Lec 3: Cell Structure
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
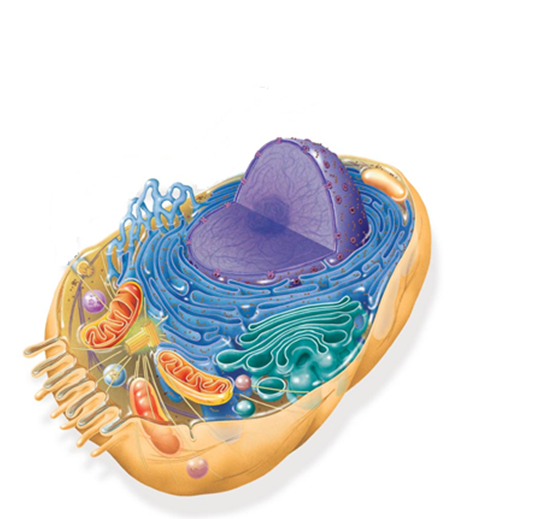
What organism cell is this?
animal cell
What structures are both in animal and plant cells?
mitochondria, nucleus, smooth and rough er (endoplasmic reticulum), and ribosomes, and golgi apparatus
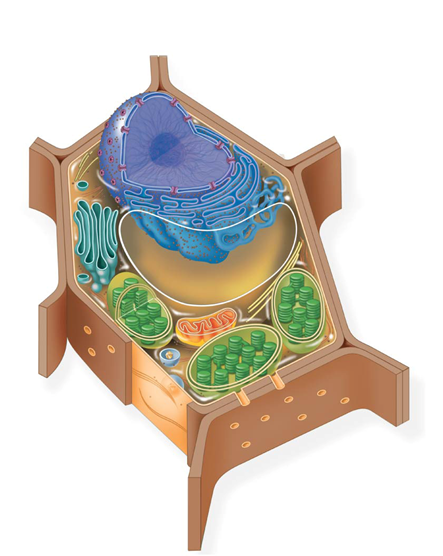
What organism cell is this?
plant cell
What structures are only in the plant cells?
cell wall, plasmodesmata, vacuole, and plastids
What is the function of a mitochrondia?
generates most cellular ATP
What is the func of a nucleus?
acts as the information center
What is the func of the smooth er? rough er?
rough ER - site of protein synthesis
smooth ER - synthesis of carbohydrates and lipids // modifies foreign substances to make them less toxic
What is the func of ribosomes?
synthesizes all cellular protein
What is the func of the golgi apparatus?
collects, packages, and distributes molecules
synthesis of cell-wall components
synthesis means the process of combining simpler substances to form more complex ones
What are plastids? Name the different types.
organelles w double membrance
chloroplasts, chromoplasts, amyloplast and etioplast
Function of chloroplasts
performs photosynthesize in order to generate ATP and sugars
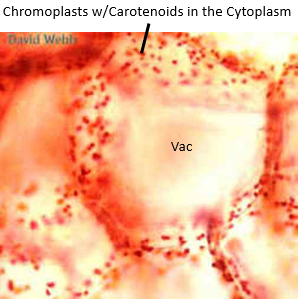
function of chromoplast
makes carotenoids
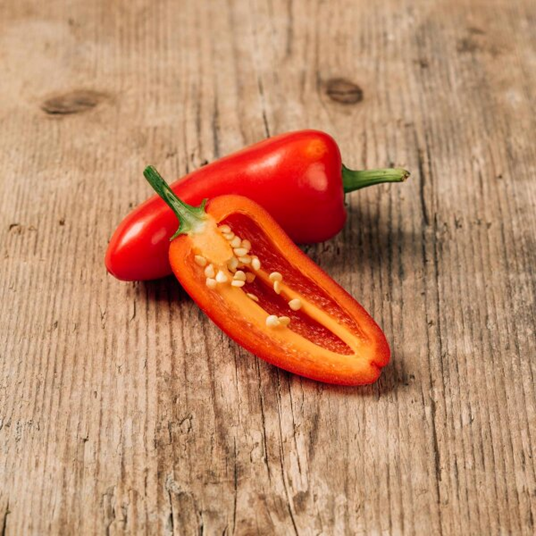

examples of chromoplasts’ functions
gives colors (yellow, orange, and red) to flower/fruit
attract pollinators in order to disperse their seeds
helps plants absorb blue light
Identify the vacuole, chromoplasts, and cytoplasm. What is inside the chromoplasts?
Function of Amyloplast
stores starch
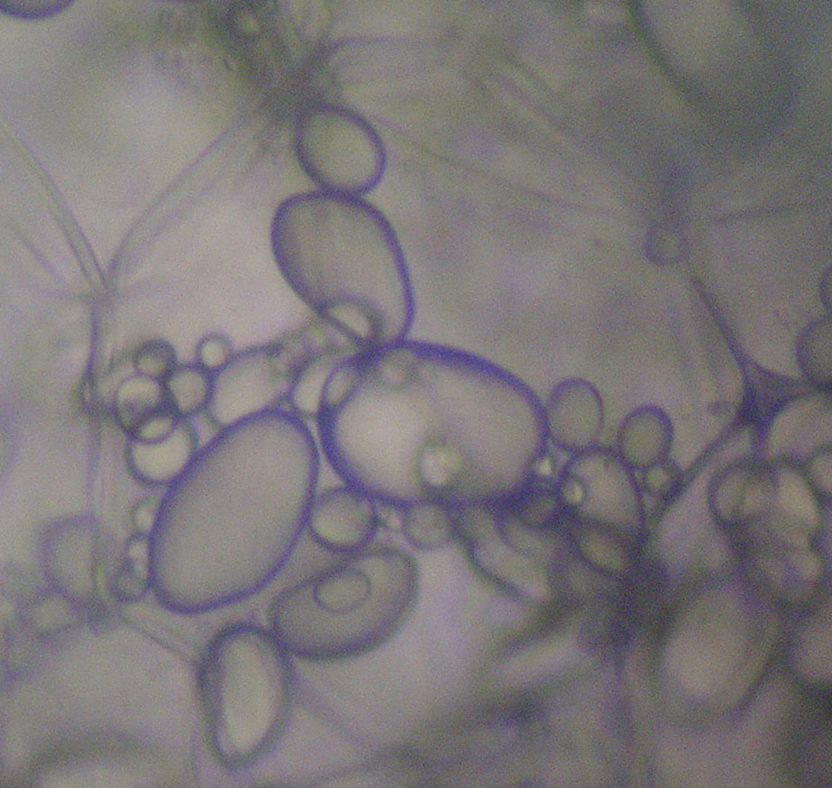
What plastid is this? What type of cell is this?
amyloplast; potato cells
Where are potatoes native to?
Peru
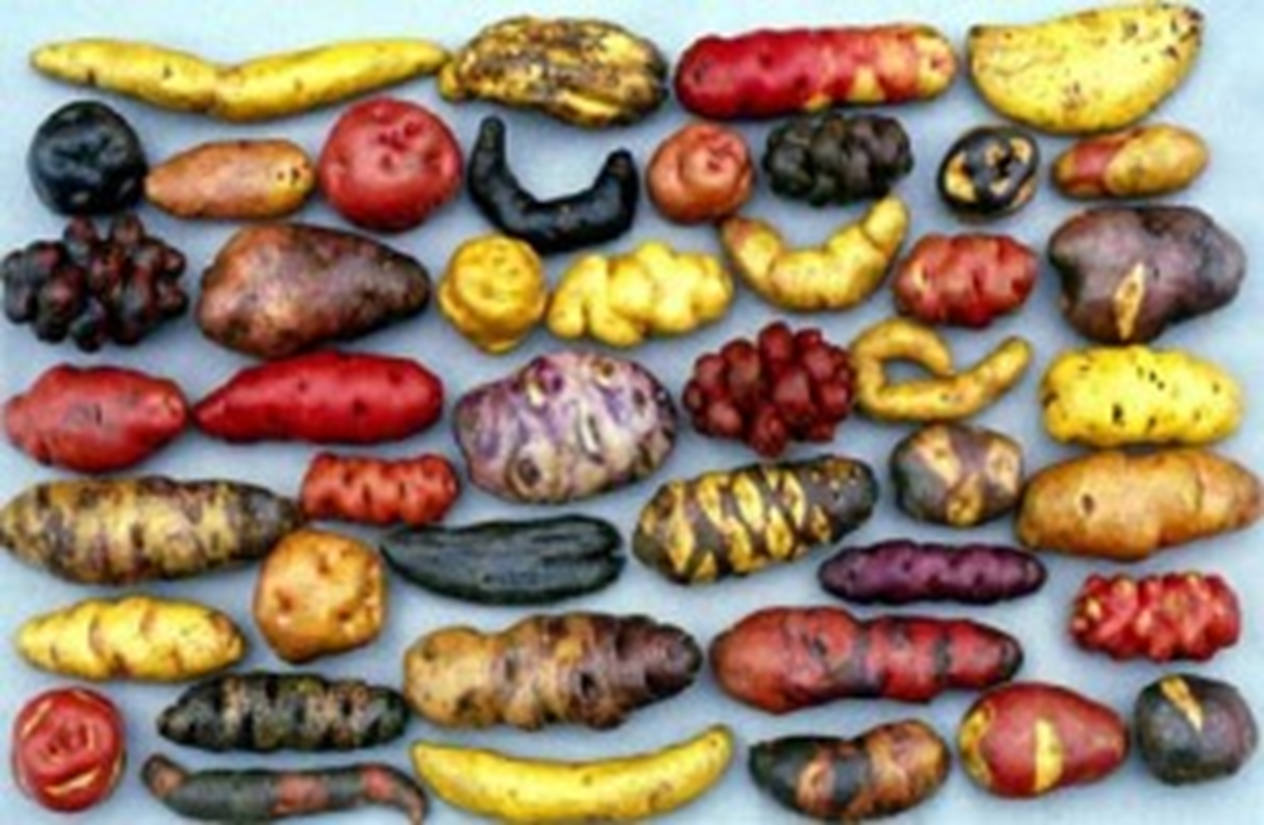

Explain the context of this photo.
indigenous Peruvians bred many potatoes into different varieties.
crop diversity is important bc they can survive climate change
other scientists learn from Peruvians on how to develop genotypic differences for potato survival
What are etioplasts?
plastid in plants grown in the dark
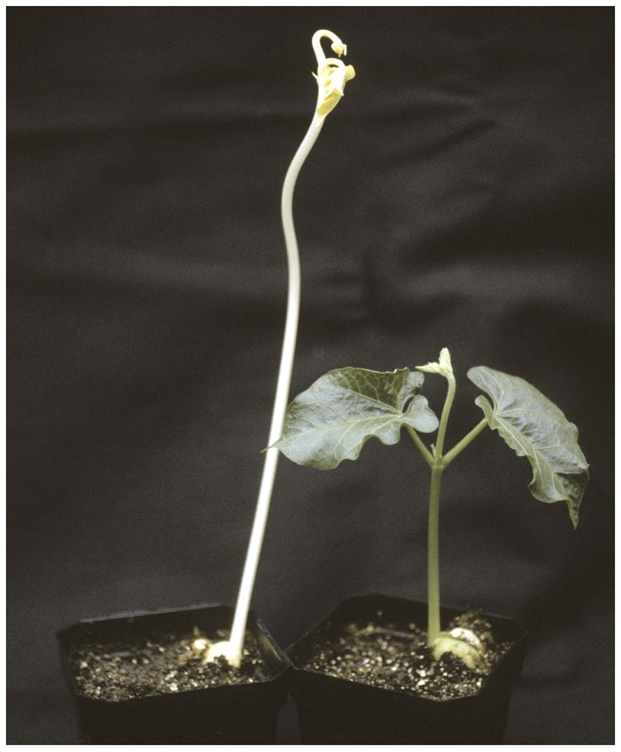

Which plant has Etioplasts?
the left one
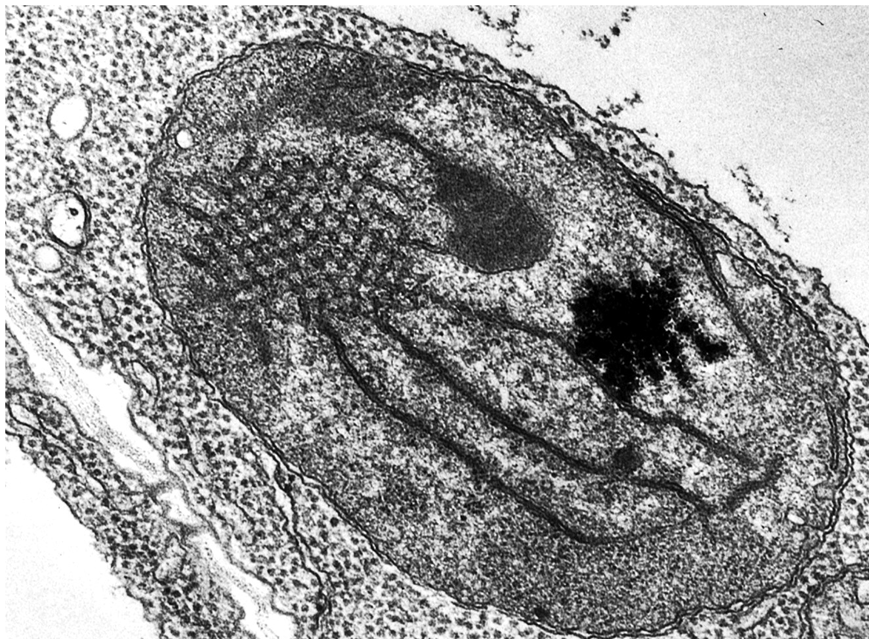
Explain the context of this image.
etioplast
basketball bumps are prolamellar bodies
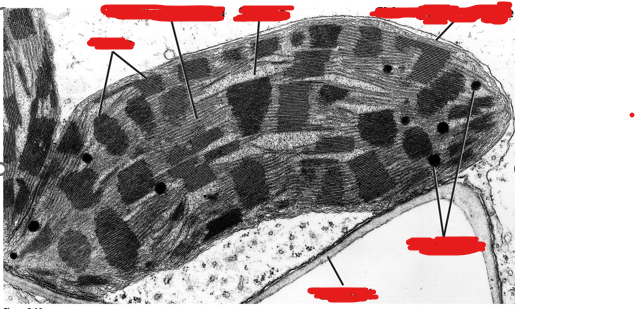
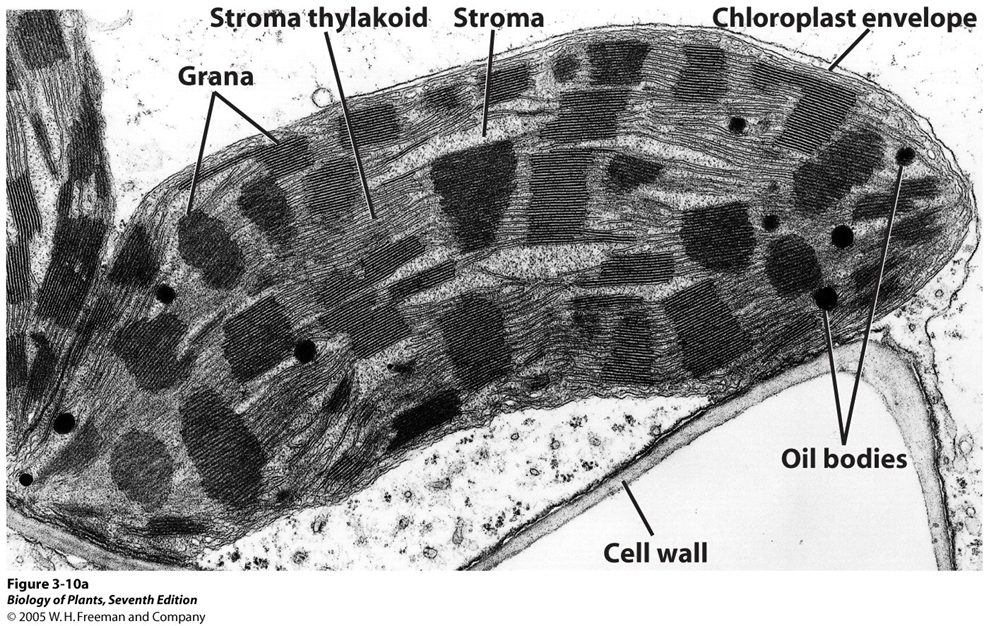
Explain the context of this image.
chloroplast
scribbles of 2nd to least darkest horizontal lines are thylakoid
What causes the white plants that grown in the dark to turn green?
light produces a hormone called cytokinin
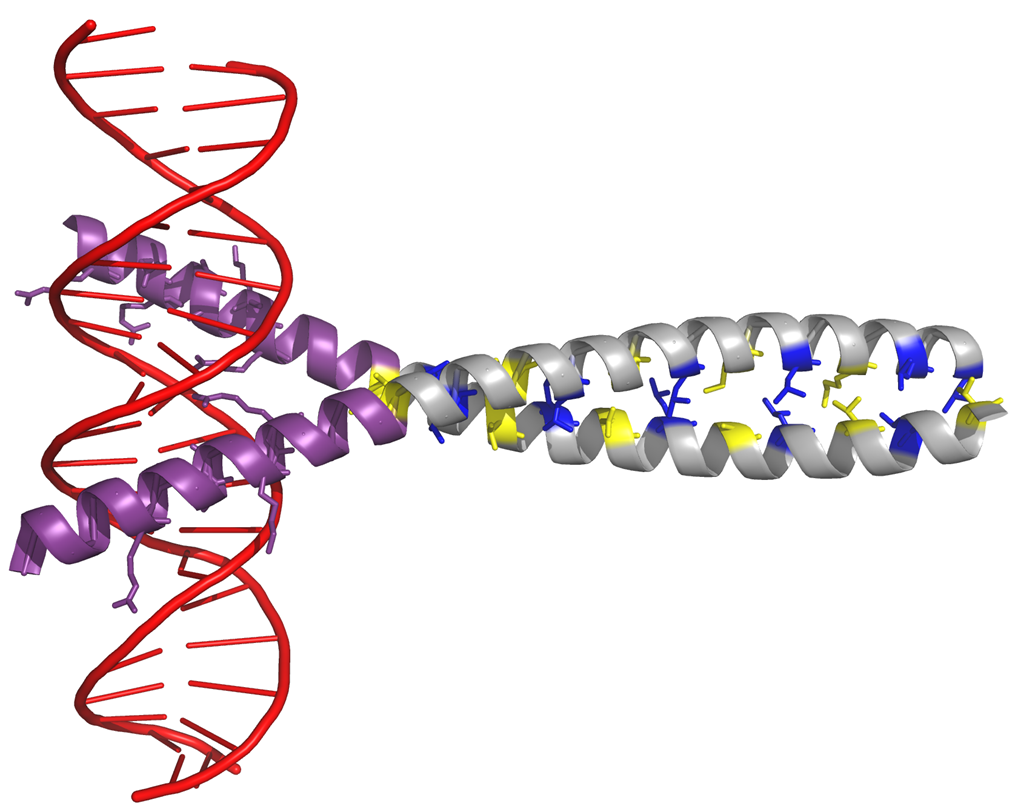
Explain the context of this image.
grey and purple are the transcription factors (TF) who are proteins that bind to DNA
func: regulate gene expression by transcribing DNA into mRNA
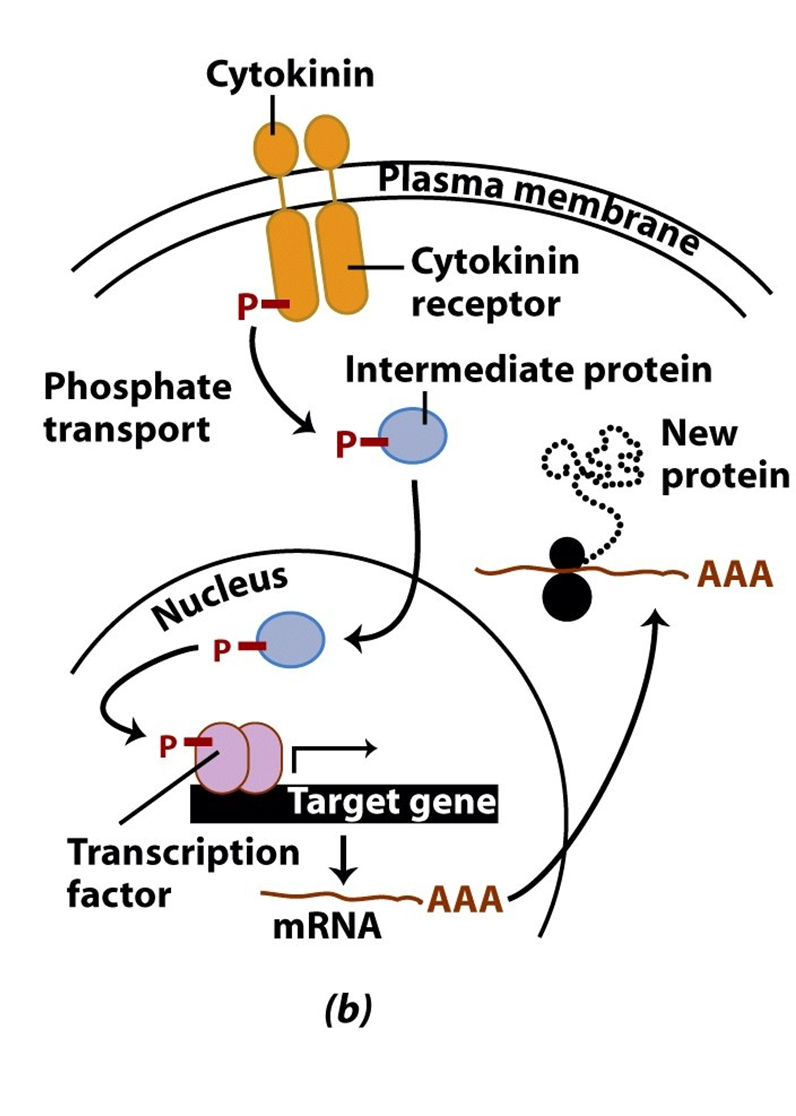
Explain the context of this image.
light strikes the etioplast —> stimulates the cytokinin
cytokinin binds to the plasma membrane and releases intermediate protein inside the cell
intermediate proteins travel into the nucleus and become TFs that bind to the DNA
mRNA transcribe in the nucleus and travels into the cytoplasm
tRNA translates the mRNA into a new protein
new protein travels in the cell to the etioplast and goes inside the prolamellar bodies
new protein stimulate the dissociation of the prolamella bodies and formation of thylakoids
Why are etioplasts important?
quicker method to transform into chloroplast rather than assemble chloroplast from scratch
Give an example of plastids interchange. Explain its importance.
Ripening: fruits turn from green to red
the hormone ethlyene stimulates the chloroplasts into becoming chromoplasts
Why? to attract seed dispersal agents.
Note: the hormone mechanism is similar to TFs.
What is a vacuole and its function? Explain how its function works.
organelle that takes up 90% of the cell volume
funcs:
cell growth
How? turgor pressure = vacuole fills with H2O + presses on cell walls
storage
sugars, proteins, ions, anthocyanins
digests and recycles old organelles (mitochondria + plastids)
store secondary metabolites (are chemicals indirectly essential for plants)
What are anthocyanins? Their function?
water soluble pigments in the vacuole
func
creates red, purple and blue
uv protection that almost covers the entire cell
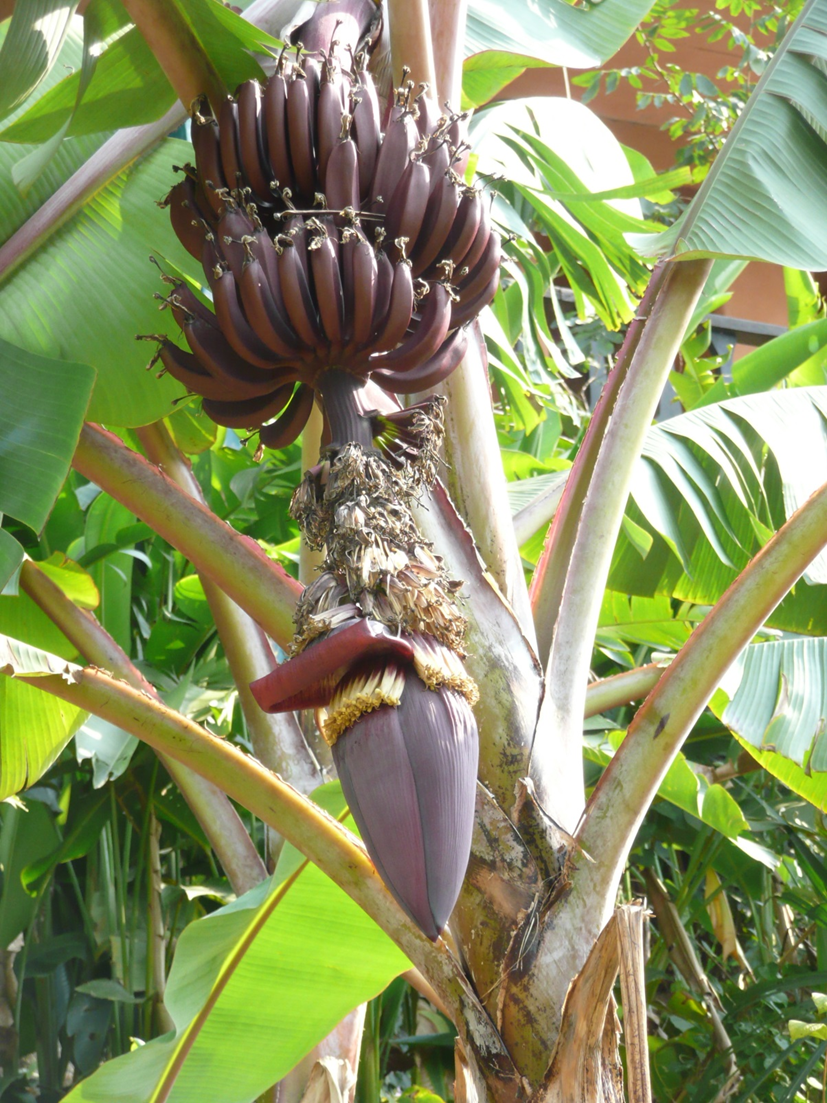

Explain the context of this image.
anthocyanin protects the bananas from uv rays
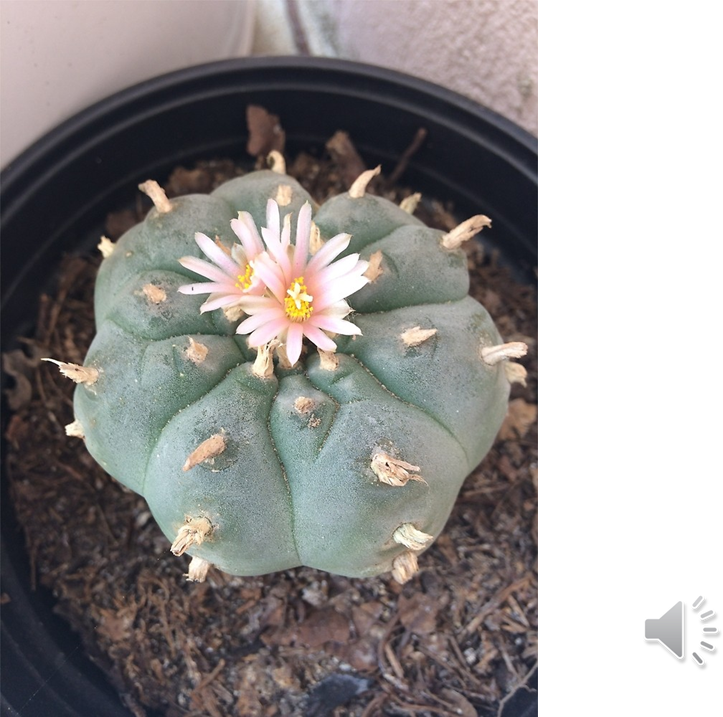

Explain the context of this photo.
mescaline (is a substance that make the cactus hallucinogenic) in the peyote cactus
func:
anti-predation
How? The animals who eats it gets hallucinations and cannot remember to eat or drink water. It will die.
fact:
some peyote are spineless bc their mescaline is so strong that it protects the cactus enough
Why is peyote threaten in the wild? Who does it affect?
harvested for recreational or hallucinogenic use; indigenous people using the plants for sacred ceremony
Provide examples of secondary metabolites.
1) THC in cannabis
2) caffeine in coffee plant
3) nicotine in tobacco plant
4) all spices (ex: bay, ginger, and onion
Why do plants have toxic chemicals and we do not?
1) we can run from predators while plants cannot due to their rigid cell wall