week 3 binocular vision
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is abduction? *
Eye moves out (temporal direction)
What is adduction?*
Eye moves in (nasal)
What is supraduction?
vertical movement around x-axis
Moves upwards from primary to secondary position
What is infraduction?
vertical movement around x-axis
Moves downwards from primary to secondary position
What is torsion?
Rotation around the y-axis
Involuntary control
Occour in response to vestibular and proprioceptive neck reflex
What is intortion?
Rotation around the y-axis
Upper pole of eye rotates towards the nose
Involuntary
What is extortion?
Rotation around the y-axis
Upper pole of eye rotates away from the nose
Involuntary
RADSIN
What is version movement?
Conjugate movement of two eyes in the same direction
From primary to secondary position
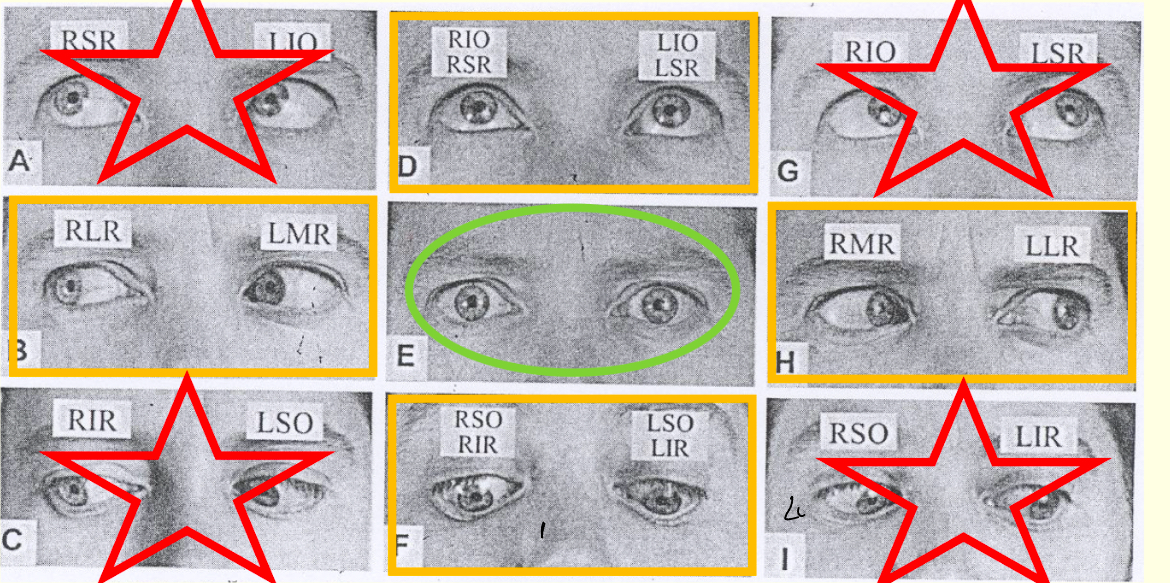
supraversion?
Both eyes turn up
superior recti and inferior oblique
Infraversion?
Both eyes turn down
Inferior recti and superior oblique
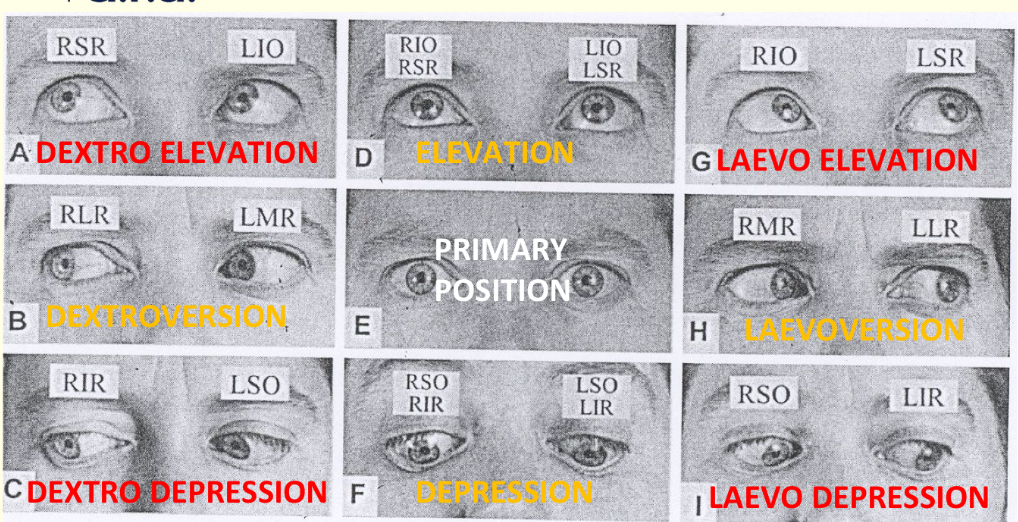
Dextroversion?
Both eyes turn to the right
RLR
LMR
Levoversion?
Both eyes turn to left
RMR and LLR
Primary position?
Eye looking straight and head is erect
Median and face planes are vertical
Secondary position?
Eye makes a purely horizontal/vertical movement starting from primary position
Arrives at secondary
Tertiary position?
Oblique movement
Both horizontal and vertical
From primary to tertiary position
Complete this
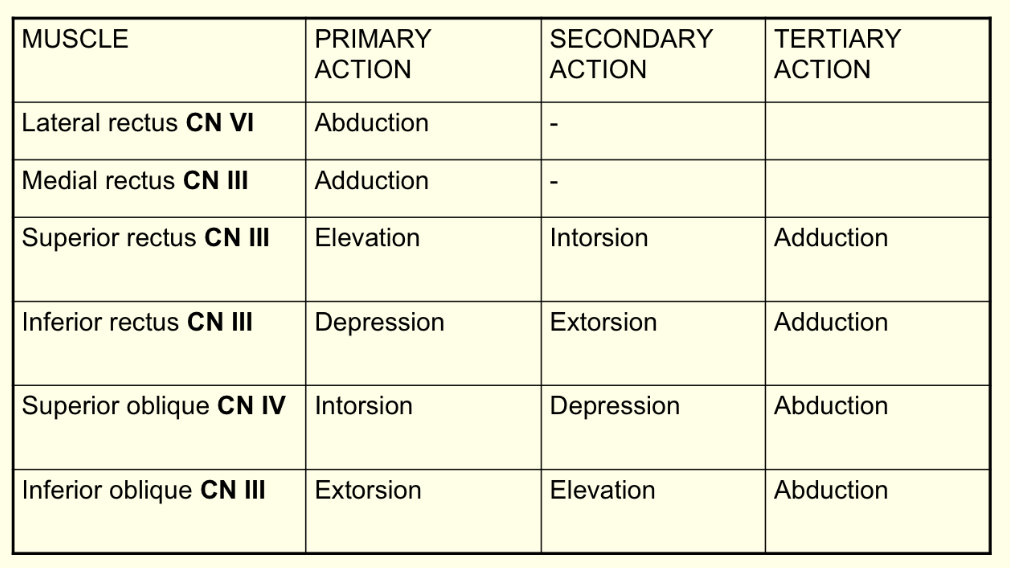
What are the muscle actions of the superior rectus? *complete same for all
Primary - elevation
Secondary - intersion
Tertiary - adduction
What’s hering’s law of equal innervation?
innervation to the EOM is equal in both eyes
Afk movement of two eyes are equal and symmetrical
Identify underactions or overactions of EOMs
What is Sherrington’s law of reciprocal innervation?
Contraction of a muscle is accompanied by the simultaneous and proportional relaxation of its antagonist
Eg RLR contracts then RMR will relax
What are synergists and give an example?
Muscles of the same eye that cause similar movement
Eg LSR and RIO
What are antagonists and give an example
Muscles that oppose the action of each other
Eg RMR and RLR
What Can you infer if a muscle is overacting or under-acting?
*
incomitant deviations
Strabismus - differs depending upon direction of gaze and associated with defective movement of the eye
Congenital or acquired
Neurogenic/myogenic/mechnical
What happens when a muscle underacts?
overacting of the contralateral synergist
Over action of the ipsilateral antagonist
Inhibition (under action of the contralateral agonist)
LR palsy:
Right lateral rectus under action
Left medial rectus overaction
Right medial rectus overaction
Left lateral rectus underaction
What happens during lateral rectus palsy (underaction)*
Left medial rectus overaction - herrings law
Right medial rectus overaction - Sherrings law
Left lateral rectus underaction- herrings law
Do you get primary overaction?
No. There is an underaction
If patient reports diplopia in up gaze, what do you ask?*
which image is higher
Indicates lower eye
If patient reports diplopia in the left gaze, what do you ask?
Which image is further to the left
If patient reports diplopia in right gaze, what do you ask?
Which image is further to the right?
If patient reports diplopia in down gaze, what do you ask?*
Which image is lower?
Indicates lower eye
incomitant deviations?
Strabismus - differs depending upon direction of gaze and associated with defective movement of the eye
Congenital or acquired
Neurogenic/myogenic/mechnica
What are indications of incomitant deviations?
head tilt
Face turn
Chin elevation or depression
What effects are caused by third nerve palsy cause and incomitant eye movements?*
ptosis (lavatory palprebrae?)
Abduction in primary position (intact LR)
Normal abduction
Limited adduction, elevation, depression
Mydriasis, defective accommodation
What effects are caused by fourth nerve palsy cause and incomitant eye movements?*
if LE affected
L hypertropia in primary position
Increase in L hyperT on right gaze due to LIO o/a
Limitation of left depresssion on adduction
Normal left abduction, elevation and depression
(Only affects superior oblique?)
What effects are caused by sixth nerve palsy cause and incomitant eye movements?*
SOT (esotropia) in primary position
Limited abduction
What is brown’s syndrome?
mechanical restriction of the SO muscle tendon
Congenital and idiopathic
Caused by trauma/inflammation
Treatment not required if BSV is ok
Related to trochlear nerve
Limited elevation of eye in adduction
Normal e;elation in abduction
What is DUane’s retraction syndrome?
lateral rectus failure to be powered by the 6th CN
Born with it
Anomalous innervation of the LR by CN 3
Often bilateral but asymmetrical congenital
What are the 3 types of Duane retraction syndrome?
Type I - limited abduction
Type II - limited adduction Normal left
Type III - both abduction and adduction are restricted
slide 58
Slide 59
Slide 60
Which patients do you refer?
any patient with sudden onset binocular diplopia (horizontal, vertical or torsional)
Any patient with acquired diplopia which is worse in different positions - incomitant
Any patient who requires an increase in their prismatic correction to keep them asymptomatic