Chemistry IGCSE - Chemistry of the environment
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
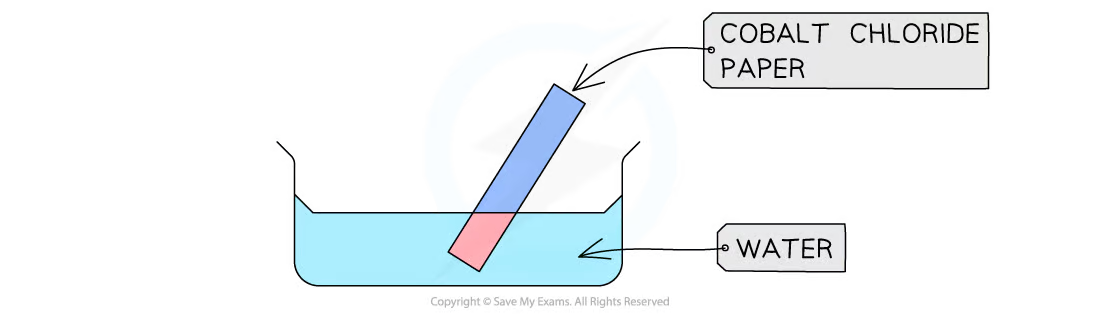
Test with using cobalt(II) chloride for presence of water
Blue → pink (+)
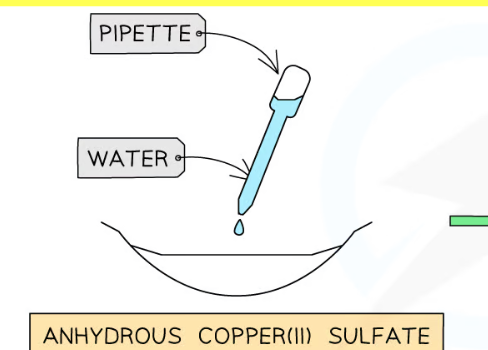
Test with copper(II) sulfate for presence of water
White → blue (+)
Test for purity of water using melting point and boiling point
Pure water → boiling point of 100°C → begins to boil either below or above 100°C → liquid contains impurities
Distilled water is used in practical chemistry → contains fewer chemical impurities rather than tap water
Describe treatment of domestic water supply in terms of sedimentation and filtration to remove solids
Sedimentation → allows solid particles in water to settle to bottom of tank → easier to remove them → filtration further cleanses water by passing it through layers of sand, gravel, or other materials to trap → remove remaining solid particles
Describe treatment of domestic water supply in terms of use of carbon to remove tastes and odours
Carbon filters → used to absorb and remove organic compounds that can cause undesirable tastes + odours in water → helps in reducing chemical pollutants
Describe treatment of domestic water supply in terms of chlorination to kill microbes (pathogens)
Chlorination → adding chlorine/chlorine compounds to water as a disinfectant → method to kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens → water safe for human consumption
Composition of clean, dry air
78% nitrogen (N2) + 21% oxygen (O2)
rest → mixture of noble gases + carbon dioxide (CO2)
Source of this air pollutants: carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide → complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels
Source of this air pollutants: carbon monoxide and particulates
Carbon monoxide and particulates → incomplete combustion of carbon containing fuels
Source of this air pollutants: methane
Methane → decomposition of vegetation and waste gases from digestion in animals
Source of this air pollutants: oxides of nitrogen
Oxides of nitrogen → car engines
Source of this air pollutants: sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide → combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur compounds
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide → higher levels of carbon dioxide → increased global warming → climate change
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide → toxic gas
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: particulates
Particulates → increased risk of respiratory problems + cancer
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: methane
Methane → higher levels of methane → increased global warming → climate change
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: oxides of nitrogen
Oxides of nitrogen → acid rain + respiratory problems
Adverse effect of these air pollutants: sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide → acid rain
Explain strategies to reduce effects of climate change: planting trees
Trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis → removing it from atmosphere → reduce greenhouse effect → improves air quality + provides ecological benefits
Explain strategies to reduce the effects of climate change: reduction in livestock farming
Livestock farming produces methane → reducing livestock farming → decrease methane emissions → encourage more sustainable agricultural practices
Explain strategies to reduce the effects of climate change: decreasing use of fossil fuels
Fossil fuels release carbon dioxide when burned → reducing their use + transitioning to cleaner energy sources → can cut emissions + reduce air pollution
Explain strategies to reduce the effects of climate change: increasing use of hydrogen and renewable energy, e.g. wind, solar
Hydrogen energy produces water as a byproduct → cleaner alternative to fossil fuels → renewable energy sources → e.g. wind + solar power generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases → help replace fossil fuel-based power generation → reduce global warming
Explain strategies to reduce the effects of acid rain: reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide by using low-sulfur fuels
Switching to fuels with lower sulfur content → reduces sulfur dioxide emissions during combustion → decreasing primary contributor to acid rain
Explain strategies to reduce the effects of acid rain: flue gas desulfurization with calcium oxide
Treats flue gases with calcium oxide to chemically remove sulfur dioxide → converts it into calcium sulfate → non-harmful + can be utilized in industrial products → cuts emission of sulfur dioxide into atmosphere
Describe how the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane cause global warming: absorption, reflection and emission of thermal energy
Both gases absorb infrared radiation (thermal energy) from Earth → re-emits it in all directions → including back toward the surface → trapping heat in atmosphere
Describe how the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane cause global warming: reducing thermal energy loss to space
By absorbing and re-emitting infrared radiation → CO2 + CH4 decrease amount of heat that escapes into space → enhancing greenhouse effect → warming the planet
Explain how oxides of nitrogen form in car engines
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) form in car engines → due to high-temperature combustion → at these temperatures → nitrogen (N2) + oxygen (O2) from air react to form NO and NO2
Describe their removal by catalytic converters:
2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2
Catalytic converters reduce NOx emissions by fusing the reaction: 2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N22 → carbon monoxide (CO) reacts with nitric oxide (NO) → produces nitrogen gas (N2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) → converts harmful emissions into less harmful gases before they are released into atmosphere