 cmH2O below set PEEP
trigger sensitivity
flow
inspiration starts due to change in flow during exhalation
most patients find this comfortable
trigger sensitivity
volume
inspiration starts due to volume drop during exhalation
limit variables
what limits inspiration before cycle variable is reached
can be pressure, volume, or flow
cycling variables
pressure
inspiration ends once set pressure is reached
cycling variables
volume
inspiration ends once set volume is reached
cycling variables
flow
inspiration ends once flow has decreased to a set percentage
cycling variables
time
inspiration ends once set time elapses (i-time)