Practice Problems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
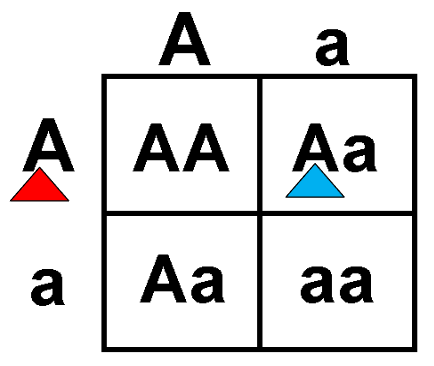
The A tagged in blue represents which?
A. Allele in a gamete
B. Allele in a parent genotype
C. Allele in an offspring genotype
D. Phenotype in either parent or offspring
C
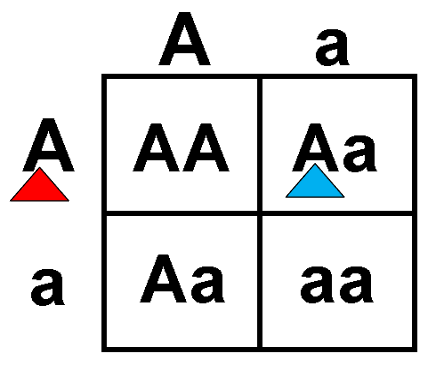
The A tagged in red represents which?
A. Allele in a gamete
B. Allele in a parent genotype
C. Allele in an offspring genotype
D. Phenotype in either parent or offspring
A
What proportion of the progeny are YY Rr in the following cross?
Yy Rr × Yy Rr
A. 1/4
B. 1/2
C. 1/16
D. 1/8
D
The A allele frequency is 0.7 means...
A. the proportion of individuals
showing the A trait in their
phenotype
B. the proportion of individuals with
any A alleles in their genotype
C. the proportion of A alleles in the
total gene pool
C
There are two alleles for a certain gene locus, A and a.
70% of the alleles in a particular gene pool are A.
What is the allele frequency of a ?
A. 0.20
B. 0.30
C. 0.50
D. 0.50
B
In the H-W equation p + q = 1, the term “p” usually refers to which?
A. frequency of individuals showing the dominant trait
B. frequency of individuals showing recessive trait
C. frequency of the dominant allele in the gene pool
C
In the H-W equation p2 + 2pq + q2, the term “2pq” refers to the frequency
of which?
A. individuals showing the dominant trait
B. individuals that are heterozygotes
C. individuals showing the recessive trait
B
Is a geographic barrier alone an evolved
reproductive isolating mechanism?
A. Yes, because it is currently keeping the
two populations apart.
B. Yes, because the two populations would
always adapt to different environments
on different sides of the barrier.
C. No, because if the geography changes
and the two separate populations are
together, they can still potentially
interbreed.
C
In cattle, roan coat color (a mixture of separate red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (Rr)
offspring of red (RR) and white (rr) homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce
offspring in the ratio of 1 red: 2 roan: 1 white? Circle or highlight the correct answer.
a) red × white
b) roan × roan
c) white × roan
d) red × roan
B
For a certain mouse trait, allele D is dominant over allele d. A mouse with genotype
DD is mated with a mouse with genotype dd. Of their offspring ___ are expected to
show trait d, and ___ are expected to be heterozygous carriers of the d trait.
A. 50%, 50%
B. 0%, 50%
C. 0%, 100%
D. 50%, 100%
E. 50%, 0%
C
When a chestnut-colored horse is mated with a cream-colored horse, all the offspring are
palomino (incomplete dominance). When two palomino horses are mated, what proportion of
their offspring would be expected to be palomino?
A. 0 (none)
B. 0.25
C. 0.50
D. 0.75
E. 1.0 (all)
C
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a treatable metabolic disease inherited as a simple
recessive trait. Jack and his wife Brittany do not have PKU, but both have a member of
their extended family with PKU. When they have the genetic test, they both learn they
are carriers of the PKU allele. (a) What is the probability their first child will be born with
PKU, and then (b) what is the probability that if they have two children, both children will
have PKU?
A. 1/2; 1/2
B. 1/2; 1/4
C. 1/2; 1/8
D. 1/4; 1/16
D
A woman of blood type B marries a man with blood type A. Both of them have a
parent with type O blood. From the information given, determine the genotypes of the
couple, draw a Punnett square, and answer what blood types (phenotypes) are possible
in their children?
A. Only blood types A or B.
B. Blood types A or B or O
C. Blood types A or B or AB
D. Blood types A or B or AB or O
D
A fruit fly population has a gene with two alleles, A1 and A2. Tests show that 70% of the gametes produced in the population contain the A1 allele. If the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what proportion of the flies carry both A1 and A2?
A. 0.70
B. 0.49
C. 0.42
D. 0.21
C
In a population of mice in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, 4% (= 0.04) of individuals are albino (show the recessive a trait); the rest show the dominant agouti (A). What is the frequency of agouti A allele?
A. 0.04
B. 0.20
C. 0.40
D. 0.80
D
In a population of fish, the frequency of the dominant allele A at a locus is 0.8. If the population has 500 individuals, what is the expected number of A alleles in the gene pool? [Think first – how many total alleles are in this gene pool?]
A. 320
B. 400
C. 480
D. 800
D
Black fur in mice (B) is dominant to brown fur (b). In a population of 100 mice, the frequency of the dominant allele is 0.6. How many mice in the population, randomly picked, are expected to have brown fur?
A. 16
B. 36
C. 40
D. 48
A
The ultimate (original) origin of genetic variation is
a. gene flow
b. natural selection
c. Mutation
d. a founder effect
e. non-random mating
C
Sparrows with average-sized wings survive severe storms better than either those with
longer wings or those with shorter wings, illustrating which of these?
a. The bottleneck effect
b. Disruptive selection
c. Stabilizing selection
d. Sexual selection
C
Microevolution is best defined as which of the following?
a. a change in population size for a species
b. a change in living conditions for an organism
c. a change in genetic composition of a population from one day to the next day
d. a change in genetic composition of a population from generation to generation
D
What are adaptations?
a. inherited characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and
reproduction in specific environments
b. acquired characteristics of organisms that enhance their survival and
reproduction in specific environments
c. processes that allow individuals with certain inherited traits to survive and
reproduce
d. patterns seen in fossils documenting the origins of other new groups of
organisms
A
A genetic analysis of a certain species found that all individuals were homozygous at
many gene loci, even for genes that were not at all important to survival, so any
variation there would have been neutral (zero selection). The most likely explanation is
a history of
a. large population size
b. high rates of mutation
c. genetic bottleneck
d. extensive gene flow with other populations
C
According to the biological species definition, two populations of individuals are
considered members of the same species if they
a. resemble each other in color patterns
b. can potentially interbreed
c. overlap in their geographic range and habitat
d. share the same morphological traits
B
Species-specific courtship behaviors serve as which type of reproductive isolating
mechanism?
a. habitat isolation
b. behavioral isolation
c. mechanical isolation
d. gametic isolation
B
Banana plantations depend on asexual cloning of individual plants (growing new trees
from cuttings of the stems). When a new virus invades and can successfully infect a
non-resistant banana plant, the virus spreads quickly through the entire population.
Why?
a. they are genetically identical
b. some genetic variants are resistant to the virus
c. the virus modifies the banana plant genes to make them resistant
d. it only depends on insects transmitting the virus from one plant to another
A
A population of lizards is isolated such that no new lizards can move into their territory.
Which of the following is primarily responsible for new alleles in this population?
a. Independent assortment of chromosomes during the process of creating sperm
or eggs.
b. mutations in cells that will become sperm or eggs.
c. random mating between the lizards in the population.
d. changes in the environment that favor some lizard traits over others.
B
Which mechanism would reverse or stop the process of speciation?
A. increased gene flow between groups
B. gene pools of the two species becoming increasingly different
C. increased ability of females to discriminate mates
D. decreased production of hybrids
A
Individual plants that are known to have exactly the same genotype sometimes vary in their phenotype. This variation is most likely due to:
A. new mutations in the individual
B. incomplete dominance;
C. Co-dominance
D. environmental effects.
D
Mitosis is ONLY needed for how many of the following scenarios?
-growing 2 inches between the ages of 5 and 6 years
-the healing of a scraped knee
-growth of a developing embryo
-production of pollen by the stamen of a diploid (2N) flowering plant
-replacement of the epithelial cells of your stomach lining
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 5
D
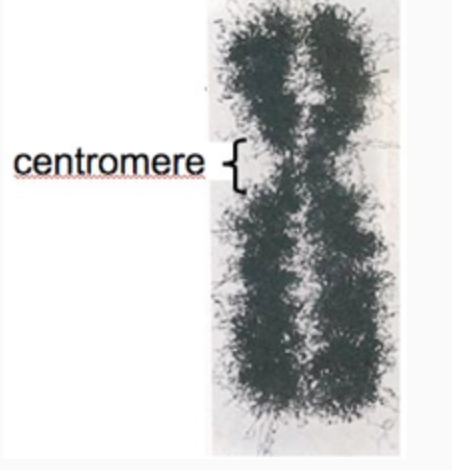
This replicated chromosome contains which
A. two single-stranded DNA molecules.
B. one double-stranded DNA molecule.
C. two double-stranded DNA molecules.
D. many double-stranded DNA molecules.
C
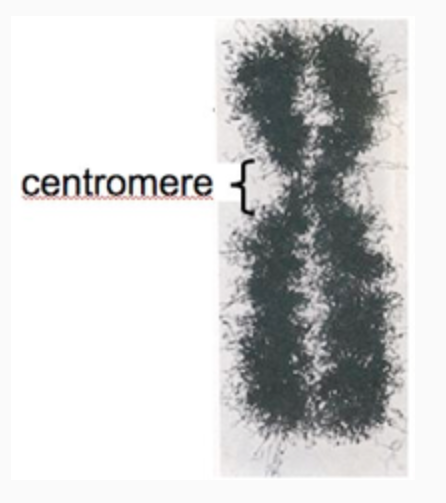
The image shown here contains which?
A. DNA from one of your parents on the left and DNA from the other parent on the right
B. DNA from only one of your parents
B
Which of the following best describes the two members of a homologous pair?
A. They have identical DNA.
B. They have genes controlling the same characters.
C. They were inherited from the same parent.
D. They pair up during mitosis.
B
During Meiosis I, what separates during anaphase?
A. Homologous chromosomes
B. Sister chromatids
C. Non-homologous chromosomes
D. Non-sister chromatids
A
If a cell with genome of 20 pairs of chromosomes undergoes normal meiosis, how many cells result, and how many chromosomes are in each of the resulting cells?
A. Two cells, each with 20 chromosomes
B. Two cells, each with 40 chromosomes
C. Four cells, each with 10 chromosomes
D. Four cells, each with 20 chromosomes
D
If the diploid number (2n) for a species is 50, how many homologous pairs are in that species’ genome, and how many chromosomes are in a sperm cell of that species ?
A. 50, 50
B. 50, 25
C. 25, 25
D. 25, 50
C
You have a purple flower that has one purple allele and one white allele. You also have a white flower with two white alleles. Are BOTH of these plants true-breeding?
A. Yes
B. No
B
Consider a gene that has 4 alleles (A, B, C, and D) in a plant population. A certain plant individual has the genotype AC. What are the chances that this individual will pass allele C to one of its offspring?
A. 0
B. 25%
C. 50%
D. 75%
C
Which of these sets of parents (blood type phenotype given) is probably not correctly matched to their child (by blood type)?
A. Parents A and B, child AB
B. Parents A and O, child AB
C. Parents A and O, child O
D. Parents A and B, child O
B
The AA genotype frequency is is 0.7 and this means...
A. the proportion of individuals showing the A trait in their phenotype.
B. the proportion of individuals with genotype AA.
C. the proportion of A alleles in the total gene pool.
B
A population of cattle has two alleles for coat color - red and white. Red cattle are homozygous for the red allele, white cattle are homozygous for the white allele, and roan cattle are heterozygotes. Our population consists of 50% red, 30% white, and 20% roan individuals. What are the allele frequencies?
A. red=0.36, white=0.16
B. red=0.6, white=0.4
C. red=0.5, white=0.5
D. red=0.5; white=0.3
B
In a population of 1000 diploid individuals the gene pool for one trait like eye color would consist of how many alleles?
A. 500
B. 1000
C. 2000
D. Another number
C
A population that is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (no microevolution) has 10% of its individuals showing the recessive trait. Under normal reproduction conditions, what percent of the next generation will show the recessive trait?
A. 10% (stays the same)
B. it will decrease
C. cannot be determined
A
Which of these different individuals (within the same population) has the highest relative fitness?
A. Individual that lives the longest
B. Individual that acquires the most food and other resources
C. Individual that produces the most offspring
C