NPTE Integumentary
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Normal capillary refill time
< 3 seconds

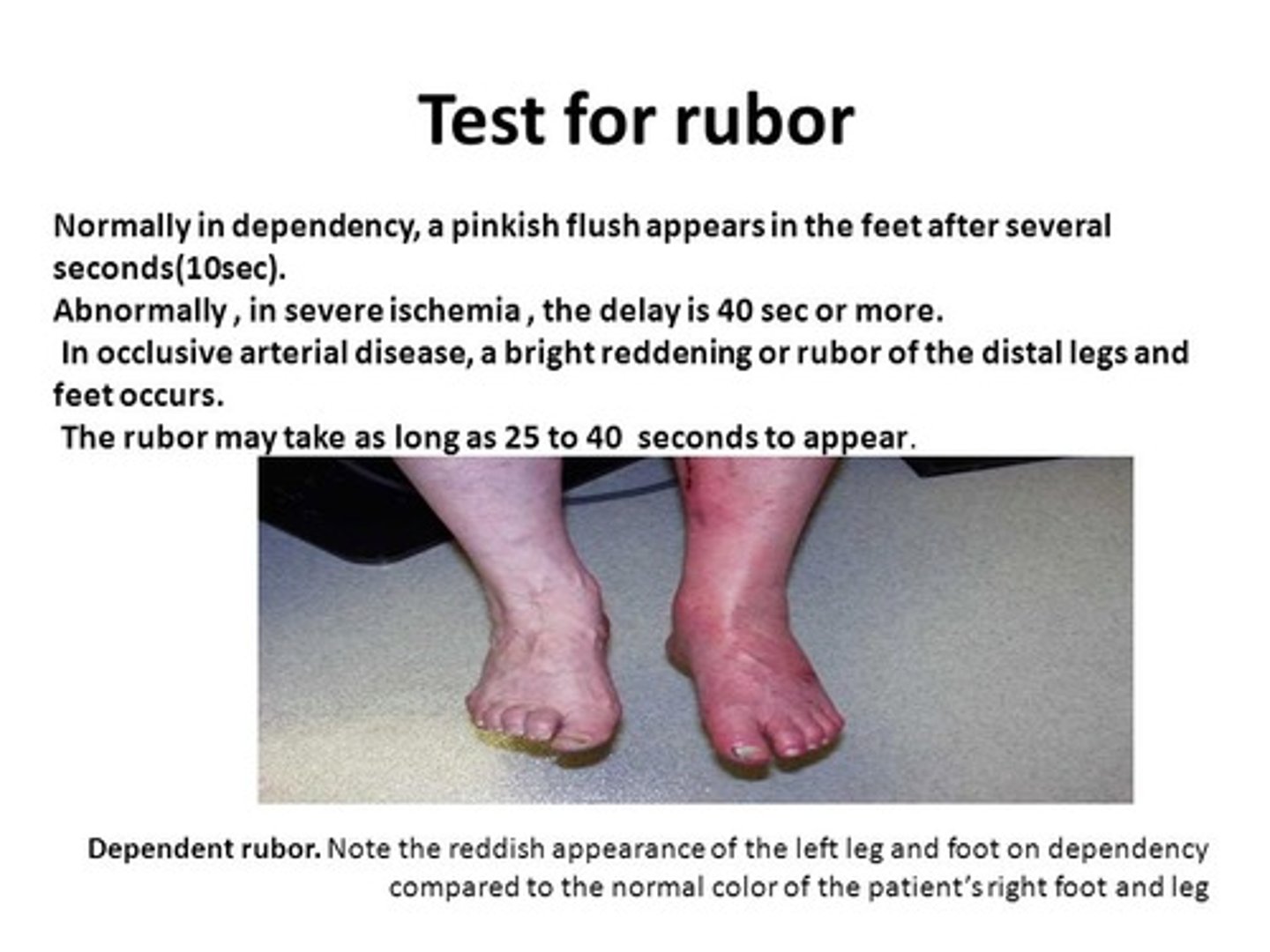
Rubor Dependency Test
elevate LE for 1 minute
sole of the foot goes pale
then you lower the LE
and the sole should exhibit rubor in less than 15 sec
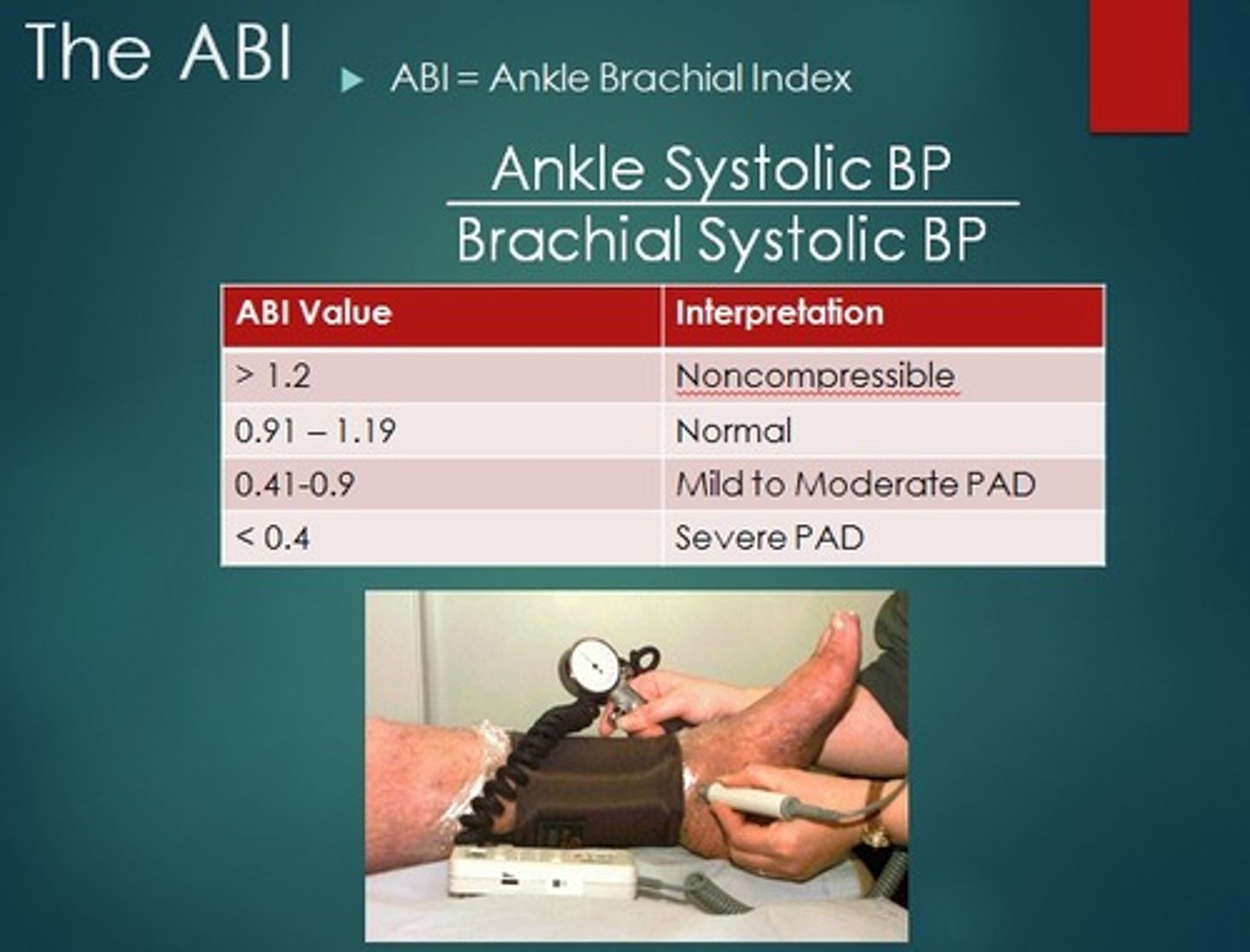
Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
What: ratio of the ankle systolic pressure to the brachial systolic pressure; an objective measurement of arterial disease that provides quantification of the degree of stenosis
>1.4 = calcified/non-compressible
1.0-1.4 = normal
0.9-0.99 = borderline
<0.9 = abnormal
<0.5 = severe arterial dz, risk for ischemia --> refer to vascular specialist
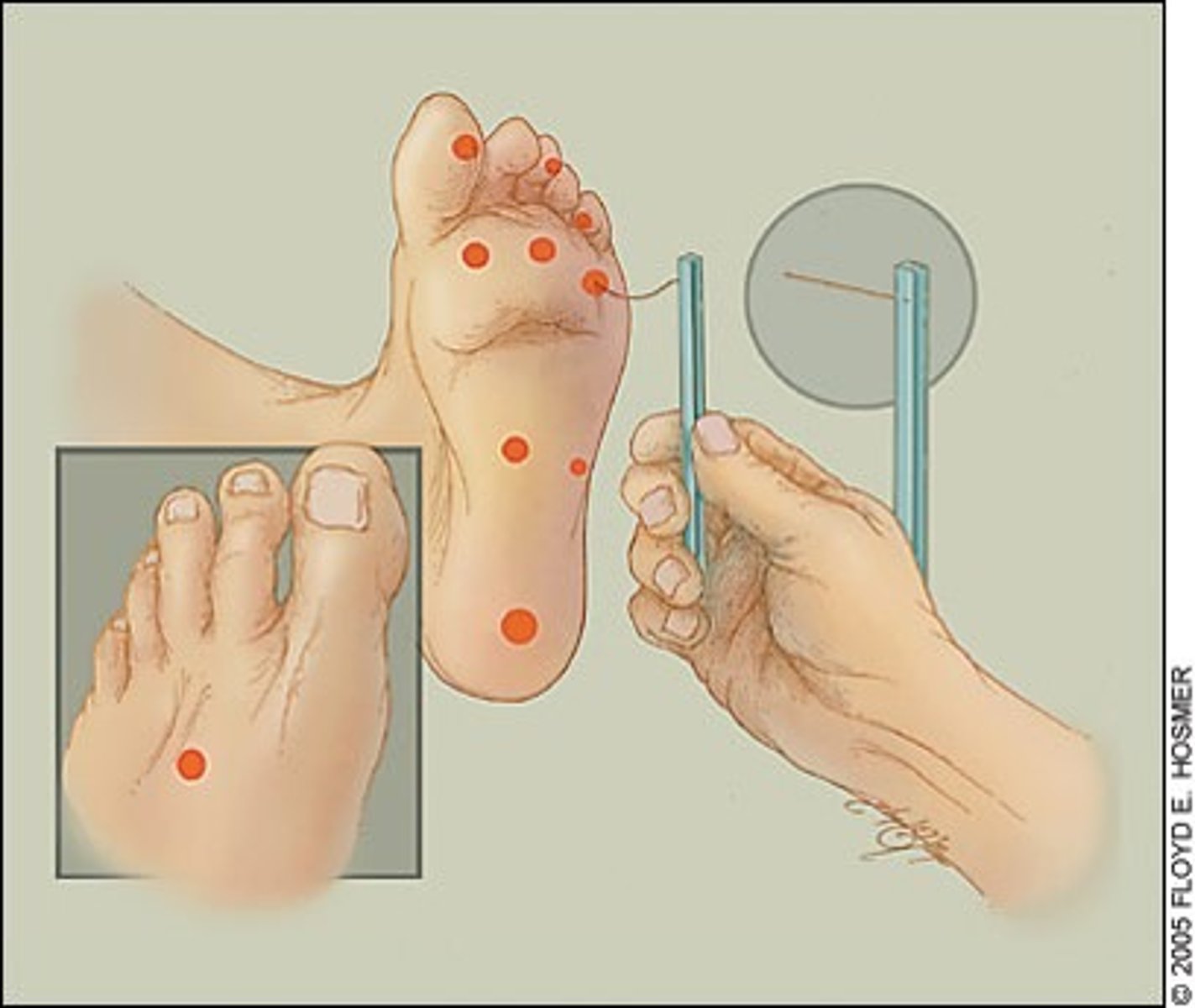
Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament Test: Protective senstation for 2-pt discrimination
5.07 (10g)
Cellulitis
What: inflammation of the connective tissue often accompanied by infection
Where: widespread and poorly defined
Diff Dx:
-Hot, reed and edematous area
-Skin resembles an orange
Tx: antibiotics, elevation of part, and cool, wet dressing

Dermatitis
What: Superficial inflammation of skin, characterized by vesicles, redness, edema, oozing, crusting, scaling and usually itchy
Diff Dx: pt h/o
Tx: topical medications but is dependent on the kind they have

Herpes Zoster
AKA: Shingles
What: Acute CNS viral infection involving dorsal root ganglia,
characterized by vesicular eruptions (blisters) and neuralgic pain in the cutaneous areas (supplied by peripheral sensory nerves arising along the infected dermatome or myotome_
Clinical Presentation:
-dermatomal pattern on thorax
-Mostly unilateral
-raised to palpation <2 mm hiehgt
Diff Dx: vesicle eruption appearing in the nerve root distribution and UL severe pain
Tx: corticosteroids (early) to relieve pain and prevent host-herpetic pain in severe cases
-use AIRBORNE + CONTACT precautions]
(N95, gown, gloves)
![<p>AKA: Shingles</p><p>What: Acute CNS viral infection involving dorsal root ganglia,</p><p>characterized by vesicular eruptions (blisters) and neuralgic pain in the cutaneous areas (supplied by peripheral sensory nerves arising along the infected dermatome or myotome_</p><p>Clinical Presentation:</p><p>-dermatomal pattern on thorax</p><p>-Mostly unilateral</p><p>-raised to palpation <2 mm hiehgt</p><p>Diff Dx: vesicle eruption appearing in the nerve root distribution and UL severe pain</p><p>Tx: corticosteroids (early) to relieve pain and prevent host-herpetic pain in severe cases</p><p>-use AIRBORNE + CONTACT precautions]</p><p>(N95, gown, gloves)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4ec6f2ce-5cb3-4593-a669-5ebc8f9fede8.jpg)
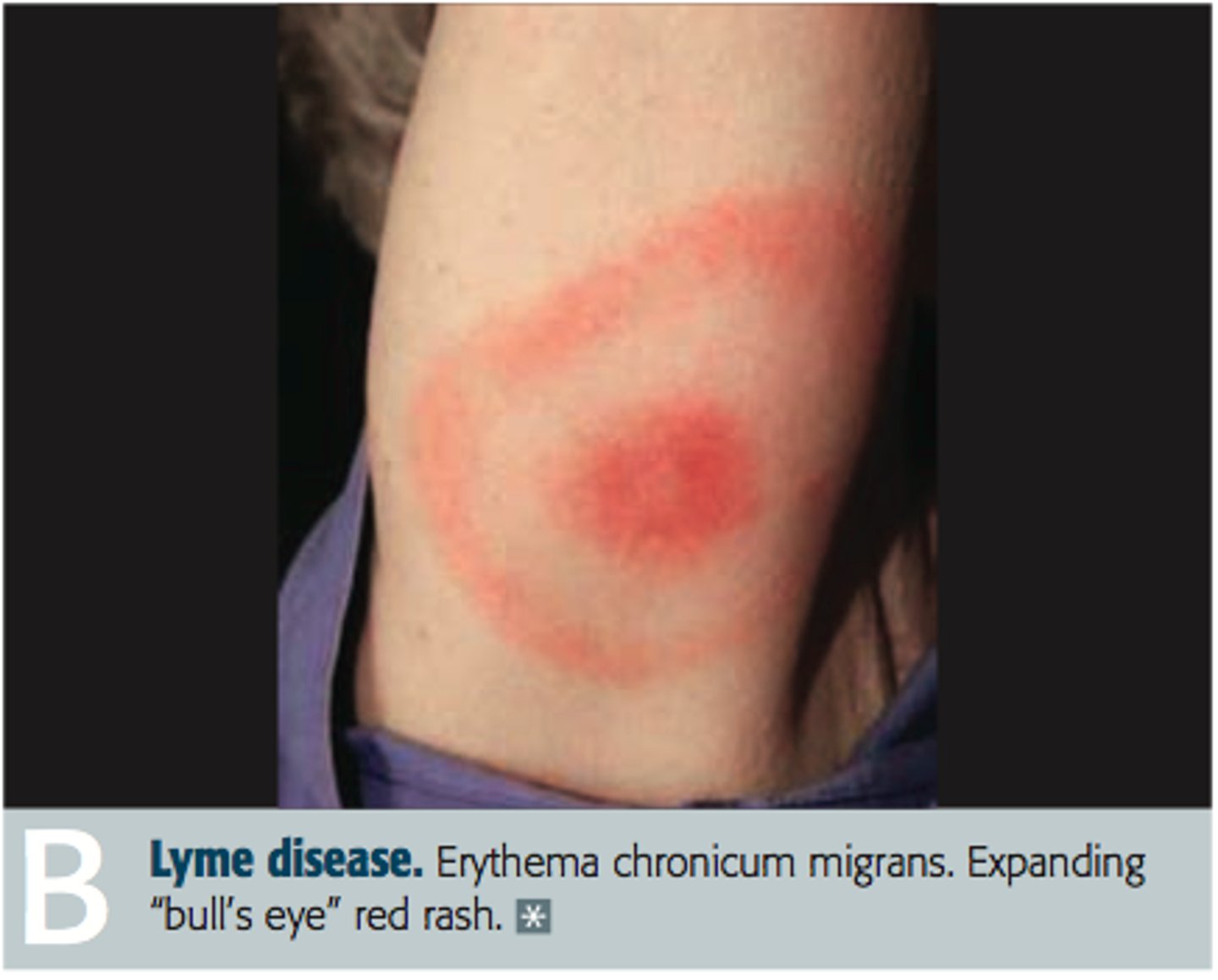
Lyme Disease
What: Inflammatory disease of skin caused by spirochete transmitted to humans by tick bite
Where: common in US
Diff Dx: "bulls eye" round rash with flu-like symptoms, later can develop to include arthritis, neurological disorders (neuritis, ataxia, meningitis, cardiac abnormalities)
Tx: antibiotics, pain meds, aspiration of knee joint fluid, AD to reduce WB
Psoriasis
What: Chronic dz of skin with erythematous plaques covered with silver scale
Where: Scalp, knee, elbows, genitalia
Diff Dx: medical/family h/o, precipitating factors trauma, infection, pregnancy, cold weather, smoking, anxiety, stress
Tx: long-wave UV light, oral photosensitizing drug (psoralen)

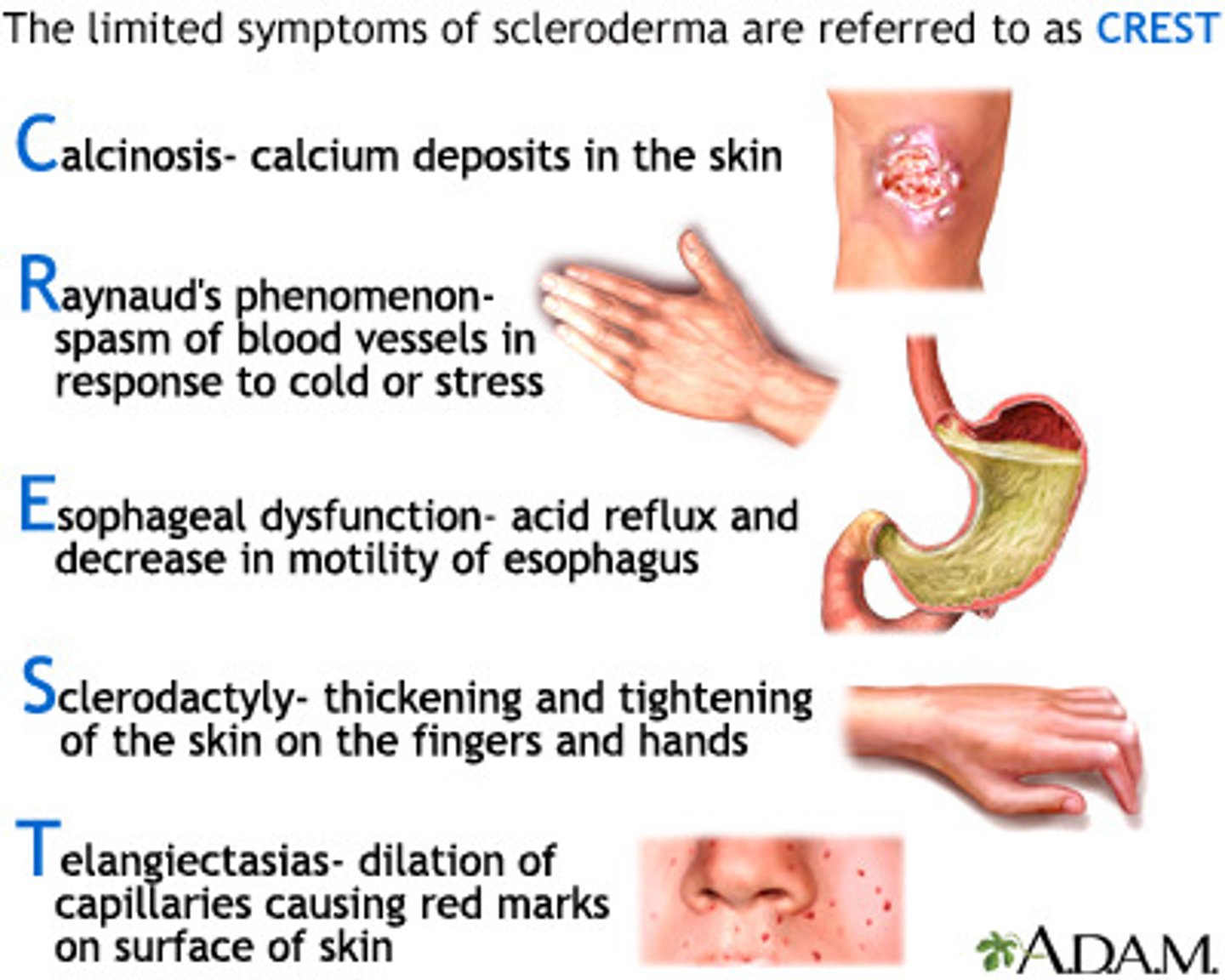
Scleroderma
What: A chronic, diffuse dz of connective tissue causing fibrosis of skin, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs
usually accompanied by Raynaud's phenomenon
Diff Dx
-Symmetrical skin induration of distal extremities and face with skin taut, firm, edematous and firmly bound to subcutaneous tissue
-Polyarthralgia, with flexion contracture of fingers, wrist, and elbows from fibrosis of synovium
Tx: no cure
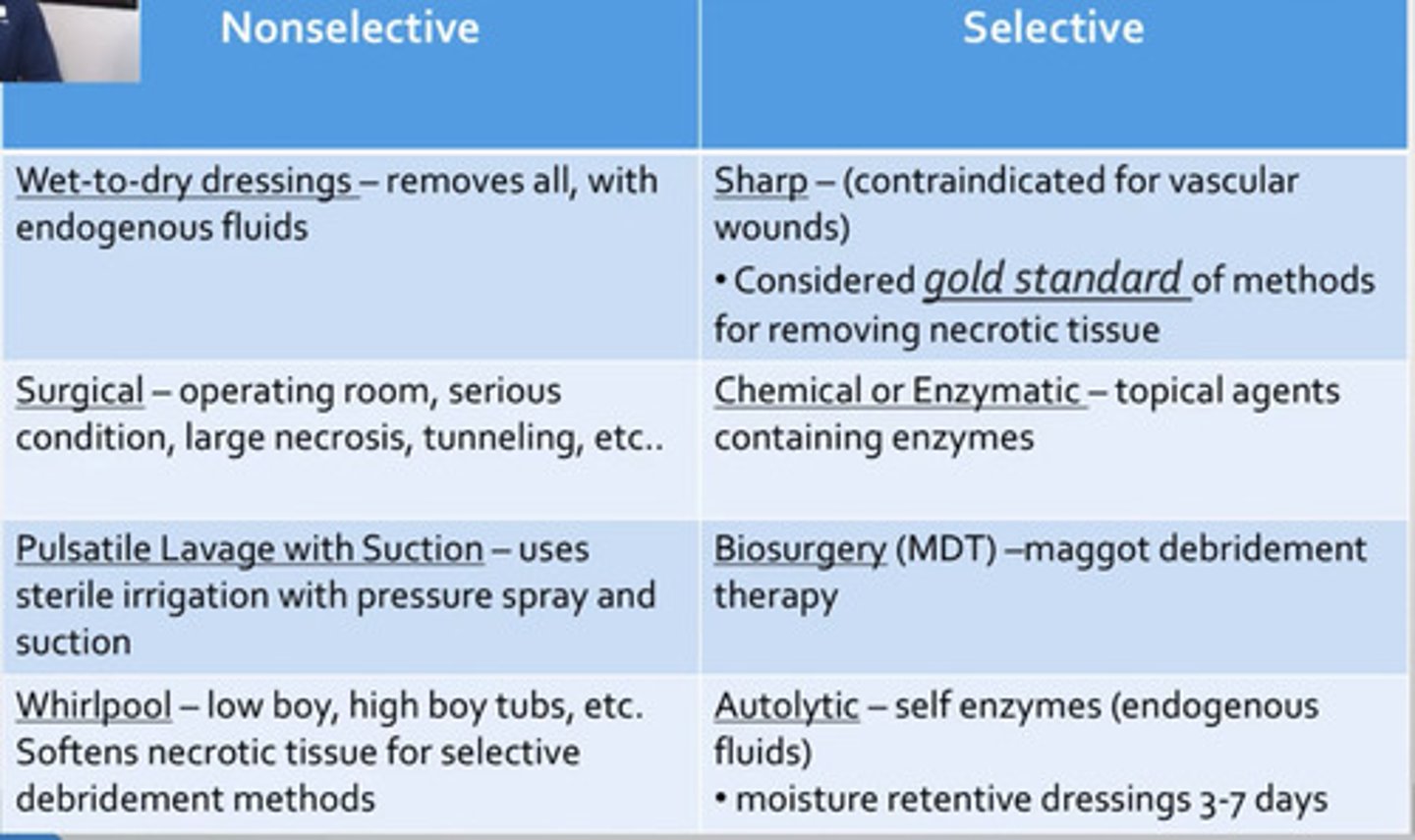
Selective Debridement
-Sharps/scalpel
-Scissors
-Enzymes
-Surgery
-Autolytic Dressings
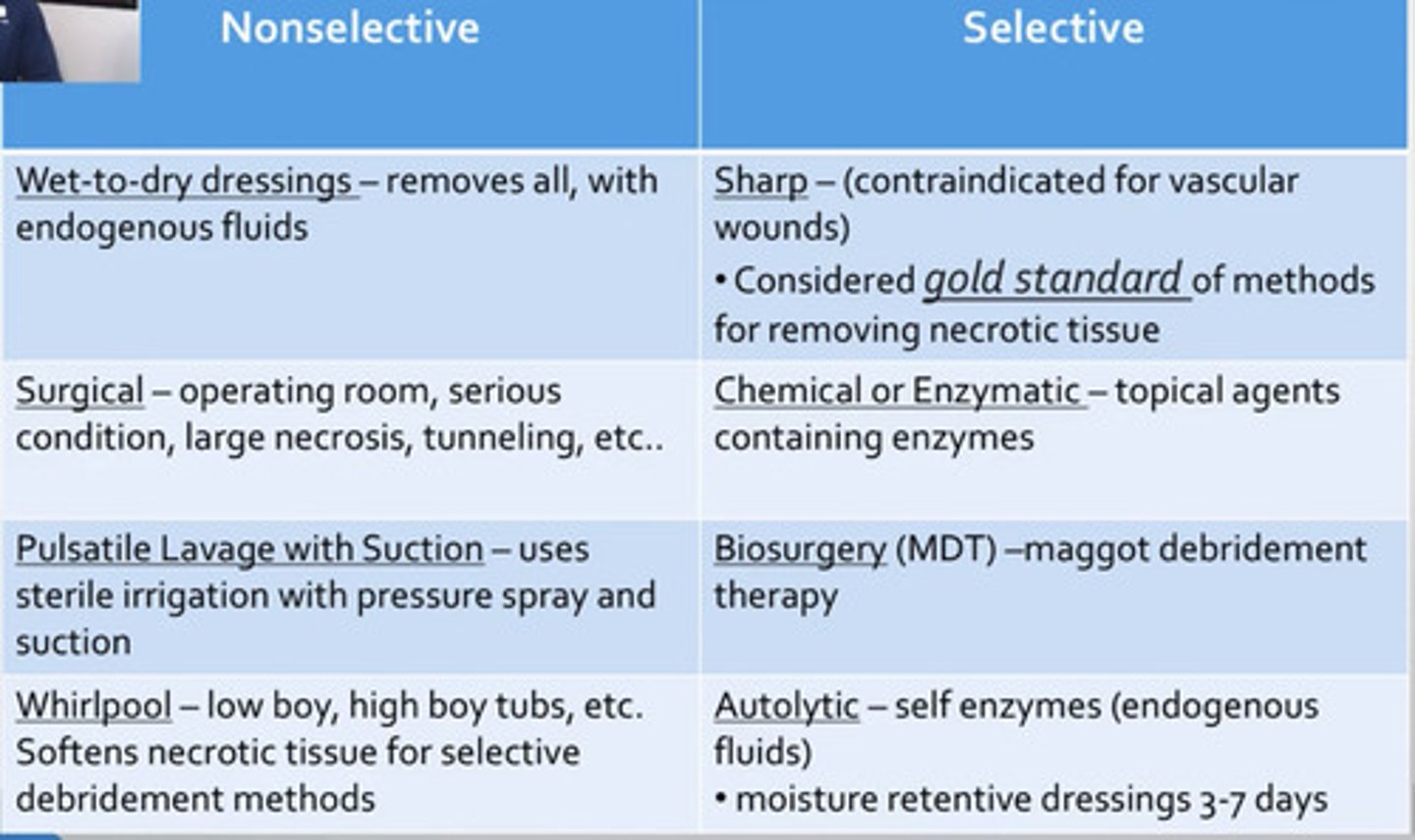
Nonselective Debridement
-Pulsed lavage
-Various dressings
-Whirlpool
Gauze Dressings
-Useful in early debridement, exudate present, wound with dead spaces or tunneling, necrotic exudate
Wet to dry: mechanical debridement of necrotic tissue and slough (goes on wet and dries then takes off tissue when you remove it)
Continuous dry: heavily exudating wounds
Continuous moist: protect clean wounds, autolytic debridement of eschar, delivery of topical needs
Advantages: available, used with saline, gels or topical antimicrobials, can be used on infected wounds, good mechanical debridement, and cost-effective filler for larger wounds
Disadvantages: Requires frequent changes that can disrupt granulation tissue formation, pain on removal (wet-dry), labor-intensive, delayed healing if improperly placed
Contraindication : do not place gauze over granulation tissue without some type of intermediate non-adherent dressing

Autolytic definition
Autolytic debridement is the lysis, or breakdown, of damaged tissue at a wound site by the body's natural defence system by enzymes that digest specific components of body tissues or cells, e.g. proteins, fibrin and collagen

Occlusive Dressings
Used to maintain hydration, facilitates autolytic debridement, wound healing with less pain
Contraindication : Do not place over infected wounds, deep ischemic ulcers, full thickness burns or in some cases very heavy exudates or over Stage IV uclers
Alginates
Derived from seaweed and react with exudate to form gel over wound, used in wounds with moderate to large amount of exudate or with combination of exudate and necrosis
-these wounds require packing and absorption
Advantages: easy to apply, supports debridement in presence of exudate, fills dead space, can be used over infected wounds
Disadvantages: needs secondary gauze or film dressing on top, not recommended for dry or lightly exudating wounds bc this can dry out the wound bed

Films Dressings
clear adhesive membrane permeable to atmospheric oxygen and impermeable to water, bacteria
Used generally with stage 1 and 2 ulcers ot maintain moist wound bed
Advantages: minimize friction, transparent, comfortable, excellent bacterial barrier, promotes faster healing and autolytic debridement, visual evaluation of wound
Disadvantages: non-absorptive, application difficult, not to be used on wounds with fragile surrounding skin or infected wounds
Black/yellow wound with minimal exudate that is partial or full thickness gets what kind of dressing>
-hydrogel
-hydrocolloid
-gauze
-enzyme
Black/yellow wound with moderate to heavy exudate that is partial thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-hydrocolloid
-exudate absorbers
-enzymes
-gauze
Black/yellow wound with minimal exudate that is full thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-Hydrocolloids (paste, granules, powder)
-Exudate absorbers
-Enzymes
-Foam cavity dressing
-Wound VAC

Red/pink wound with minimal exudate that is partial thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-hydrogel
-hydrocolloid (thin)
-enzymes
-film
-non-adherent
Red/pink wound with minimal exudate that is full thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-Hydrocolloids (paste, granules, powder)
-Exudate absorbers
-Foam cavity dressing
Red/pink wound with moderate to heavy exudate that is partial thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-Foams
-Hydrocolloids
-Exudate Absorbers
Red/pink wound with moderate to heavy exudate that is full thickness gets what kind of dressing?
-Hydrocolloids (paste, granules, powder)
-Exudate absorbers
-Foam cavity dressing
-Wound VAC
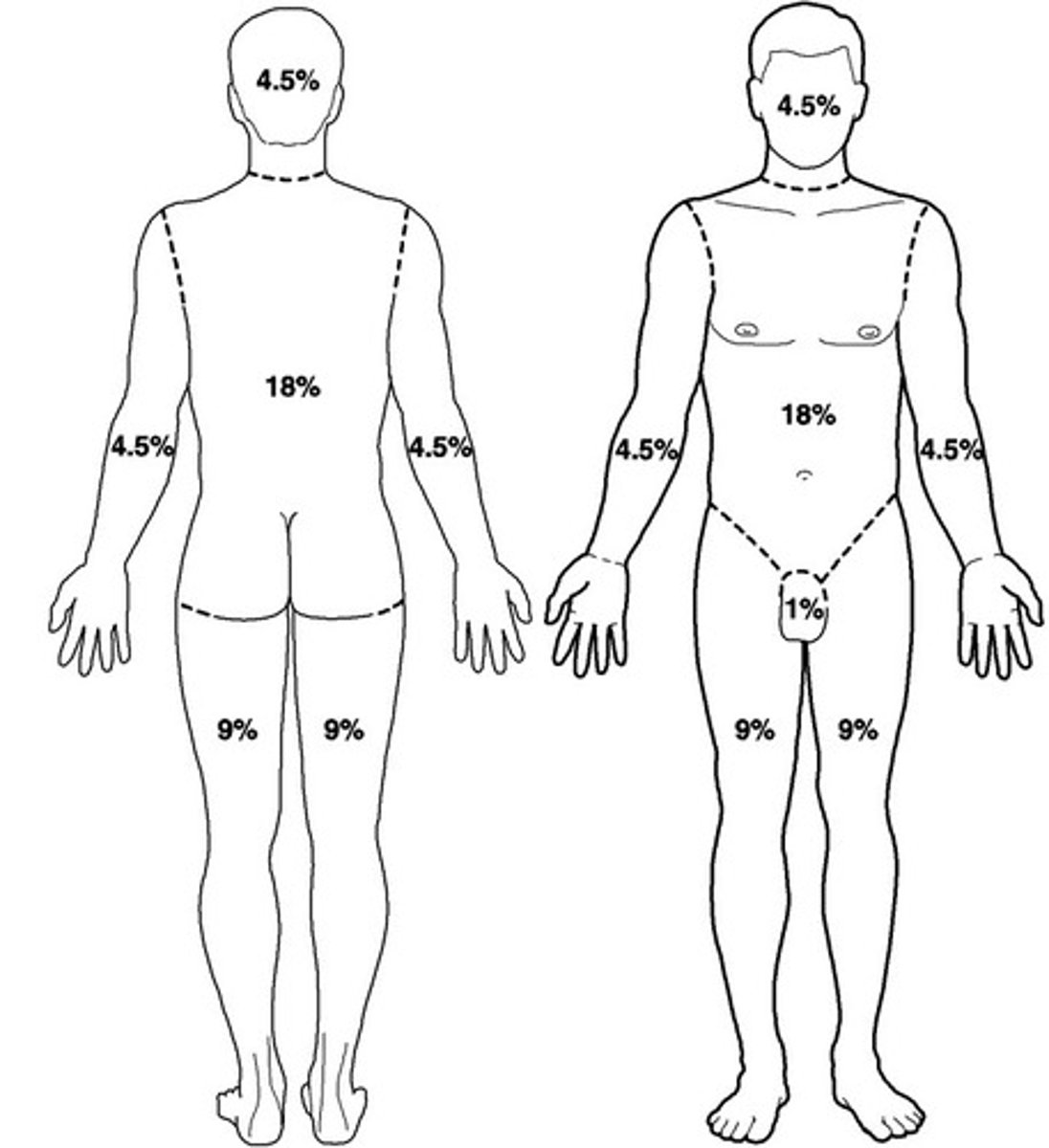
Adult Rule of 9's
Anterior arm=4.5%
Posterior arm= 4.5%
Anterior leg= 9%
Posterior leg= 9%
Anterior Thorax= 18%
Posterior Thorax= 18%
Face=4.5%
Posterior head=4.5%
Perineum/genitals= 1%
Approx 1% of total body surface area (TBSA) may be depicted by the size of the patients palm
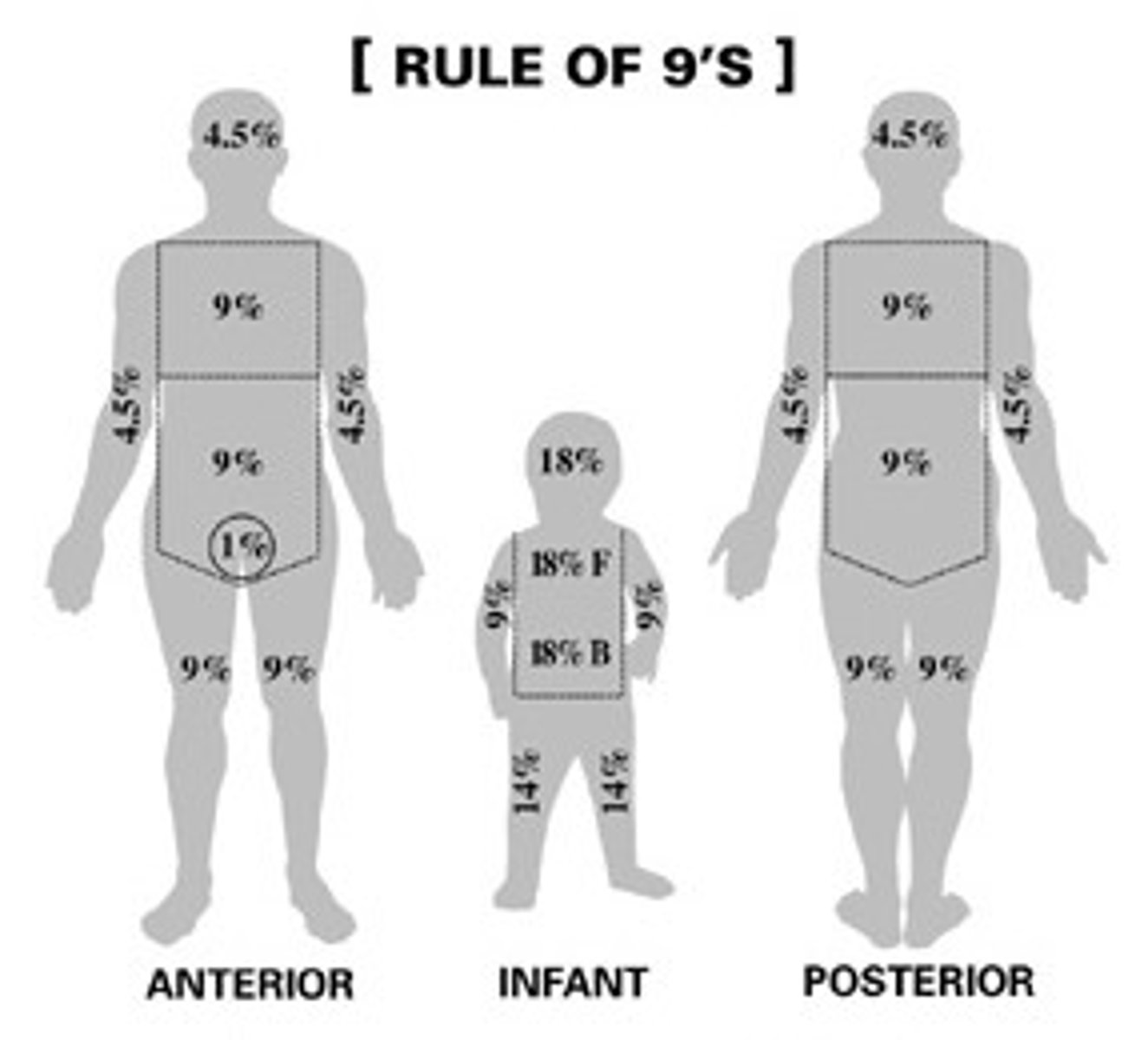
% of TBS for burns on kiddos
Face= 8.5%
Posterior head= 8.5%
Anterior Thorax= 18%
Posterior Thorax= 18%
Anterior arm= 4.5%
Posterior arm= 4.5%
Anterior leg= 6.5%
Posterior leg= 6.5%
Perineum/genitals= 1%
Foams
Cushion and protect the wound
-hydrophilic (absorb moisture) on side of wound and hydrophobic on non-wound side
Advantages: insulate wound, provide padding, absorb large amounts of exudate, east to use and conformable
Disadvantages: require secondary dressing, not for use of dry eschar wounds or wounds with no exudate, nontransparent

Hydrocolloid
adhesive wafers that interact with wound to form gelatinous mass, may be occlusive or semiocclusive, absorbs minimal to moderate exudate, protects partial thickness wounds
When: mild to moderate exudate
Advantages: maintains moist environment, excellent bacterial barrier, nonadhesive to healing tissue, conformable, supports autolytic debridement, reduces pain, easy to apply, time saving, decrease friction
Disadvantages: not used over infected wounds, nontransparent, may soften or changes shape with heat or friction, not for wound with heavy exudate or fragile surrounding tissue, dressing edges may curl

Hydrogels
water or glycerine based gels, used with partial or full thickness wounds with necrosis (tissue damage from burns or radiation), absorbs minimal exudate but lets some pass through secondary dressing
When: arterial insufficiency wounds
Advantages: conforms to wound, rehydrates/moistens wound bed, promotes autolytic debridement, soothing and cooling, transparent, non-adherent, amorphous form can be used when infection present
Disadvantages: not used with high exudate, most require secondary dressing, may macerate surrounding skin
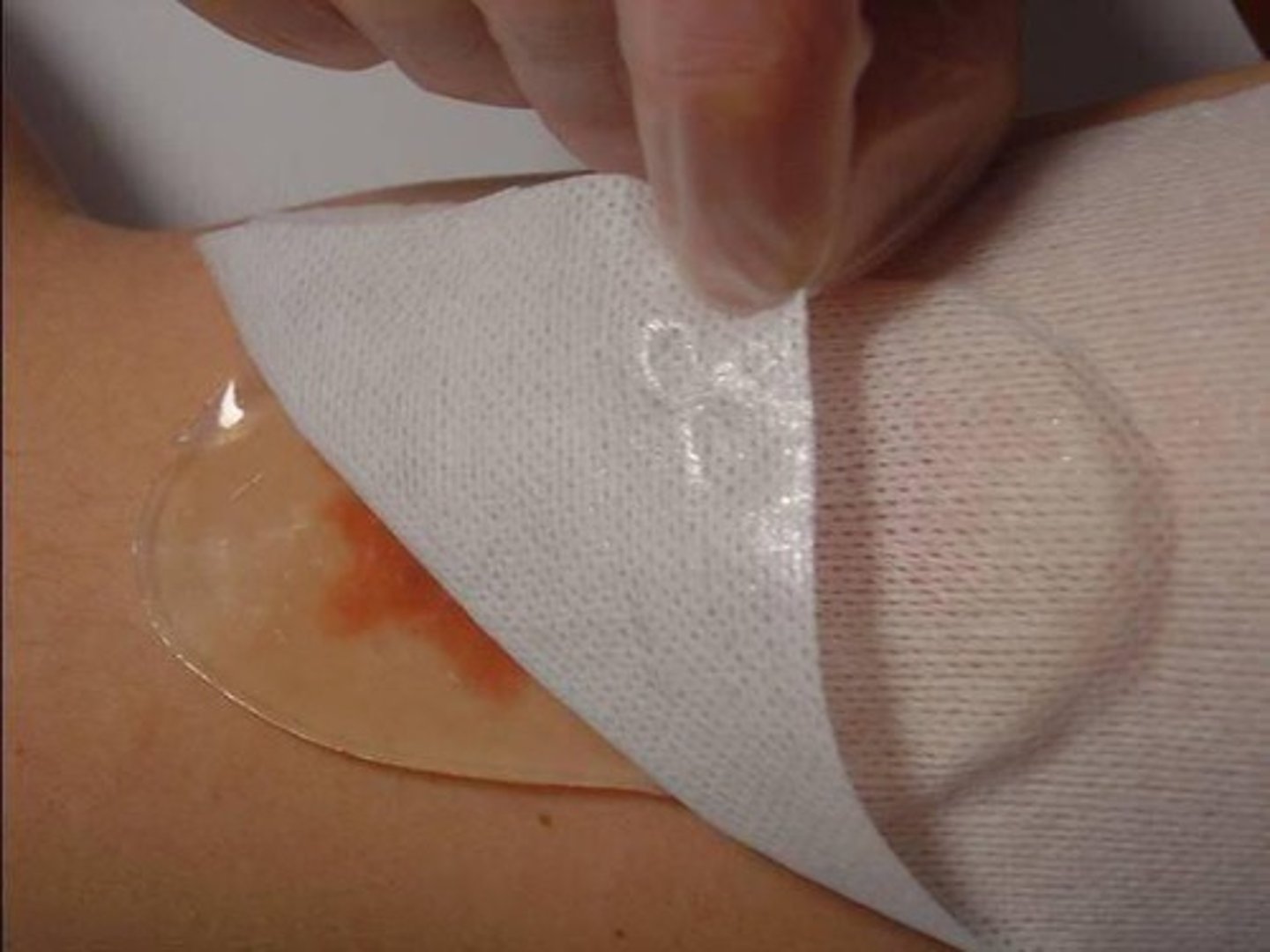
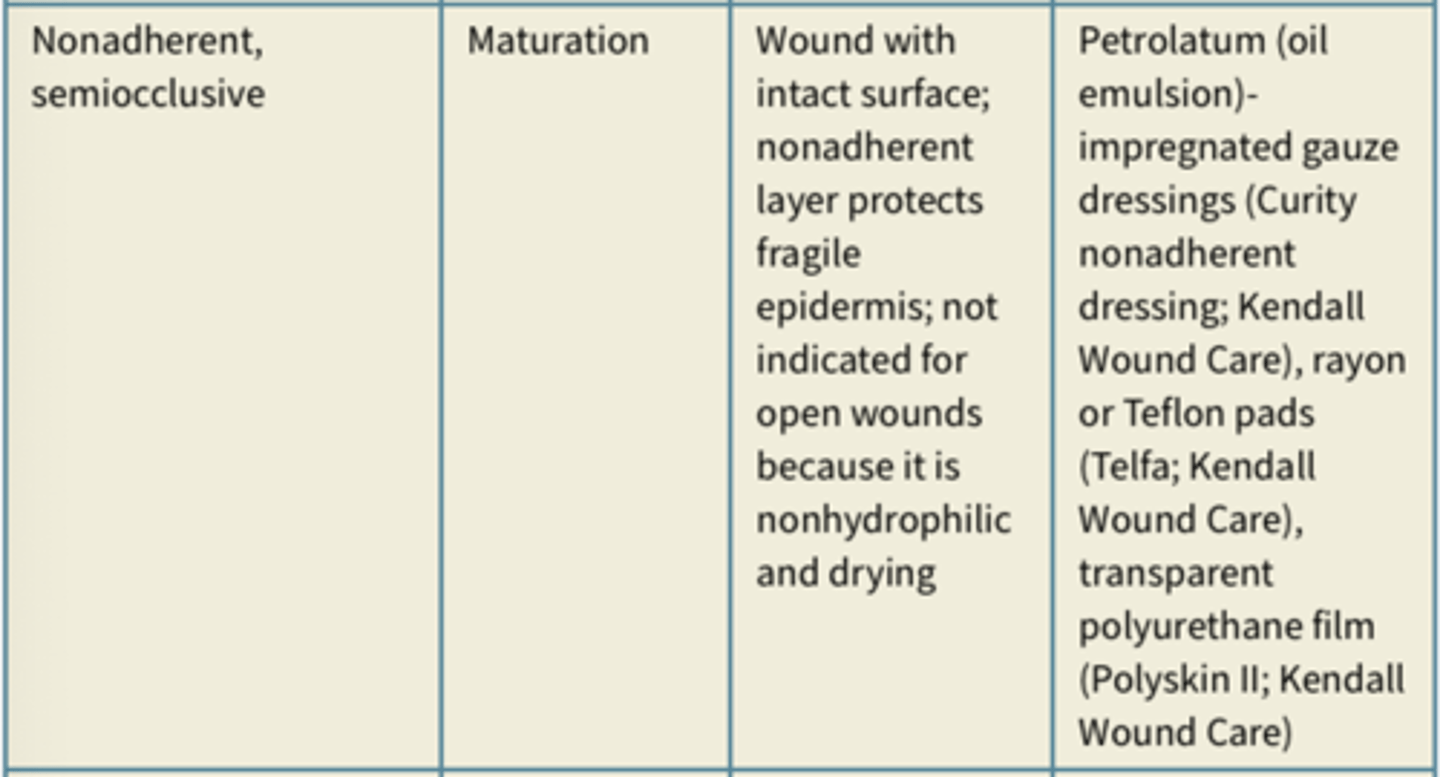
Nonadherent dressing
Gauze like dressing that do not adhere to wound, often petroleum based and impregnated with solution to promote granulation or inhibit bacterial infection
-require secondary dressing
Semirigid dressings
Unna boot is pliable, non-stretchable dressing impregnated with ointments used for venous insufficiency ulcers to control edema and help with healing
Iontophoresis for wound healing
Zinc or histamine with delivery electrode as (+)
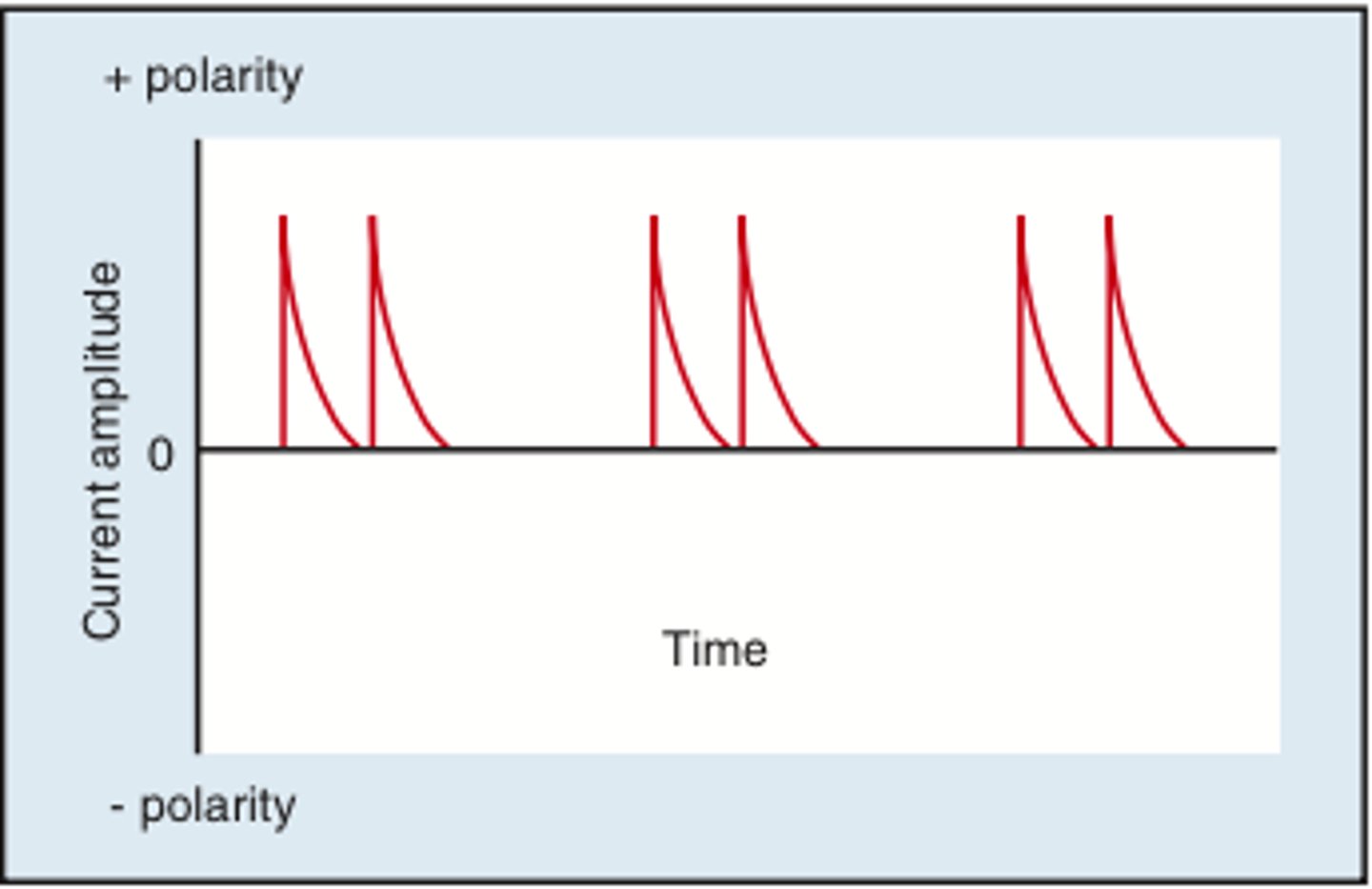
HVPC
high volt pulsed current used tor promote healing
Anode (+): When tissue is in proliferative phase and granulation present, helps promote epithelial cell migration for reactivation of inflammatory process
Cathode (-): use when wound is infected and non-healing
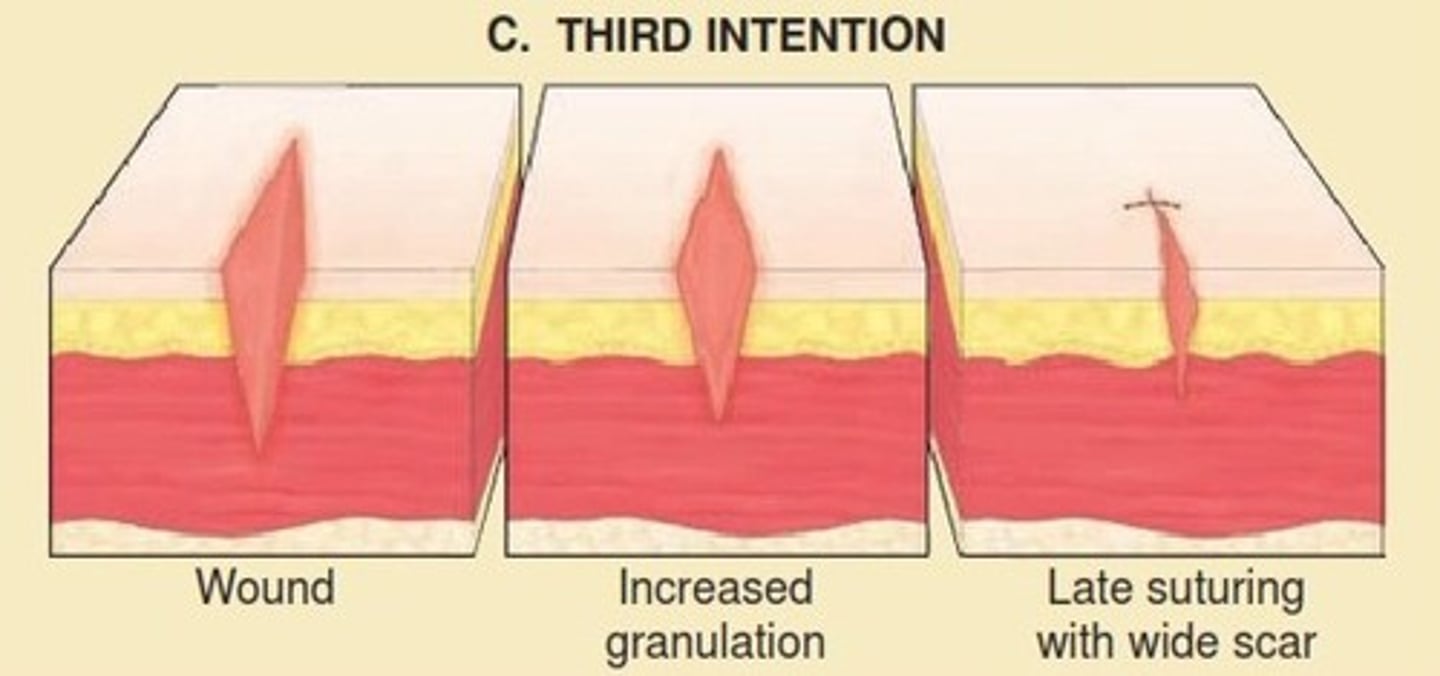
Tertiary (delayed primary) union
A delay in wound healing resulting in suturing of sit for 5-7 days in the presence of wound contamination, large tissue loss, or excessive edema
-Healing sequence is similar to injury treated with primary union except for delay about a week
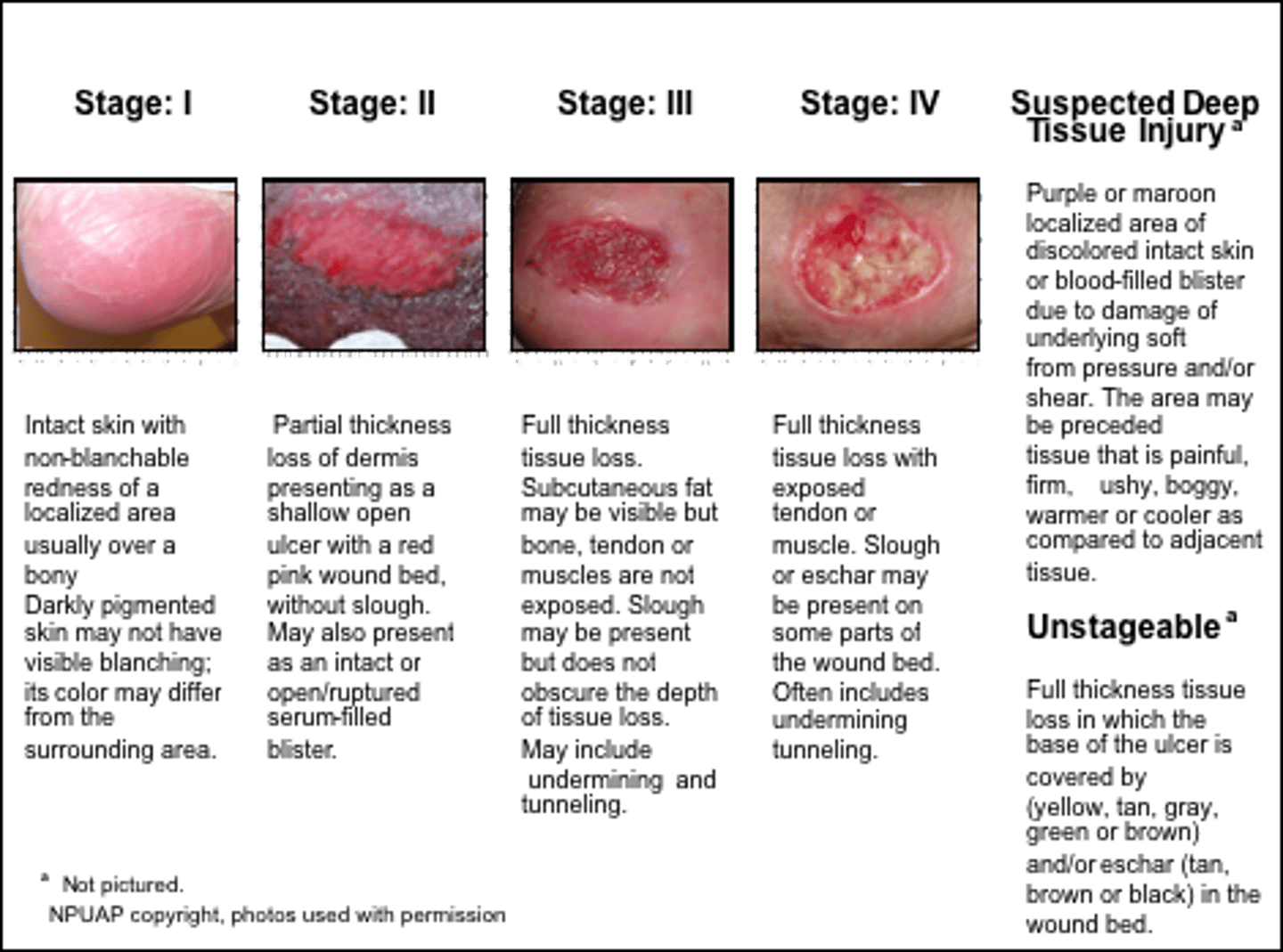
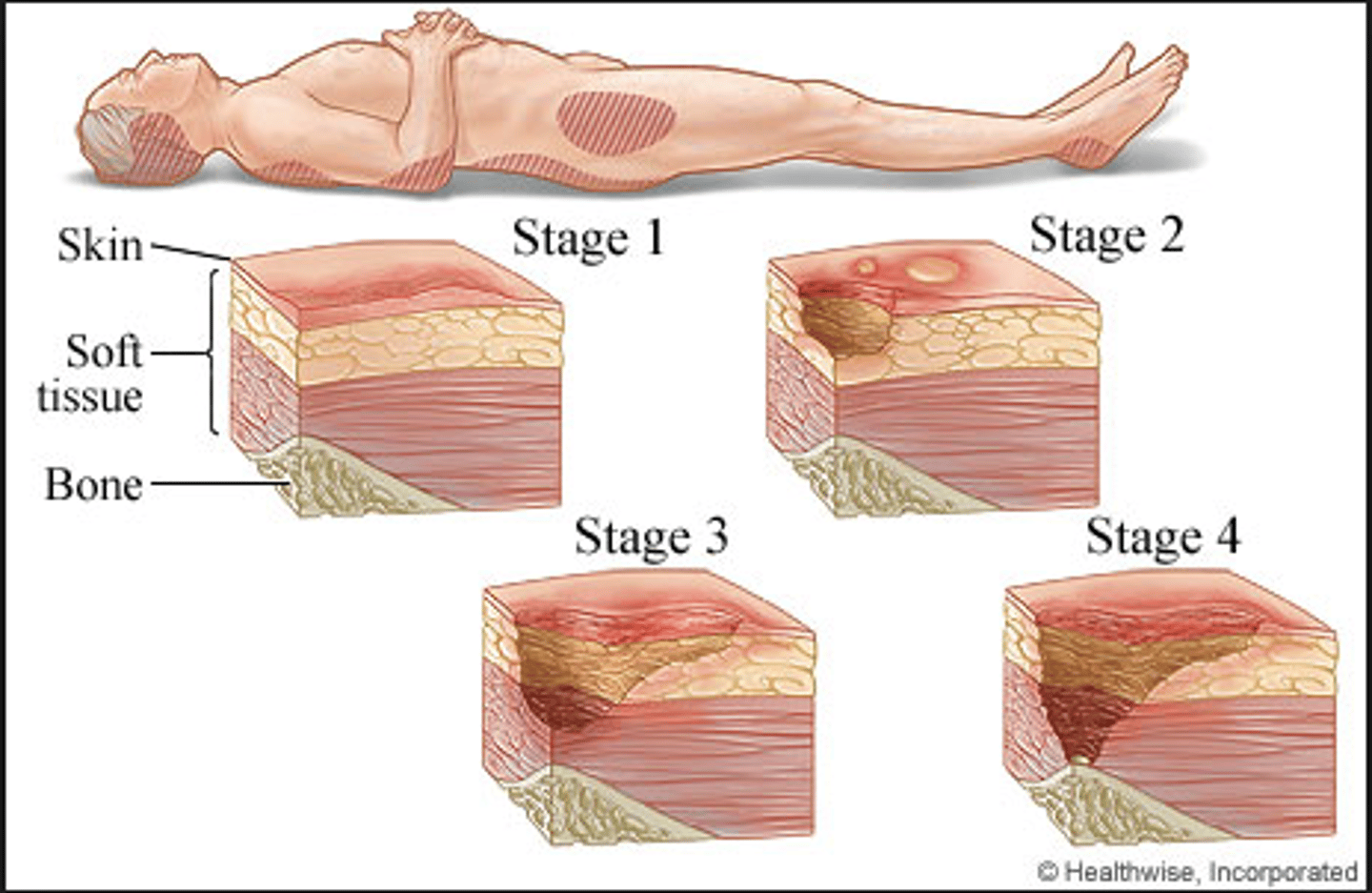
Stages of Pressure Ulcers
stage 1 - nonblanchable erythema of intact skin, reversible with intervention (also discoloration, warmth, edema)
stage 2 - partial-thickness skin loss (epidermis and dermis involved, presents as abrasion, blister, or shallow crater
stage 3 - full-thickness skin loss; into fat layer but not involving underlying fascia
stage 4 - full-thickness skin loss with extensive destruction, beyond fascia and muscle, tendons or capsule may be exposed, ulcer may extend to bone and bone destruction
unstageable - base of ulcer covered by slough and/or eschar in wound bed
Treatment for Pressure Ulcers
Stage 1: vigorous pressure, friction and moisture-alleviating measures required (positioning and off loading)
Stage 2: dermis is exposed - if no infection, appropriate dressing that occludes wounds from environment, pressure alleivating and mositure-alleviating techniques
Stage 3: Requires debridement, dressings and advanced pressure alleviating measures
Stage 4: debridement, dressings, pressure alleviating, surgery and grafting
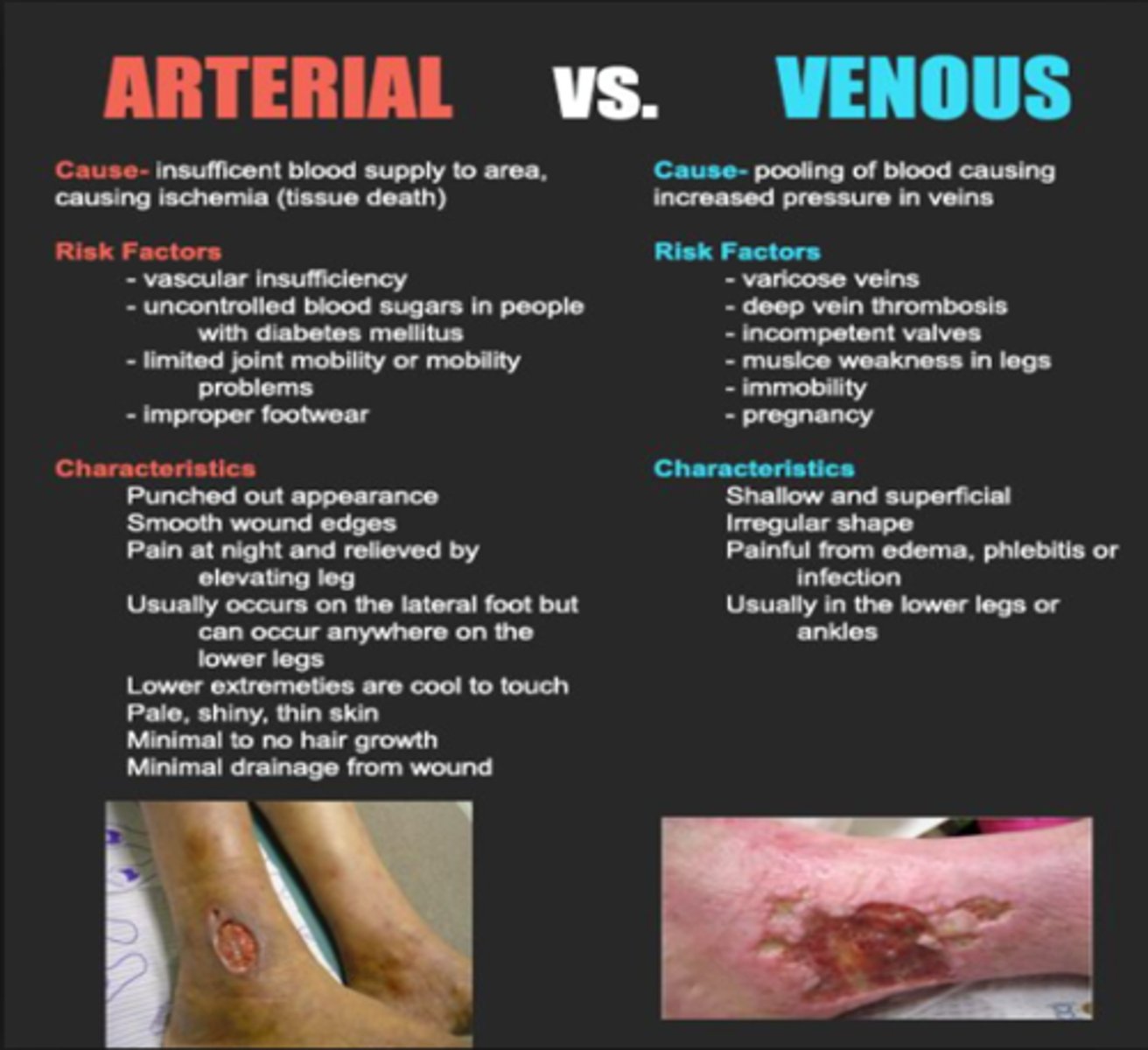
Arterial Insufficiency Ulcers
What: Caused by arteriosclerosis obliteran (often pt with DM)
Clinical presentation:
-Deep and painful wounds with cold and pale skin
-lateral malleolus and toes, lower 1/3 of leg
-smooth edges, well defined, tend to be deep
-thin and shiny hair loss, yellow nails
-SEVERE pain and elevation increases pain
Dx: ABI <0.5 and wounds will not heal with out medical interventions
Tx:
-bed rest with HOB elevated
-stop smoking
-wound care
-ROM
-Wound VAC
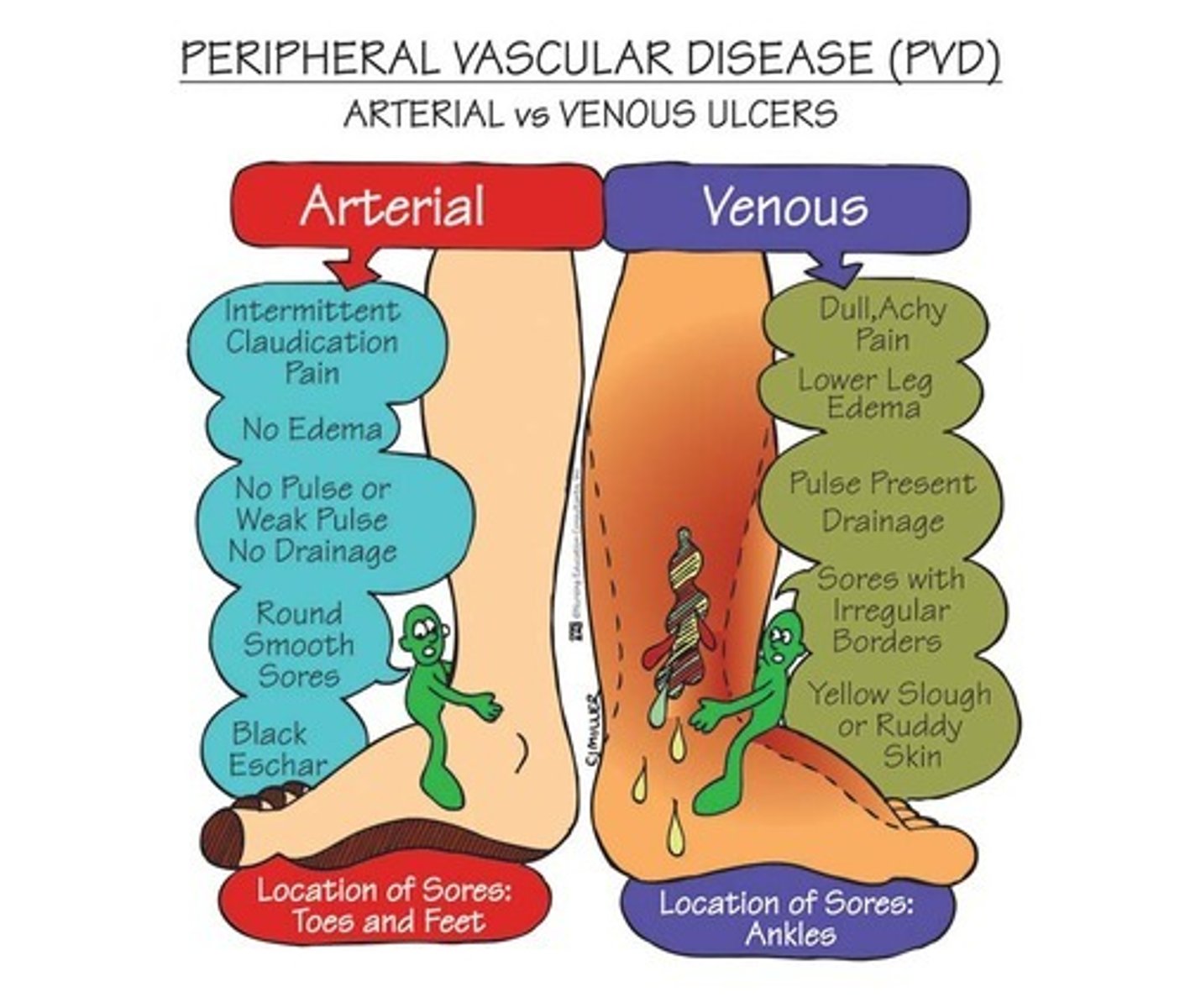
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers
What: venous thrombosis, varicose veins, and others
Clinical Presentation:
-proximal to medial malleolus wounds
-irregular, shallow appearance
-Painless and superficial wounds with good peripheral pulse
-Edema present and hemosiderinosis of the skin
-mild to moderate pain but elevation decreases pain
Tx:
-elevation and compression for edema
-Active exercise
-compression stockings for LT management
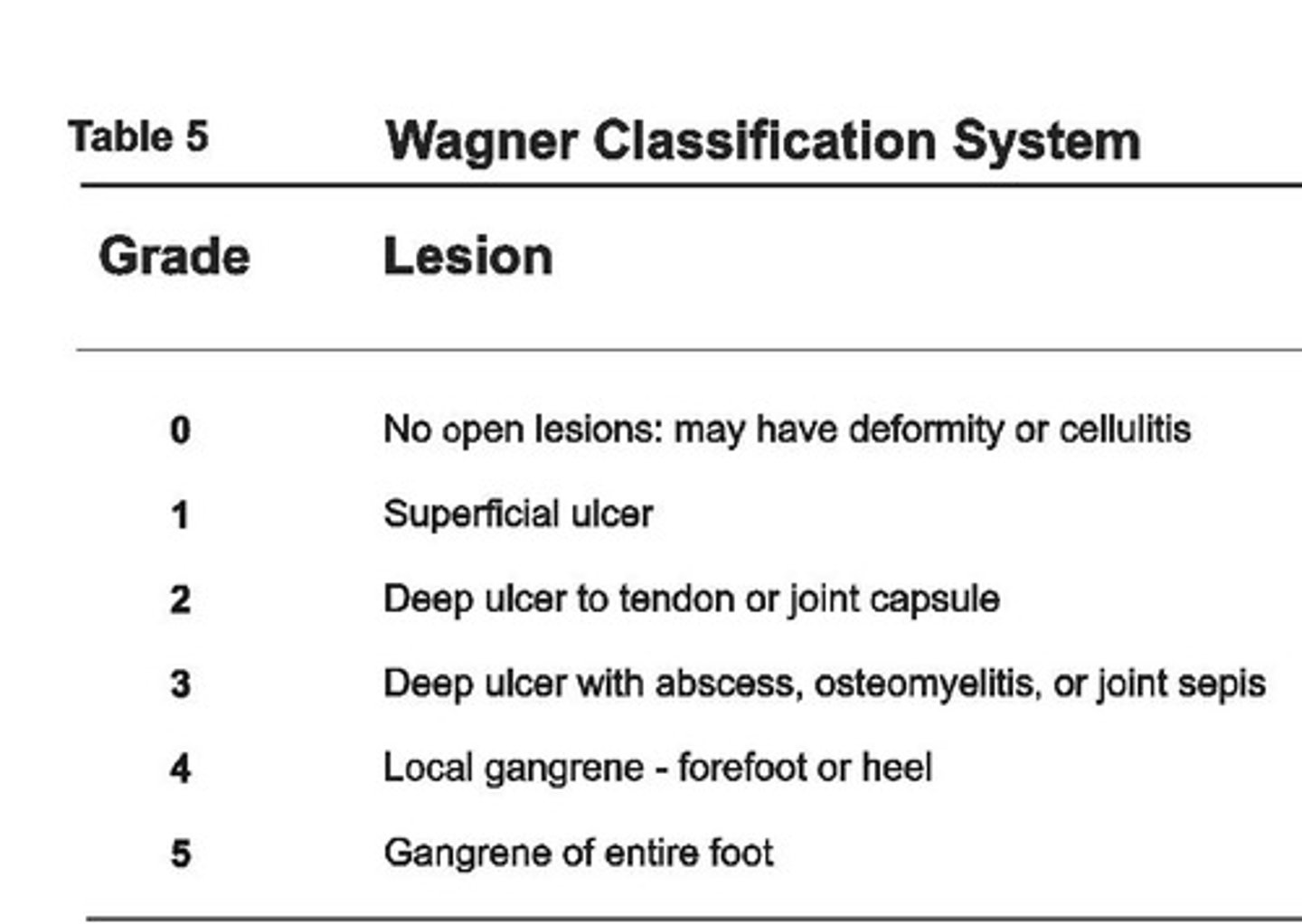
Diabetic Foot Ulcers
What: peripheral vascular disease and neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy (decreased perspiration, dry cracked skin), decreased sensation and circulation, Charcot foot
Staging using the Wagner Scale
Tx:
-debride necrotic tissue and promote moist wound bed
-offload ulcer from abnormal pressures
-rocker bottom shoe sole
-contact casting or WB stats with AD
Contraindications for total contact casting: infection or ulcer depth greater than width
Burns Classification
Superficial (1st degree)
-only epidermis
-erythema, slight edema, tenderness & no blistering
-Some peeling over 2-5 days
Superficial partial thickness (2nd degree)
-damage to upper layers of dermis and epidermis]
-blisters, inflammation severe pain
-can heal on own
-7-10 days of healing
Deep partial thickness (2nd degree)
-most of dermis and injury to hair follicles, nerve endings and sweat glands
-red or white appearance, edema , blistering, and severe pain
-pain due to not all nerve endings destroyed
-healing 3-5 weeks (hypertrophic and keloid scarring common)
Full thickness (3rd degree)
-destruction of epi, dermis and subcut tissue with some muscle involvement
-tissue is white, gray or black with dry surface, edema, eschar formation and insensate or little pain
-nerves endings destroyed
-Surgical removal of eschar (escharotomy) and skin graft necessary for healing
-infection and hypertrophic scarring
-keloid scarring
Subdermal (4th degree)
-complete skin destruction and involves muscle and bone
-Skin charred, dray and mummified
-destruction of vascular system may lead to tissue necrosis
-Caused by prolonged flame or hot liquid or from electrical burn
-Amputation and muscle paralysis common
![<p>Superficial (1st degree)</p><p>-only epidermis</p><p>-erythema, slight edema, tenderness & no blistering</p><p>-Some peeling over 2-5 days</p><p>Superficial partial thickness (2nd degree)</p><p>-damage to upper layers of dermis and epidermis]</p><p>-blisters, inflammation severe pain</p><p>-can heal on own</p><p>-7-10 days of healing</p><p>Deep partial thickness (2nd degree)</p><p>-most of dermis and injury to hair follicles, nerve endings and sweat glands</p><p>-red or white appearance, edema , blistering, and severe pain</p><p>-pain due to not all nerve endings destroyed</p><p>-healing 3-5 weeks (hypertrophic and keloid scarring common)</p><p>Full thickness (3rd degree)</p><p>-destruction of epi, dermis and subcut tissue with some muscle involvement</p><p>-tissue is white, gray or black with dry surface, edema, eschar formation and insensate or little pain</p><p>-nerves endings destroyed</p><p>-Surgical removal of eschar (escharotomy) and skin graft necessary for healing</p><p>-infection and hypertrophic scarring</p><p>-keloid scarring</p><p>Subdermal (4th degree)</p><p>-complete skin destruction and involves muscle and bone</p><p>-Skin charred, dray and mummified</p><p>-destruction of vascular system may lead to tissue necrosis</p><p>-Caused by prolonged flame or hot liquid or from electrical burn</p><p>-Amputation and muscle paralysis common</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/62c31c43-86f9-471a-bea6-cdb22d70f947.jpg)
Metabolic effects of burn injuries on the body
increased metabolic process results in
-rapid decrease in body weight
-negative nitrogen balance
-decreased energy stores
Cardiac and circulatory effects of burn injuries on the body
-loss of plasma and intravascular fluid follows a serious burn
-fluid loss results in decreased cardiac output
Topical medications for burns
-silver sulfadiazine
-bacitracin
-Neosporin
-Sulfamylon

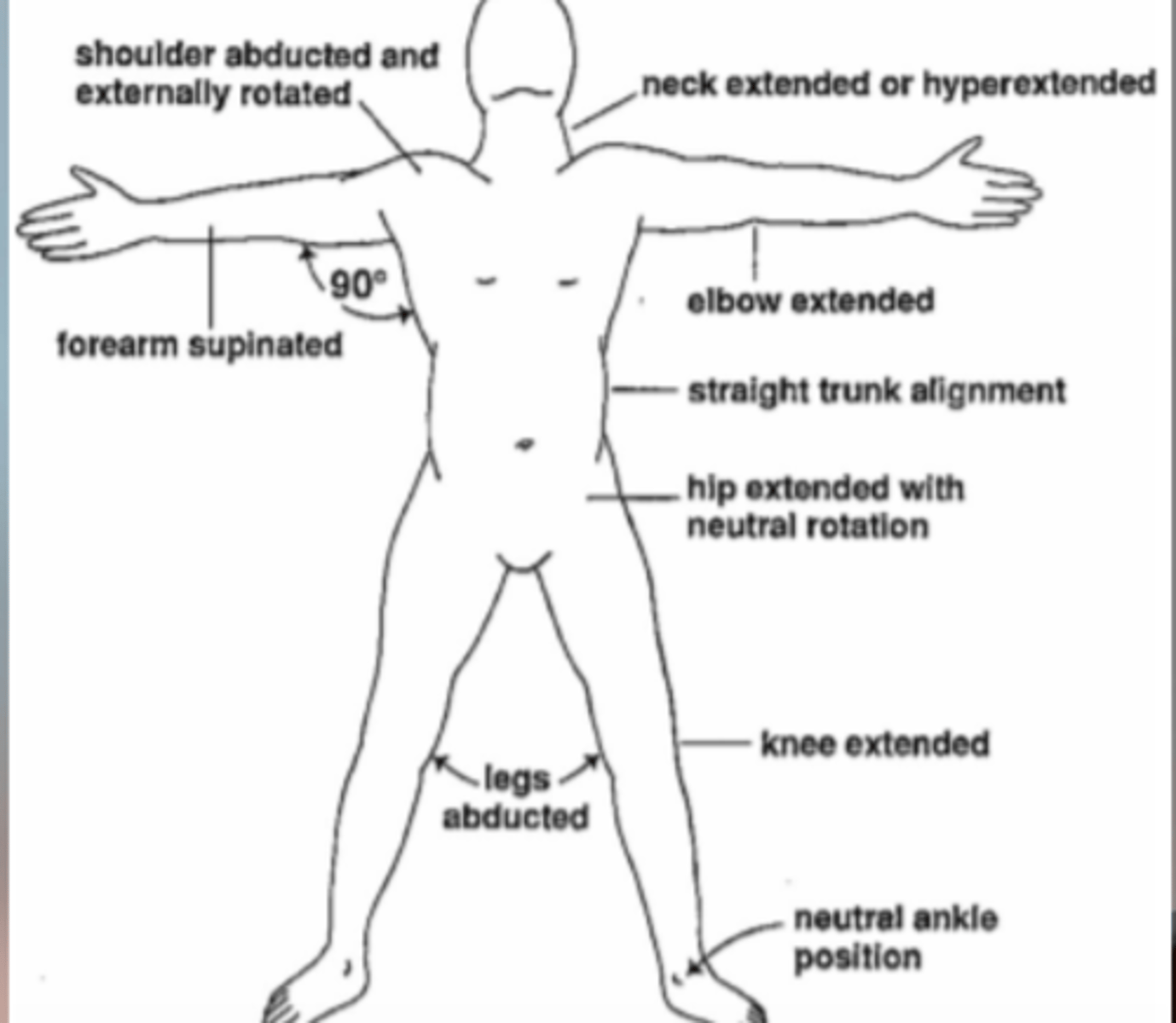
Positioning to prevent contractures due to burns
Anterior neck: hyperextension with firm cervical brace
Shoulder: ABD and ER in airplane splint
Elbow: extension and supination
Hand: wrist ext, MCP flexion , IP extension brace; extension and ABD brace
Knee: extension, posterior knee splint
Ankle: DF spint or in neutral in AFO
Cutaneous Nerve Endings: Krause end bulbs
Cold
(Santa Klaus in the Kold)
Cutaneous Nerve Endings: Messiner Corpuscles
Touch and texture
Cutaneous Nerve Endings: Ruffini endings
Heat/hot
Cutaneous Nerve Endings: merkel discs
light touch (finger tips)
Cutaneous Nerve Endings: Pacinian corpuscle
Vibration and pressure
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers: VENMO
VENous Medial malleOli
Arterial Insufficiency Ulcers: ALMA
Arterial Lateral MAlleolus
Can the stage of a pressure ulcer be "renamed or backstagesd"
NO, no, no
-if it is dx as a stage 3 it is always a stage 3 but can document about "improving stage 3 ulcer with more than 50% granulation tissue and ...."
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and 2
Type 1: occurs on the face
Type 2: occurs on the genitals
Exudate amount and type of dressing to use
Very mild exudate - transparent films
Mild exudate- hydrogel dressing, hydrocolloid
Moderate exudate - foams
Heavy exudate- Alginates, hydrofiber
General rule, if there is more than 50% necrotic tissue present you can use,
a non-selective method of debridement
When to use what dressing (condensed)
Transparent films: no exudate and no infection present, to allow autolytic debridement, stage 1-2 pressure ulcer, skin donor sites (note: leave 1-2 in margin on application)
Hydrocolloids: protecting partial thickness wounds (stage 2 pressure ulcer), not for infections or heavy exudate or fragile surrounding skin
Hydrogels: Partial or full-thickness, necrosis/slough but NOT heavy exudate or infected ulcers
Alginates and Hydrofibers: best for heavy exudate, necrosis, packing, infected or not infected wounds, not for dry wounds, NOT for arterial wounds but maybe venous
Gauze Wet to Dry: necrotic tissue that needs removal (arterial ulcers) (but not venous as it would pull of granulation