Lobes of the liver
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What are the two classifications of the lobes of the liver?
Anatomical lobes
and Functional (Physiological) lobes.
By what structure are the anatomical lobes divided on the diaphragmatic surface?
The falciform ligament divides the liver into right and left lobes.
How many anatomical lobes are seen on the visceral surface of the liver, and what are they?
Four lobes
is right,
left,
quadrate,
and caudate lobes.
Which structures on the visceral surface form the H-shaped figure?
Fissure for ligamentum teres
Fissure for ligamentum venosum
Porta hepatis
Groove for inferior vena cava
Fossa for gallbladder
On what basis are the functional (physiological) lobes divided?
Based on intrahepatic distribution of the
bile ducts,
hepatic artery,
and portal vein.
What plane divides the functional right and left lobes of the liver?
The imaginary sagittal plane (Cantlie’s plane).
How does Cantlie’s plane pass on the diaphragmatic surface?
From the inferior vena cava to the cystic notch.
How does Cantlie’s plane pass on the visceral surface?
Through the fossa for the gallbladder to the groove for the inferior vena cava.
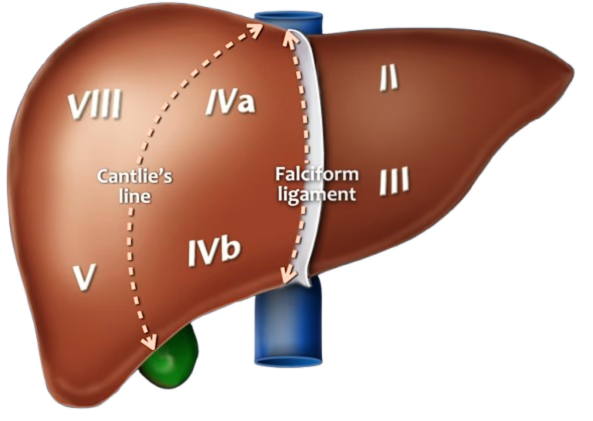
Compare the sizes of the functional right and left lobes.
The functional right and left lobes are approximately equal in size.
What does each functional lobe have of its own?
Each lobe has its own primary branch of the hepatic artery and portal vein, and is drained by its own hepatic duct.