🧬variation & inheritance🧬
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
where is the genetic information carried?
in the nucleus cells and is passed from generation to generation during reproduction
chromosomes
made up a large molecules of a special chemicals called DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA
long molecule made up of two strands that are twisted together to make a spiral
units of inheritance
each of your chromosomes contains thousands of genes joined together
what are the properties of genes?
controls what an orgnaism is like and determines the size,shape, colour
inherited traits
physical or behavioral features that are passed from parents of offspring through genes
examples: eye colour, hair texture, etc…
acquired traits
characteristic or attitude that organsims develop during their lifetime due to experiences and environmental influence
examples: reading skills, playing a musical instrument, etc…
why do chromosomes in pairs?
because we inherit one set from each parent, which allows for genetic diversity, ensures traits are passes down, and provides a backup if one chromosome has a problem. Humans have 23 pairs, including one pair of sex chromosomes
why do genes come in pairs?
because chromosomes that carry genes come in pairs. We inherit one copy of each gene from our mother and one from our father. This pairing allows for genetic diversity and ensures there’s a backup copy of each gene, which one help if one copy is faulty
what are the two types of reproduction?
sexual and asexual
what’s another name for sex cells?
gametes
how many chromosomes do egg and sperm have?
23
allele
alternative of a gene
what are the properties of asexual reproduction?
only involves one parent
gives rise to genetically identical offspring known as clones
the cells in your body divide into two identical cells for growth and to replace worn-out tissues
what are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
many identical offspring can be produced when conditions are favourable which is faster
more efficient because only one parent is involved in the process of reproduction
what are the disadvantages of asexual reproduction?
no genetic variation - new diseases to a single organism may destroy the whole
cannot adopt to environment
what are the properties of sexual reproduction?
involves a male sex cell and a female sex cell from two parents
these two special sex cells (gametes) join together to form a zygote which goes on to develop into a new individual
what are the gametes in plants?
ovales and pollen
what are the gametes in animals?
ova (eggs) and sperm
why is sexual reproduction so important?
The variation it produces is a great advantage in making sure that a species survives. Variation makes it more likely that at least a few of the offspring will have the ability to survive difficult conditions
gamete
a reproduction cell (sperm or cell) that contains half the genetic information of the parent
variation
differences in characteristics among individuals of the same species, caused by genetic or environmental factor
what is the new plant produced by?
asexual reproduction
in asexual reproduction, how do body cells divide?
mitosis
haploid cells
contains just half of the number of chromosomes and gametes
diploid cells
almost all other cells, complete number of chromosomes
meiosis
a form of cell division which produces four non-identical, haploid sex cells or gametes
what happens when a meiosis cell divide to form gametes?
copies of the genetic information are made
the cell divides twice to form four gametes, each with a single set of chromosomes
gametes are haploid
all gametes are genetically different from each other
what are the causes of variation?
some differences between the organisms of a species are entirely due to the environment they live in
genetically identical plants can be grown under different conditions of light, carbon dioxide, or nutrients or don’t make as much food as plants with plenty of everything
will be smaller and weaker
haven’t been able to fulfill their genetic potential
what’s the same ONLY genetically identical humans?
identical twins who came from the same fertilised egg
continuous variation
gradual transition between two extremes
features are determined by a number of different genes are affected by the environment
discontinuous variation
little or no environment impact on the features
features are determined by a single gene (or chromosome)
genes control the development of characteristics
may be changed by the environment
how many pairs of chromosomes do humans have?
23 pairs of chromosomes
each chromosome in the pair is a similar shape
sex chromosome
one pair of is different
two X chromosomes: female
one X chromosomes + a smaller one, Y chromosomes: male
Parents: Genetype = XX x YY
Phenotype = female x male

genotype
genetic make-up of an individual regarding a particular characteristic
phenotype
the physical appearance of an individual regarding a particular characteristic
dominant allele
alleles that control the development of a characteristic even when they are only present on both chromosomes
recessive alleles
alleles that only present on both chromosomes
homozygous
an individual with two identical alleles for a characteristic
heterozygous
an individual with different alleles for a characteristic
monohybrid crosses
genetic cross involving the inheritance of a single gene
what does a punnett square show us?
the alleles for a characteristic carried by the parents (the genotype of the parents)
the possible gametes which can be formed from these
how these combine to form the characteristic in their offspring
what are the family tree annotations for mother and father genotype?
mother genotype = ee
father genotype = EE
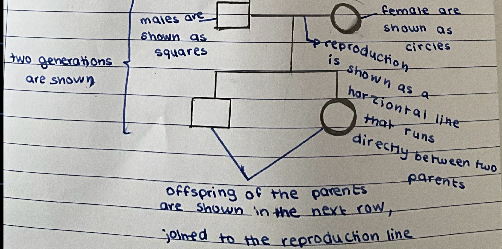
a family tree diagram
a model of inheritance showing characteristic was passed from parents to offspring
what is the property of a carrier of a recessive genetic disoder?
a carrier of a recessive genetic disorder does not express the disorder in their phenotype but one recessive allele in their genotype that can be passed to offspring
inheritance
the passing of genetic information from parents to offspring by reproduction
diagram of a family pedigree
nucleotides
the building blocks of DNA
four different types
linked together to form strands
base
part of nucleotide that can make it different from others
double helix
two strands of nucleotides twisted around each other to form a shape
what holds a double helix’s two strands together?
by weak bonds between pairs of bases
what determines the sequence of bases in a DNA molecule?
can determine the order of animo acids in a protein molecule
what’s the 2 different location where the instructions for making proteins and the structures where protein are made?
DNA is stored in the nucleus
ribosomes
ribosomes
proteins are assembled from free amino acids in the cytoplasm in structures
how is the chemical messenger RNA (MRNA) mode?
made in the nucleus and carries a copy of the DNA base sequence of a specific gene to the cytoplasm
polydactyly
a dominant condition where a body is born with extra finger or toes
it can be inherited from one parent who has the condition
what are the properties of polydactyly’s?
if one your parents has polydactyl and is heterozygous, you have a 50% (one in two) chances of inherit the disorder
because half of their gametes will contain a faulty a dominant allele
meiosis
results in the formation of four genetically non-identical daughter cells
used in sexual reproduction
what are the 4 features of asexual reproduction ?
no gamete fusion
offspring are clones
cells divide by mitosis
two sets of chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell, then the nucleus divides into two
only one parent
what happens to cell in the reproductive organs?
divide by meiosis to create gametes (contain half of the number of chromosomes which contains DNA found in all body cells
how are gametes formed, and what happens during meiosis?
gametes are formed through meiosis, where a diploid cell replicates its chromosomes, splits into two, and divides again to create 4 genetically different haploid cells
what happens after fertilisation?
the make and female gametes fuse to form a zygote with 46 chromosomes. The zygote with 46 chromosomes. The zygote then divides by mitosis, and as it grows into an embryo, its cells differentiate to perform specific functions
what are the advantages of sexual reproduction?
variation in offspring: increases the chances of the population being able to survive environmental change by natural selection
artificial selection: humans can speed up artificial selection breeding of plants & animals
depends on genetic variation
what are the advantages of asexual reproduction?
no mate
faster
lots of identical offspring
what are the levels of organisation?
DNA: double helix polymer
means it’s a polymer (a large molecule made up of many subunits) made up of two strands forming a twisted shape
genes: a small section of DNA
chromosomes: long strands of DNA are coiled up to form chromosomes
humans body cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes, one of each pair coming from each parent
domaint allele
always expressed
only needs one copy present to be expressed (BB or Bb)
recessive allele
only expresses if the other allele is also recessive
needs two copies to be present to be expressed (bb)
genetype
combination of alleles an organism has
if the two alleles are different, we say that the person is heterozygous (Bb)
if the two alleles are the same, we say that the person is homozygous (BB or Bb)
phenotype
alleles present will determine a characteristic, unless the environment interferes
what is the name of the diagram that can used to visualise the outcome of monohybrid cross?
punnet square
how can punnet squares be used to visualise the outcome of a monohybrid cross?
1) the alleles of the parents are drawn along the top and side of a grid
2) in the punnet square diagrams, a capital letter shows a dominant allele
3) the pairs of alleles that the offspring could have are then filled into the grid in the four middle squares
what are family rees can be used to visualise?
the transmission of inherited disorders from one generation to the next
what form of genome screening can be used to prevent a baby growing up suffering with a genetic disorder?
embryonic screening
what are the disadvantages of embryonic screening?
since the embryo that aren’t are destroyed, this can be unethical
expensive
discrimination
parents become selective
what are the two types of chromosomes?
males: XY; so a sperm contains either one X or Y one chromosome
females: XX; so an egg contains one X chromosome
what are the differences in variation?
genetics (inherited genes)
genetics and environment
the environment
what does speciation happen?
happens when the average phenotypes (observed characteristics) of two populations have diverged (changed) so much that the populations can longer breed to produce fertile offspring (offspring can reproduce)
what are the properties of natural selection?
the characteristics that maximise survival chances are passed on
individuals display genetic variation
those with the best characteristics are more likely to breed
what does selective breeding happens?
happens when humans chose animals and crops to breed, based on their genetic characteristics
after breeding parents with the desired characteristic, what is the next step in the selective breeding process?
from the resultant offspring, chose the ones who most strongly display the desired characteristics and breed them
what are the 2 most common reasons for a characteristic being considered desirable?
usefulness and appearance
what are the problems of selective breeding?
Inbreeding: some breeds become particularly susceptible to disease or inherited defects
Reduced variation: makes it harder for a species to adapt to environmental change
what are the properties of genetic engineering?
modifying an organism’s genome
introducing a gene from another organism
what type of crops are through by some people to negatively impact wild flower and insect populations, and reduce biodiversity?
GM crop
what are the ways plants can be cloned?
tissue cultures
cuttings