DNA structure
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Nucleotide
A building block of DNA, consisting of a five-carbon (deoxyribose) sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group.
Deoxyribose sugar
sugar used in DNA to make up the "backbone"
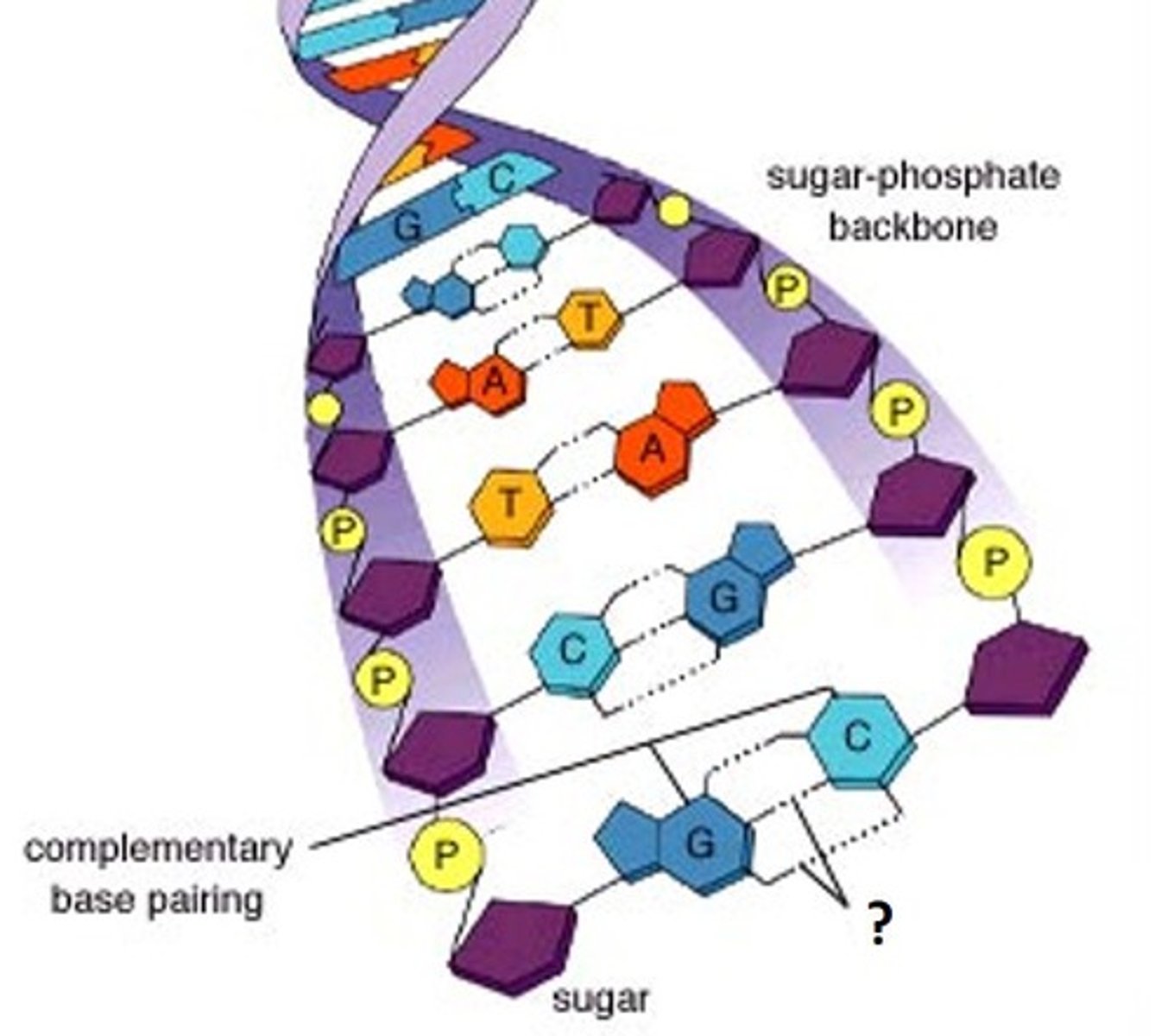
Complementary Base to Adenine
Thymine
Complementary Base to Cytosine
Guanine
Double Helix
shape of the DNA molecule
Watson and Crick
Developed an accurate model of DNA
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for a trait
Deoxyribose
A five-carbon sugar that is a component of DNA nucleotides
DNA Back Bone
Made from Phosphate and Deoxiribose
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain many genes
Gene
A segment of DNA on a chromosome that codes for a specific trait
nucleic acid
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus
covalent bond
the type of bond that hold nucleotides together
hydrogen bond
the type of bond that holds the two sides of DNA together
RNA
single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose
AUGC
RNA bases
Helicase
enzyme that unzips DNA
Primase
An enzyme that joins RNA nucleotides to start DNA replication
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand made with one primer
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments
Ligase
enzyme that glues okazaki fragments together