4. Lecture 4 - Lec 15 (Exam 3): Benign tumors of the Jaws
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
round/oval
what is the normal shape of benign tumors?
-Well-defined
-Smooth, regular
-Mostly corticated
what is the normal periphery/margins of benign tumors?
•Expansion
•Thinning
•Erosion (if aggressive)
benign tumors have what affect on cortical bone surrounding structures?
displacement
benign tumors have what affect on the maxillary sinus?
•Displacement of teeth
•May prevent eruption of teeth
•Root Resorption
benign tumors have what affect on teeth?
displacement/ no sensory-neural defects
benign tumors have what affect on the IAN canal?
benign
Localized root destruction usually is associated with pressure resorption from slowly growing lesions or _______ neoplasms
Ameloblastoma
What is the most common benign tumor of the jaw?
posterior mandible
what is the most common location of an Ameloblastoma?
40
what is the average age for patients that present with an Ameloblastoma?
Ameloblastoma
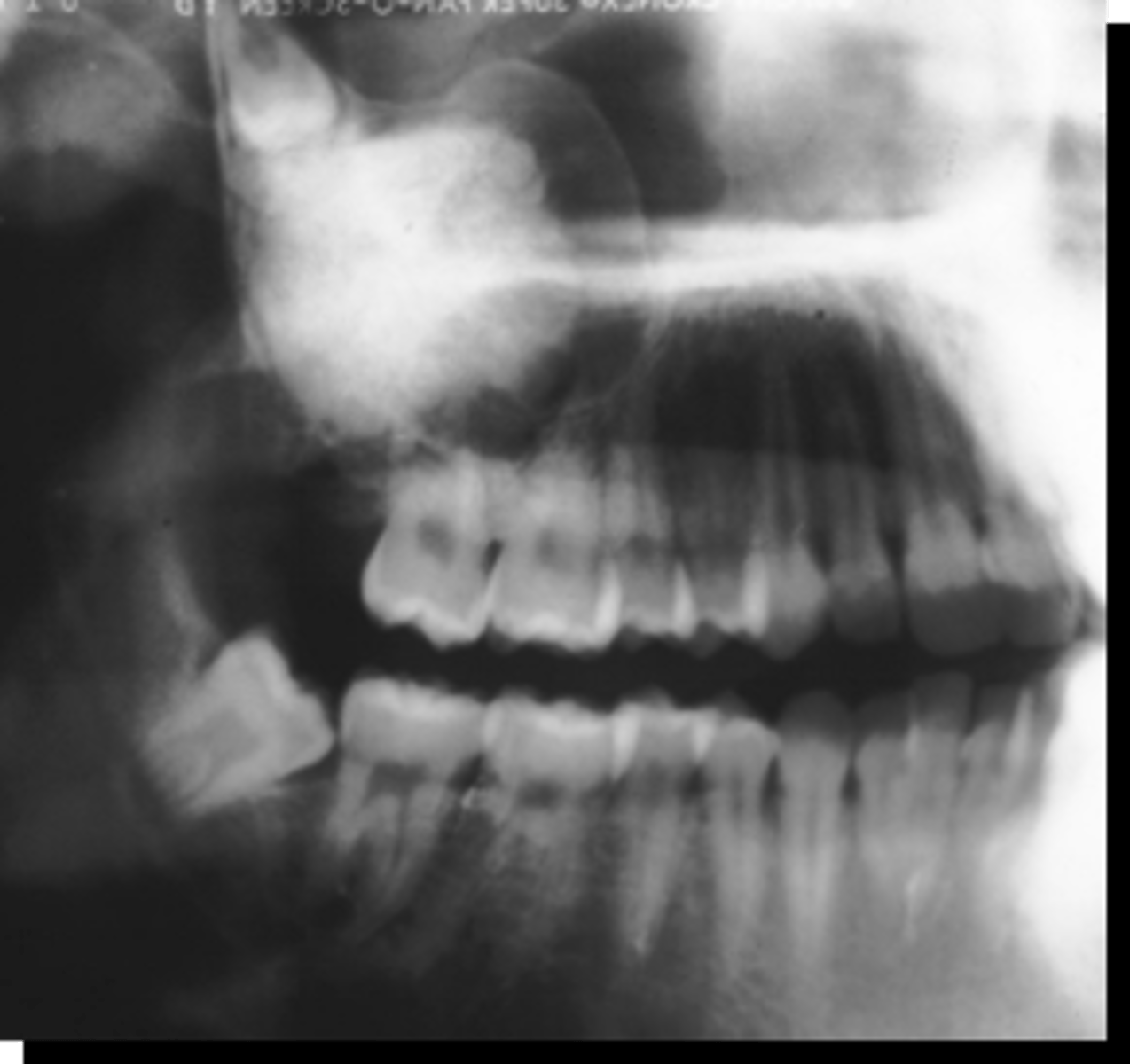
40 y/o patient presents with a well defined, corticated, multi-locular with thick/coarse curved septae lesion on the posterior mandible. Thinning and expansion of the border of the mandible is evident and it displaces the IAN inferiorly. The roots of tooth #30 are resorbed. The lesion is VERY expansile. What is the diagnosis?
Ameloblastoma
KOT
40 y/o patient presents with a well defined, corticated, multi-locular with thick/coarse curved septae lesion on the posterior mandible. Thinning and expansion of the border of the mandible is evident and it displaces the IAN inferiorly. The roots of tooth #30 are resorbed. What pathologies are included in your differential diagnosis?
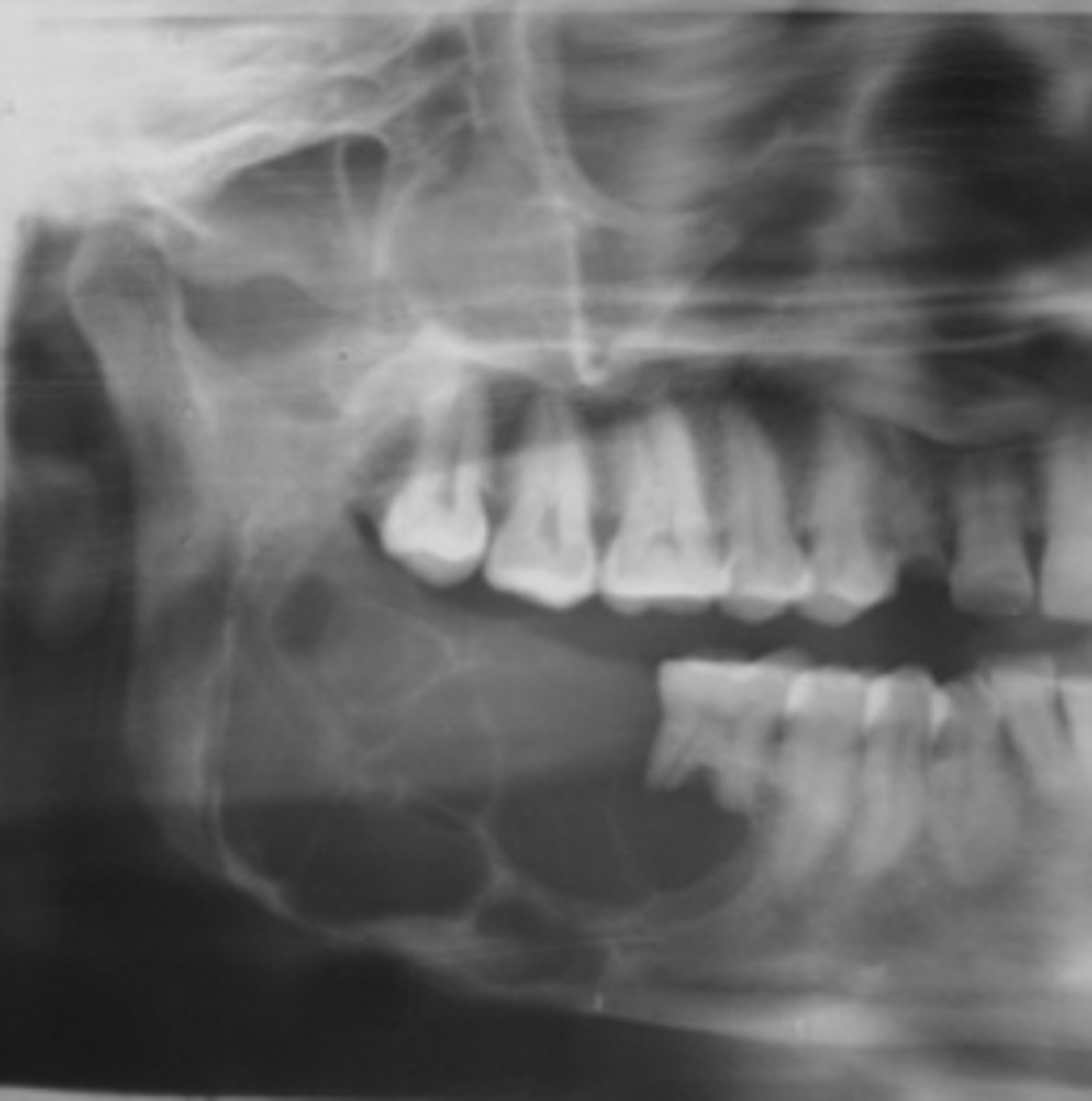
Ameloblastoma
KOT
Dentigerous Cyst
40 y/o patient presents with a well defined, corticated, uni-locular, peri-coronal lesion that displaces #32 on the posterior mandible. Thinning and expansion of the border of the mandible is evident and it displaces the IAN inferiorly. What pathologies are included in your differential diagnosis?
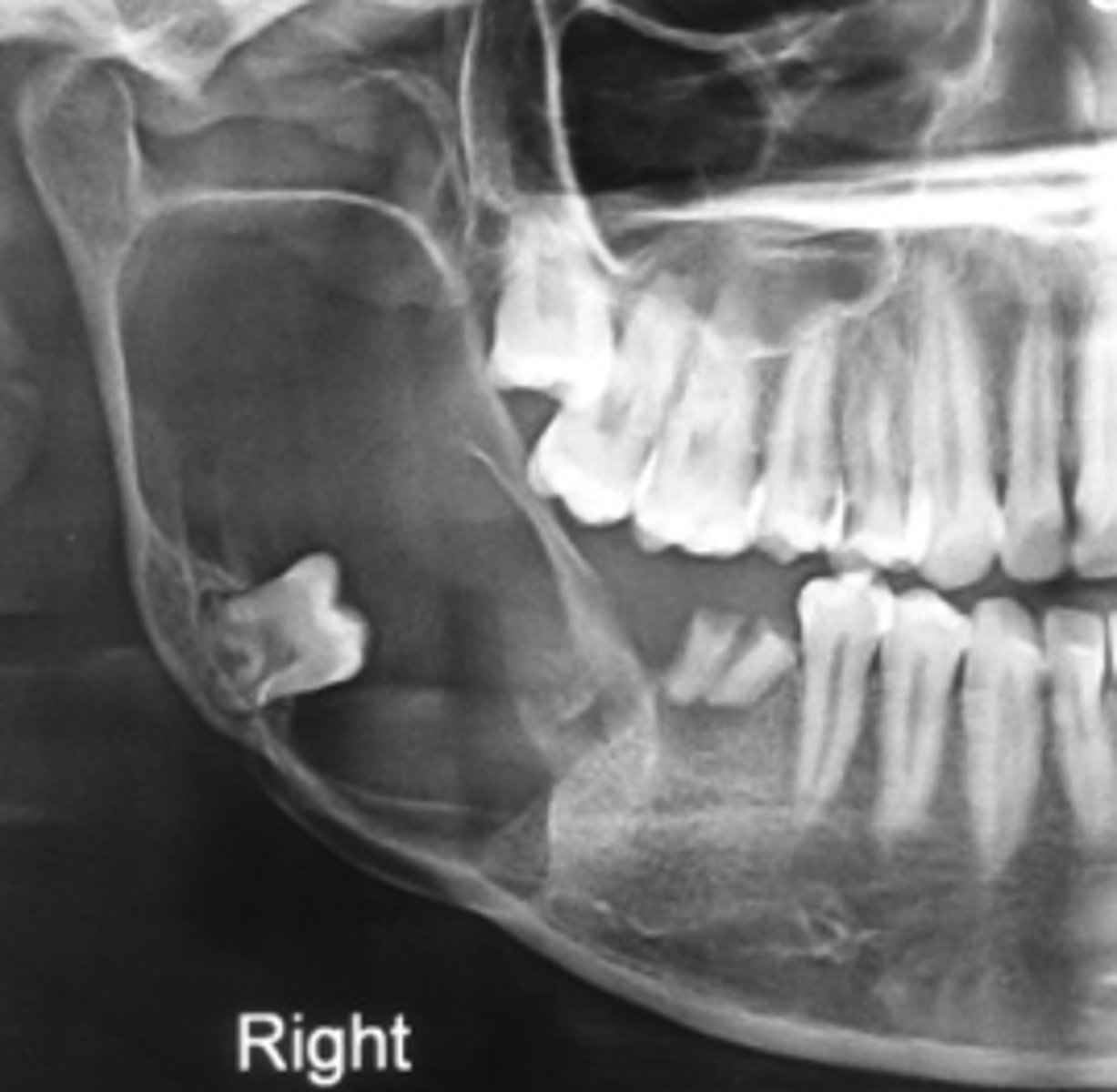
Ameloblastoma
40 y/o patient presents with a well defined, corticated, multi-locular with thick/coarse curved septae lesion on the posterior mandible. Thinning and expansion of the border of the mandible is evident and it displaces the IAN inferiorly. The roots of the surrounding teeth are displaced. The lesion is VERY expansile. What is the diagnosis?
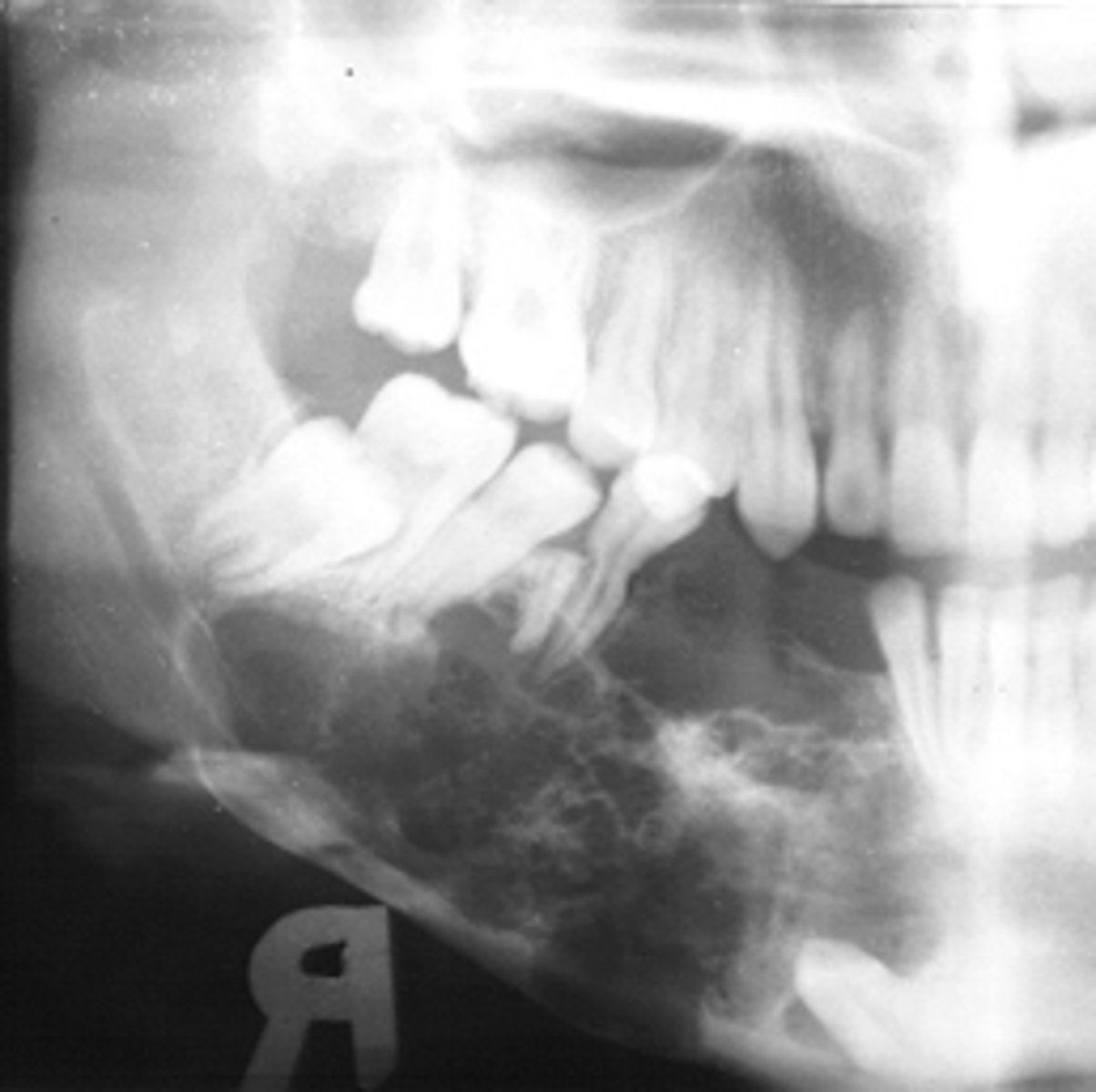
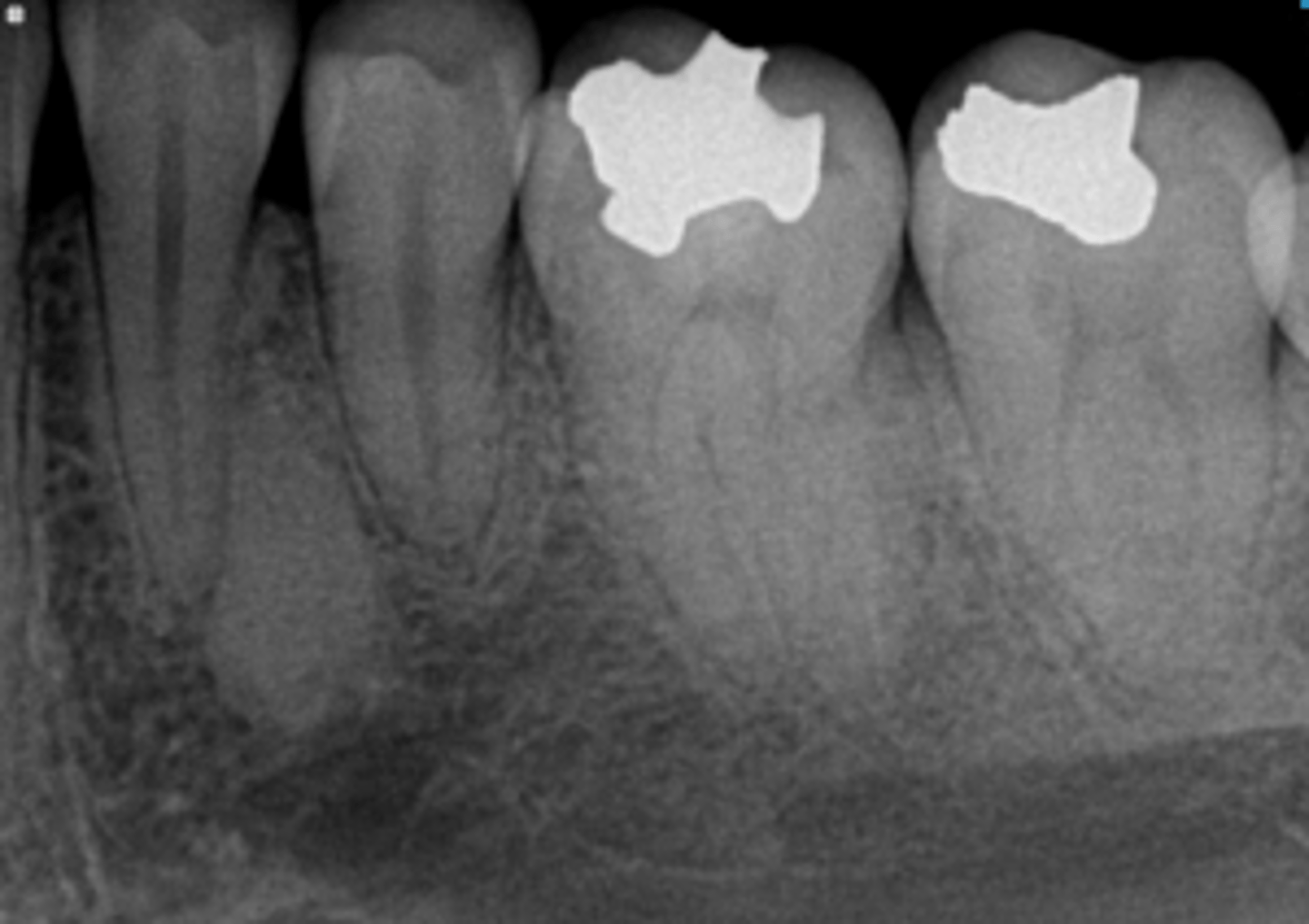
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT)
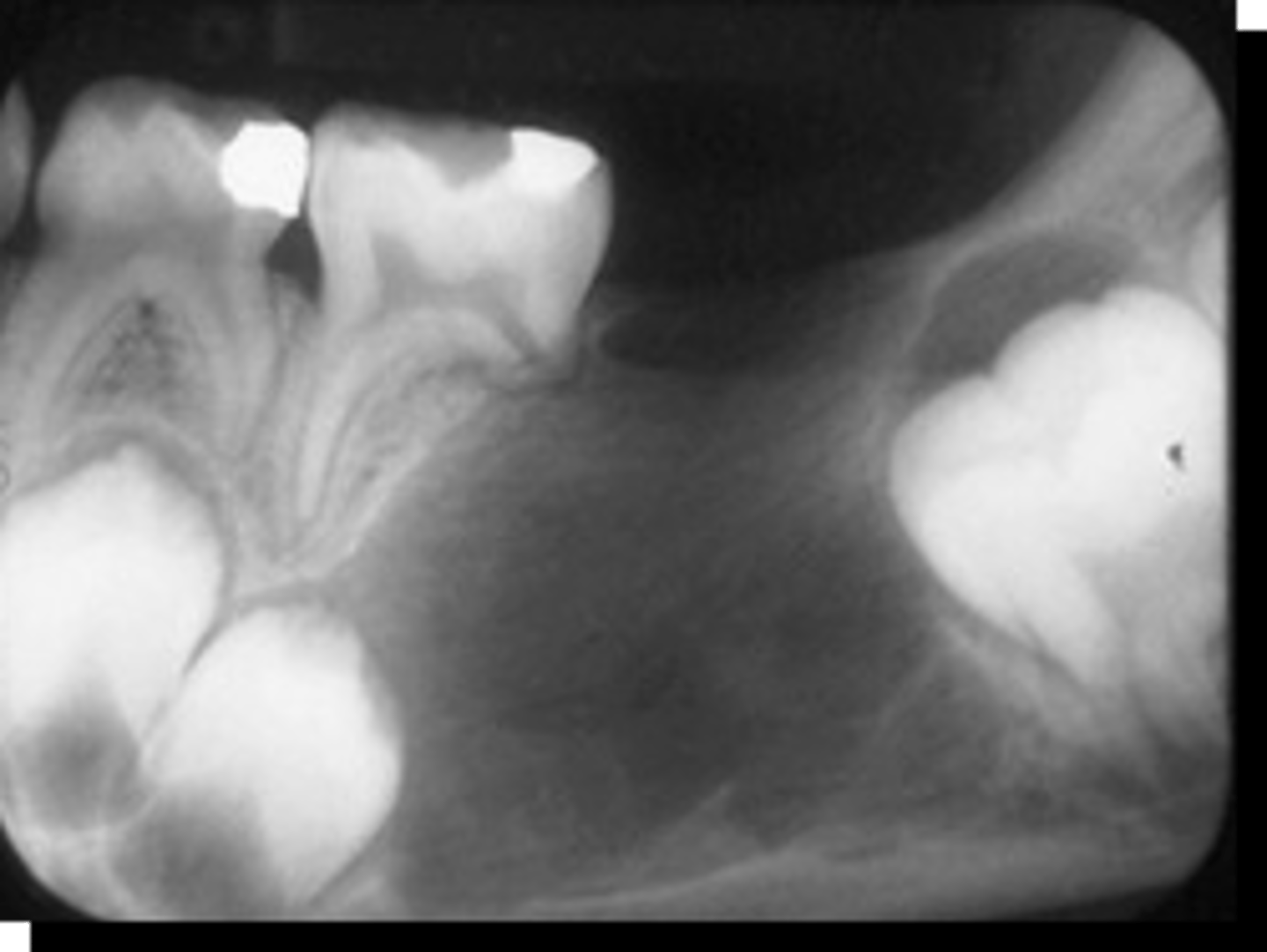
20 y/o patient presents with well circumscribed, corticated unilocular lesion on the anterior maxilla that surrounds the entire tooth #6, with mixed radiopacities around the crown of the tooth. The roots of the surrounding teeth are displaced.
What is the diagnosis?
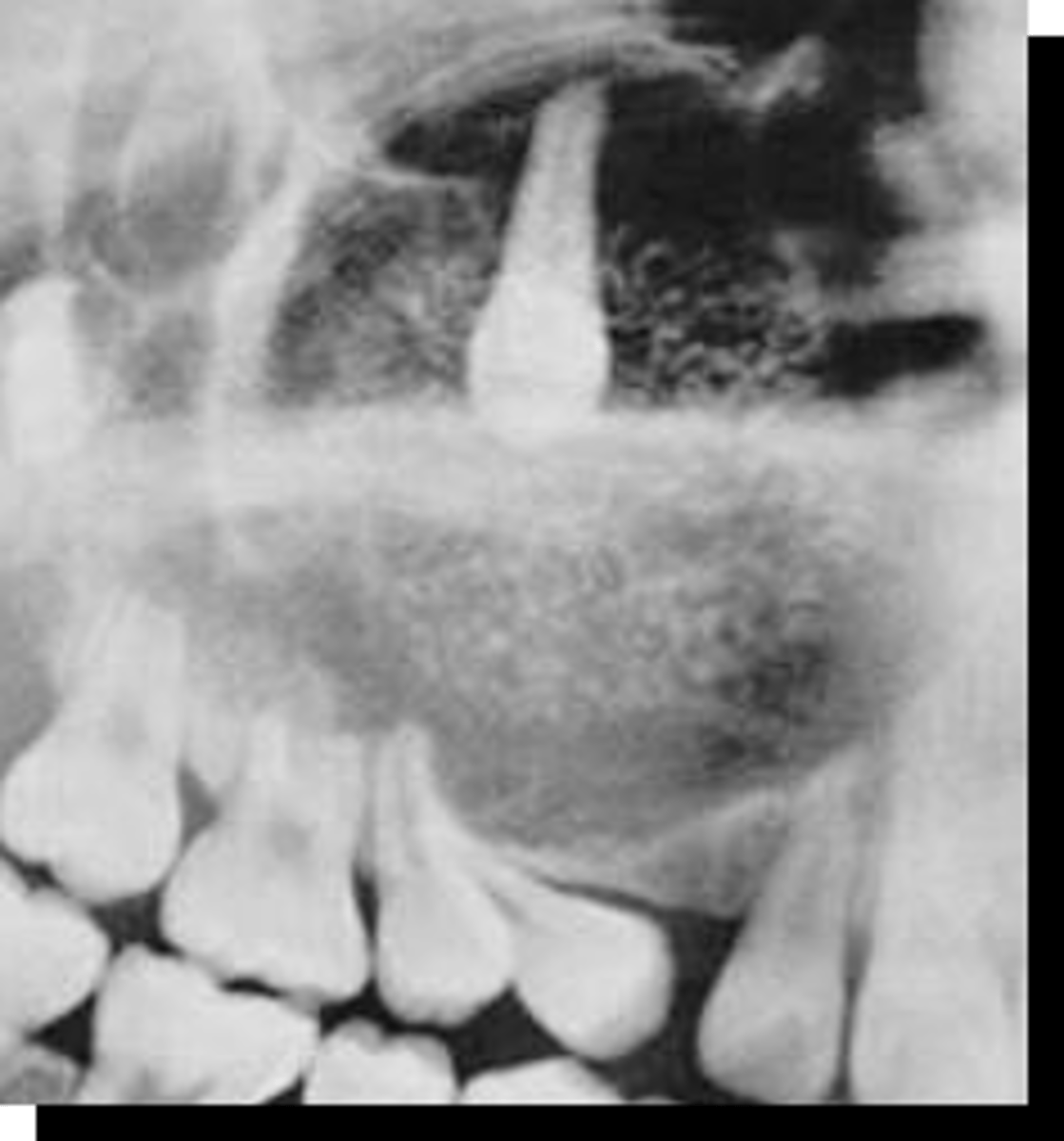
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT)
this pathology is associated with unerupted/impacted maxillary anterior teeth and, cortication surrounds the entire tooth and radiopacities surround the crown of the impacted tooth:
10-20 y/o
what is the average age for patients that present with an Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT)?
anterior maxilla
what is the most common location for an Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT) to present?
Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor (AOT)
ID the pathology:
-Well defined, corticated
-Mixed density (predominantly radiolucent with some radiopacity around crown within)
-Associated with impacted maxillary lateral incisor
-Displacement of adjacent teeth
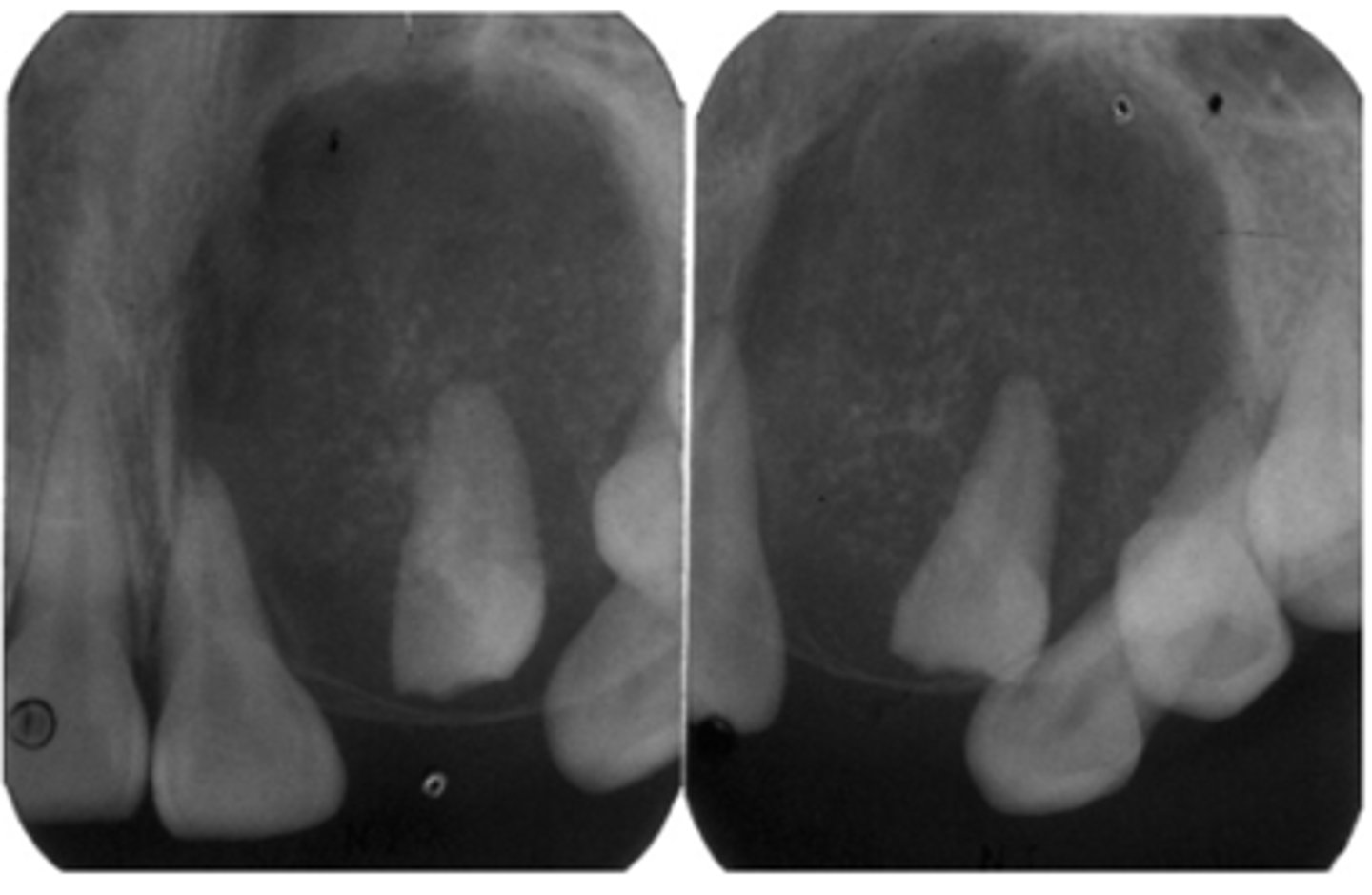
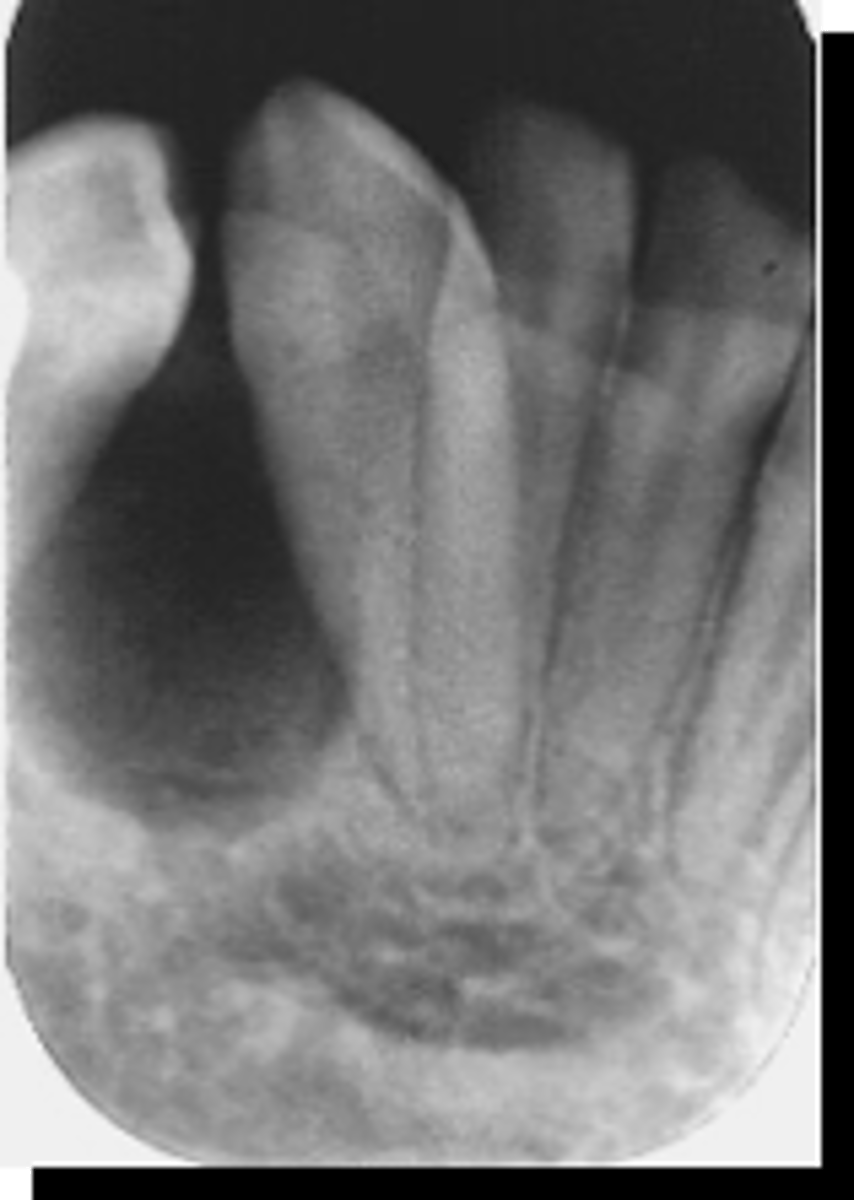
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor) (CEOT)
36 y/o patient presents with well circumscribed, corticated unilocular lesion on the posterior mandible that surrounds the crown of tooth #3, with mixed radiopacities around the crown of the tooth. Lesion is expansile and root resorption possible. What is the diagnosis?
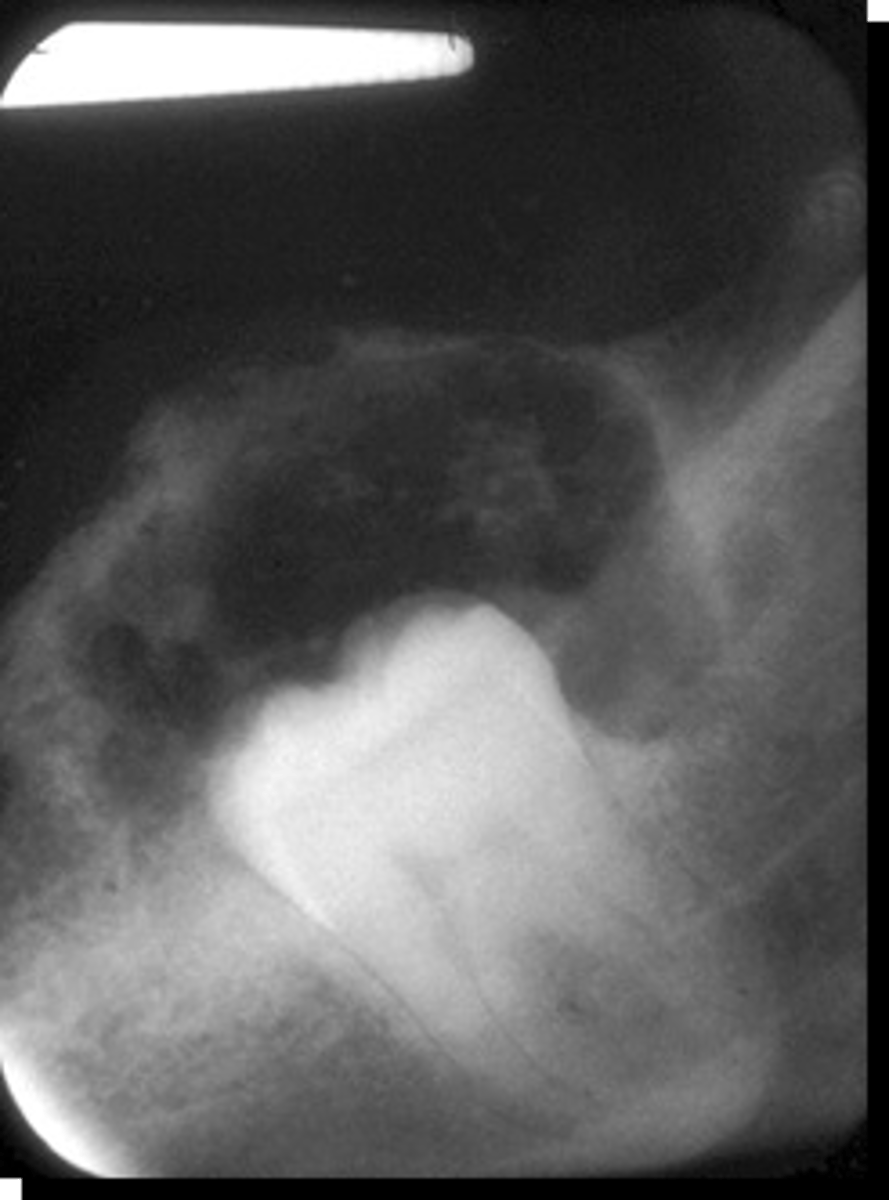
36 (8-92, any age)
what is the mean age for patients that present with a Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor)?
posterior mandible
what is the most common location for a Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor) to present?
Calcifying Epithelial Odontogenic Tumor (Pindborg tumor) (CEOT)
ID the pathology:
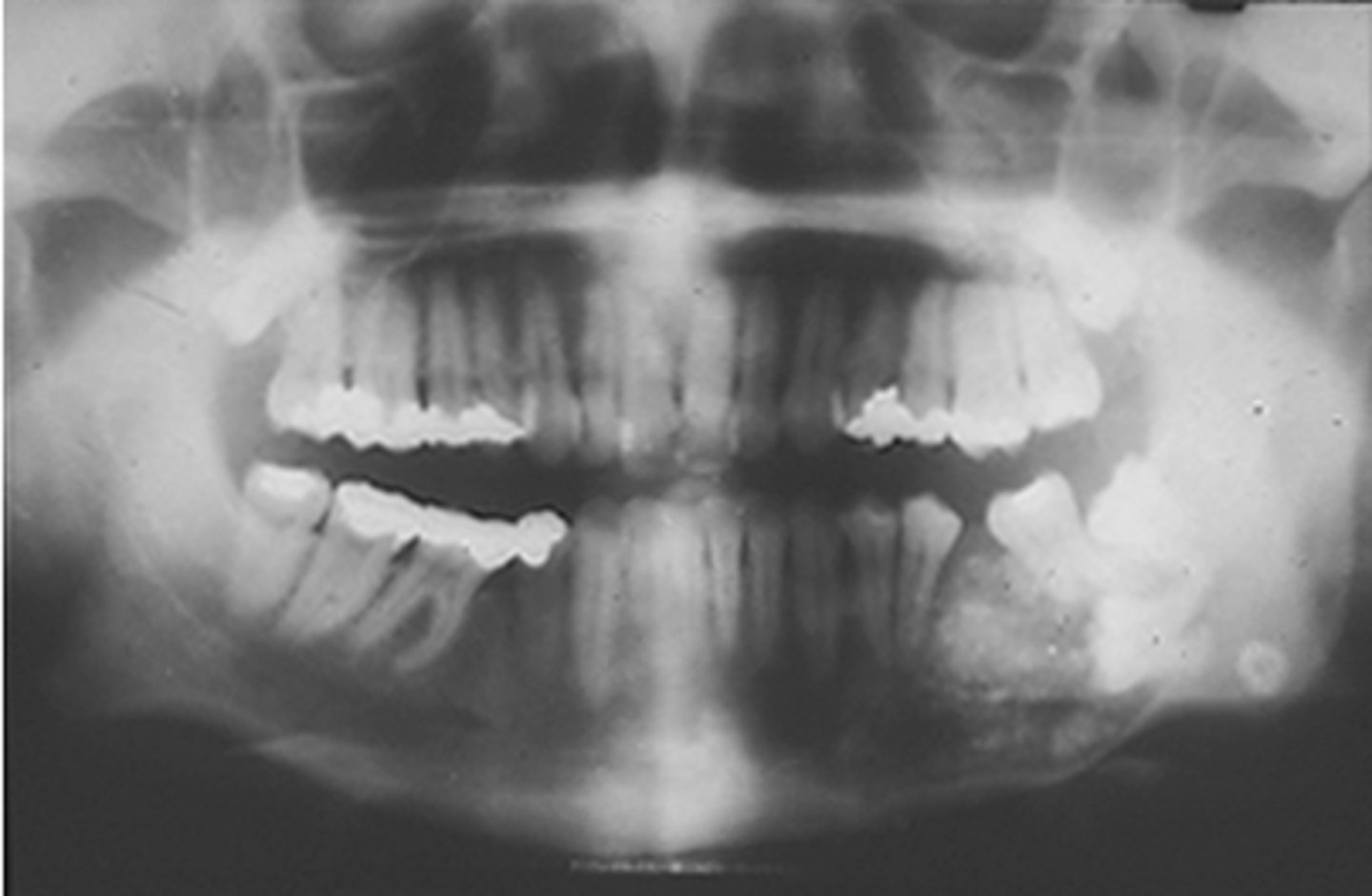
Odontogenic myxoma
15 y/o patient presents with a lesion with mix of well and ill-defined margins, radiolucent, multilocular with very thin straight and curved septae. Lesion in expansile and can cause tooth displacement. Has "tennis -racket" pattern. What is the diagnosis?
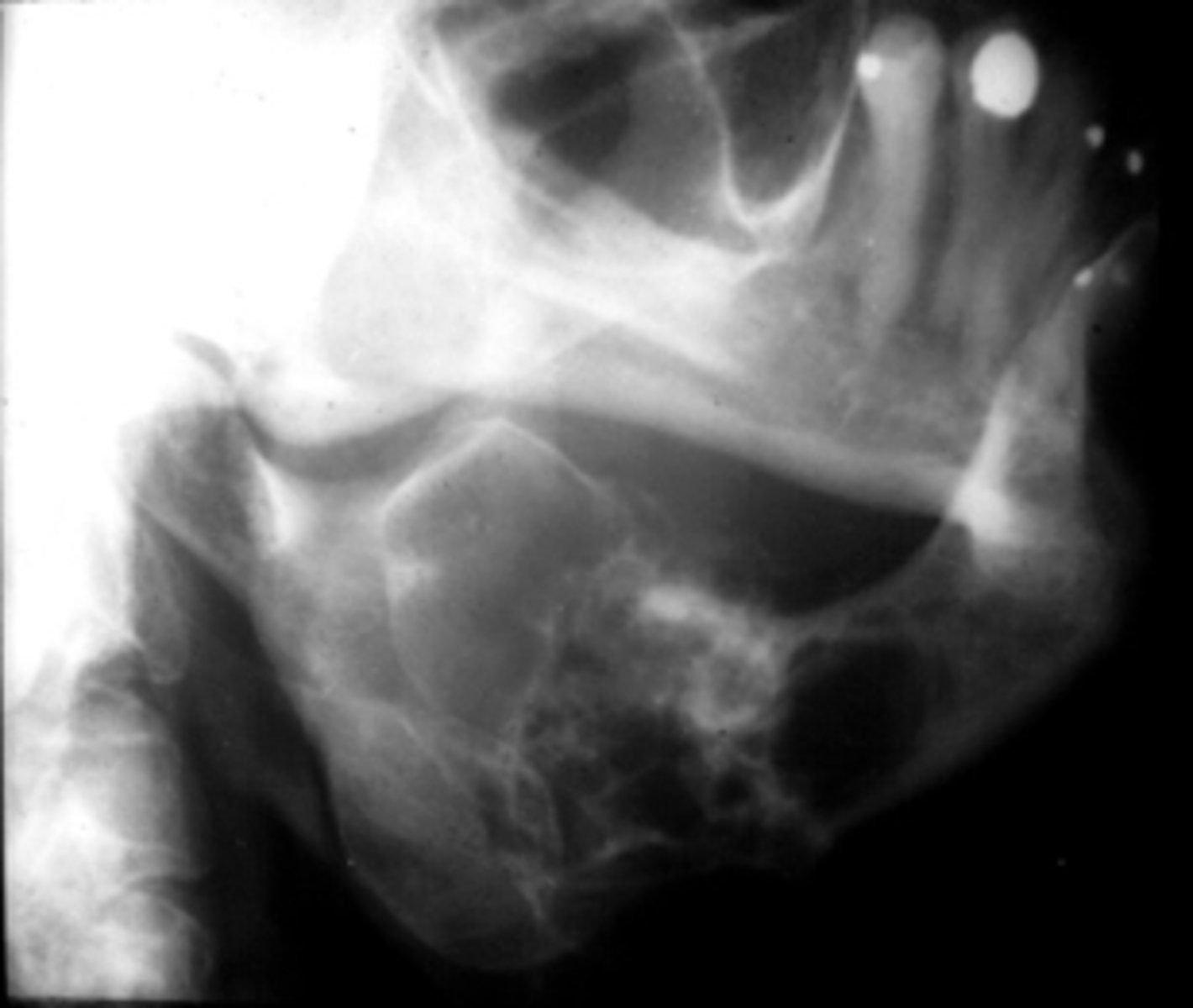
Odontogenic myxoma
this pathology cannot rule out malignancy because of it variable margins:
Odontogenic myxoma
this lesion has been described as having "tennis racket" appearance due to its thin straight septations:
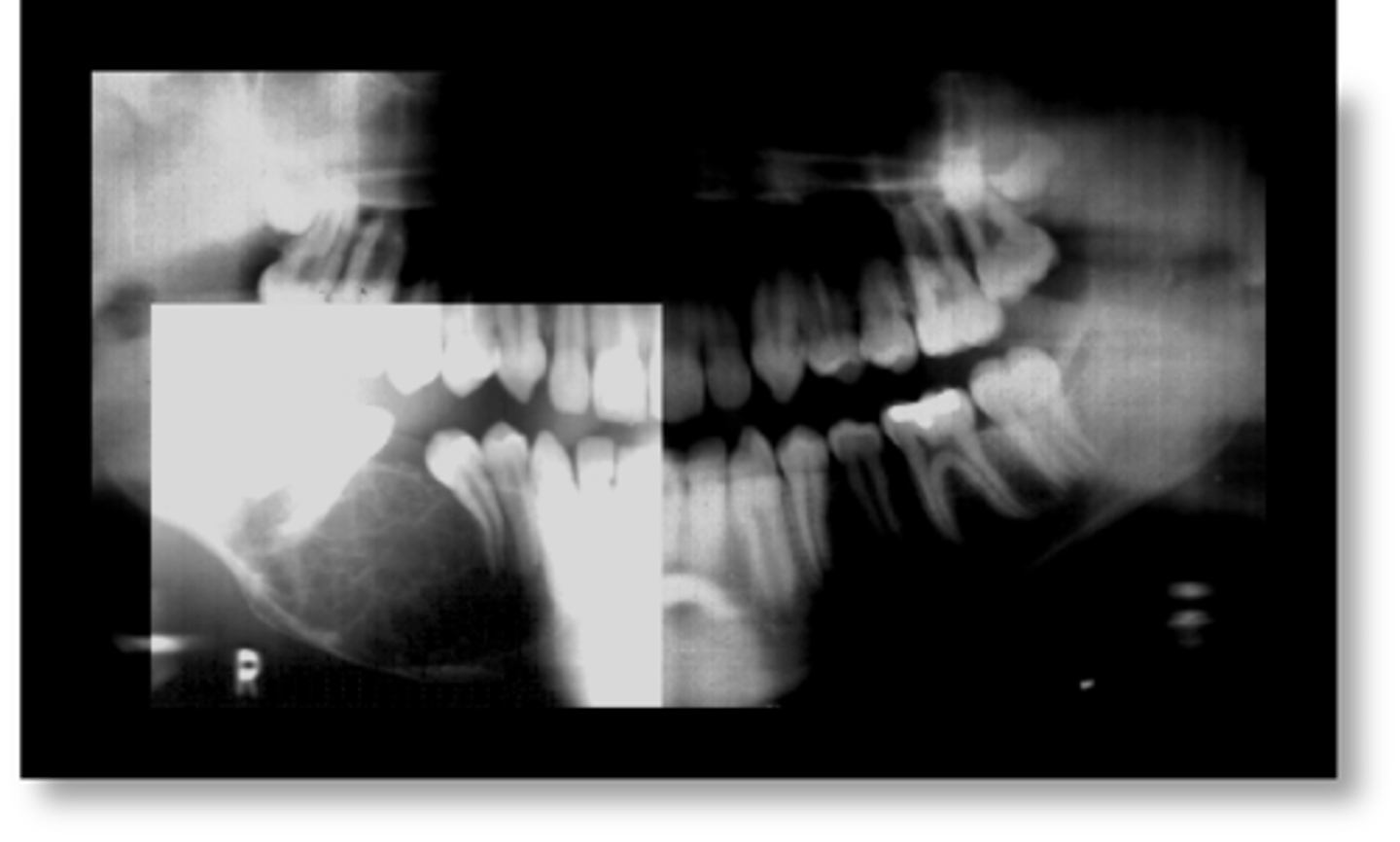
Odontogenic myxoma
ID the pathology:
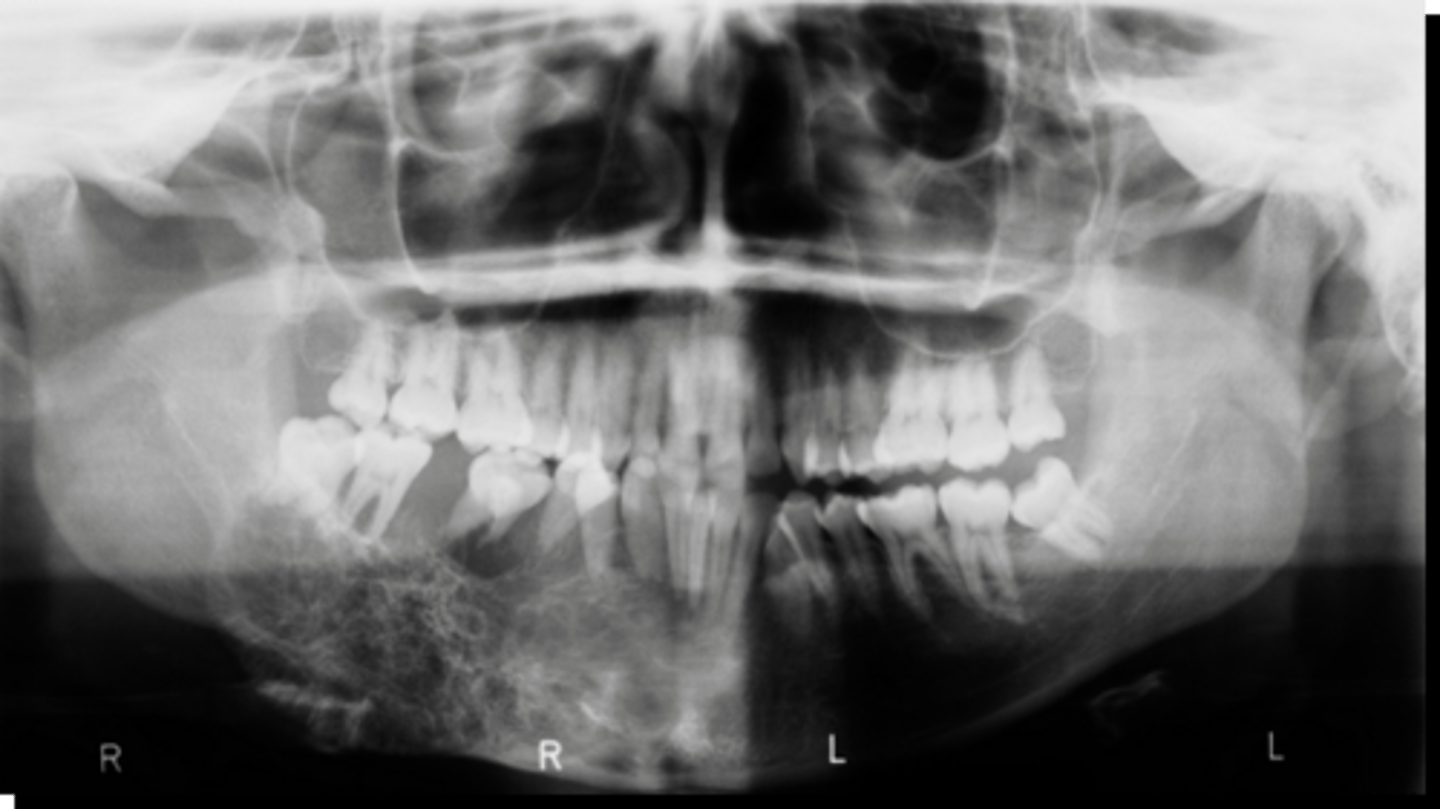
10-30 years
what is the mean age for patients that present with a Odontogenic myxoma?
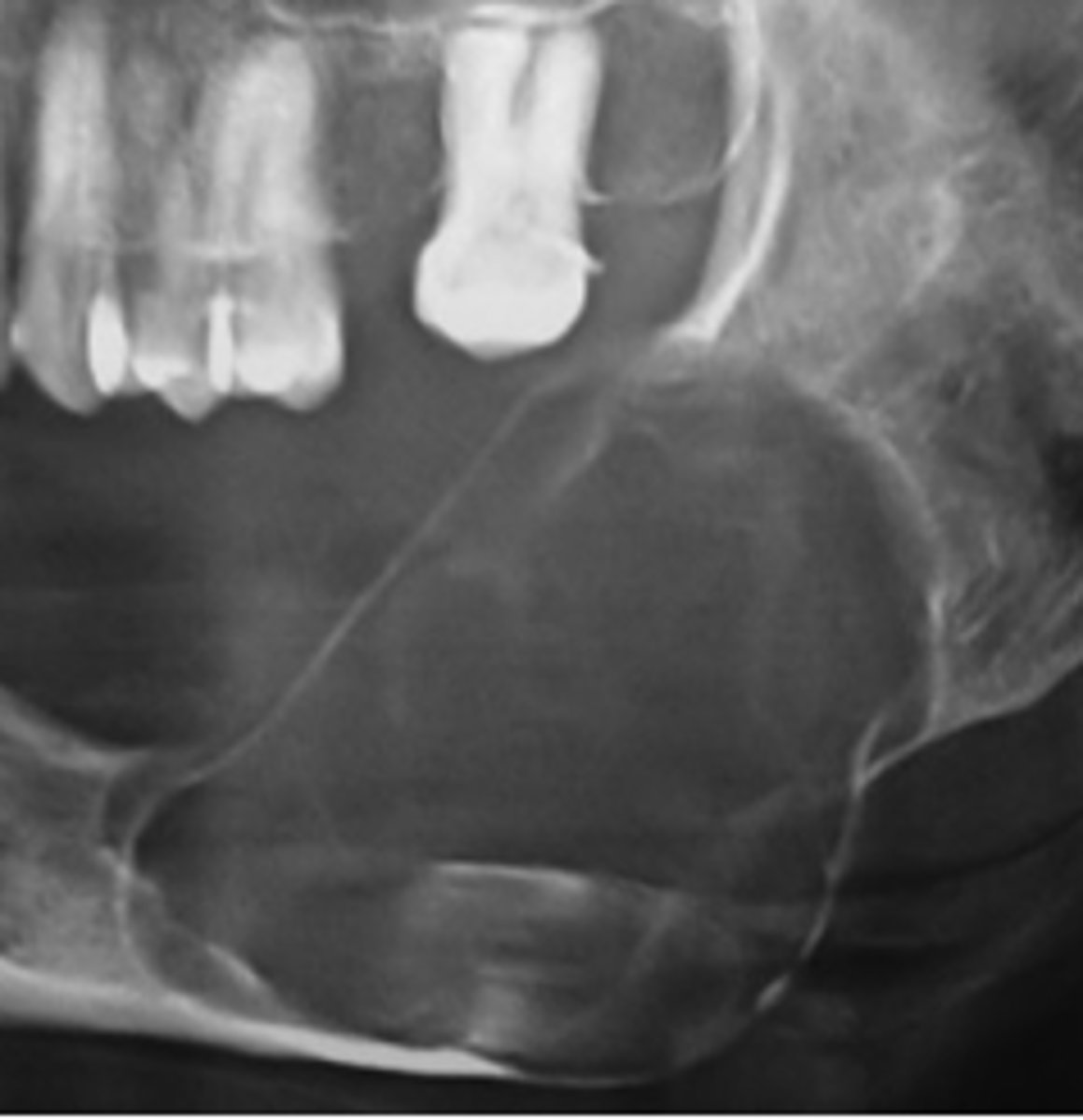
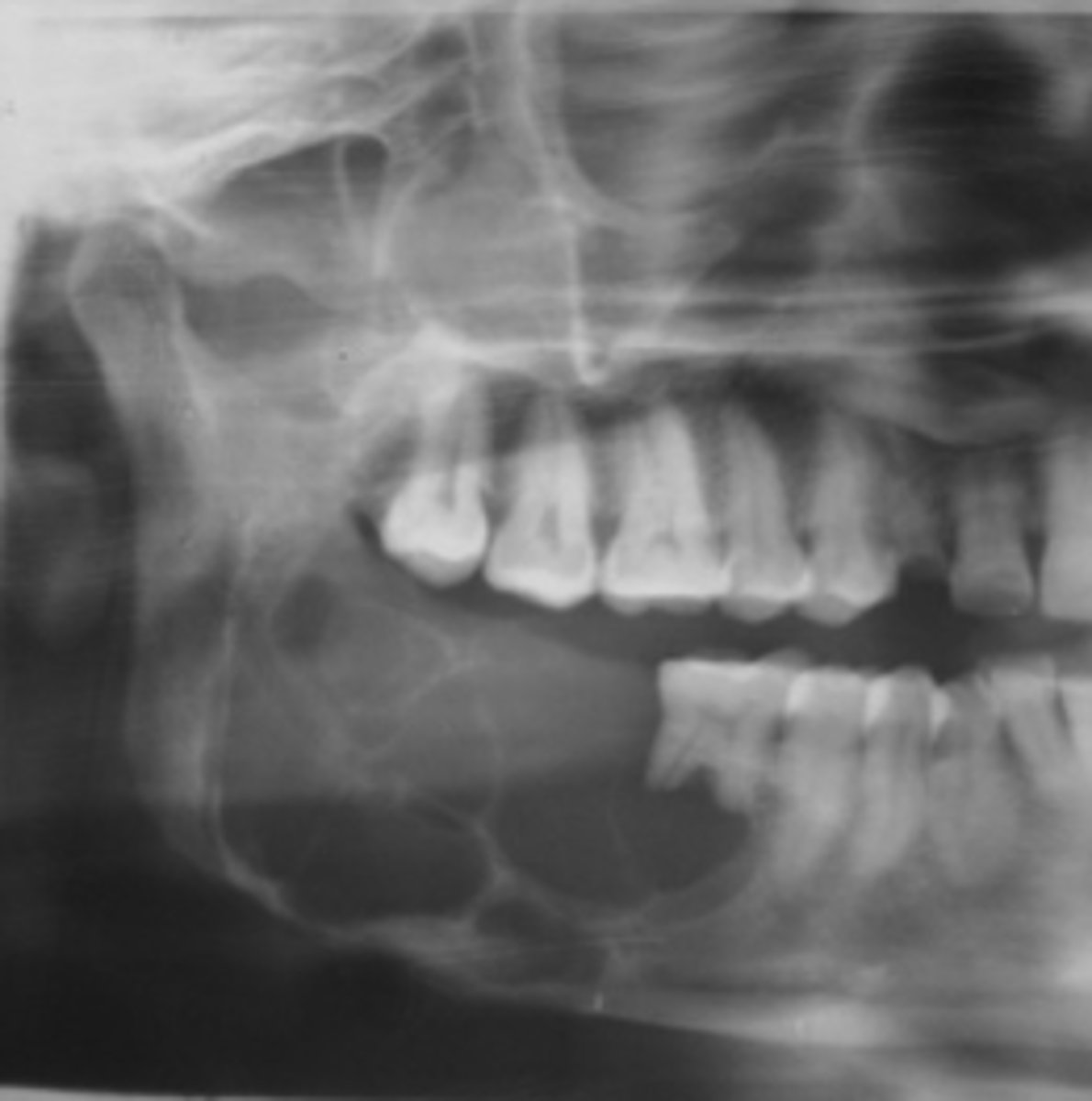
Benign Cementoblastoma
Young adult male patient presents to your office with pain and swelling. Radiograph shows a a radiopaque bulbous lesion that is attached to the root of the mandibular 1st molar (# 19), with a radiolucent corticated halo that is continuous with the PDL space of the root. Some root resorption is noted. The tooth is still vital. What is the diagnosis?
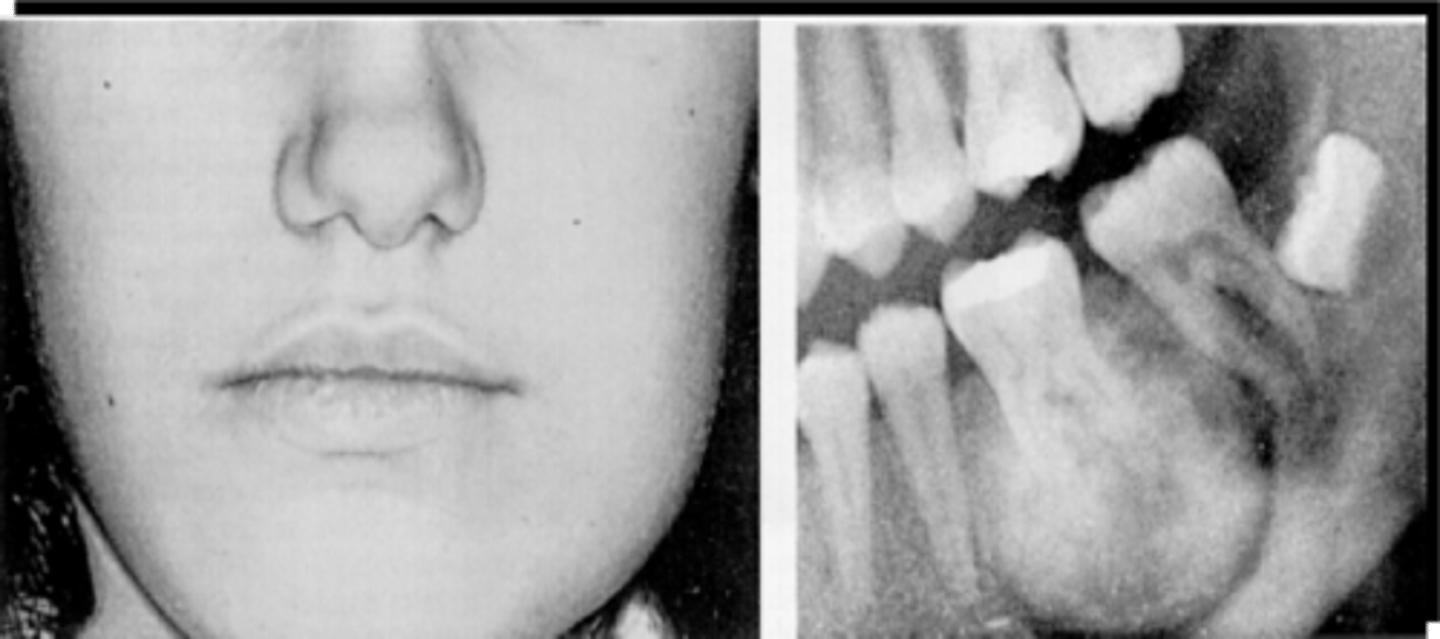
Benign Cementoblastoma
this pathology radiopaque with radiolucent rim that is continuous with the PDL space, and will be associated with the roots of #19 and #30:
Benign Cementoblastoma
ID the pathology:
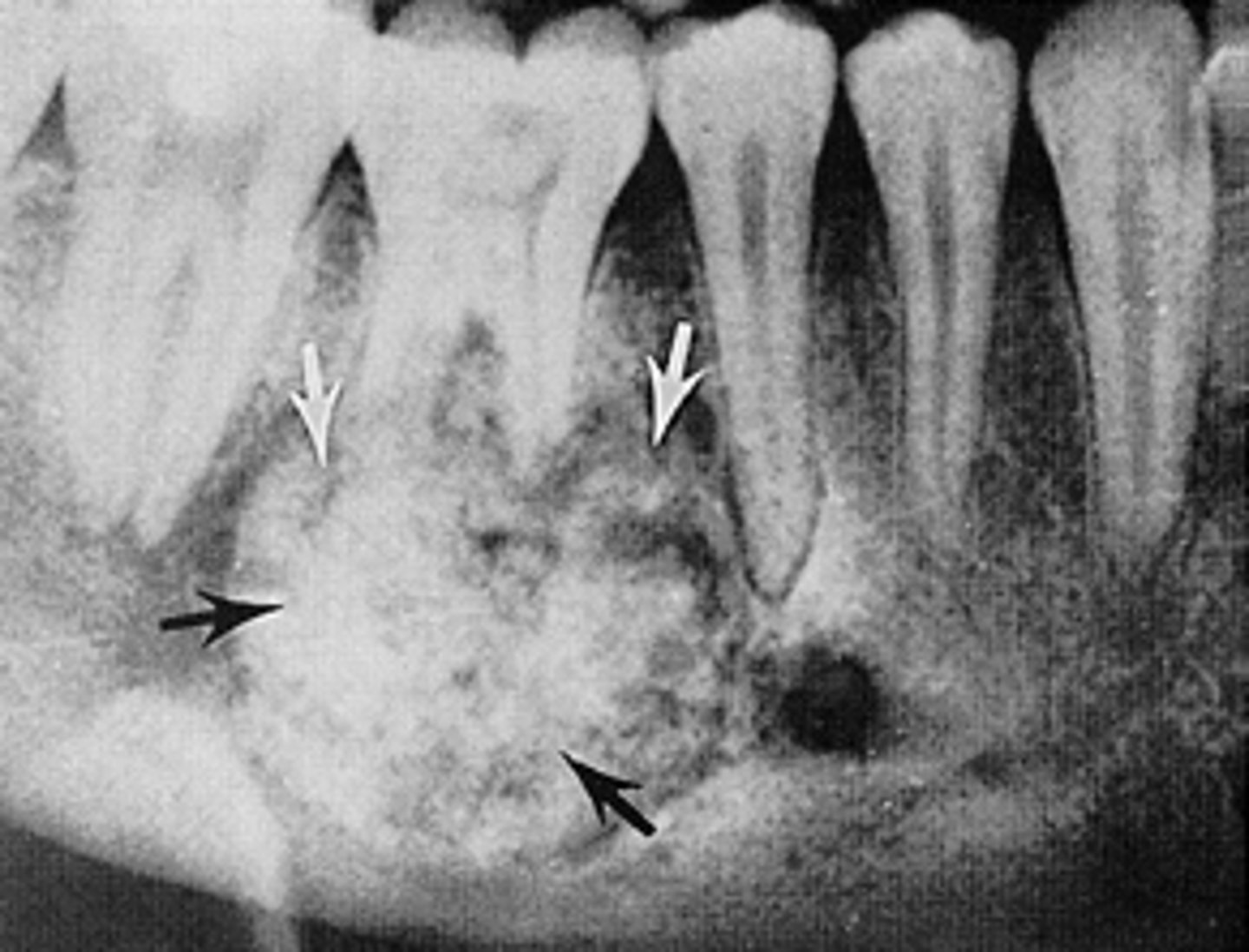
Benign Cementoblastoma
ID the pathology:
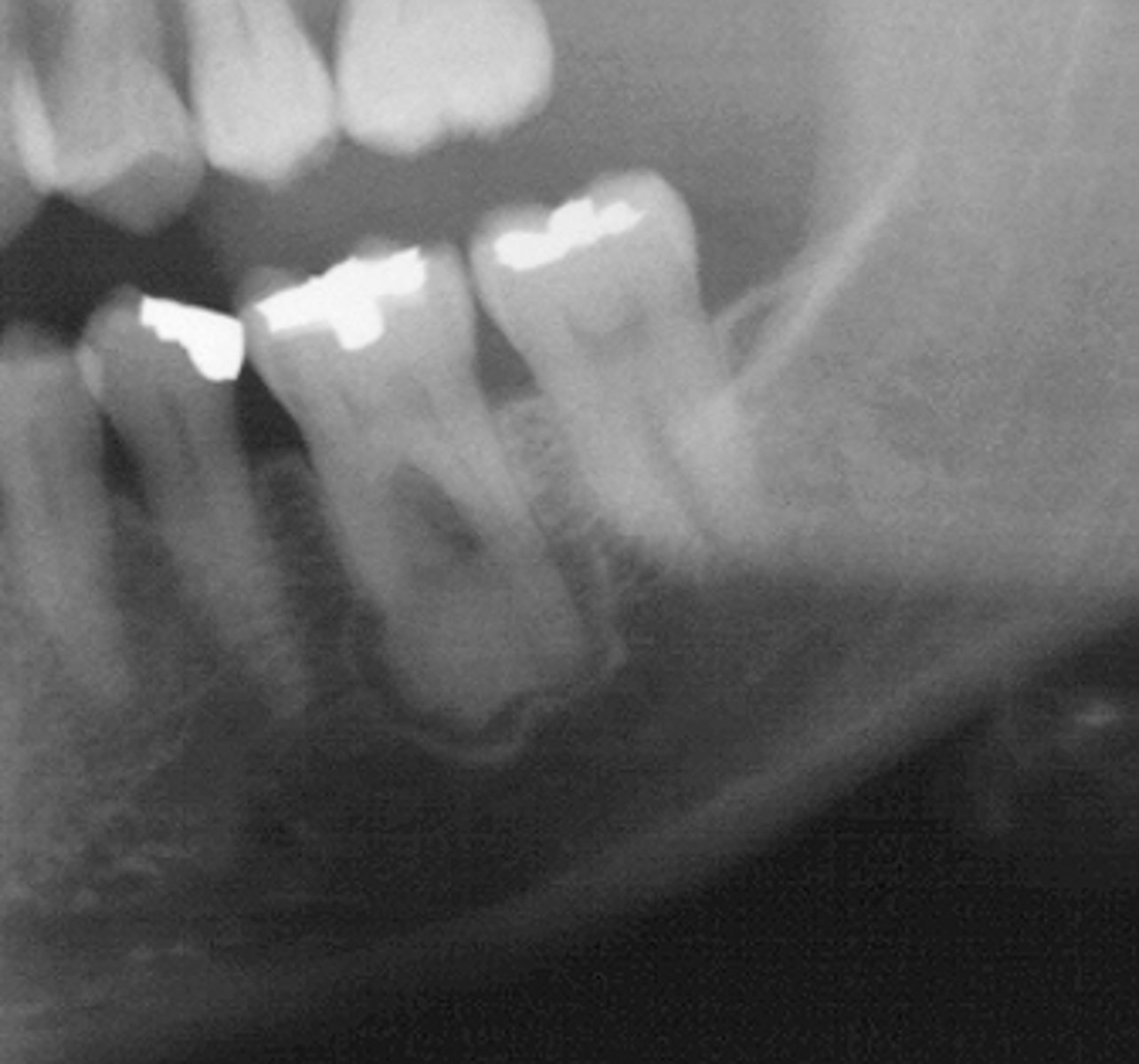
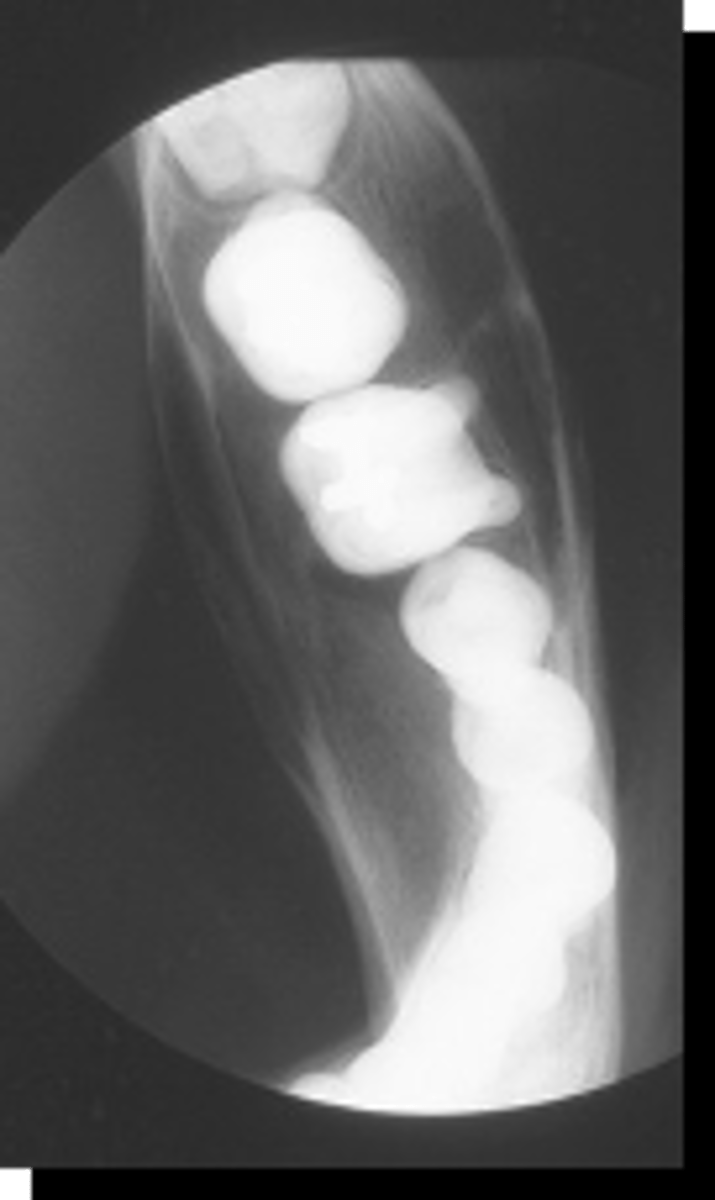
Compound Odontoma
Patient presents with well defined, corticated, radiolucent band that surrounds many radiopacities that are similar in density to enamel, located on the posterior mandible. The roots of adjacent teeth are displaced. What is the diagnosis?
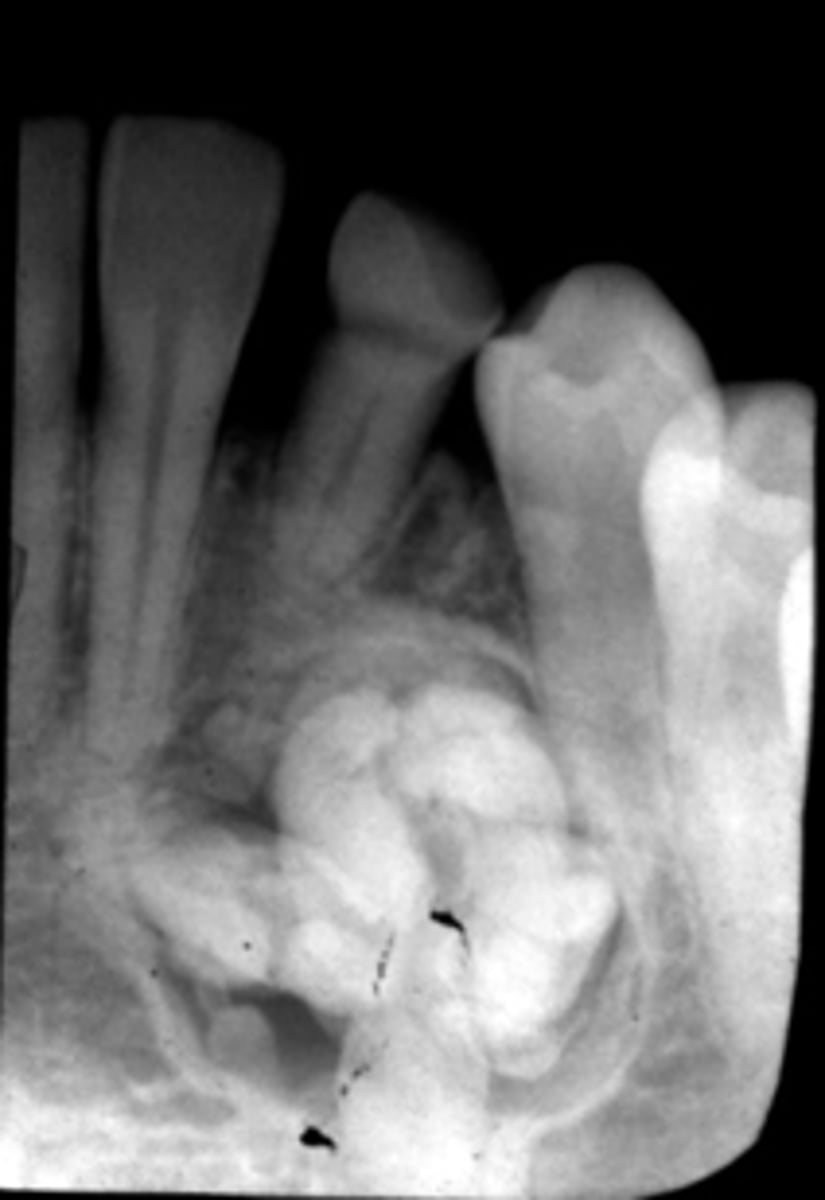
Complex Odontoma
Patient presents with well defined, corticated, radiolucent band that surrounds one large homogenous radiopacity, located on the posterior mandible. Cortical thinning and expansion, tooth impaction and root resorption is noted. What is the diagnosis?
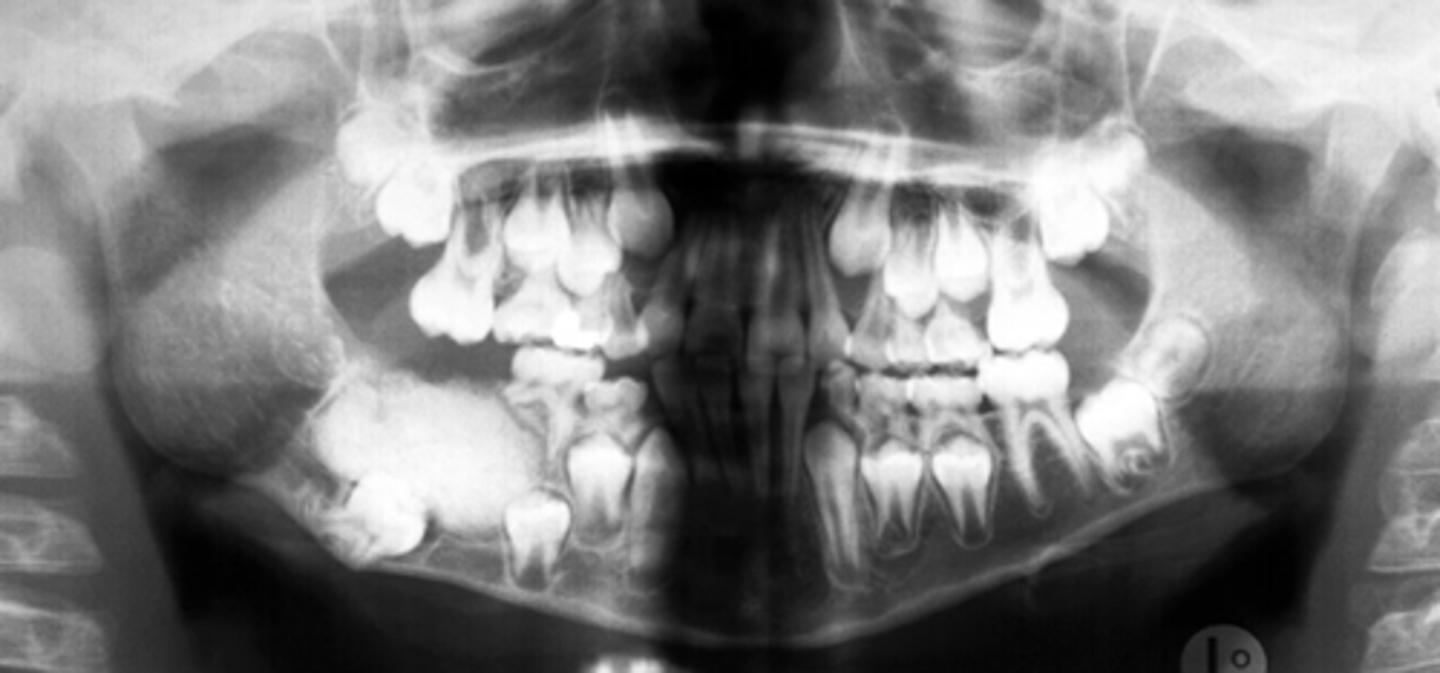
Compound-Complex Odontoma
ID the pathology:
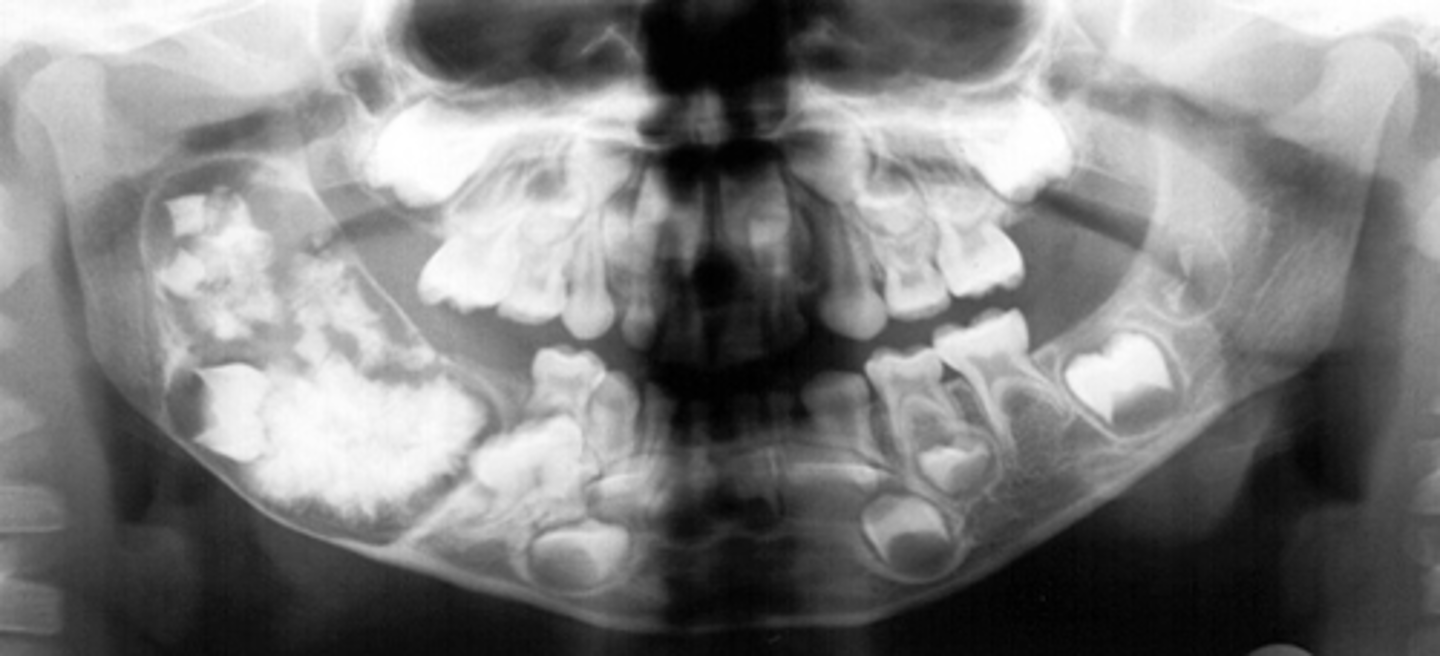
Osteoma
Patient presents with a radiograph that shows a well defined, uniformly radiopaque exophytic mass (the same density as cortical bone), located on the posterior inferior mandible. What is the diagnosis?
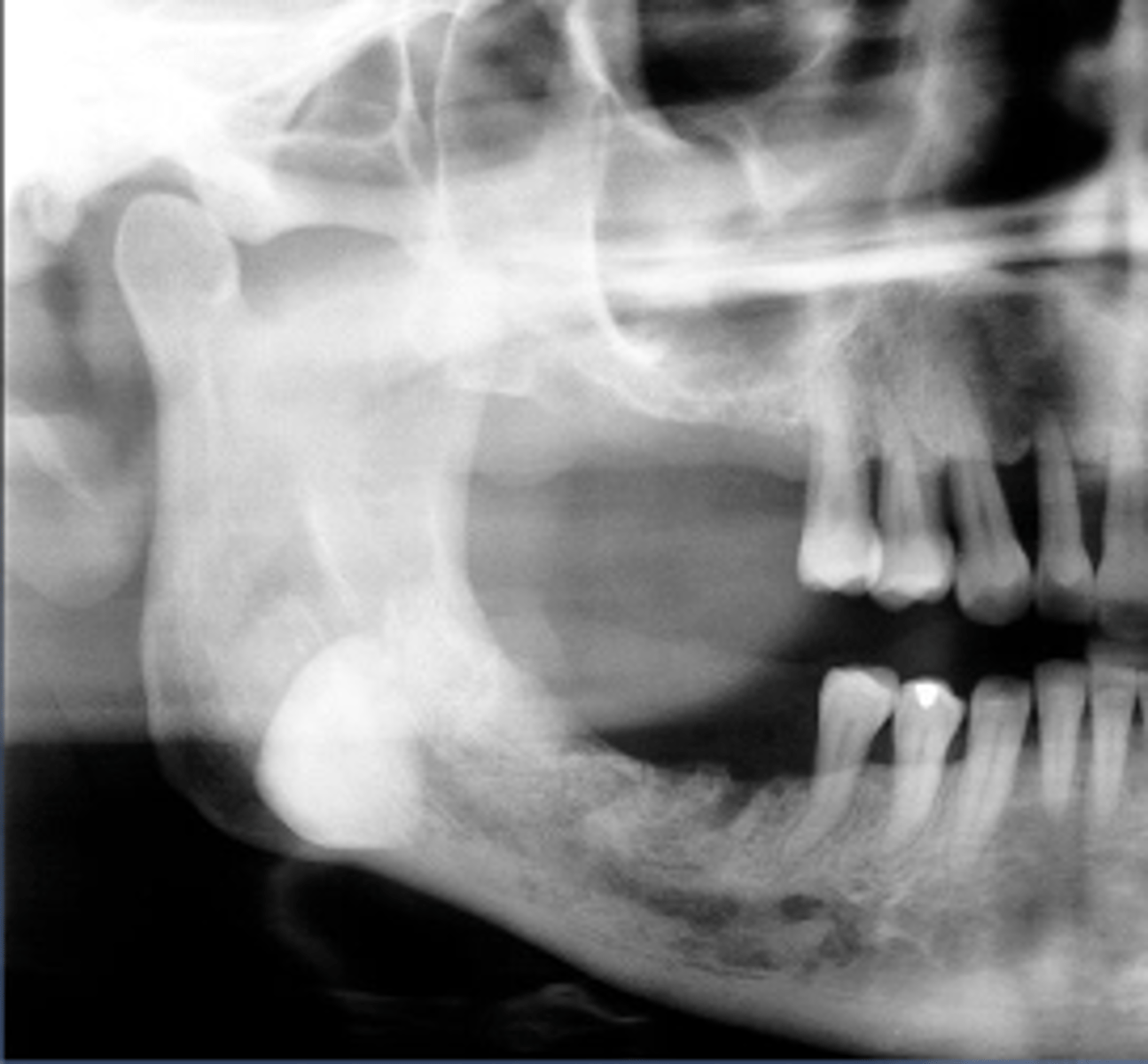
Osteoma
ID the pathology:
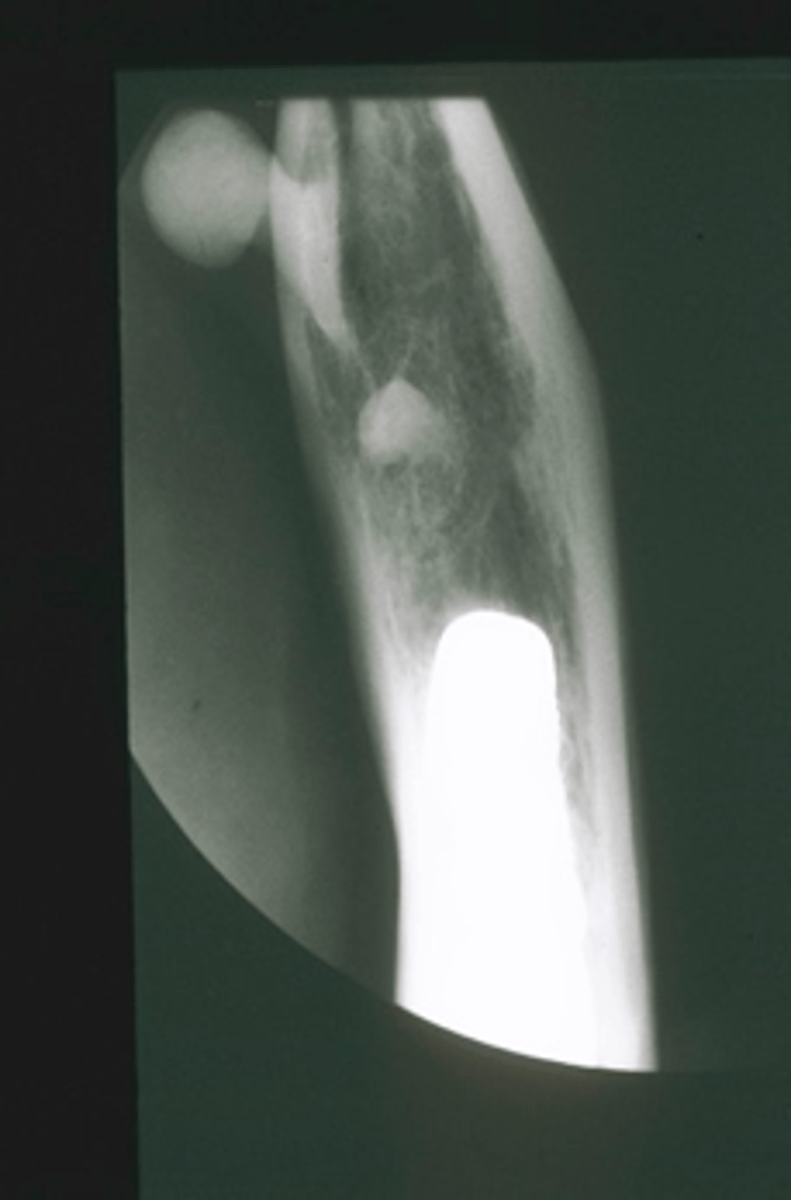
Osteoma
ID the pathology:
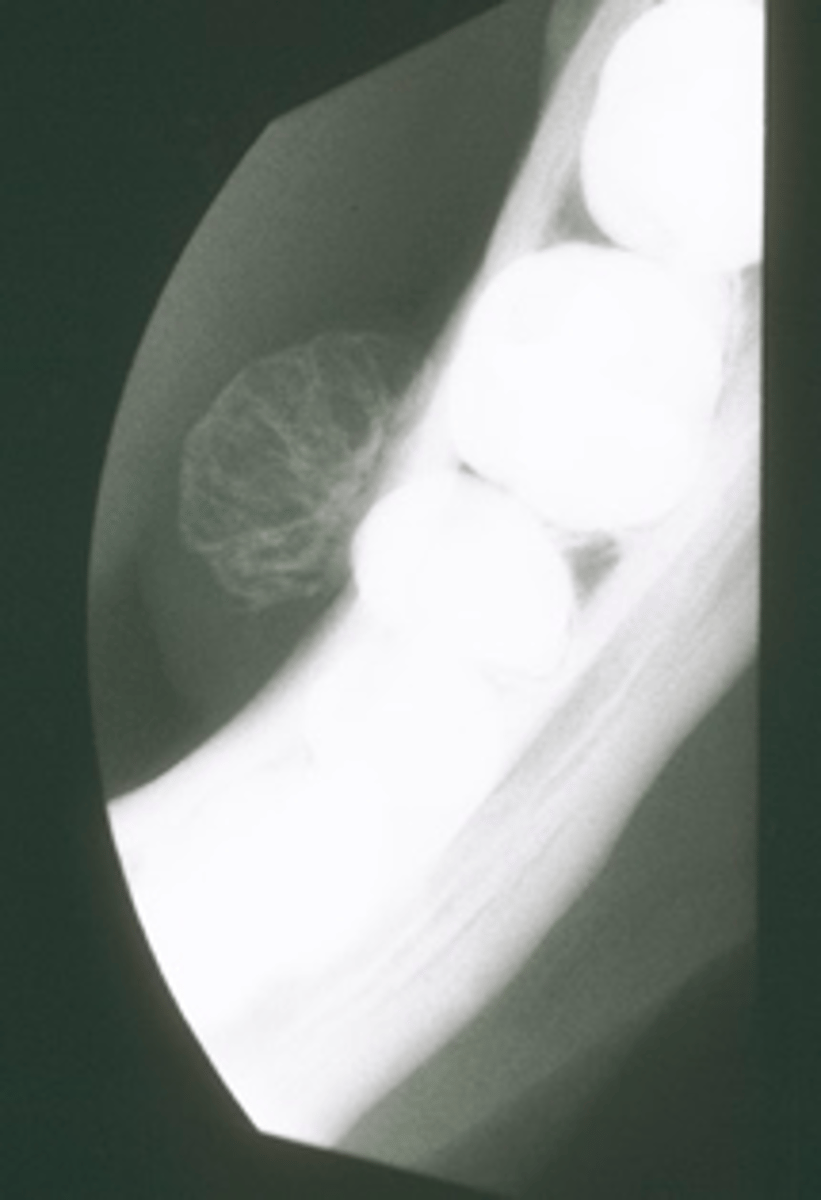
Gardner's Syndrome
Patient presents with multiple osteomas and multiple unerupted supernumerary. retained primary and unerupted permanent teeth . What is the diagnosis?
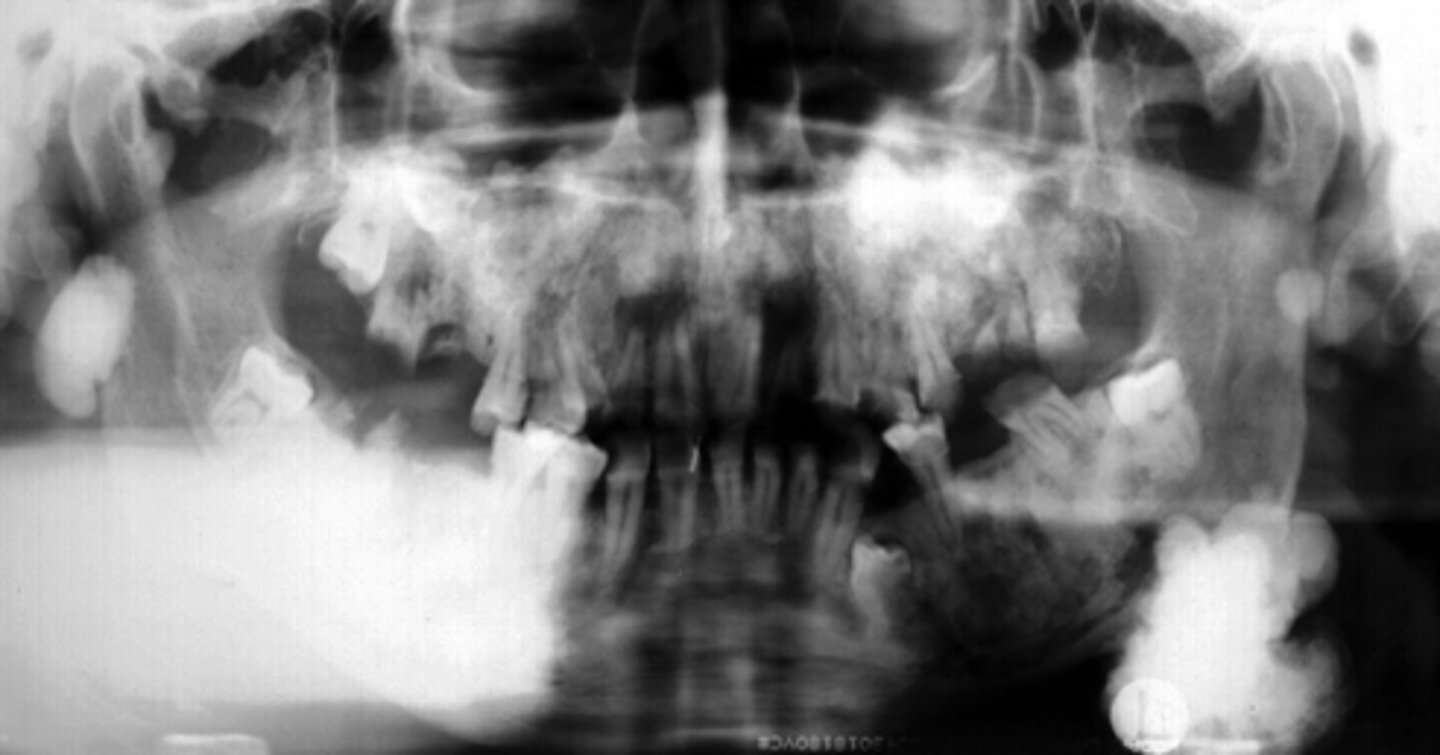
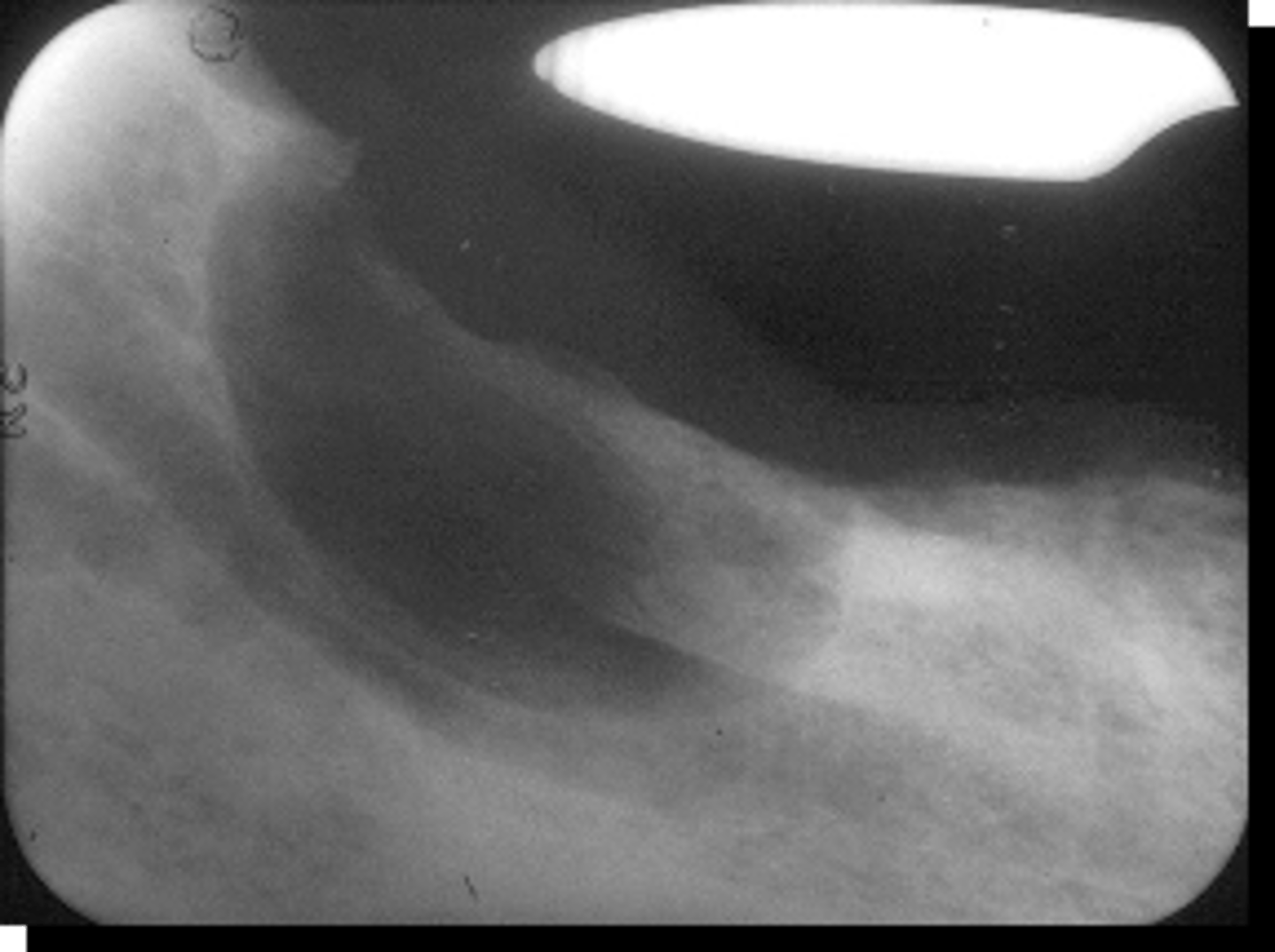
Neurofibroma
Patient presents with a radiolucent, well defined, corticated, fusiform enlargement of the neurovascular (IAN) canal. What is the diagnosis?
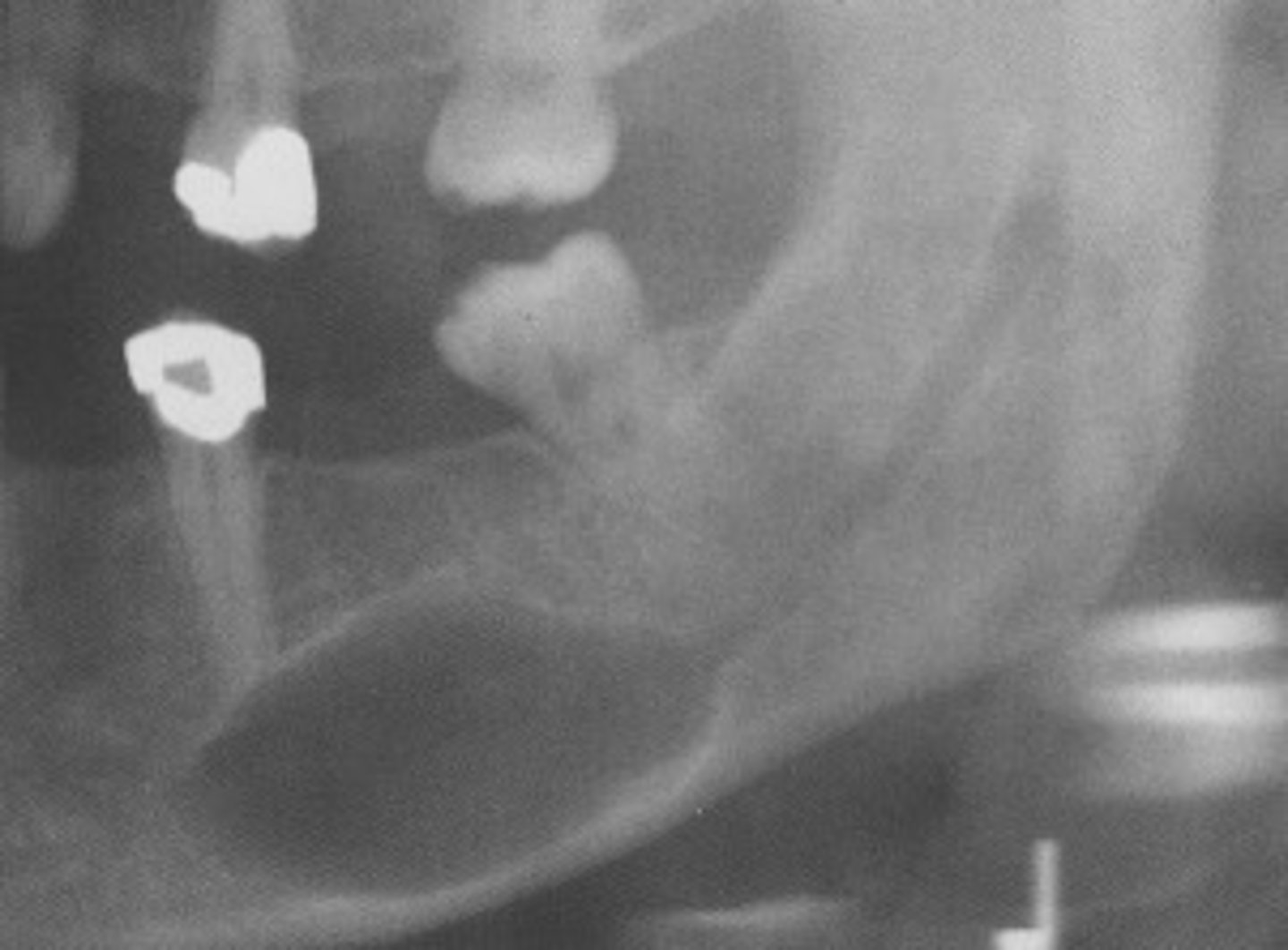
Hemangioma
This non-odontogenic tumor can present with a "sun-ray" pattern:
Hemangioma
patient presents with radiolucent lesion with a mix of well and ill defined margins, that has a "sun-ray" or 'honeycomb" periosteal reaction pattern that causes displacement of teeth and root resorption. What is the diagnosis?
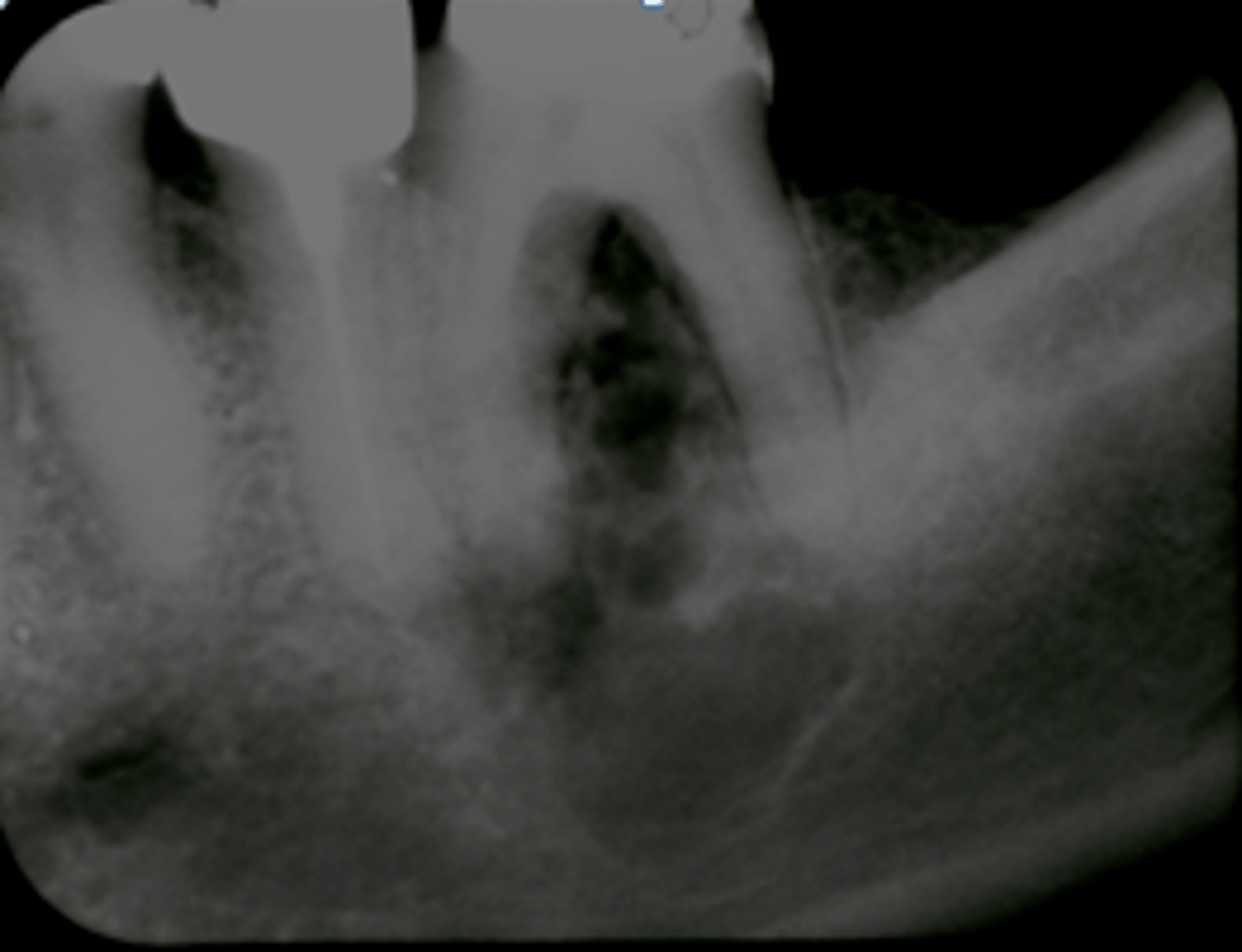
Hemangioma
ID the pathology:
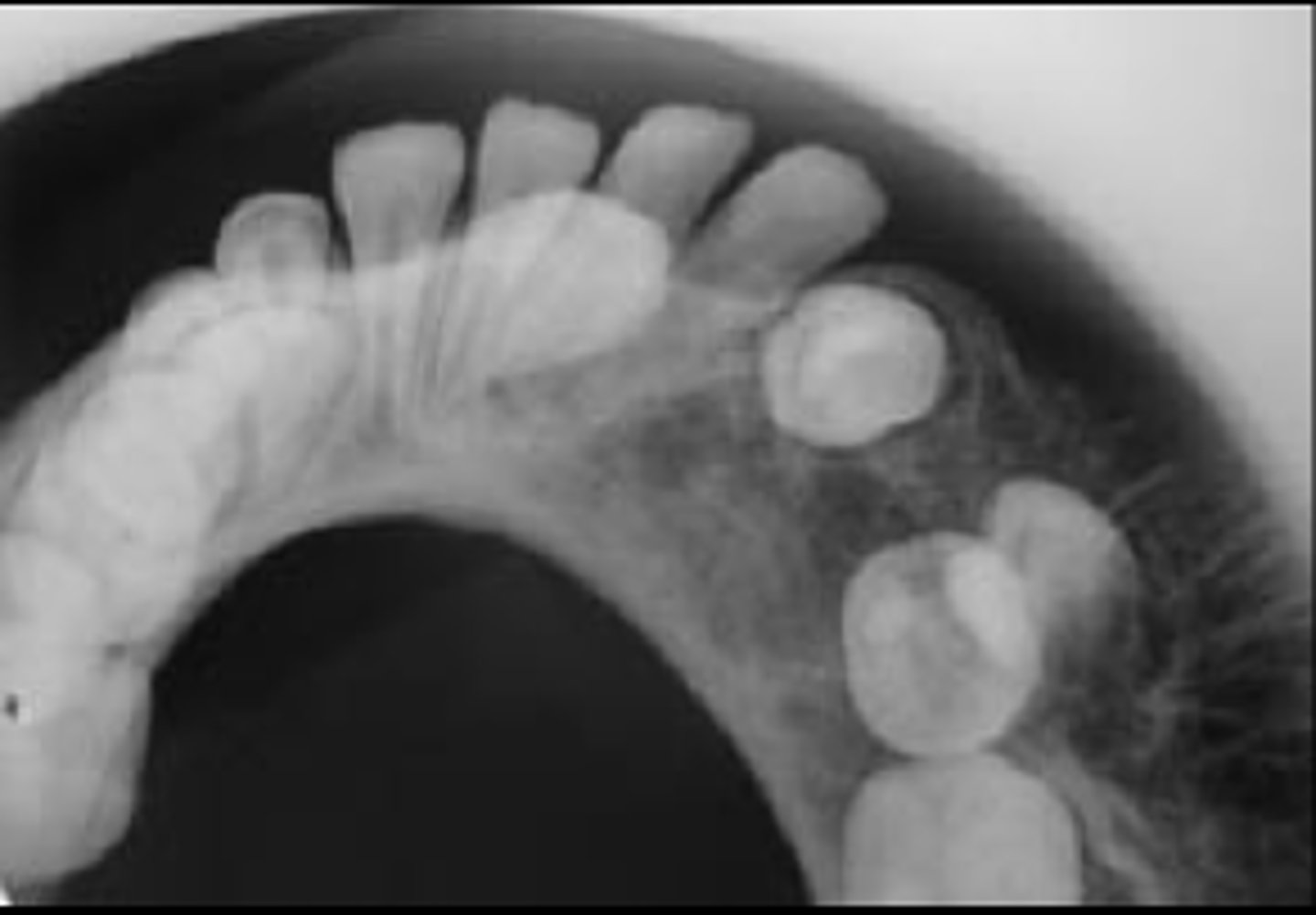
Torus Palatinus
Patient presents with a dense, radiopaque shadow in the midline of the hard palate area that has a well defined periphery and is superimposed over the roots of the maxillary teeth. Patient opens their mouth and the etiology is visible. What is the diagnosis?
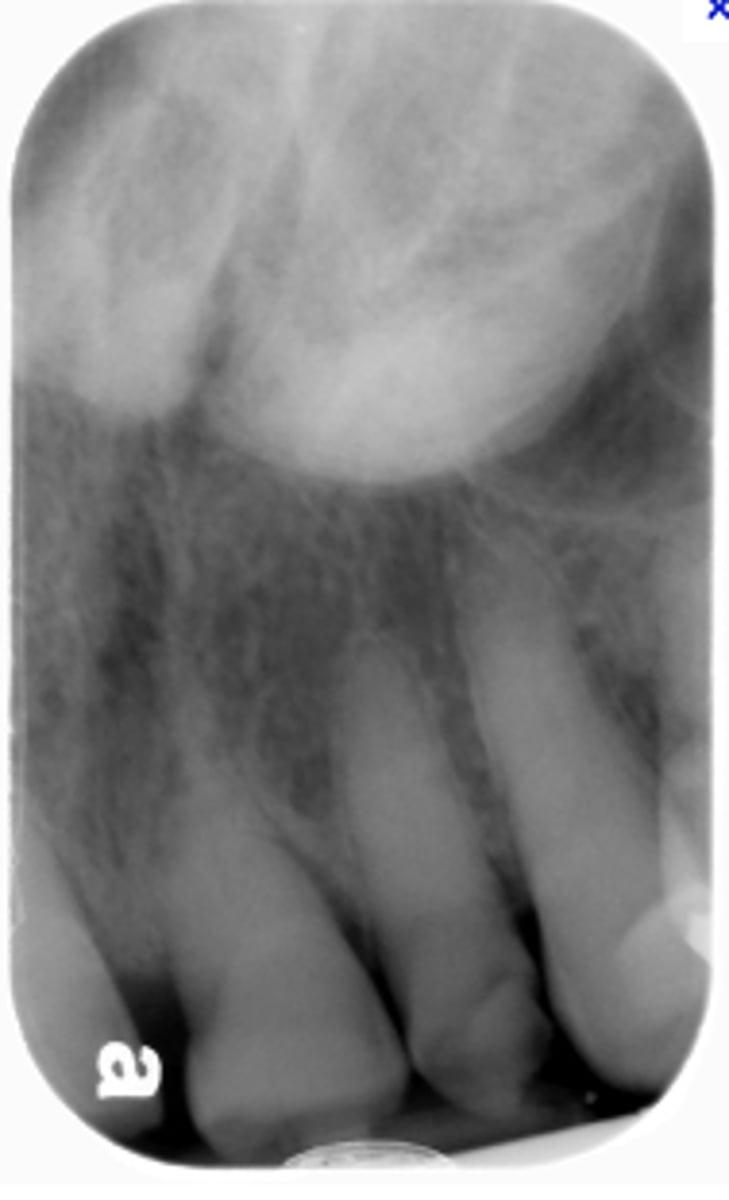
Torus Mandibularis
Patient presents with a dense, bilateral oval radiopaque shadows that superimposed over the roots of the mandibular premolar teeth. Patient opens their mouth and the etiology is visible. What is the diagnosis?
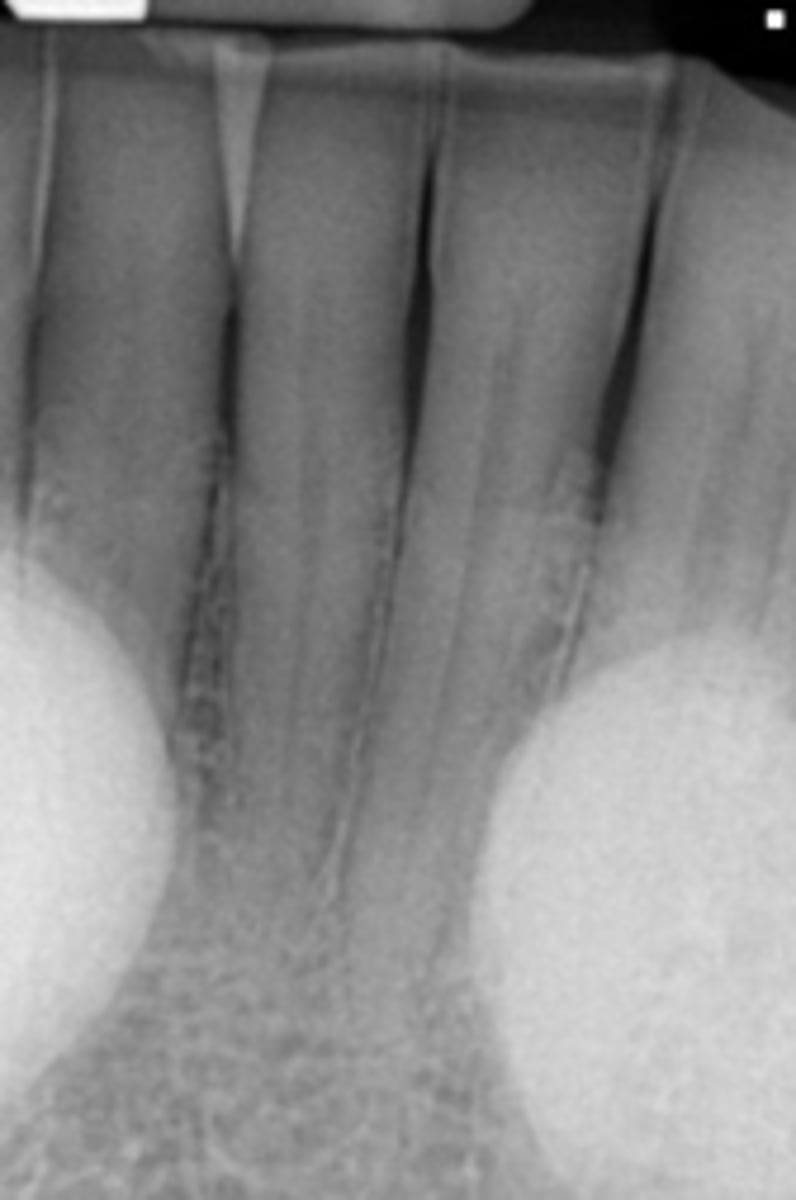
Enostosis (dense bone island/ idiopathic osteosclerosis)
Patient presents with a radiograph that has a well defined radiopaque lesion that seems to blend with trabeculae of surrounding bone. It has no affect on the adjacent teeth. This condition is contraindicated for ortho and implants due to decreased vascular supply in that region.What is the diagnosis?