Fat soluble Vits & vitamin A (mine)
1/184
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
185 Terms
fat soluble vits dissolve in
organic solvent
fat soluble vits excretion
not readily excreted, can cause toxicity
fat soluble vits are absorbed with
along with fat
there is concern for what with fat soluble vits
Concern for people with fat malabsorption or use of certain medication (e.g. orlistat or Xenical)
transportation of fat soluble vits occurs how
like fat in chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL
Transportation for fat soluble takes place in...
lymphatic system w/ bile
VIT A
Vitamin A is the most common cause of....
non-accidental blindness, worldwide
Preformed Vitamin A forms are called
retinoids
retinoids are what form of vit A
active form (ready to use)
retinoids are found in
found in animal products
Retinoid forms****
retinal
retinol
retinoic acid
aldehyde form of vit A
Retinal
proformed forms of vitamin A are called
carotenoids
what must occur to proformed vit A (carotenoids)
must be converted to retinoid form
intestinal cells can do what to carotene?
intestinal cells split carotene in 2 molecules of retinoids
carotenoids are found in
plant products
carotenoids forms
beta-carotene
alpha-carotene
lutein
lycopene
zeaxanthin
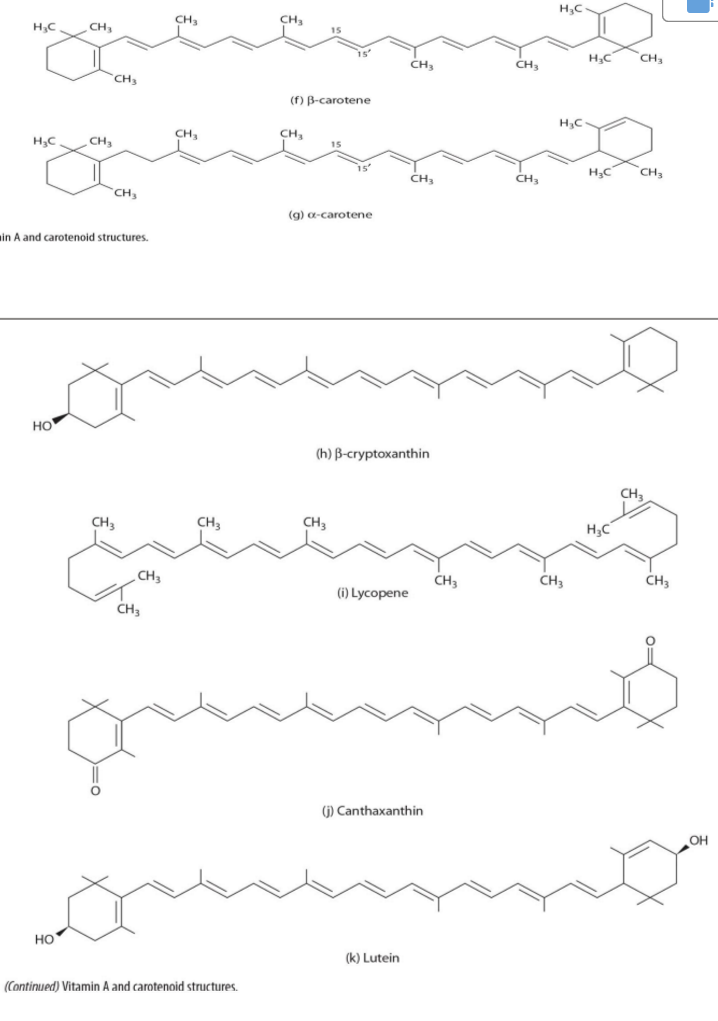
what carotene form is largely the form received from diet
beta-carotene
antioxidant function of “vit A” is related to
carotenoids!! so it is not actually vit A function because carotenoids are not Vit A until they are converted into retinoids
Digestion of VitA requires...
digestion prior to absorption
what can weaken some complexes
heating plant food
even with weakening complexes of plant foods, what is still needed?
enzymatic digestion is still required
how well is vit A absorbed
from meal with fat
raw veg
pure oil
- 70-90% vit A absorbed from meal (w/ fat)
- carotenoid absorption is <5% for uncooked vegs
-60% as pure oil
retinoids are most commonly found in what form
all-trans form
retinoids tend to be attached to what
a fatty acid
since it retinoids tend to be attached to FA, what must occur prior to absorption?
they must be de-esterified (remove the FA)
when retinoids are going to be stored, what happens to them
they are reesterified
what are retinyl esters?
esterified retinoids (so retinal, retinol, or retinoic acid attached to FA)
why do we need proteolytic enzymes in the duodenum (2)
retinol bound to fatty acid esters
retinyl esters and carotenes are often complexed with protein
What enzymes hydrolyze long chain retinyl esters in the brush border? (2)
Retinyl ester hydrolases and esterases
What is the role of pancreatic hydrolases in vitamin A digestion?
They cleave short chain retinyl esters.
What process is involved in the digestion of fat globules?
Emulsification
retinol absorption in the body is dependent on
protein carrier
What transporters are involved in the absorption of carotenoids?
Scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1) and passive diffusion
absorption of vit A requires what? (3- think digestive system)
bile, digestive enzymes, integration into micelles
absorption of vit A is depended on what from the diet?
fat
How much of retinoids can be absorbed?
90%
How much of carotenoids can be absorbed?
5%
how much beta-carotene can be absorbed?
20-50% (higher)
intestinal cells can convert what into what relating to vit A?
carotenoids to retinoids
Where are carotenoids & retinoids metabolized
in enterocytes to some extent
To leave the intestinal cell and travel to other tissues in the body, retinol must be
esterified
once retinol is esterified, it can
it can be incorporated into chylomicrons
the main metabolic pathway for retinol depends on what protein?
Cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP)
Conversion of carotenoids is dependent on...
vit A status of person & intake of carotenoids
Higher intake of Vit A ___ receptor mediated carotenoid absorption & conversion to vit A is ____
decreases
decreased
What non central enzyme converts carotenoids in the intestine?
9,10 dioxygenase
What central enzyme hydrolyzes carotenoids in the intestine and other organs?
15,15 monooxygenase (fe dependent)
15,15 monooxygenase is dependent on
iron
Conversion to retinal is ___% efficient
50%
CRBP transports in ____
tissue
RBP transports in ____
blood
B-carotene is converted into what when absorbed into intestinal cell?
two retinal molecules
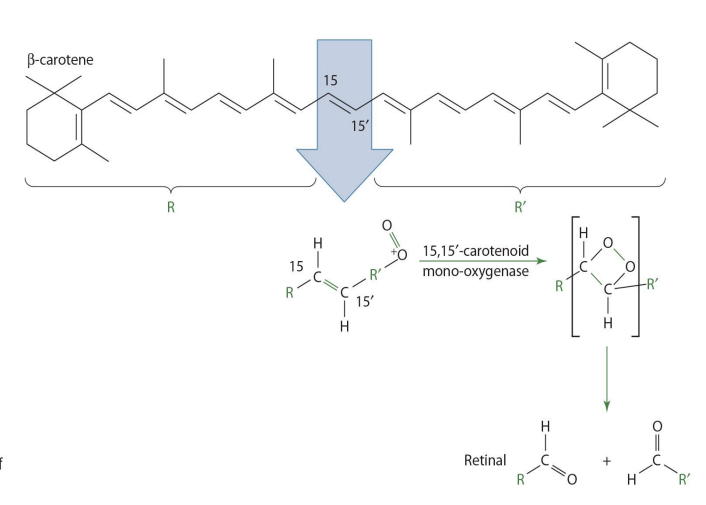
how is b-carotenoid converted into retinal? (enzyme)
15,15 carotenoid monooxygenase will split b-carotene into 2 retinal molecules
free Carotene enters intestinal cell how?
absorption by scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1) on the brush border membrane
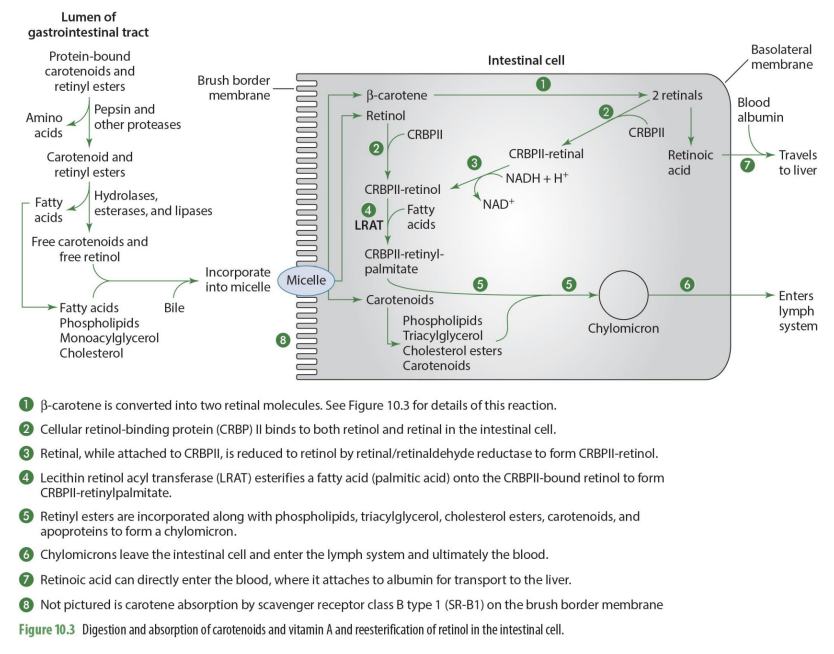
beta carotene and retinol enter intestinal cell from what structure?
micelle
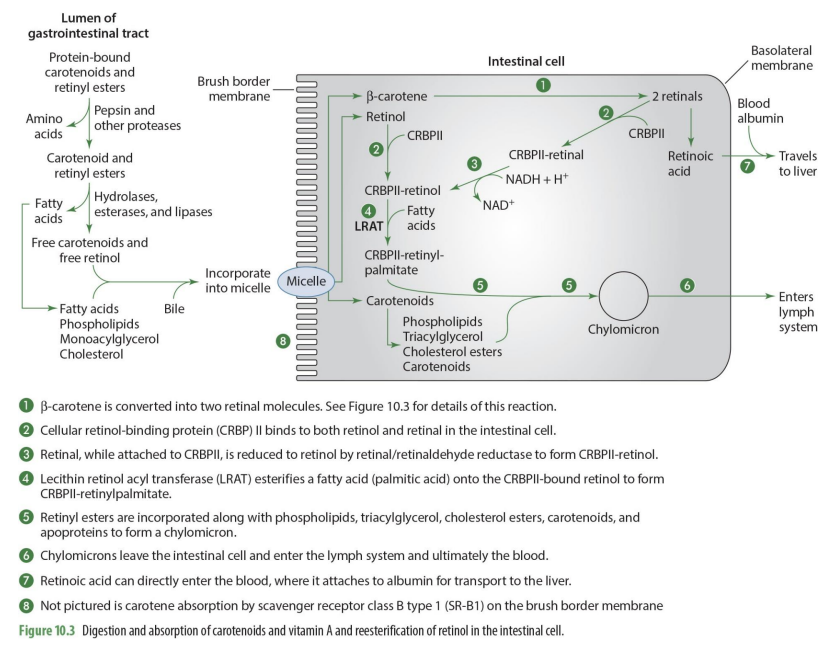
b-carotene is converted into what?
2 retinal molecules via 15,15 carotenoid monooxygenase
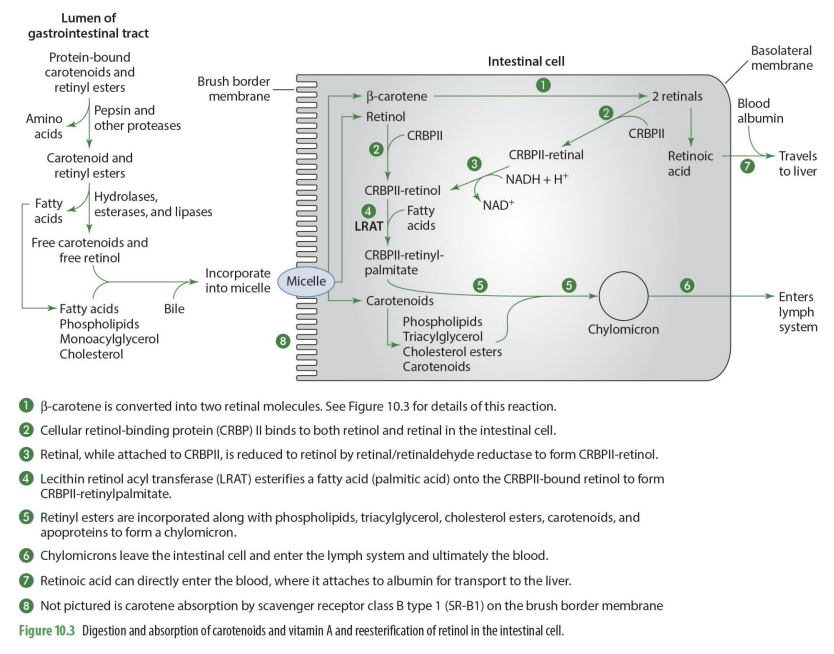
retinal can undergo what 2 different paths?
can be converted into retinoic acid to go into the blood OR can be esterified to go into chylomicron and enter lymphatic system
what is unique about retinoid acid?
it can enter directly into the blood to go to the liver (does not need to go through lymphatic system)
what binds to both retinol & retinal in the intestinal cell
CRBP II (cellular retinol binding protein)
what is formed when CRPBII attached to retinal
CRBPII-retinal
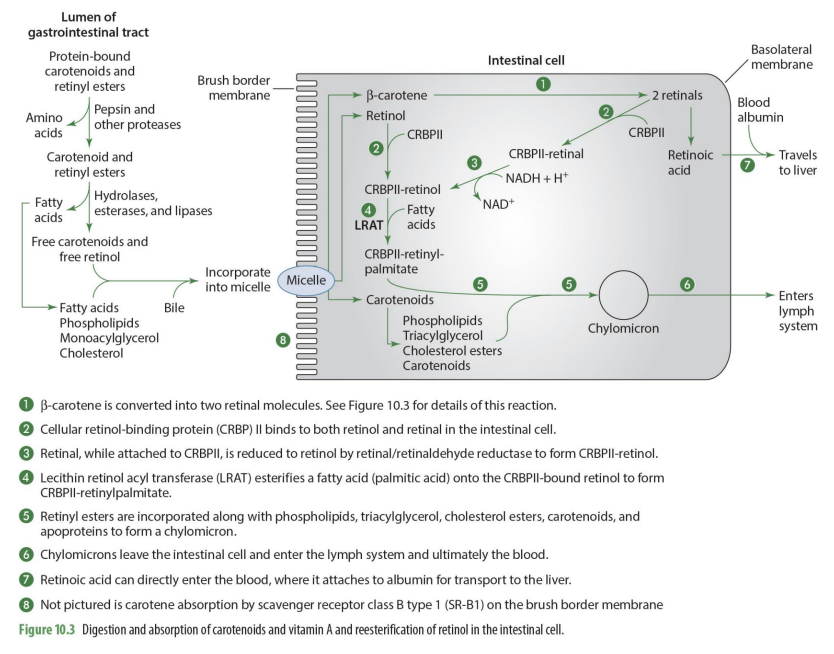
CRBPII-retinal is then needed to be converted into
CRBPII-retinol
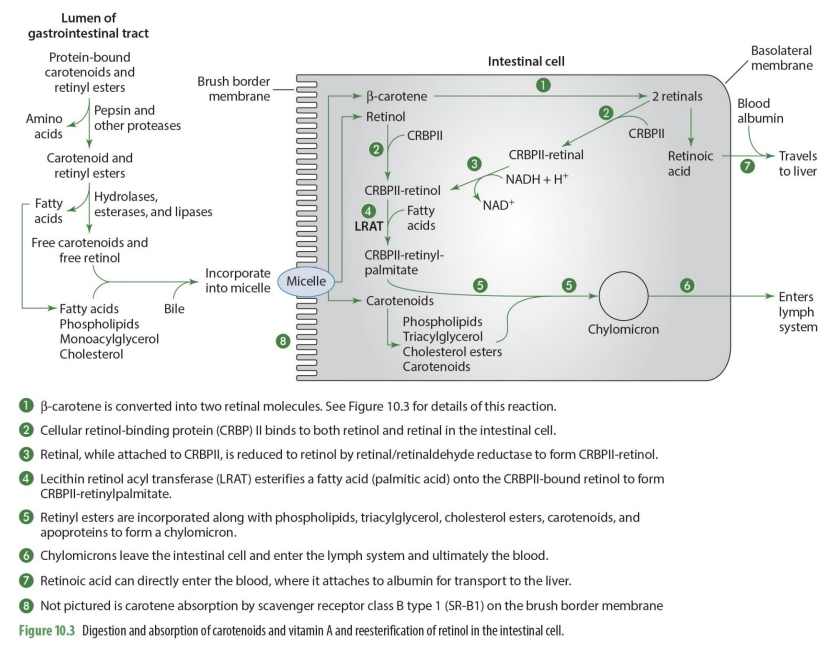
how is CRBPII-retinal converted to CRBPII-retinol? (enzyme)
via retinal/retinaldehyde reductase to form CRBPII-retinol
retinal-CRPBII —> CRBPII-retinol
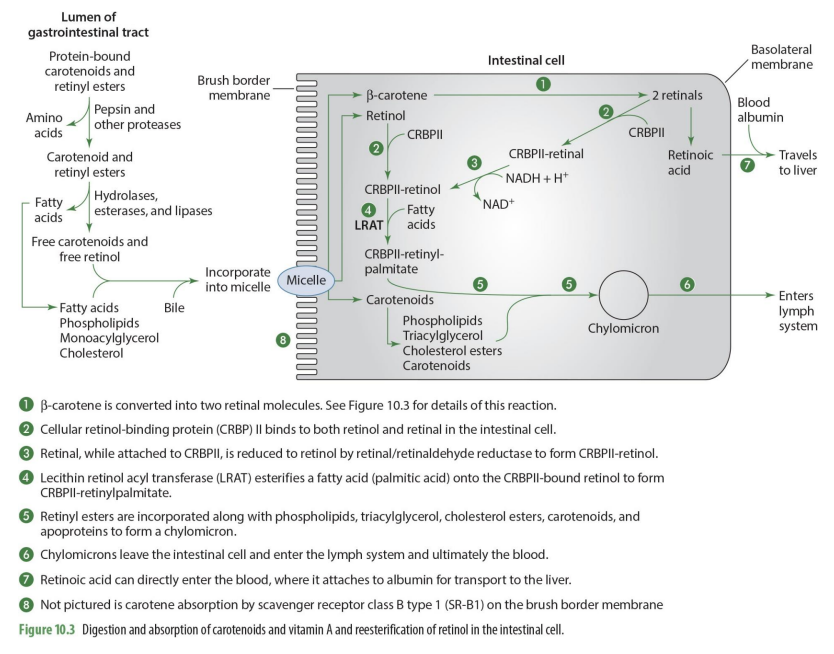
when retinol has CRBPII added to it, it becomes?
CRBPII-retinol
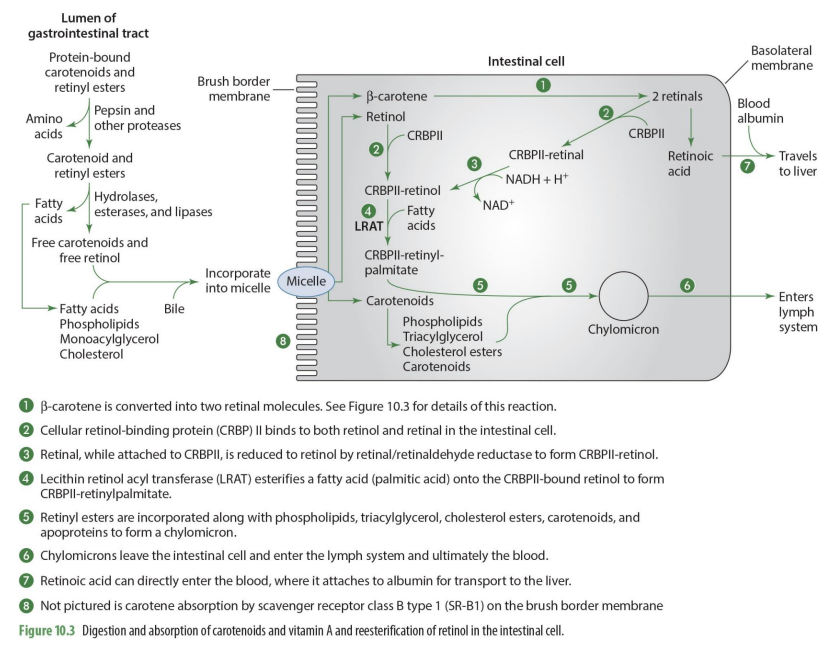
what happens to CRBPII-retinol?
it has a FA added to it to form CRBPII-retinylpalmitate
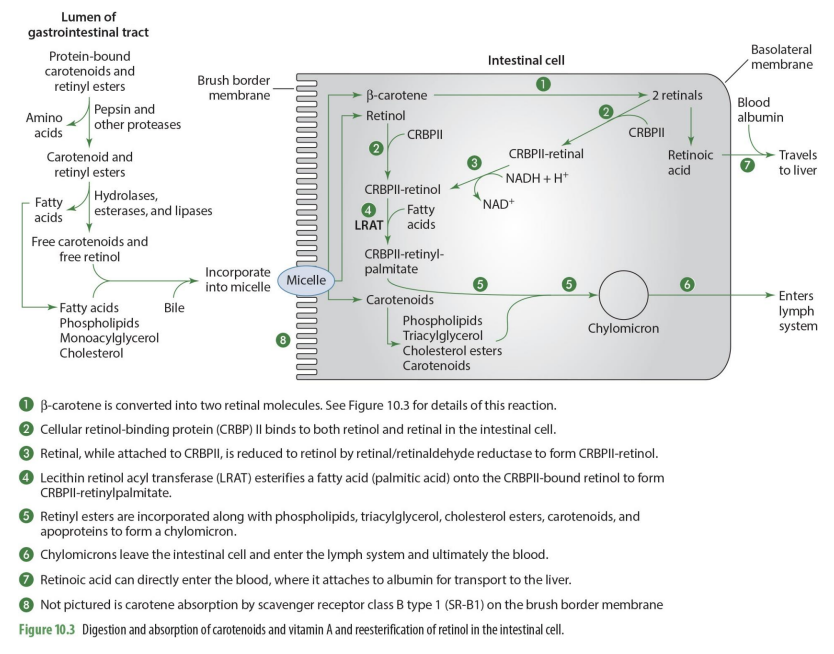
what enzymes esterifies a FA (palmitic acid) to form CRBPII-retinylpalmitate
lecitin retinol acyl tranferase (LRAT)
so LRAT is the enzyme that esterifies retinol
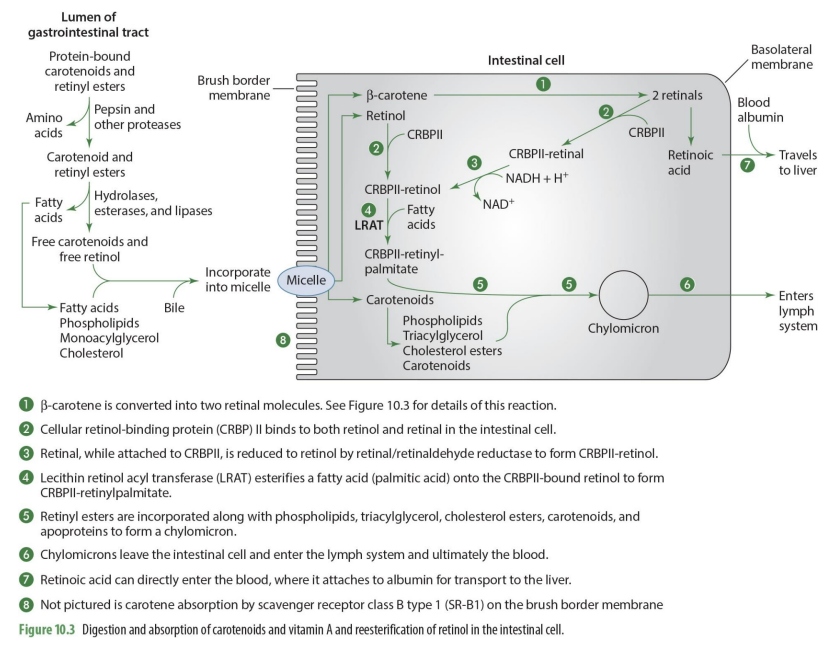
what are retinyl esters?
FA esterified by adding CRPBII-retinol
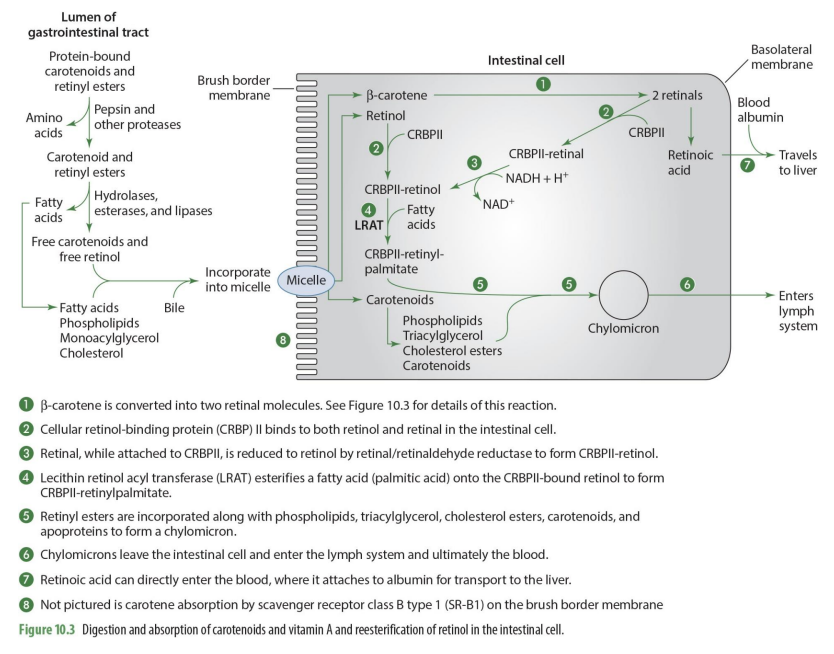
Retinyl esters (retinal + FA) are incorporated what compounds to form what?
phospholipids, TG, Chol esters, carotenoid & apoproteins to form chylomicron
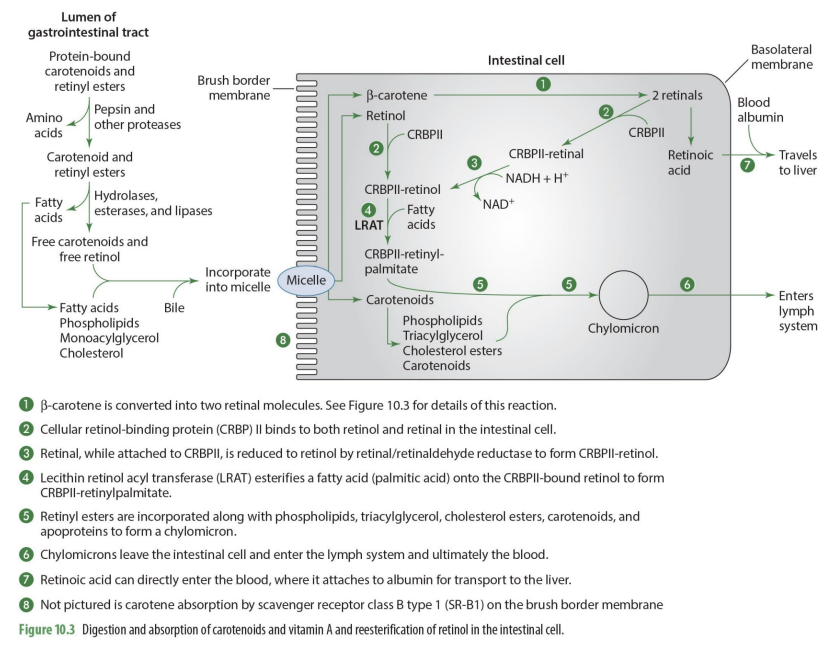
what happens to chylomicrons
they enter the lymph system and then ultimately the blood
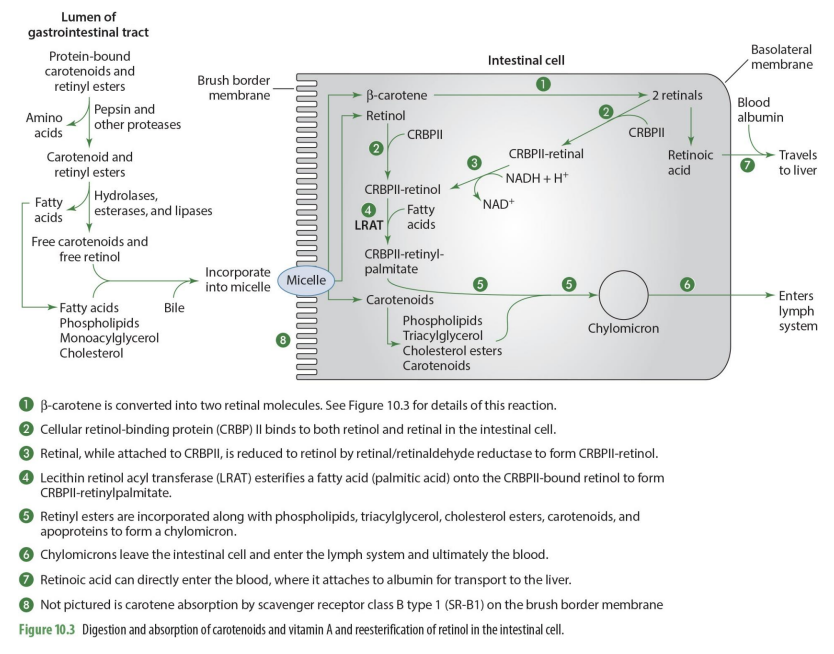
what happens to carotenoids that enter intestinal cell but not going to be used as Vit A
enter intestinal cell and are directly incorporated into chylomicrons
is conversion of retinal to retinol reversible?
yes
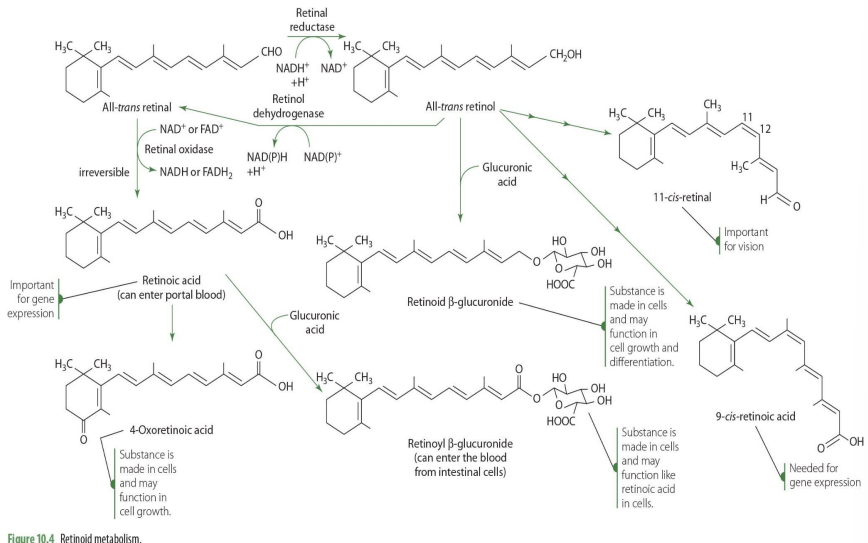
How is retinal —> retinol (enzyme and coenzyme)
retinal reductase (NADH)
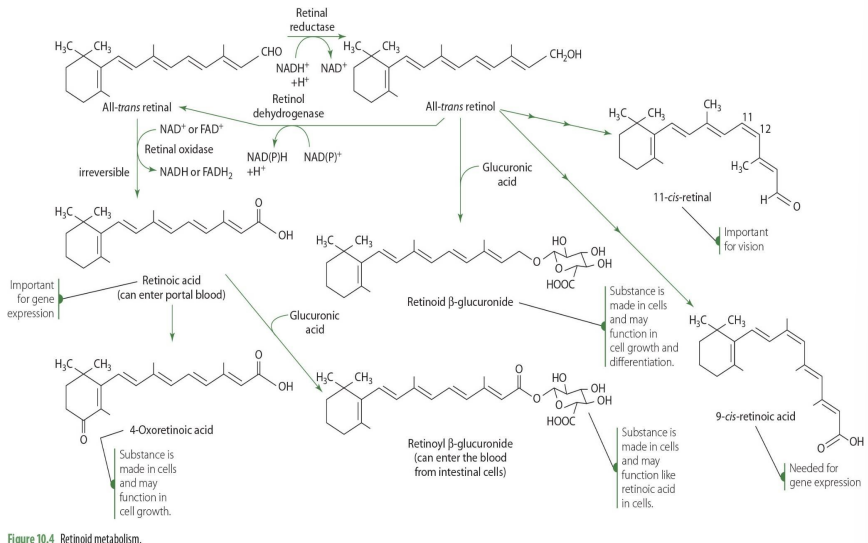
how is retinol—> retinal? (enzyme, coenzyme)
retinal dehydrogenase (NADPH/ NADH)
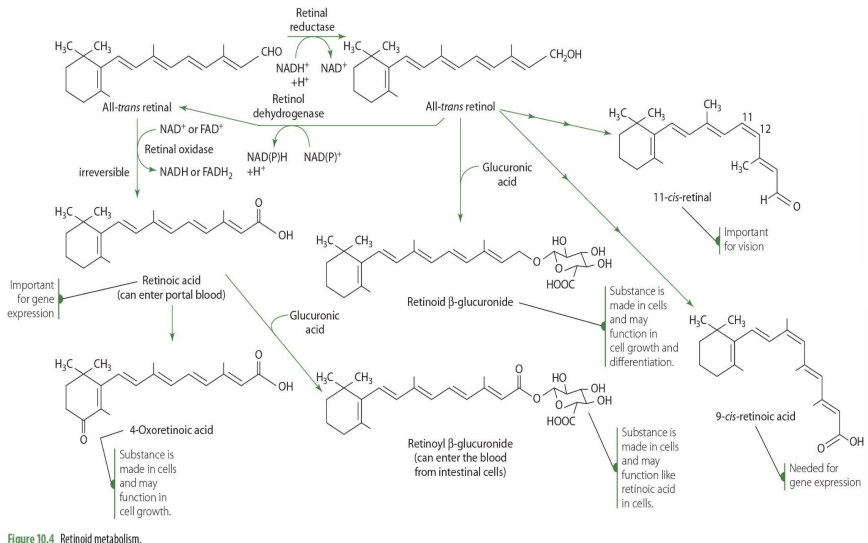
is conversion of retinal to retinoic acid reversible?
no
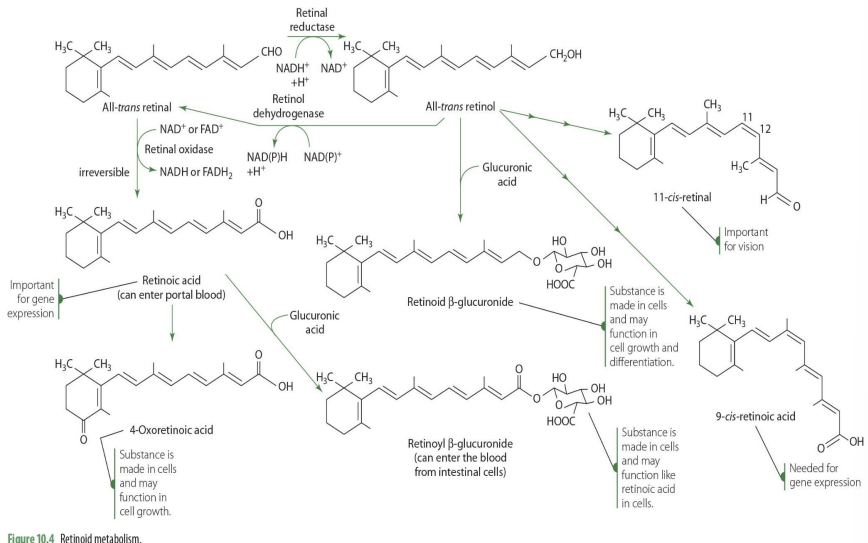
retinal to retinoic acid (enzyme, coenzyme)
retinal oxidase (NAD or FAD)
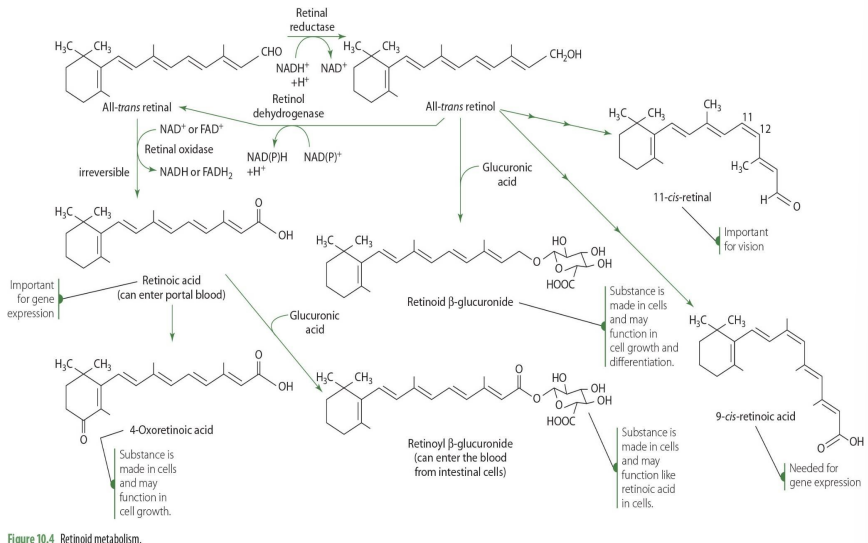
9-cis retinoic acid comes from what retinoid?
all-cis-retinol
9-cis retinoic acid plays a role in?
gene expression
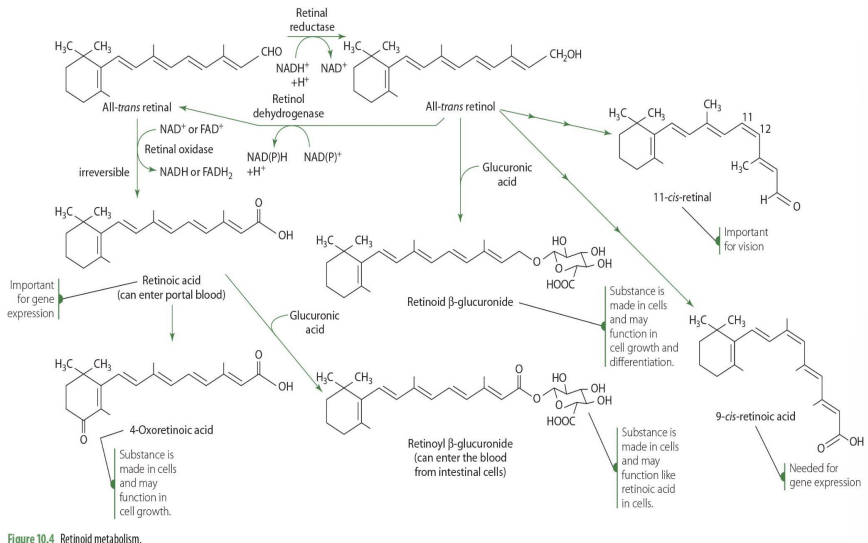
4-oxoretinoic acid comes from what retinoid?
retinoic acid in blood
4-oxoretinoic acid role?
cell cycle, cell growth
what forms of Vit A enters the liver?
retinyl esters are taken into the liver cells
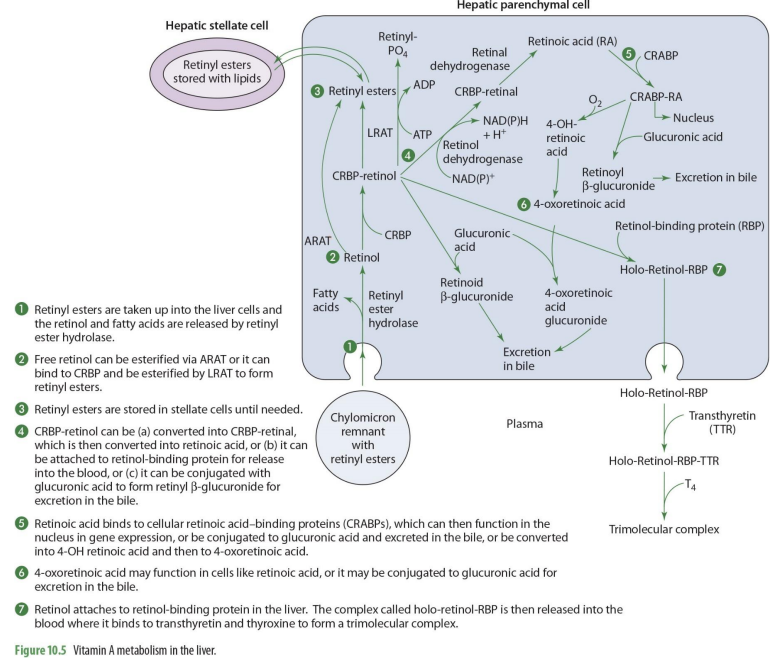
retinyl esters that enter liver can come from what 2 things?
stellate cells or chylomicrons
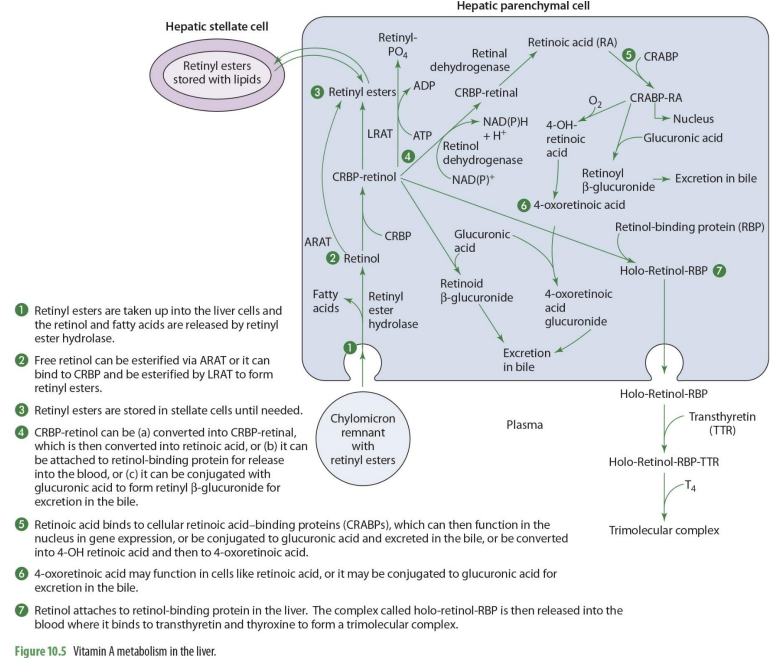
what happens once retinyl esters enter the cell
the retinol and FA are released
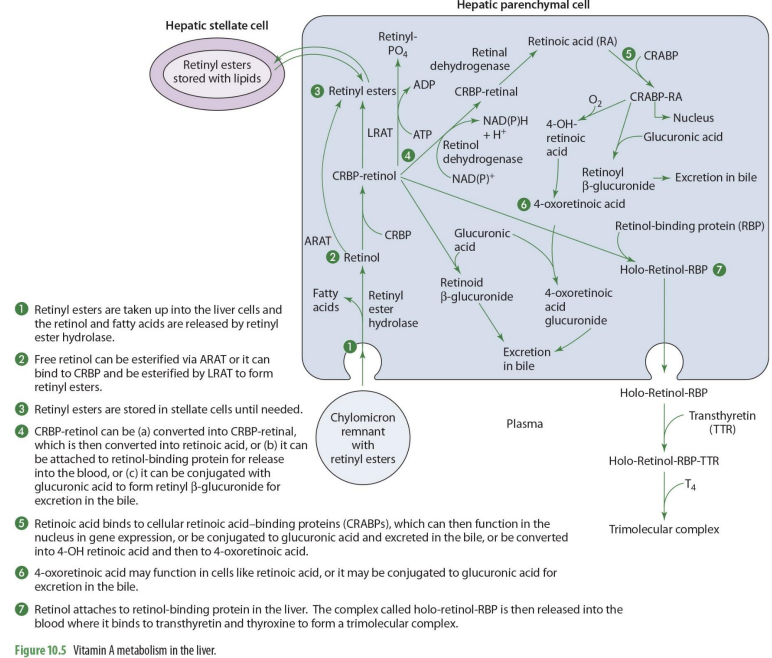
what enzyme releases FA’s and retinyl esters?
retinyl ester hydrolase
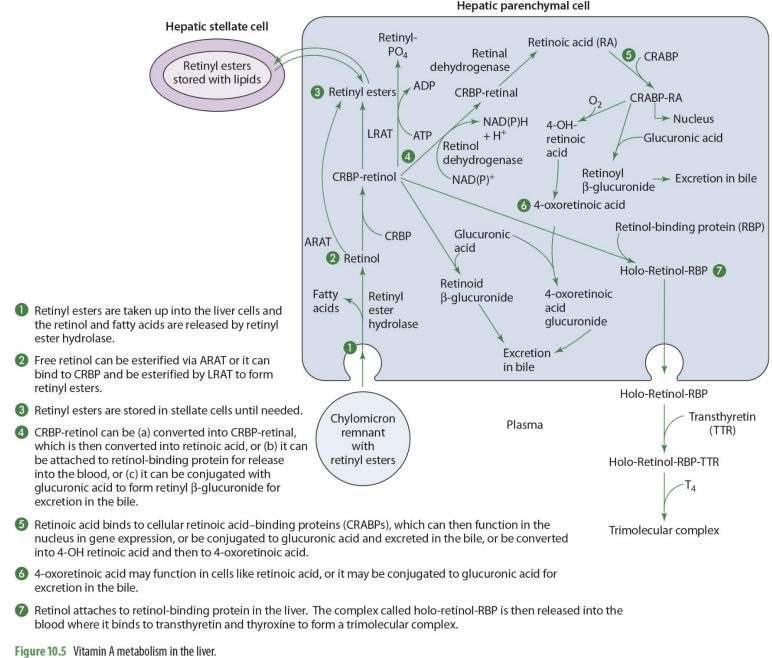
retinol entering the liver can go to what 2 paths?
storage or metabolism
if retinol will go into storage (hepatic stellate cells), it must be converted into
back into retinyl esters
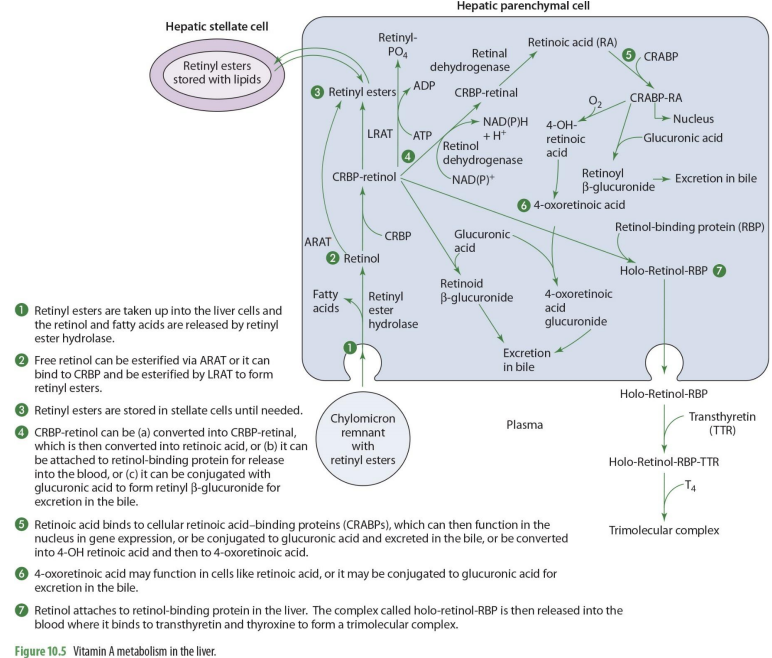
how can retinol go back to retinyl esters (2 options)
can be esterified via ARAT to form retinyl esters
OR
can bind to CRBP 1 to form RCBP-retinol in order to be esterified by LRAT to form retinyl esters
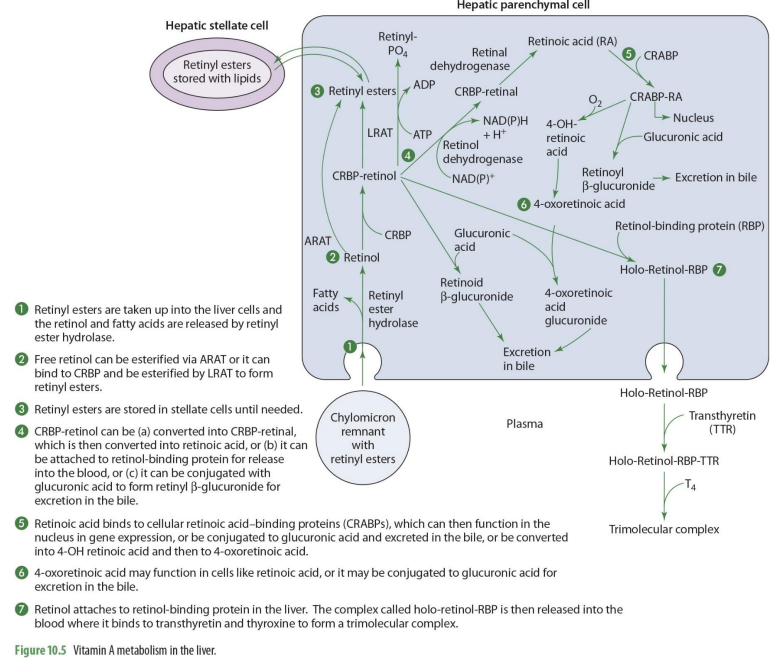
if going to be used for metabolism, retinol will
remail unesterified
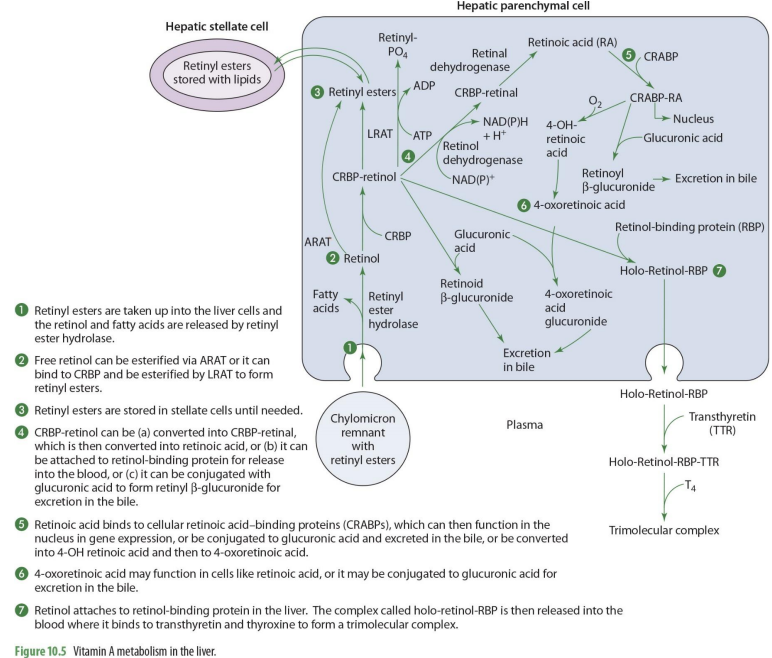
what form of retinol is used for metabolism (that will then be converted to other forms)
CRBP-retinol
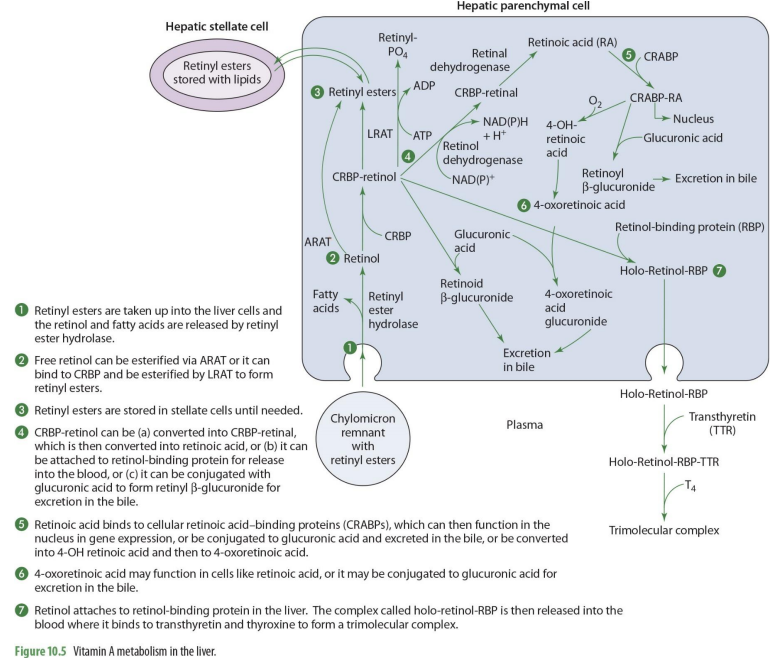
If going to leave the liver cell, CRBP-retinol will bind to
retinal binding protein (RBP)
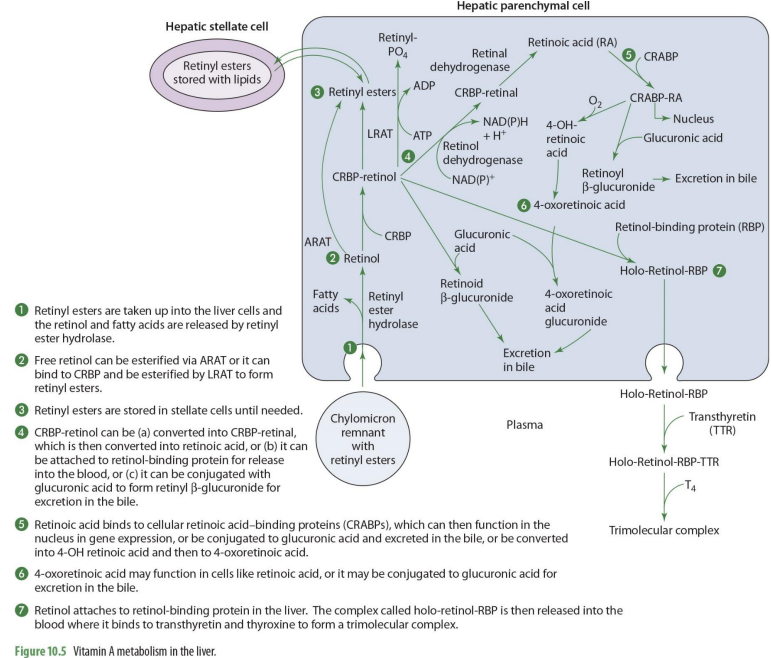
CRBP-retinol binding to RBP forms
holo-retinol-RBP
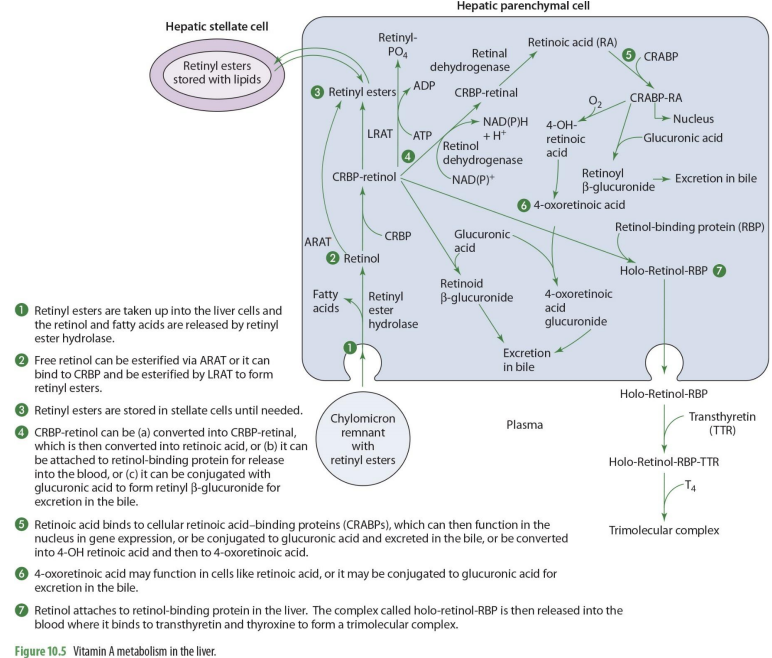
CRPB-retinol to holo-retinol-RBP how?
CRBP-retinol —→ holo-retinol-RBP by adding retinol-binding protein (RBP)
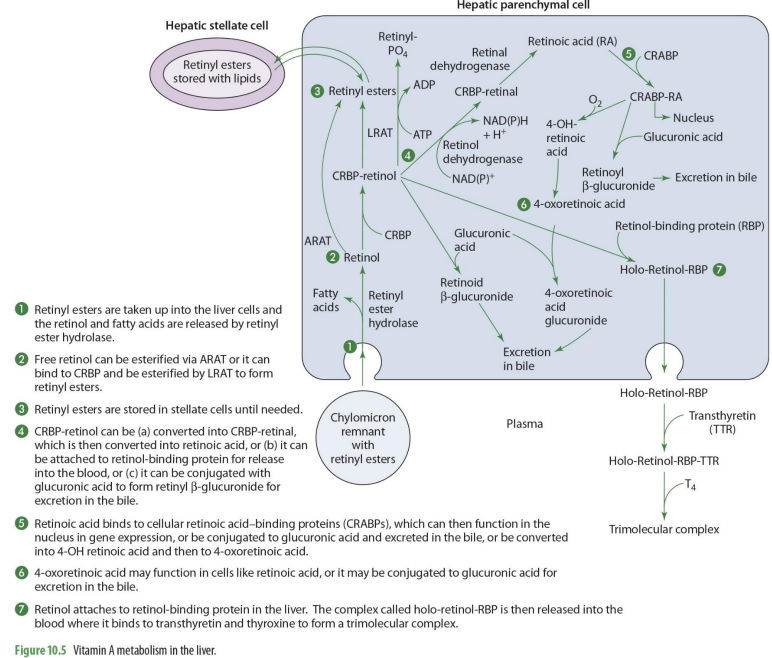
holo-retinol-RBP goes where?
enters the blood (plasma)
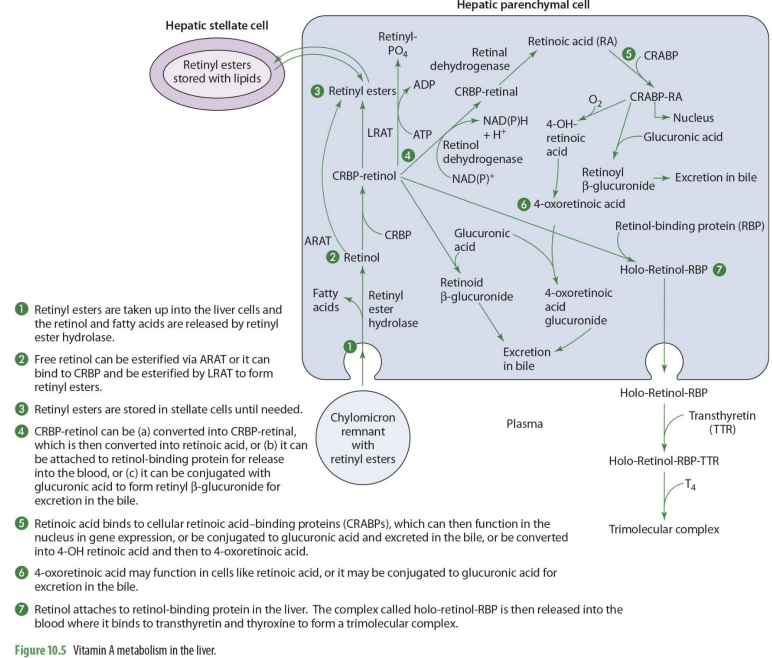
to travel in the blood, holo-retinol-RBP has what added to it? (2)
transthyretin (TTR) and thyroxin (T4) to become trimolecular complex
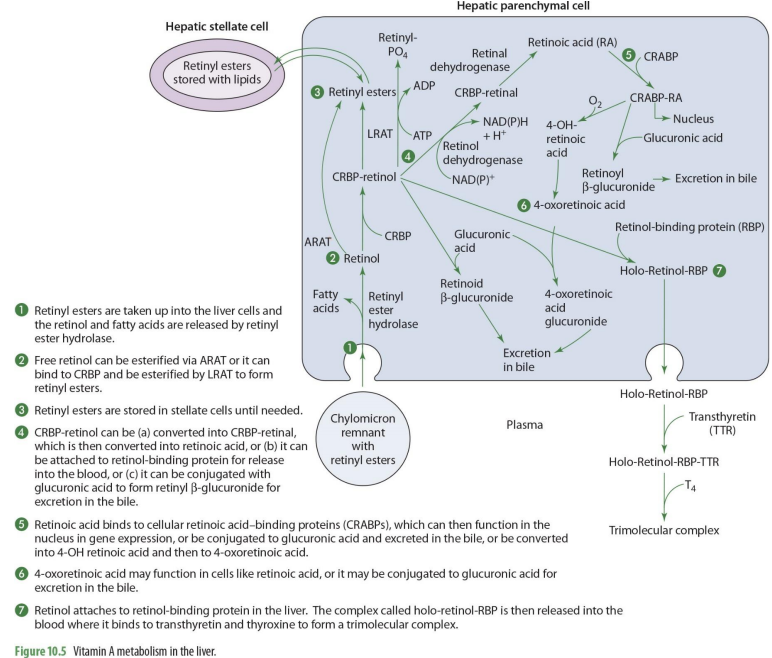
by adding transthyretin (TTR) and thyroxin (T4) to holo-retinol-RBP, it forms
trimolecular complex
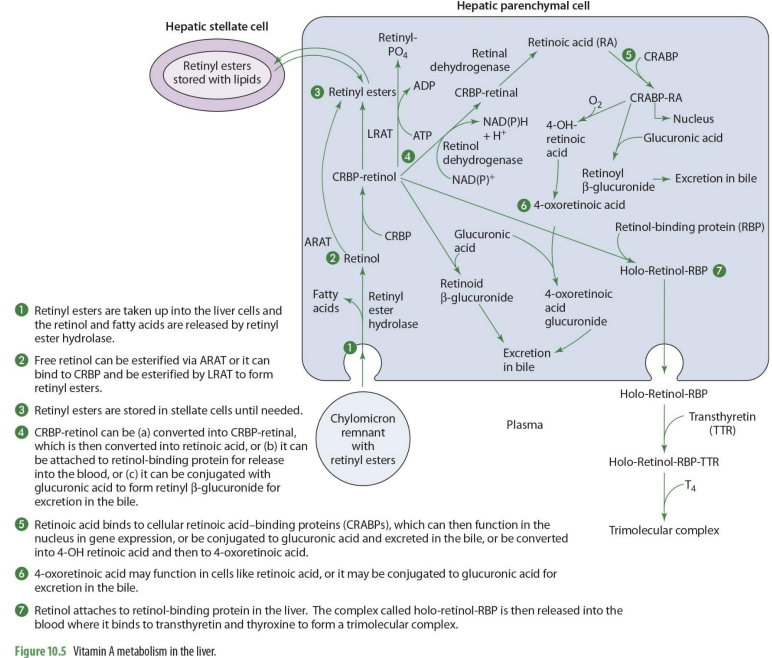
retinol that is esterified may be stored in the ___ via ____ cells
liver
stellate and parenchymal cells
Proteins that transport via the blood (2)
Retinol-binding protein (RBP)
Transthyretin (TTR)
Carotenoids transported as part of ___ & stored in ___ & ___
lipoproteins
liver & adipose
what are the 2 major receptors associated with vit A
Retinoic acid receptor (RAR) & retinoid X receptor (RXR)
Retinoic acid receptor (RAR) & retinoid X receptor (RXR) found on the ___
nucleus