The Role of Government in Society and Economy, Understanding the Great Depression and Its Impacts, Key Concepts of Classical Economics and Government Intervention
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
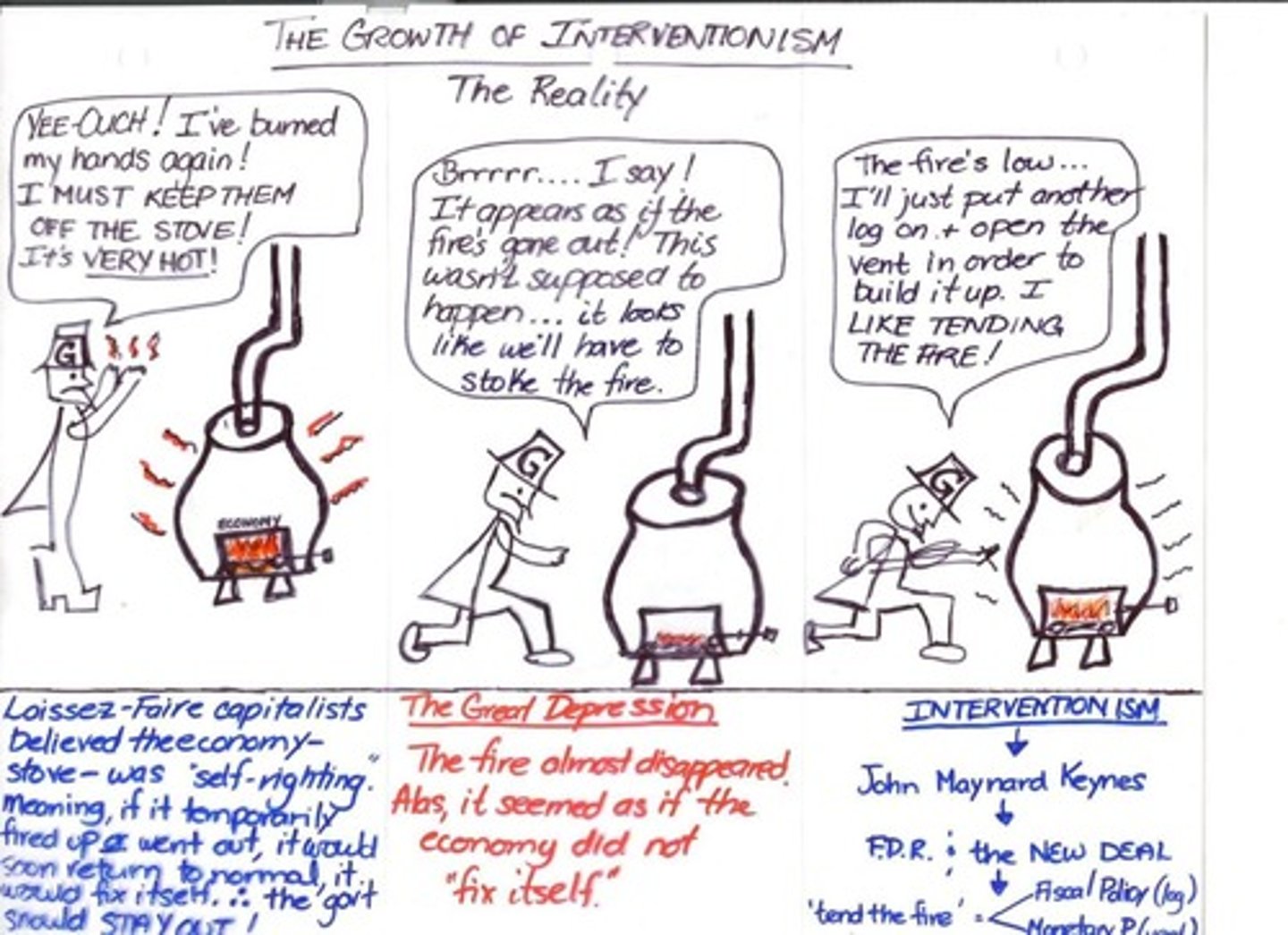
Role of Government
Uphold rights, freedoms, and protect property rights.
Conservative Ideology
Opposes government intervention and welfare spending.
Modern Welfare State
Government actively provides essential services to citizens.
Interventionism
Government intervenes in the economy for stability.
Safety Net
Programs ensuring minimum standard of living for citizens.
Socialism
Mixed economy combining private and public enterprises.
Keynesian Economics
Government actively manages economy to avoid instability.
Boom-Bust Cycle
Economic fluctuations between periods of growth and recession.
Deficit Spending
Government spends more than it earns.
Progressive Taxation
Higher income leads to higher tax rates.
Civil Servants
Public sector workers providing government services.
Economic Recovery
Period following a recession with improving economy.
Economic Depression
Severe downturn in economic activity.
Public Sector
Government-run services and industries.
Private Enterprise
Business ownership not controlled by the government.
Mixed Economy
Economy with both private and government control.
Minimum Wage
Lowest legal wage employers can pay workers.
Emergency Relief
Government assistance during natural disasters.
Tax Breaks
Reductions in tax obligations for individuals or businesses.
Economic Equality
Fair distribution of wealth among citizens.
Inflation
General increase in prices and fall in purchasing value.
Welfare Programs
Government initiatives to support the needy.
Public Assistance
Aid provided to individuals in financial need.
Social Programs
Government initiatives aimed at improving social welfare.
Taxpayer Dollars
Money collected from citizens to fund government services.
Laissez-Faire Capitalism
Minimal government interference in economic activities.
Crisis Management
Government response to emergencies or disasters.
Economic Stimulus Package
Government spending to boost economic activity.
Trillions in Relief
Massive government spending for disaster recovery.
Public Ownership
Government ownership of resources and industries.
Support for Veterans
Government assistance for military service members.
Indigenous Education Funding
Financial support for Indigenous educational initiatives.
Climate Change Spending
Government investment in environmental protection efforts.
Post-Secondary Education Funding
Financial support for higher education institutions.
Government Accountability
Responsibility of government to serve the public.
Economic Stability
Consistency in economic performance and growth.
Government's Common Good Role
Ensuring societal welfare through intervention.
Economic Assistance
Support provided to individuals during financial hardship.
Rights and Freedoms
Fundamental entitlements guaranteed to citizens.
Social Support Systems
Networks providing assistance to those in need.
Taxation During Prosperity
Increased taxes when the economy is thriving.
Taxation During Recession
Decreased taxes to stimulate economic recovery.
Government Spending Cuts
Reduction of government expenditures on services.
Balanced Budgets
Government spending equals its revenue.
Laissez-Faire Economics
Minimal government interference in economic activities.
Individual Liberty
Personal freedom in all societal aspects.
Technological Progress
Advancement in technology driving economic growth.
Monopoly
Market dominance by a single entity, limiting competition.
Economic Cycle
Fluctuations in economic activity: prosperity, recession, depression, recovery.
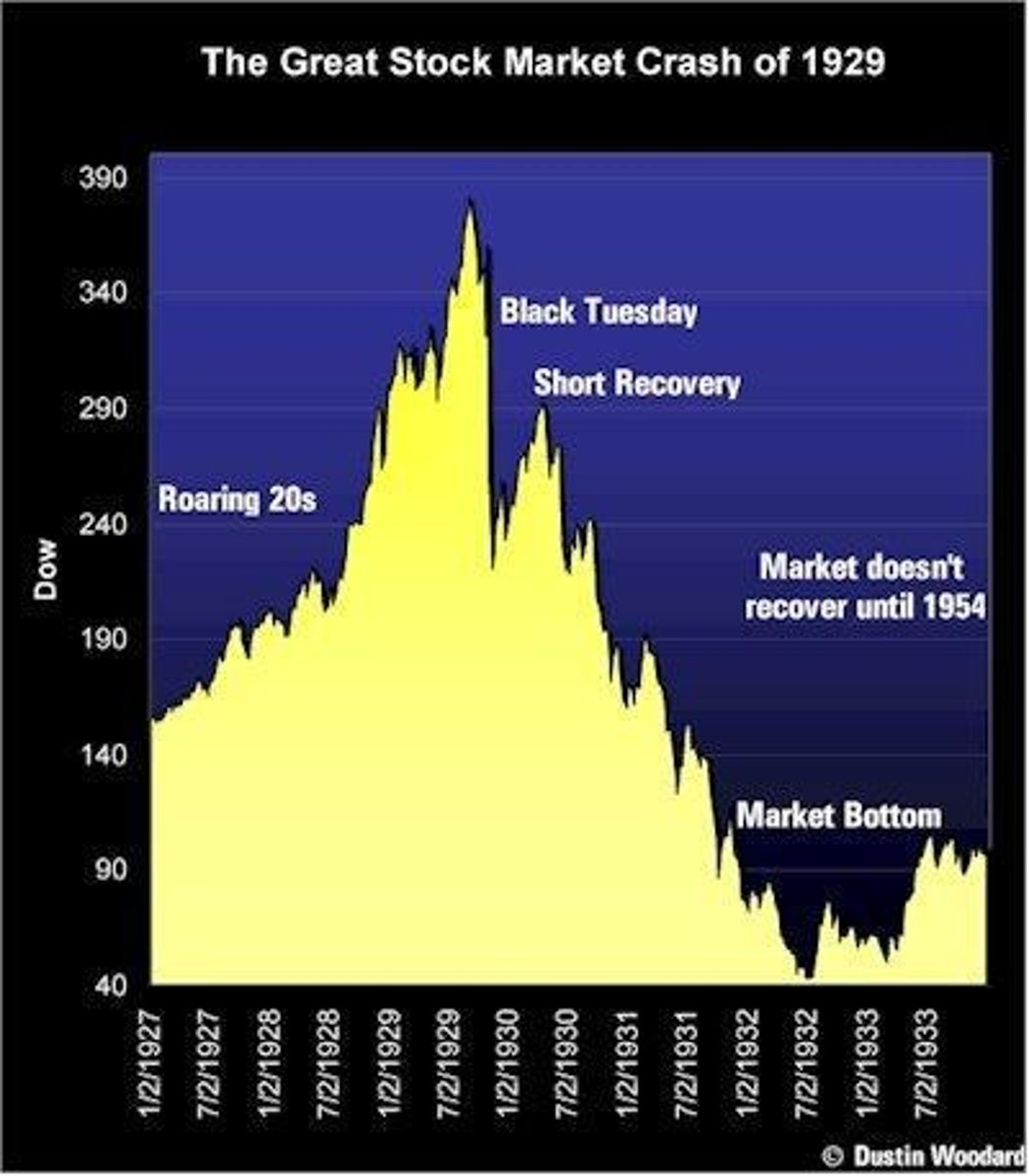
The Roaring 20s
Period of economic prosperity and cultural change in America.
Black Tuesday
Panicked selling sparked first day of most the most detrimental Stock Market crash, on October 29, 1929.
Consumer Debt
Accumulation of debt by individuals for consumption.
Stock Market Speculation
Investing based on expected price increases.
Surplus Goods
Excess products produced beyond consumer demand.
Unregulated Banking
Lack of government oversight on financial institutions.
Economic Disparity
Unequal distribution of wealth among individuals.
Investment Risks
Potential losses associated with financial investments.
Market Optimism
Positive outlook on economic growth and investments.
Get Rich Quick Schemes
Investment strategies promising fast financial returns.
Personal Savings Rate
Percentage of income saved by individuals.
Banking Institutions
Organizations providing financial services and loans.
Economic Overproduction
Production exceeding market demand, leading to waste.
Investor Panic
Mass selling of stocks due to fear.
Financial Collapse
Total failure of economic systems or institutions.
Government Regulation
Laws governing economic and business practices.
Market Restraints
Limitations placed on economic activities by authorities.
Capitalism
Economic system based on private ownership , free markets and profit.
Human Suffering
Negative impacts on individuals due to economic failures.
Environmental Tragedies
Destruction of ecosystems due to industrial practices.
Economic Competition
Rivalry among businesses for market share.
Market Crash
A sudden decline in stock prices.
Life Savings Loss
Many lost all their investments.
Bank Collapse
Hundreds of banks failed due to withdrawals.
Bank Insurance
Protection for depositors, lacking during the crash.
Great Depression
Severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1941.
Unemployment Rate
One in four people were jobless.
Laissez-faire Government
Minimal government intervention in the economy.
Herbert Hoover
Republican president during the Great Depression.
Infrastructure Projects
Government investments to create jobs.
Hoover Dam
Major project initiated to provide employment.

Dust Bowl
Severe drought affecting Midwest farming. in middle America in 1930s
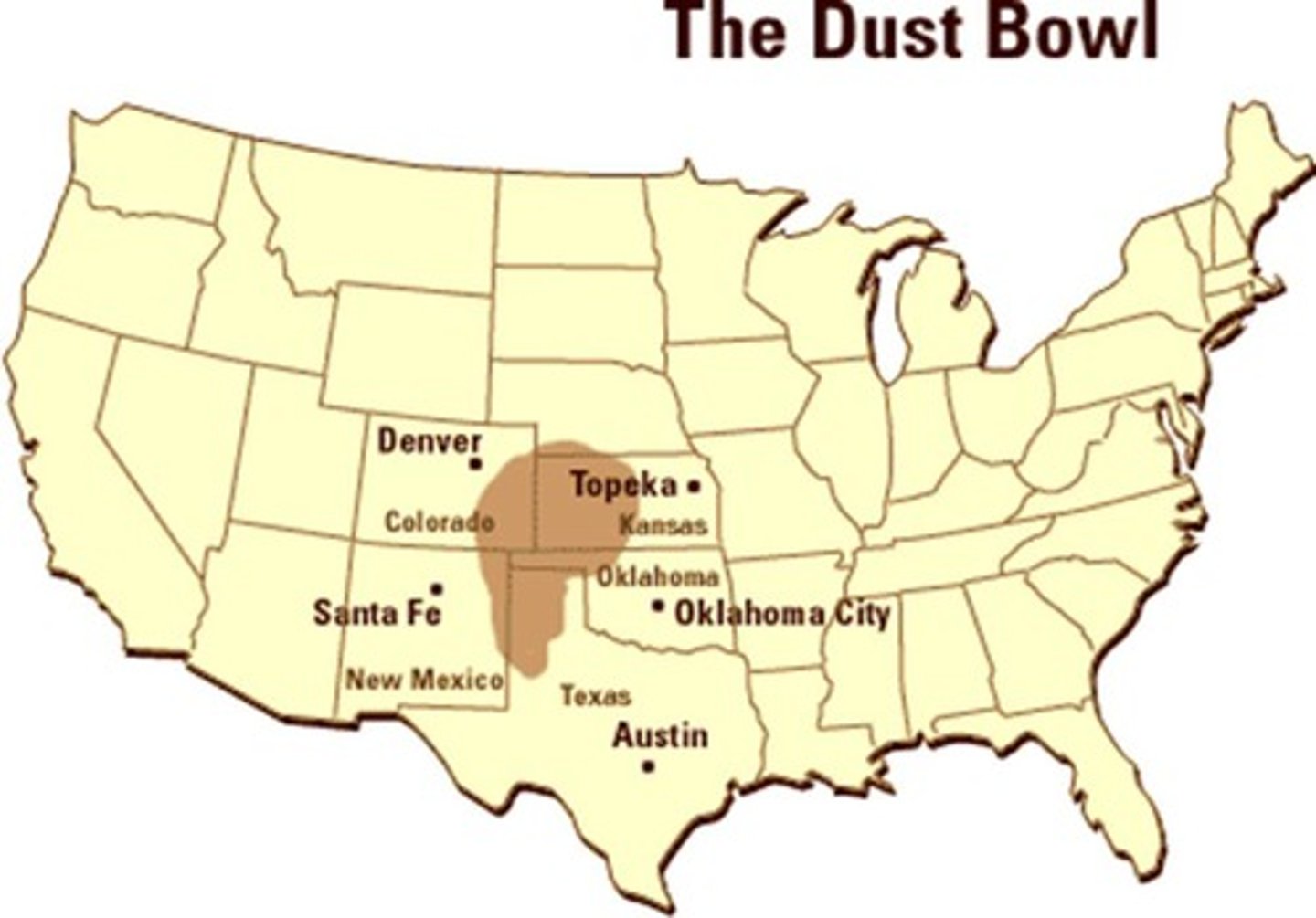
Okies
Migrants from Oklahoma seeking better opportunities.
Migrant Workers
People moving for agricultural jobs.
Dorothea Lange
Photographer known for capturing Depression-era struggles.
FDR
Franklin Delano Roosevelt, American political leader whose ideas in interventionism lead to ideas like The New Deal and countless ‘fireside chats’
The New Deal
Roosevelt's plan for economic recovery.
Welfare State
Government provides social support/services for citizens. (safety net )
Monetary Policy
Control of money supply and interest rates.
Fiscal Policy
Taxation and government collecting and spending strategies.
Inflation Control
Raising interest rates to manage inflation.
Bank Lending Rates
Cost of borrowing money from banks.
Social Welfare
Government programs to aid the needy.
Hobos
Homeless individuals traveling for work.
Joblessness
Widespread unemployment during the Great Depression.
New Deal
FDR's program for economic recovery and reform. In great depression ( designed to put people to work )
Relief
Immediate action to halt economic deterioration.
Reform
Permanent programs to prevent future economic crises.
Alphabet Agencies
Federal agencies created under the New Deal.
Social Security Act
Established old age and survivors insurance.

Fair Labor Standards Act
Set minimum wage and labor standards.