Voltage and Current
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1008: Dynamic Systems 1 - Lecture 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
Voltage
The difference in electric potential energy between two points per unit electric charge.
Other names for voltage
Electric potential difference, electric pressure or electric tension.
Voltage symbols
V or U.
The voltage between two points is equal to
the work done per unit
of charge against a static electric field to move the test charge between two points.
Voltage unit
Volts (a joule per coulomb).
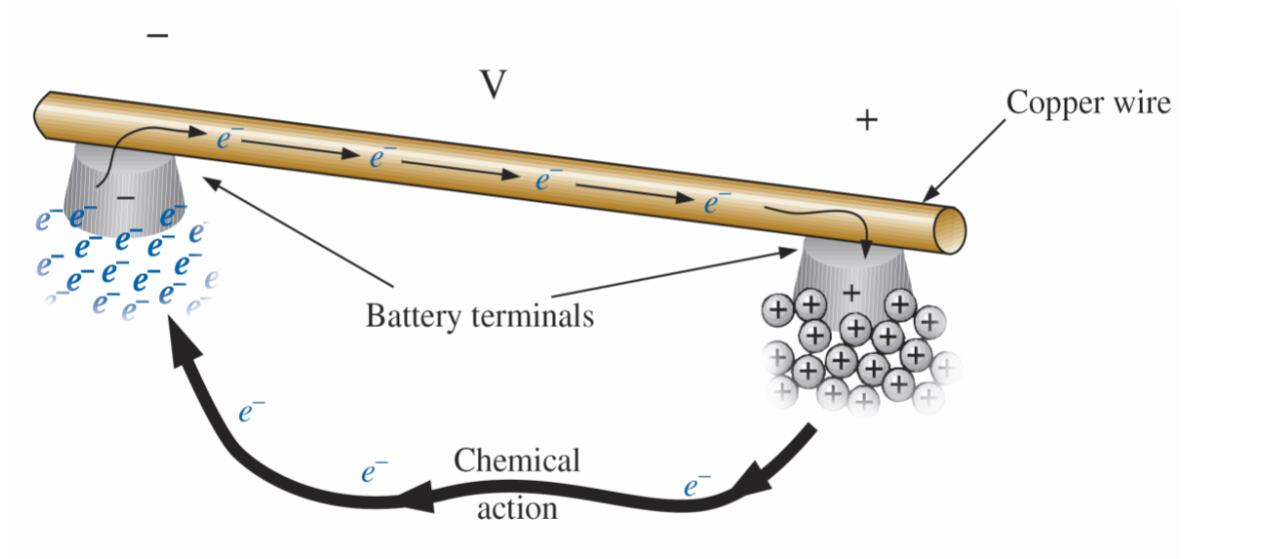
How a battery works
The applied voltage is the starting mechanism - the current is a reaction to the applied voltage.
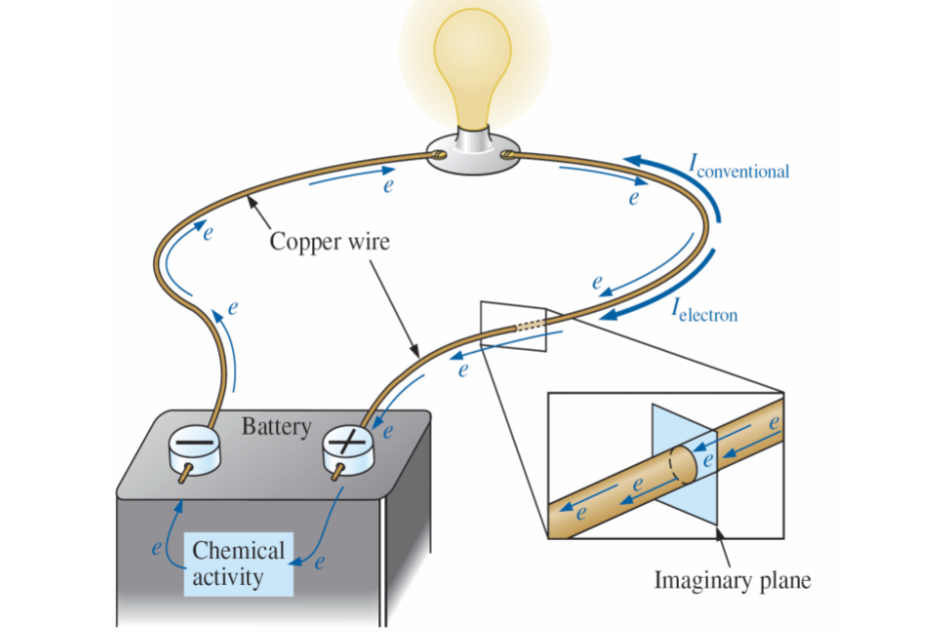
Conventional current
The direction of positive charge. (This is not how current actually flows)
Electric current formula
I = Q/t
The rate of flow of electric charge
I = dQ/dt
Unit of current
Ampere / amp (A)
Resistance
The opposition to the flow of charge through an electrical circuit.
Resistance units
Ohm (Ω)
Resistance symbol
Omega (Ω)
Factors that affect resistance
Material, length, cross-sectional area, temperature of the material.
Factors that increase resistance
A long path through which the free electron must pass, a small cross sectional area, low temperature.