Perceiving Objects and Scenes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
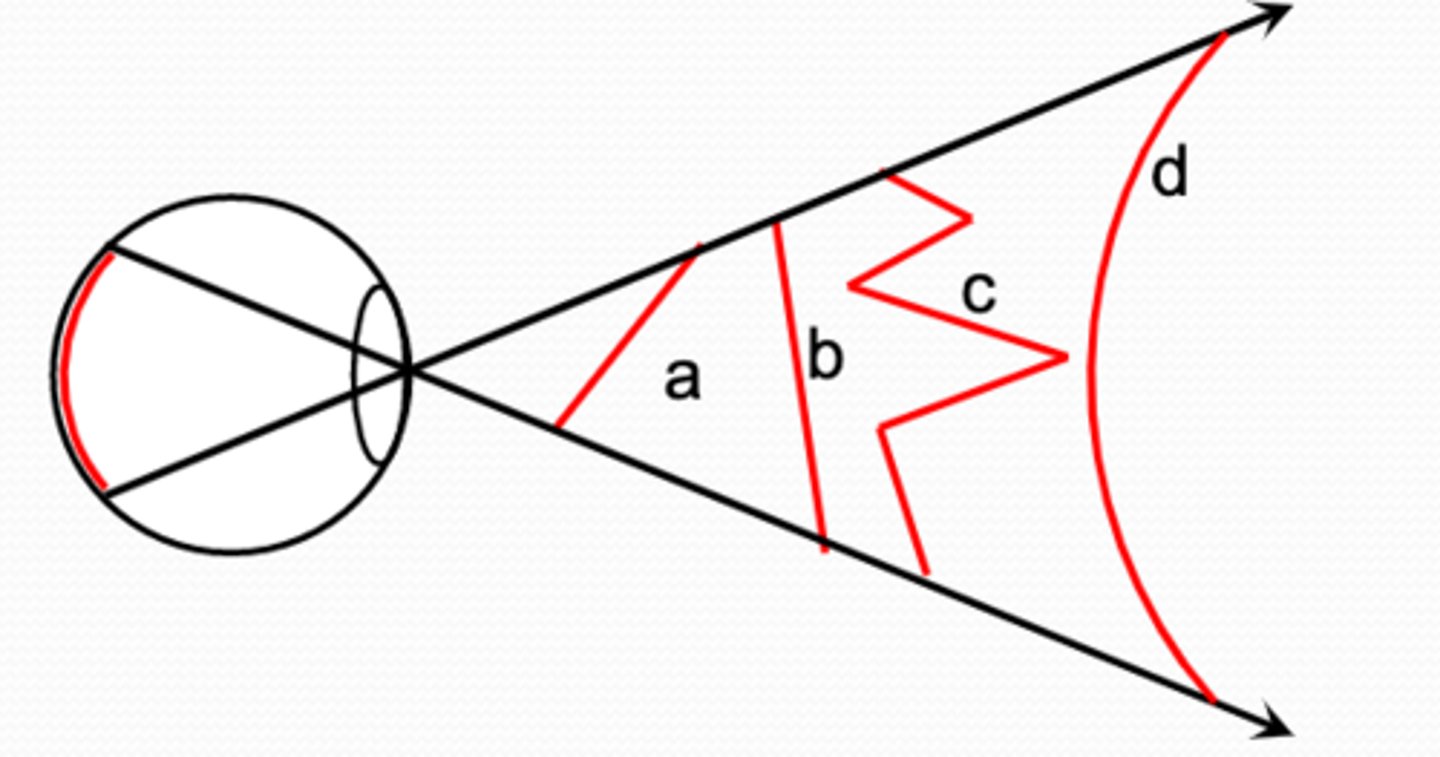
what makes scene perception difficult
stimulus on the retina is ambiguous, objects can be hidden or blurred, objects look different from different viewpoints and in different poses
stimulus on the retina is ambiguous
lines at different positions can create the same retinal image, making it difficult for the brain to determine which object it is looking at
theories that propose why humans succeed in perceiving scenes
structuralism, gestaltism
structuralism
-proposed by Edward Titchener
-claims that sensations combine to form perceptions
gestaltism
-directly contradicts structuralism
-claims that conscious awareness can have characteristics not present in any of the elementary sensations (we fill in details when perceiving)
evidence for gestaltism
apparent motion, illusory contours
apparent motion
the perception of movement from a stationary image
illusory contours
when we perceive forms in locations with no physical contours
according to gestaltism, how are humans able to perceive objects and scenes?
through perceptual organisation - humans are able to make sense of a visual image because they can perceptually organise it into constituent objects
how is perceptual organisation achieved
by the processes of grouping and segregation
grouping
the process by which parts of an image are perceptually bound together to form a perceptual whole (perception of an object)
segregation
the process by which parts of a scene are perceptually segregated to form separate wholes (perception of separate objects)
5 principles of grouping
good continuation, Pragnanz, similarity, proximity, common fate
2 additional principles of grouping
common region, uniform connectedness
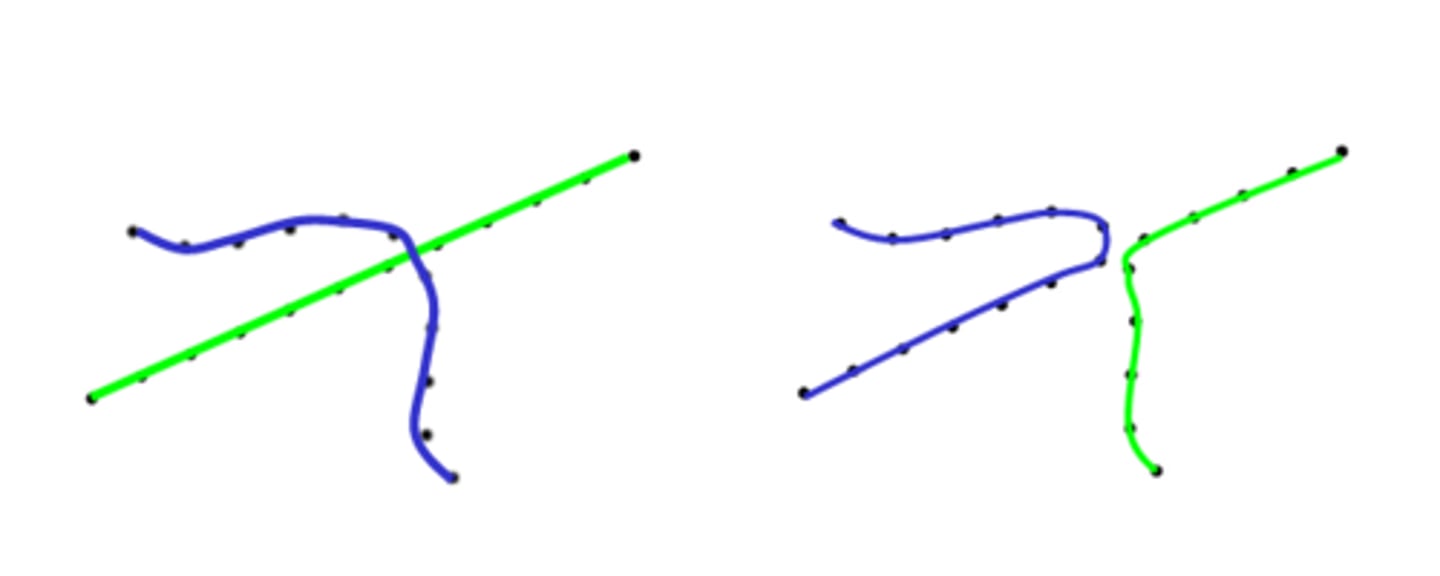
good continuation
aligned (or nearly aligned) contours are grouped together to form a single object
Pragnanz
groupings occur to make the resultant figure as simple as possible

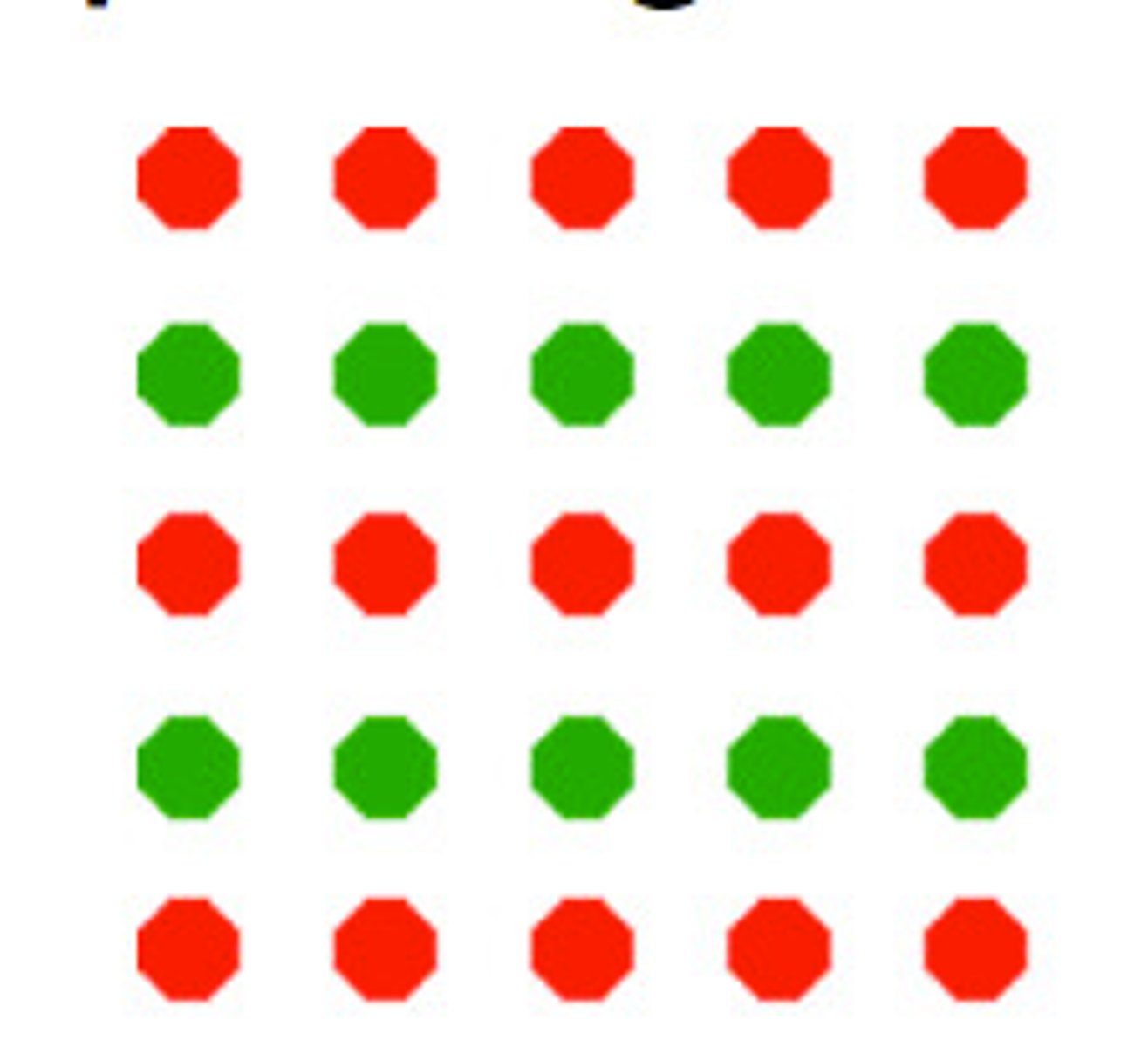
similarity
similar objects are grouped together
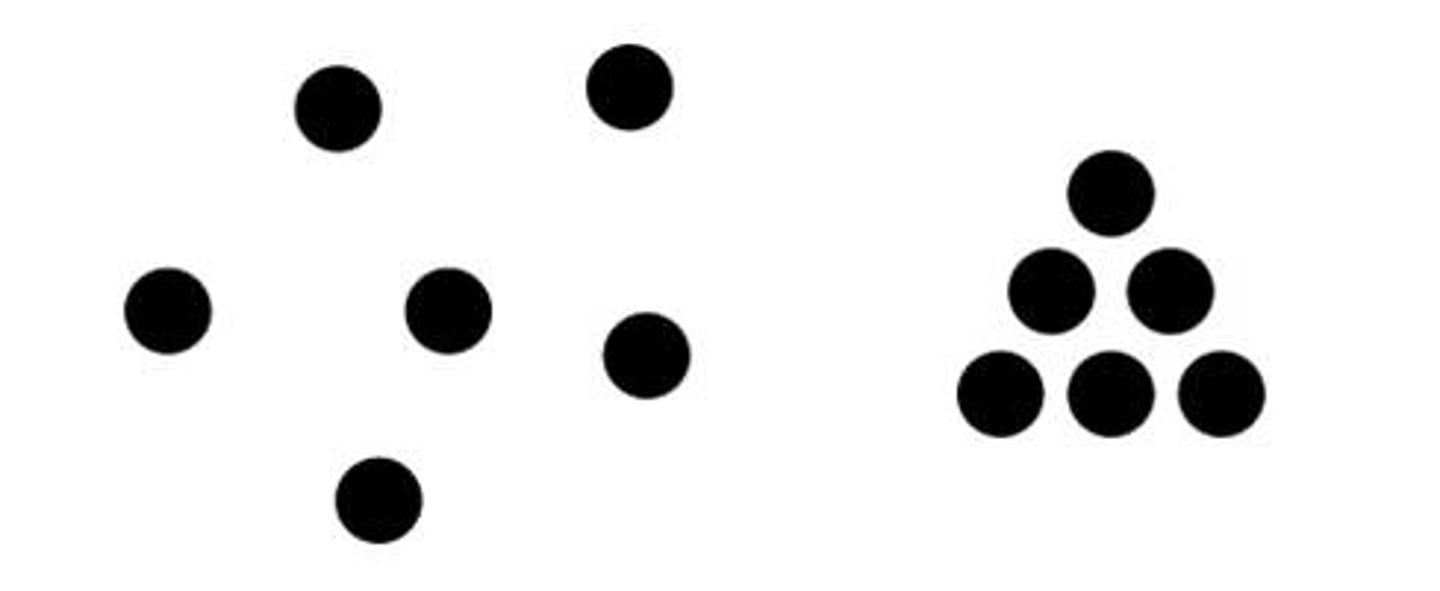
proximity
objects that are closer together tend to group together
common fate
things that are moving the same way are grouped together
common region
elements that are within the same region of space tend to group together
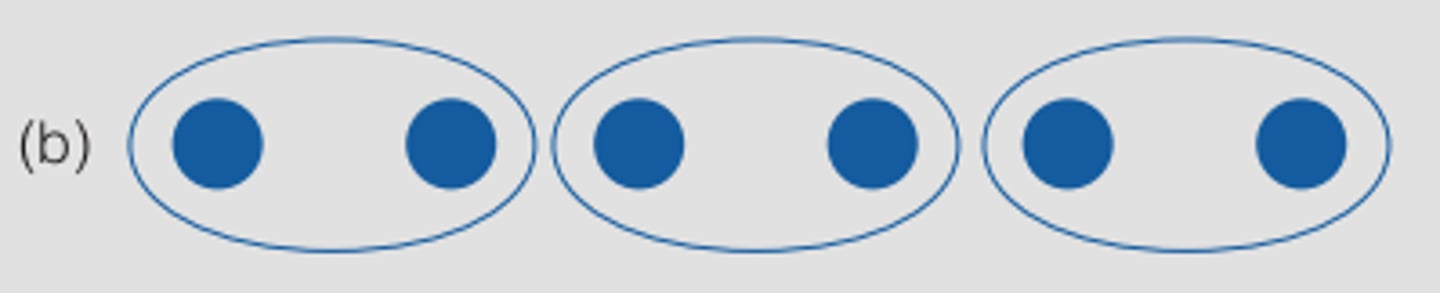
uniform connectedness
connected regions with the same visual characteristics tend to group together

figural properties
regions are more likely to be perceived as the figure if:
-they are in front of the rest of the image
-they are at the bottoms of the image
-they are convex
-they are recognisable
gist perception
the overall impression of a scene acquired from viewing rapid flashes of a scene
who studied gist perceptions and how
-Potter (1976)
-observer was cued with a particular scene description, then was presented with 16 randomly chosen scenes for 250ms each, then was asked if any of the scenes fitted the description - observers were at near 100% accuracy
who investigated the minimum scene exposure time needed to perceive a scene's gist and how?
-Fei Fei
-observers were presented with a single scene, followed by a mask, and were then asked to describe what they saw
results of Fei Fei's experiment
-the longer observers view a scene, the more detailed gist they extract
-27ms is enough to perceive some (not detailed) gists, 67ms is enough for most things, 250ms is very accurate, 500ms is everything
define sensations
elementary processes that occur in response to stimulation
define perceptions
conscious awareness of objects and scenes