Biochem 2 CH 3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Why do amino acids, when dissolved in water, become zwitterions
an H+ ion is therefore transferred from one end of the molecule to the other
zwitterions
an ion that possesses both positive and negative charges
5 major grouping of amino acids
nonpolar, polar, aromatic, positive and negatively charged
non polar amino acids
do not contain a charge and hydrophobic
aromatic amino acid
contains an aromatic ring, hydrophobic
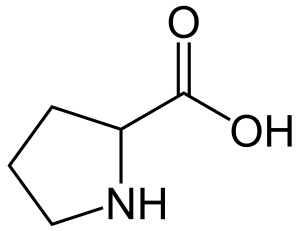
what amino acid does not have a free a-amino group
proline
structural characteristics in all amino acids found naturally occurring in proteins
an a carbon to which are attached a carboxylic acid, an amine, a hydrogen, and a variable side chain
what are the 2 amino acids that contain sulfur atoms
Methionine and cysteine
all amino acids found in protein, except for proline, contain what
Carboxyl group
Which of the following is true about aromatic amino acids
on a molar basis, tryptophan absorbs more ultraviolet light than tyrosine
Which of the following statements about cystine is correct?
Cystine forms when the —CH2—SH R group is oxidized to form a —CH2—S—S—CH2— disulfide bridge between two cysteines.
Amino acids are ampholytes because they can function as either an
acid or base
Titration of valine by a strong base, for example NaOH, reveals two pK's. The titration reaction occurring at pK2 (pK2 = 9.62) is:
—NH3+ + OH− →—NH2 + H2O
The term specific activity differs from the term activity in that specific activity:
is measured only under optimal conditions.
which of the following describes the overall three-dimensional folding of a polypeptide
tertiary structure
primary sructure
the sequence of amino acids linked together to form a polypeptide chain.
secondary structure
contains regions of amino acid chains that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds from the polypeptide backbone
quaternary structure
the interaction of two or more folded polypeptides
A polypeptide is hydrolyzed, and it is determined that there are 3 Lys residues and 2 Arg residues (as well as other residues). How many peptide fragments can be expected when the native polypeptide is incubated with the proteolytic enzyme trypsin?
Six fragments would be expected, unless the carboxyl-terminal residue is Lys or Arg; in which case there would be five.
edman reagent for protein structure analysis
directly determines the sequence of N-terminal mutated/modified proteins more accurately
protease for protein structure analysis
greatly improve the coverage of proteome sequences and PTM sites.
reducing agent for protein structure analysis (dithiothreitol or B-mercaptoethanol)
to disrupt, or reduce, disulfide bonds in peptides and proteins to view individual proteins
ion-exchange chromatography
separates proteins (or any biomolecules) based on differences in their net charge at a particular pH
size-exclusion chromatography
separates molecules based on their size by filtration through a gel
affinity chromatograghy
a separation method based on a specific binding interaction between an immobilized ligand and its binding partner
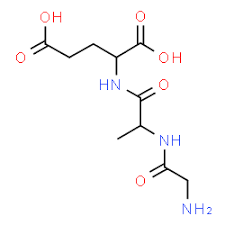
structure of gly-ala-glu in ionic form at pH 7
The amino acid histidine has three ionizable groups, with pKa values of 1.8, 6.0, and 9.2. (a) Which pKa corresponds to the histidine side chain?
6
The amino acid histidine has three ionizable groups, with pKa values of 1.8, 6.0, and 9.2. In a solution at pH 5.4, what percentage of the histidine side chains will carry a positive charge?
80%
dominant form of glycine in a basic solution
NH3+-CH2-COOH
For amino acids with neutral R groups, at any pH below the pI of the amino acid, the population of amino acids in solution will have:
a net positive charge
At the isoelectric pH of a tetrapeptide:
the total net charge is zero
The average molecular weight of the 20 standard amino acids is 138, but biochemists use 110 when estimating the number of amino acids in a protein of known molecular weight. Why?
The number 110 reflects the higher proportion of small amino acids in proteins, as well as the loss of water when the peptide bond forms.
In a conjugated protein, a prosthetic group is:
a part of the protein that is not composed of amino acids.
In a mixture of the five proteins listed below, which should elute second in size-exclusion (gel-filtration) chromatography?
immunoglobulin G Mt=145,000
By adding SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) during the electrophoresis of proteins, it is possible to:
determine a protein's isoelectric point