ECON 335: Externalities
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
externalities
one individual imposing uncompensated costs/benefits on others
what types of externalities can be imposed (not +ve or -ve)
physical
fiscal
what is the goal when reducing -ve externalities?
to reduce it to social optimum, not eliminate it
what are the two ways of addressing externalities?
not easy to measure md as it isn’t constant
shape of msc looks different for every individual
what are some examples of private responses?
assign and enforce property rights, then let individuals bargain with each other
mergers
social conventions
state the coase theorem with all assumptions
if bargaining costs (transaction costs) are low and property rights can easily be assigned/enforced, an independent solution will be achieved independent of who is initially assigned the rights, as long as someone is.
what are the problems with coase ther=orem?
transaction costs cam be high
challenges associated with assigning/enforcing property rights
political feasibility in making the initial allocation of property rights
what are the three public responses to externalities?
pigouvian tax
creating a market
regulation
what are the challenges with pigouvian taxes?
no way to tell what the ‘optimal’ pigouvian tax is?
impracticality of implementing individual-specific taxes
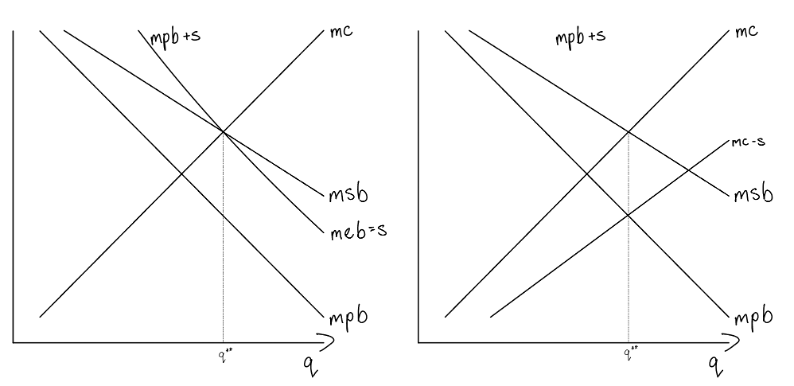
graph and label a -ve externality
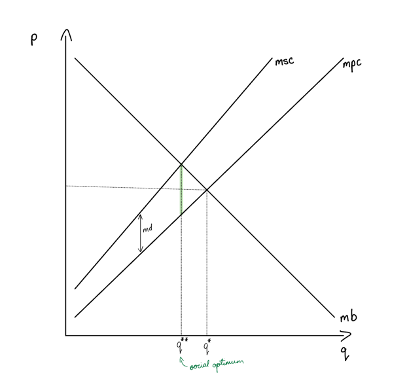
graph and label a +ve externality
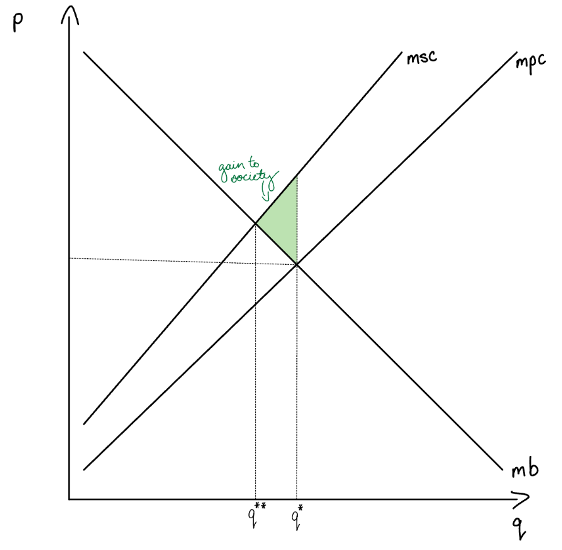
graph and label a private response to a -ve externality
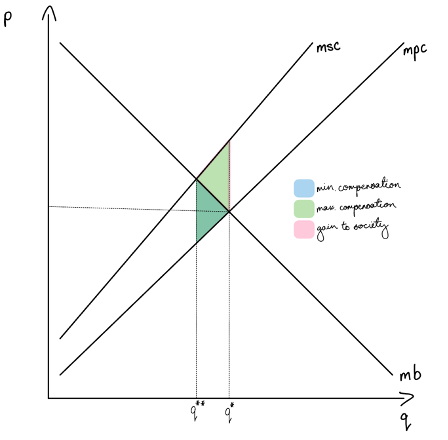
graph and label a pigouvian tax
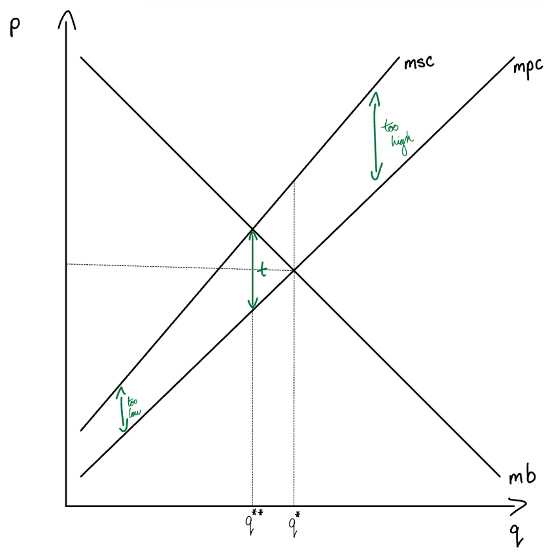
graph and label a market being created in response to a -ve externality
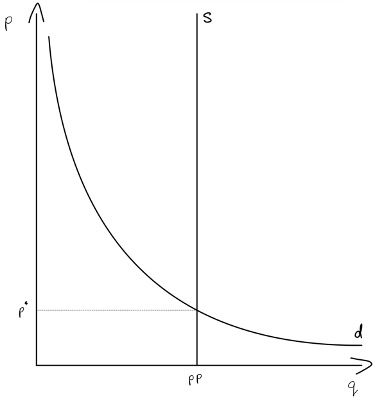
graph and label a +ve externality in consumption being produced at its social optimum
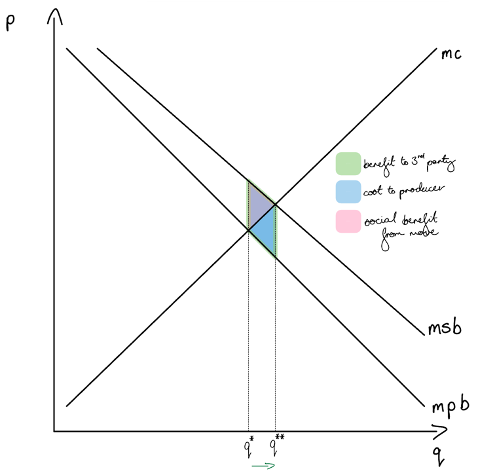
graph label a pigouvian subsidy