Perfect competition
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Characteristics of perfect competition
There are many buyers and sellers: due to the number of market participants, sellers are price takers
There are no barriers to entry and exit from the industry: firms can start-up or leave the industry with relative ease, which increases the level of competition
Buyers and sellers possess perfect knowledge of prices: this assumption presupposes perfect information, e.g if one seller lowers their price, then all buyers will know about it
The products are homogenous: this means firms are unable to build brand loyalty as perfect substitutes exist and any price changes will result in losing all customers. Demand is therefore perfectly price elastic
Profit Maximising Equilibrium in the Short and Long-run
In order to maximise profit, firms in perfect competition produce up to the level of output where marginal cost = marginal revenue (MC=MR)
The firm does not have any market power so it is unable to influence the price and quantity
The firm is a price taker due to the large number of sellers
The firm's selling price is the same as the market price, P1 = MR = AR = Demand
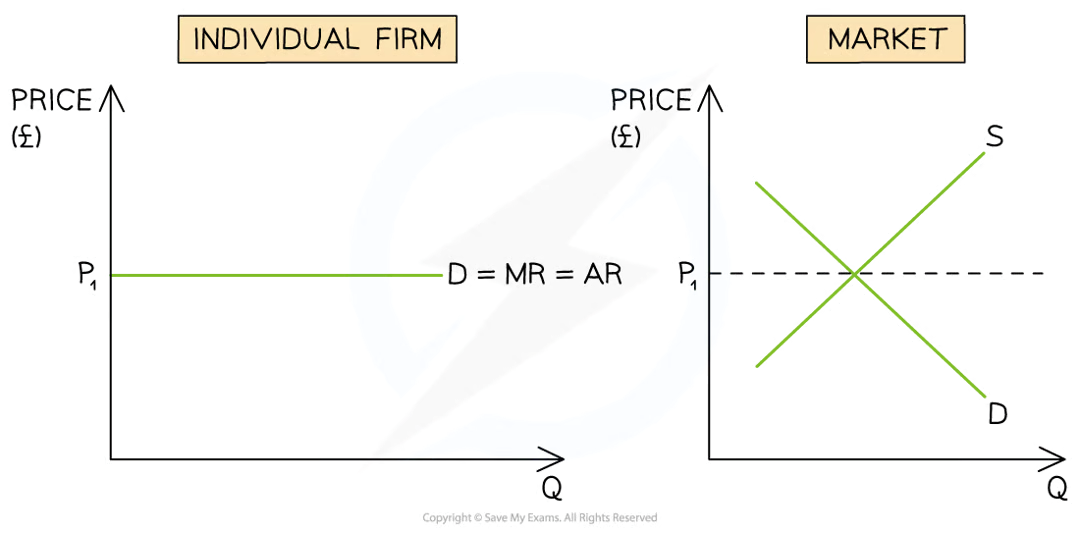
A diagram that illustrates how an individual firm in perfect competition has to accept the market/industry price (P1)
In the short-run, firms can make supernormal profit or losses in perfect competition
However, they will always return to the long-run equilibrium where they make normal profit
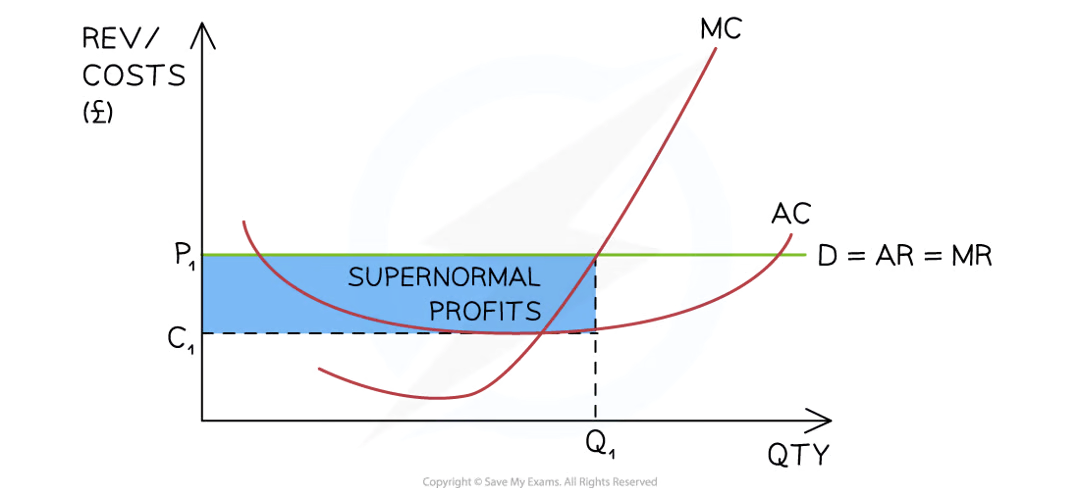
Short-run profit maximisation
Diagram analysis
The firms is producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
At this point the AR (P1) > AC (C1)
The firm is making supernormal profit
= (P1-C1)XQ1
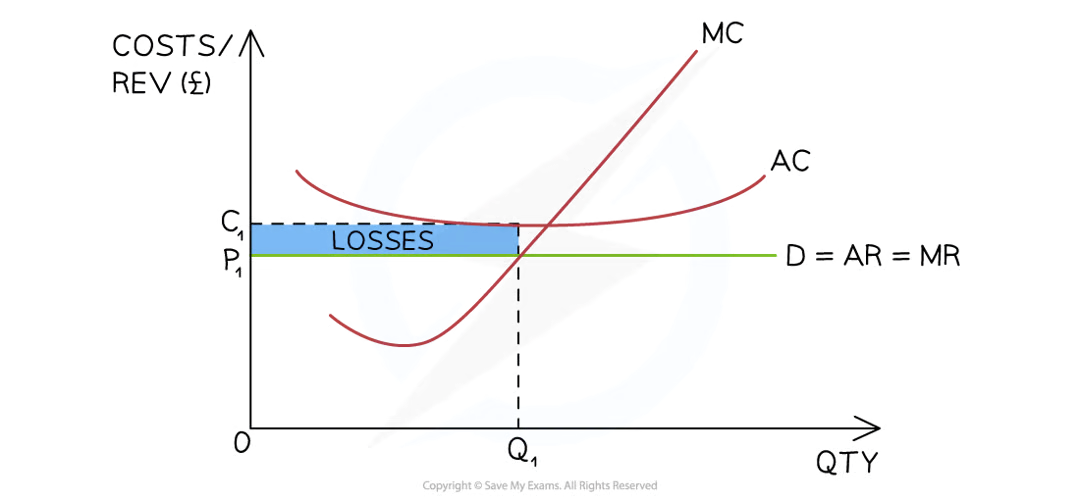
Short-run losses
Firms in perfect competition are able to make losses in the short-run
Diagram analysis
The firms are producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
At this level of output, the AR (P1) < AC (C1)
The firm's loss is equivalent to (P1-C1)XQ1
Moving from short-run profits to the long-run equilibrium
If firms in perfect competition make supernormal profit in the short-run, new entrants are attracted to the industry
They are incentivised by the opportunity to make supernormal profit
There are no barriers to entry
It is easy to join the industry
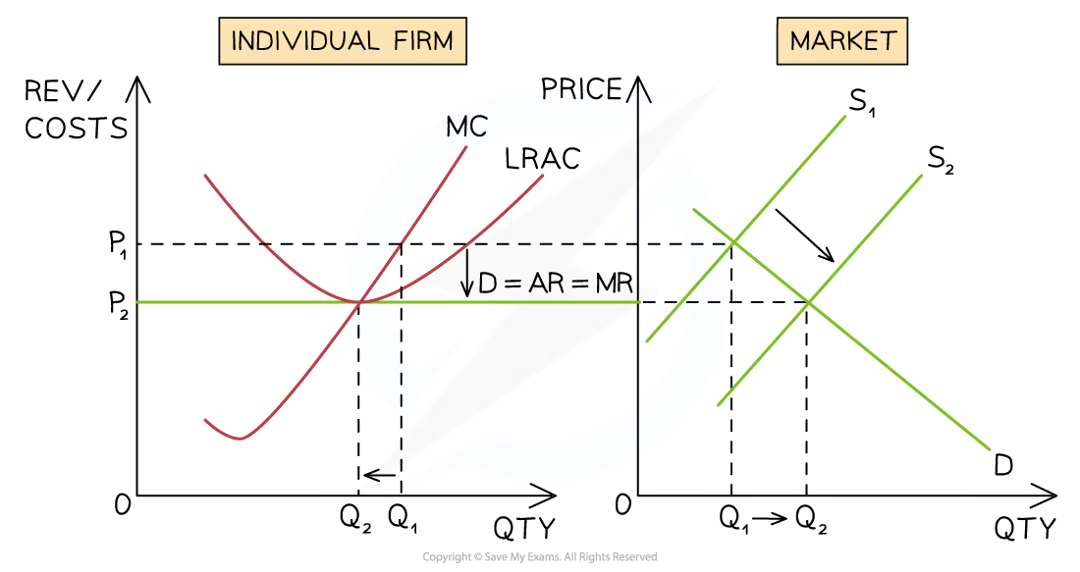
Diagram analysis
The firm is initially producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
At this level of output, the AR (P1) > AC (P2) and the firm is making supernormal profit
Incentivised by profit, new entrants join the industry and supply increases from S1→S2
Overall quantity in the industry increases from Q1→Q2
The industry price falls from P1→P2
The firm now has to sell its products at the industry price of P2
The output of the firm falls from Q1→Q2 as it now has a smaller market share of the larger industry
At the profit maximisation level of output (MC=MR) the firm is now producing at the point where AR= AC
The firm is making normal profit
In the long-run, firms in perfect competition always make normal profit
Firms making a loss leave the industry
Firms making supernormal profit see them slowly eradicated as new firms join the industry
Moving from short-run losses to long-run equilibrium
If firms in perfect competition make losses in the short-run, some will shut down
The shut down rule will determine which firms shut down
There are no barriers to exit, so it is easy to leave the industry
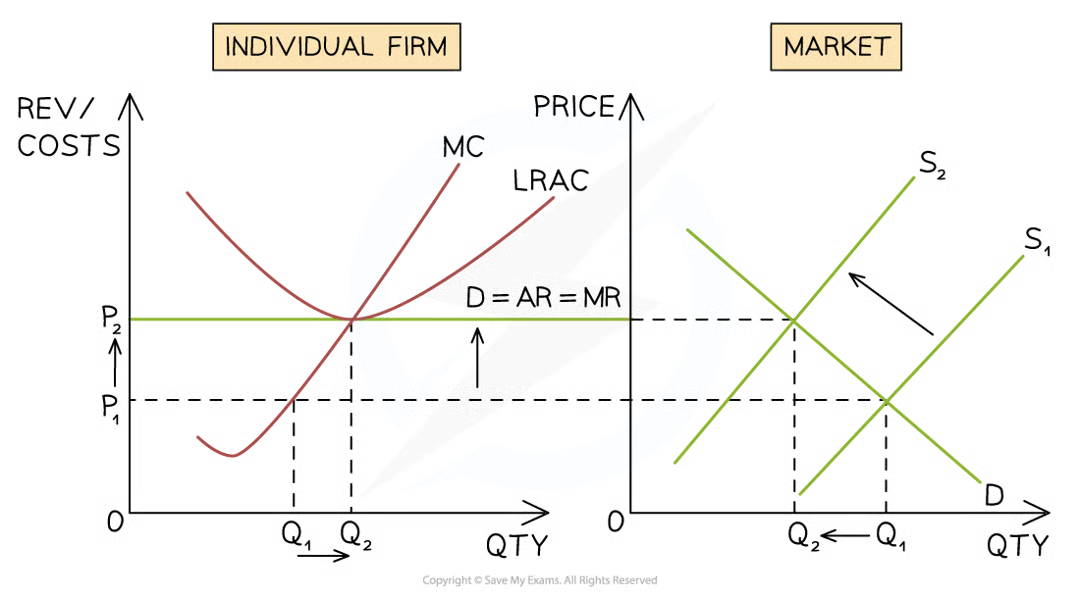
Moving from short-run losses to long-run equilibrium
Diagram analysis
The firm is initially producing at the profit maximisation level of output where MC=MR (Q1)
At this level of output, the AR (P1) < AC (C1) and the firm is making a loss
Some firms leave the industry and supply decreases from S1→S2
Overall quantity in the industry falls from Q1→Q2
The industry price increases from P1→P2
The firm now has to sell its products at the industry price of P2
The output of the firm increases from Q1→Q2 as it now has a larger market share of the smaller industry
At the profit maximisation level of output (MC=MR) the firm is now producing at the point where AR= AC
The firm is making normal profit
In the long-run, firms in perfect competition always make normal profit
Firms making a loss leave the industry
Firms making supernormal profit see them slowly eradicated as new firms join the industry