DNA SEQUENCING METHODS
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
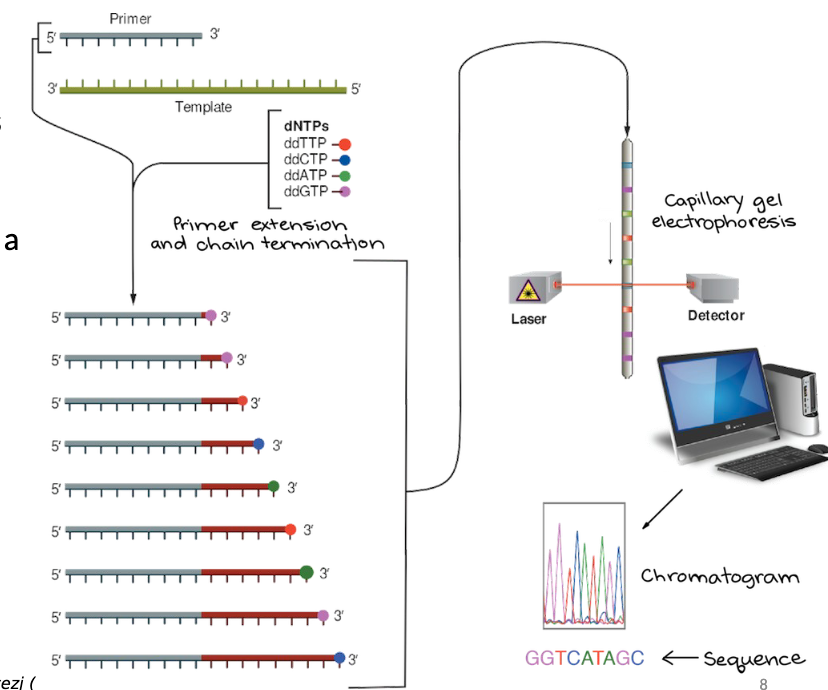
What is Sanger sequencing?
A chain termination method that starts like PCR, but adds dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) as well as dNTPs which are chain terminating versions of each nucleotide that are labelled with a different color dye.
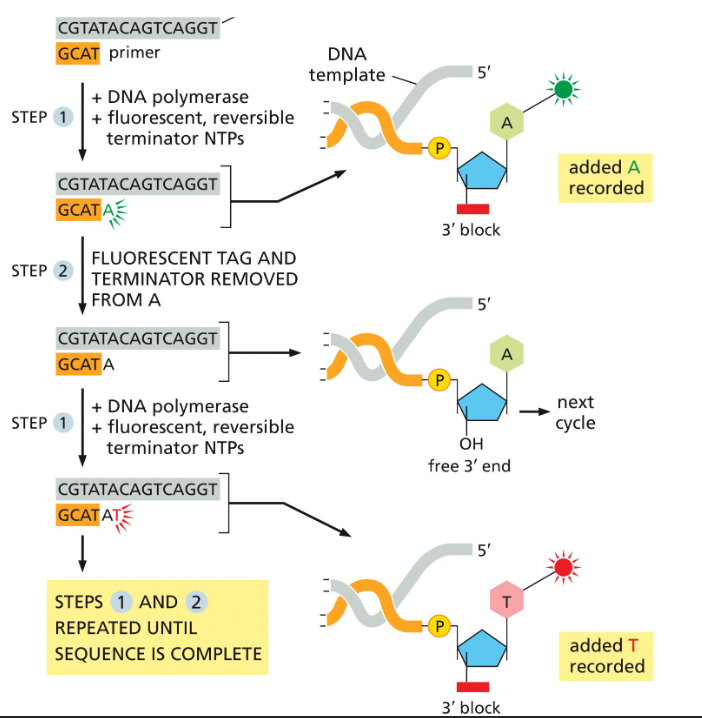
What is Illumina?
DNA is fragmented and captured onto a flow cell, where the fragments are amplified and form clusters that we can see using a fluorescent, the fluorescent light shown is associated with a specific nucleotide, and will repeat until the sequence is complete.
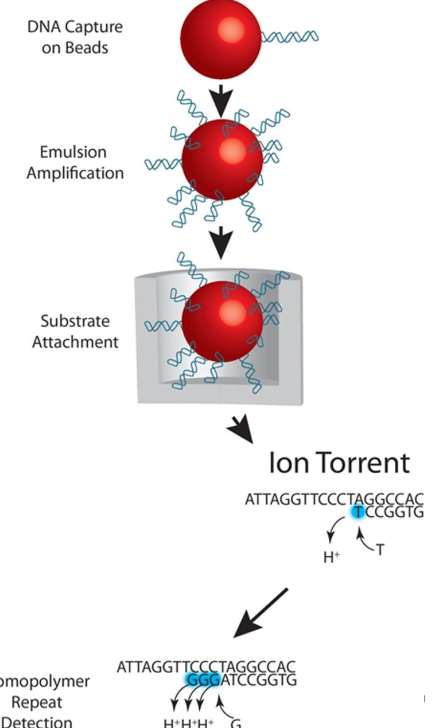
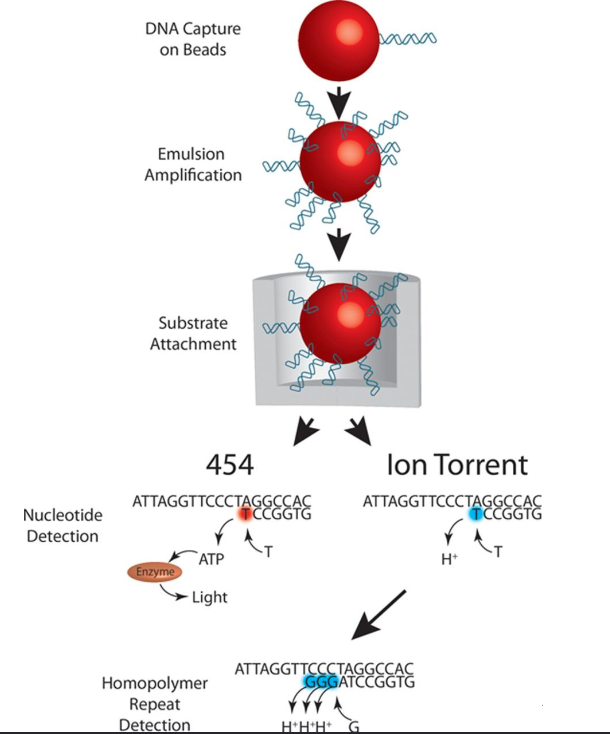
What is Ion torrent?
DNA is captured on beads, and amplified before placed into a well. The well has a ion-sensitive layer and detector beneath it, so if an incorporated nucleotide flows across the detector a proton is released, the pH changes and there is a voltage change which is converted into sequence reads.
What is 454- pyrosequencing?
DNA is captured on beads and amplified before being placed in a well. Nucleotides flow across the well plate and when a correct nucleotide is added, pyrophosphate is released and initiates a chain reaction that ends with luciferase producing light which is proportional to the number of nucleotides added. A camera is used to capture the light intensity from each well which the software translates into a DNA sequence.
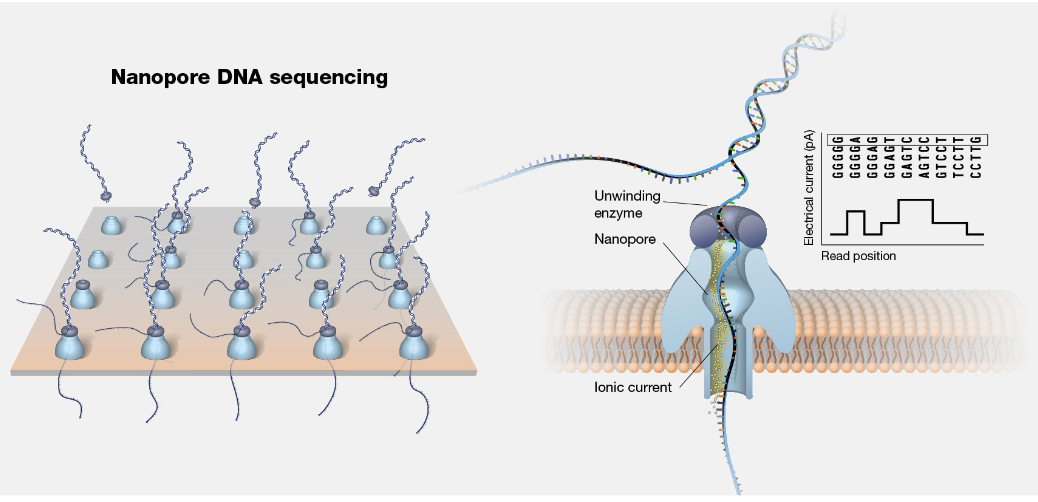
What is Nanopore?
A motor feeds DNA through a nanopore, and the DNA blocks the flow of the current through the pore and the changes in the current are decoded into the DNA sequence.
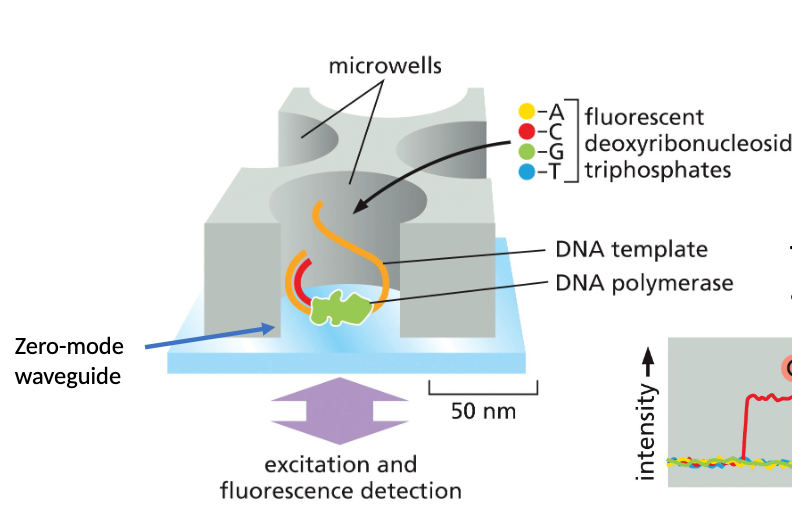
What is SMRT?
Single-molecule-real time sequencing uses deoxyribonuleoside triphosphates (fluorescent dye attached to a terminal phosphate). The fluorescent dye diffuses after each nucleotide incorporation by polymerase.