Using Microbial metabolism to produce bioplastics and biopolymers
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what are biopolymers?
Natural polymers produced by living organisms, such as polysaccharides and proteins, which can be used to create biodegradable plastics and materials.
*Biobased doesn’t equate to biodegradability just refers to its origin
how are biodegradable polymers degraded?
By microbes releasing their enzymes extracellularly i.e amylases present in microbial metabolic pathways that break down the polymer chains into its smaller subunits
what are some examples of biobased materials produced by terrestrial plants & their associated uses?
Natural fibres for construction
Cellulose for adhesives, rapid tests
Hemicellulose for paper
Lignin for fibres
Starch for biodegradable plastic bags
what is a benefit of using microbes to synthesis bioplastics?
microbes use existing starting material i.e cellulose from terrestrial plants, that absorbs CO2 in its lifetime, low emission production
what are the 3 main biobased polymers?
• Cellulose (from plants and microbes)
• Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) (from microbes) - polymers of FA
• Lignin (from plants)
what are some other biobased starting materials?
• Cellulose derived sugars (glucose, arabinose, xylose…)
• Starch derived glucose and maltose , used to create bioplastic bags
• Waste - food waste, food processing side streams, agricultural waste
what can the metabolic intermediates lactic acid and succinic acid be exploited for?
They can be used to produce biodegradable plastics, solvents, and various chemicals.
what are the 3 fermentation products generated by microbial metabolism and what are their associated plastics?
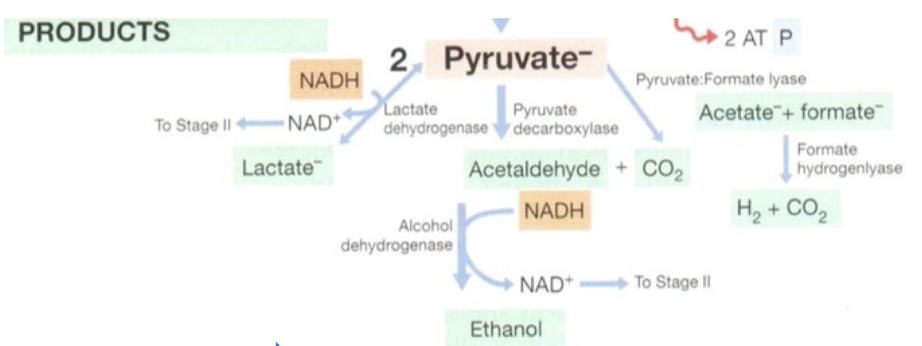
Lactic acid → Lactide → Polylactate
Ethanol → Ethylene → Polyethylene
Isobutanol → Isobutylene → Polyisobutene
Is polyetyhlene biodegradable?
No, polyethylene is not biodegradable
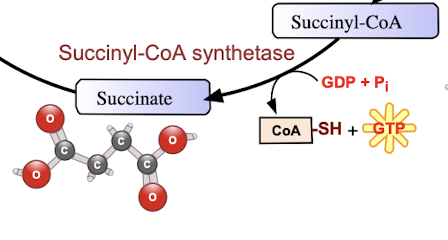
what is succinate used to make?
Polybutylene succinate (PBS), a biodegradable polymer used in packaging and other applications.
-Intermediate of respiration
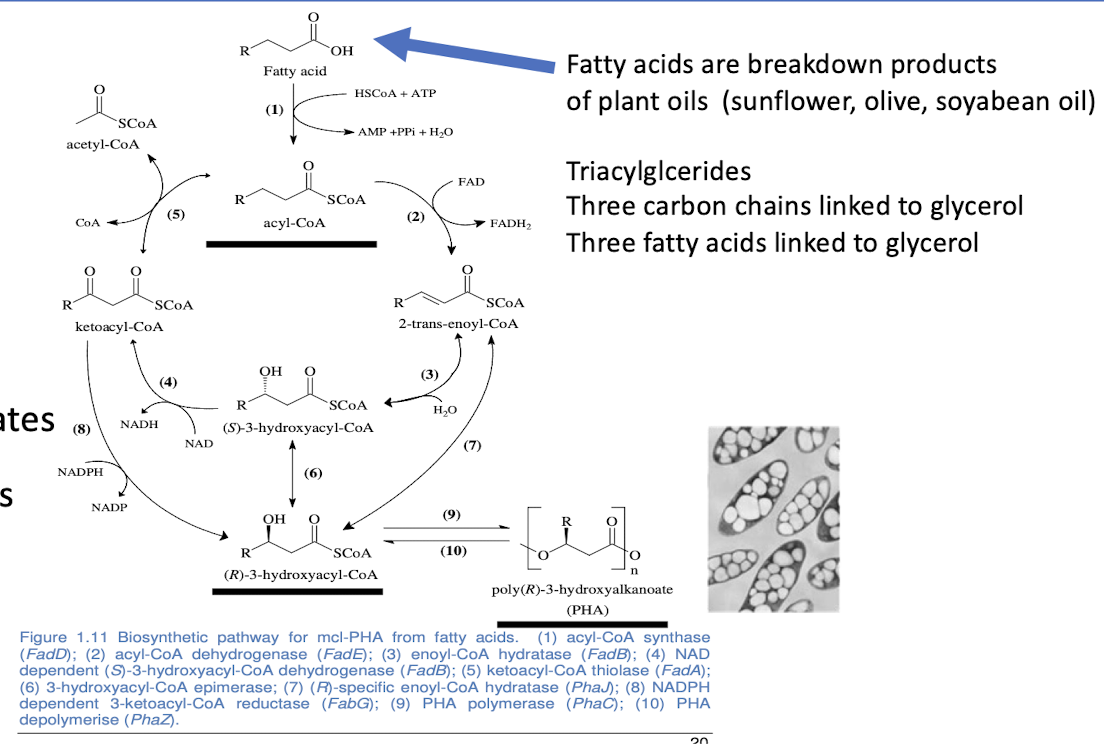
how are PHAs (polyhydroxyalkanoates) produced by fatty acid oxidation by microbes?
Fatty acid (β) oxidation into acyl-CoA → 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA → PHA - polyhydroxyalkanoate
-polymers of alkanoic acids (FA) with an -OH attached
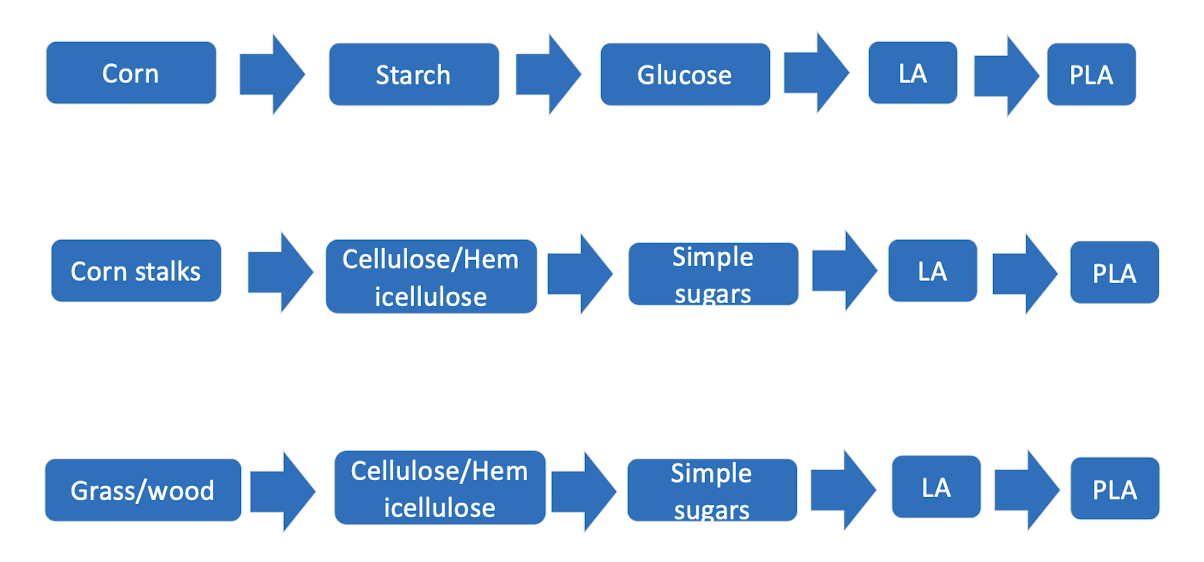
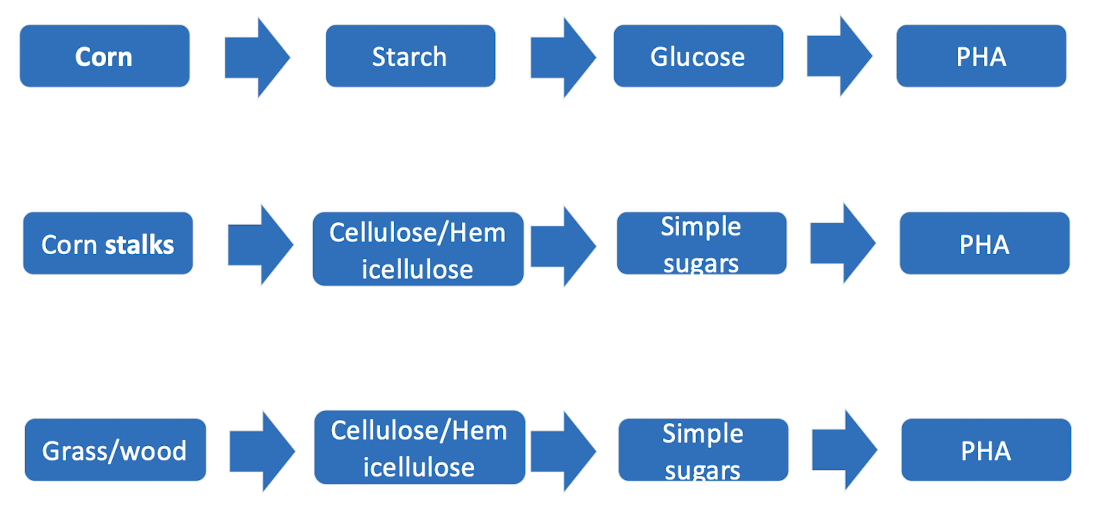
what are some examples of starting materials used to make biopolymers?
Corn, corn stalks, grass/ wood can be converted into PLAs or PHAs
Corn = 1st generation
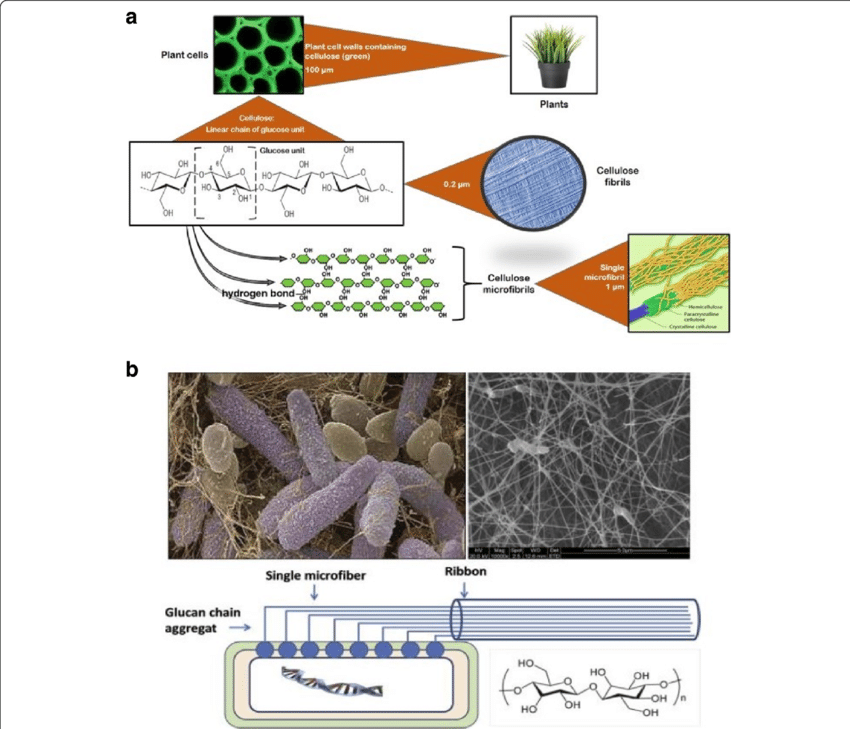
what are examples of bacteria that produce cellulose?
Acetobacter xylinum, Gluconacetobacter, and Agrobacterium, Aerobacter, Salmonella.
These bacteria synthesise cellulose as an extracellular polysaccharide.
what makes bacterial cellulose different to plant cellulose?
Microfibrils (strong threads made of long cellulose chains running parallel to one another, joined together by H bonds forming strong cross linkages) are 100x thinner than plant cellulose fibres (nanofibres)
High tensile strength and greater water retention capacity.
Bacterial cellulose is also biodegradable and can be produced in a pure form, making it useful for various applications like wound dressings and food products.
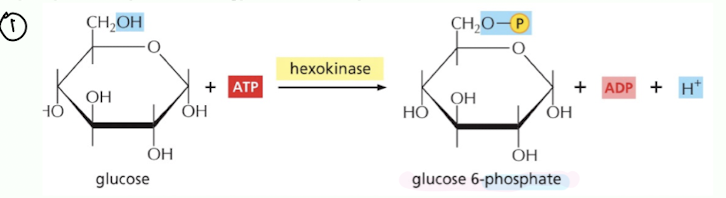
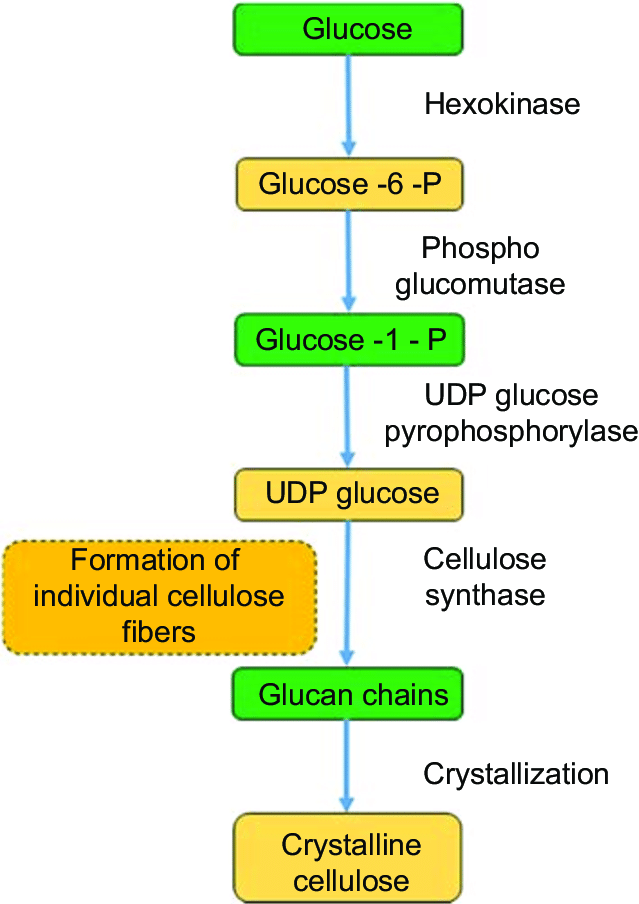
what is the pathway for bacterial cellulose synthesis?
Conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate by phosphorylation (hexokinase)
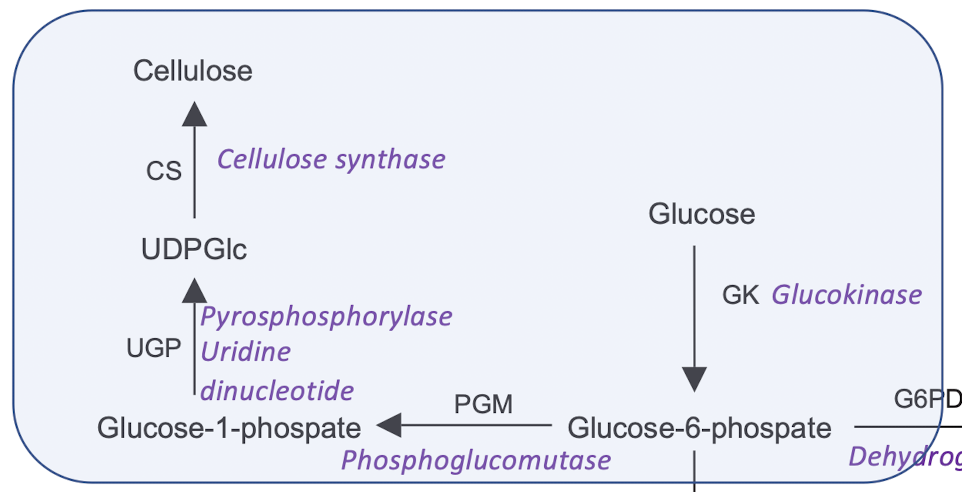
G6P into G1P using PGM (phosphoglucomutase)
G1P into UDPGlc (uridine diphosphate glucose)
UDPGlc into cellulose
UDP acts as a tag so microbes can recgonise to create cellulose from this intermediate
What biopolymers/plastics degrade the fastest in industrial composters?
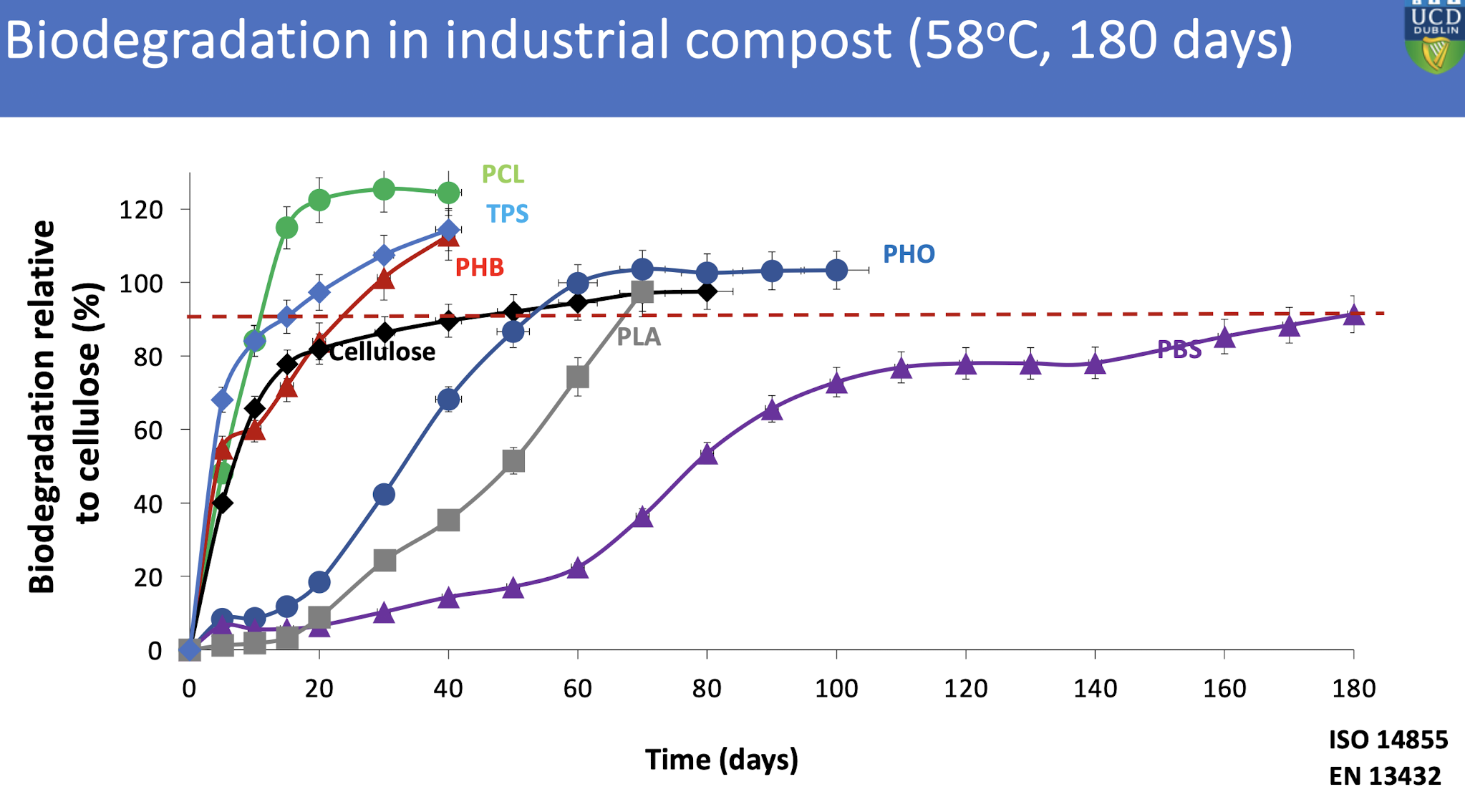
Cellulose is the standard for biodegradability with PHB degrading slightly greater than cellulose, followed by polylactic acid (PLA), which also degrades effectively in industrial composting conditions.
which bacterial biopolymers take the longest to compost?
Biopolyesters such as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) or microbial polyesters. These typically require specialized conditions for biodegradation.