Nerves and CNS EXAM 3
1/111
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
CNS
central
brain, spinal cord
PNS
peripheral
nerves
neuron
specialized cell that conduct signal processes from nerves
"excitablle cells"
- amitotic (no cell division)
- long-lived
- receive stimuli
- transmit electrical signals
- release neurotransmitters
sensory
receptor -> CNS
Motor
CNS -> effector
somatic
body wall, aware and voluntary
somatic sensory
feel temperature on the skin
somatic motor
causes to biceps to contract
autonomic/automatic/visceral
organs & vessels/ involuntary control and less aware
autonomic sensory
senses blood pressure
autonomic motor
lowers heart rate (cardiac muscle)
sympathetic
fight or flight (increasing energy)
parasympathetic
rest and digest (calming)
neuroglia
supporting cells
neuropil
background of cytoplasmic extensions of all nervous cells
Steps of neurotransmitter
- Axon: transmits signal (depolarization) -> action potential
-> opens sodium & potassium gates -> flips the charge - sends neurotransmitter vesicles to terminals
axon terminal -> release neurotrans : to the sarcolemma of muscle or to another cell (neuron)
axon terminal forms a synapse with another cell
synpase
axon terminal forms with another cell
nerve
bundle of axons that are wrapped together (mixed function)
multipolor (motor)
interneurons - between each other in the brain
- to effectors
- stuck in CNS
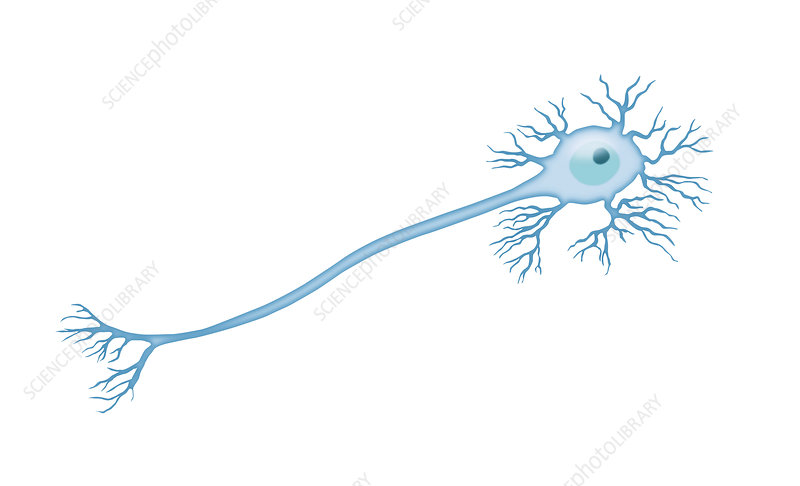
bipolar (special sensory)
special senses
go on in our head usually
- hearing, sight, taste, smell -> to CNS
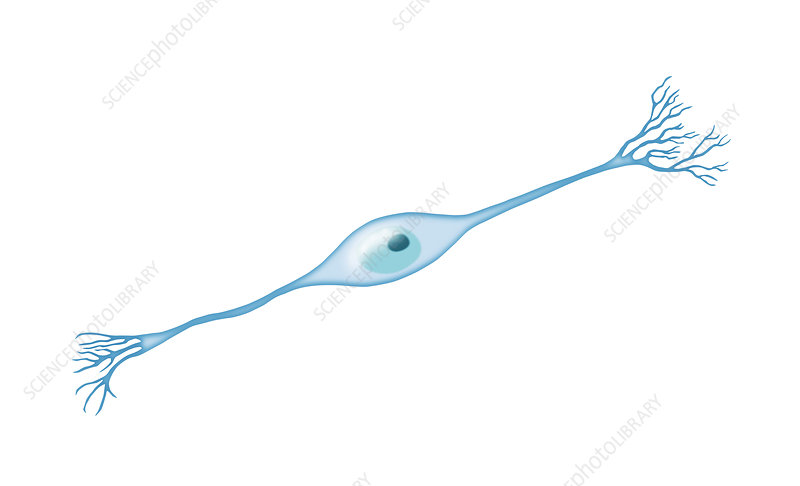
unipolar (general sensory)
forms long nerves
- mostly in skin (feeling)
- pain, pressure, temperature
skin -> CNS
cell body is always in or near CNS
neurilemma
only on axon protective coating
astrocyte cells
- filter blood in CNS
- control capillary permeability
- control chemical enviroment of neurons
- wrap blood vessels (filter)
- blood-brain barrier
- protect brain from toxins, chemicals, etc
microglial cells
phagocytic / destory pathogens (digest) debris
- part of our defense system in CNS
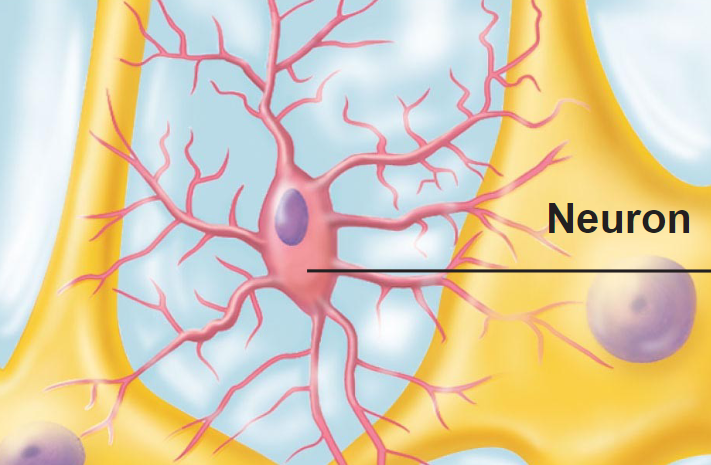
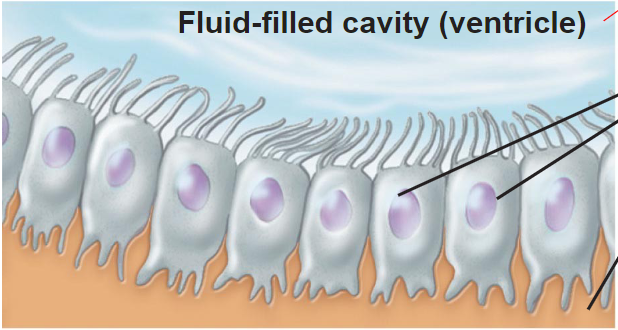
ependymal cells
- secretory
- line cavities of brain & spinal cord in CNS
- secrete cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- CSF cushions, protects, nourishes, nervous tissue
- line CSF fllied cavities/ventricles
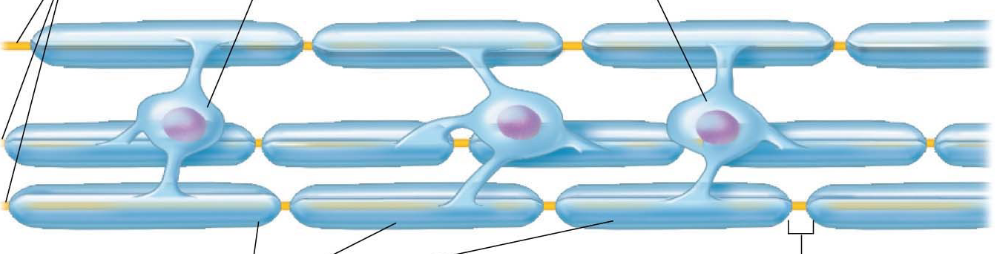
oligodendrocytes
- have processes that form myelin sheaths around CNS nerve fibers
- produce myelination in CNS (a membrane based lipid coating around axons)
- myelin insulates & protects axons, increases speed of conduction of nerve impulse
white matter
mostly myelinated axons & dendrites, paler color
gray matter
mostly cell bodies & synapses, darker color (most synapses occur)
Schwann cells
- in PNS (travel to/from distant areas)
- surround fibers
- produce myelination in PNS (membrane based lipid coating around axons) -> repeatedly wrap
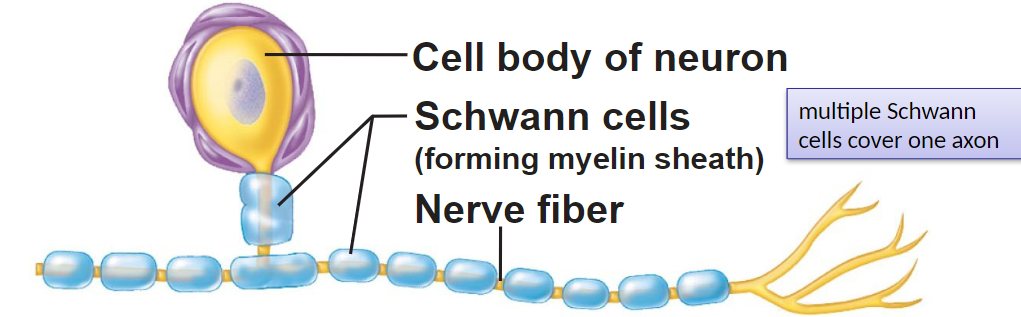
neurilemma sheath
multiple ones wrap axons
myelin sheath
repeated flat layers of lipid membrane of schwann cell
-mylein insulates, protects axons, increases speed of conduction of nerve impulse
neurilemma
ring of flattened cytoplasm & nucleus of schwann cell
unmyelinated
ion exchange continuous/slow
myelinated
few ion exchanges at nodes -> FAST
multiple functions
many axons
At rest
-70 mV inside axons (0 on outside) -> resting membrane potential
- diffusion of both sodium (IN) and potassium (OUT) MORE POTASSIUM!!
- also negative (-) proteins inside always
- also use sodium/potassium pump (active transport)
dendrities
stimulates neuron at?
ligand
chemical - neurotransmitter/hormone/ion
voltage gates
respond/open based on charge
initial stimulus
usually chemical -> to dendrite
depolarization
(sodium first …. increases charge inside)
potassium out (repolarize)
hyperpolarize
more (-) negative inside
- prevents the backward depolarization wave!
depolarization wave progresses
dendrites -> cell body membrane -> graded potential: could weaken OR stop
insidie axon cytoplasm
transport of cargo
anterograde -> (body to synapse)
vesicles of neutrotransmitter/mitochondria/microtubules
-retrograde (synapse -> cell body)
parts to recycle
extra neurotransmitters
anterograde
cell body to synapse (axon terminal)
- carry vesicles of neurotransmitter/mitochondria/microtubules
retrograde
(axon terminal) synapse to cell body
-carry old membraine parts to recycle and extra neurotransmitters
layers that protect brain
- scalp - thick skin/hair
- periosteum (connective tissue - around skull bones
- skull
- meninges - 2 here
- cerebrospinal fluid & blood-brain barrier - from ependymal cells -> fluid
- meninges (1)
meninges of brain
dura mater, arachnoid, pia mater
- cover & protect, creates spaces, form CSF, support vessels
dura mater
outer meninges
A - periosteal (inner periosteum)
B - meningeal (inner)
duran sinuses w/ blood (low O2 - veins) in between
arachnoid mater
webbly with vessels
- subarachnoid space: with CSF
- arachnoid villi: reabsord CSF
pia mater
on surface of brain
inner meninges
- sheets of meningeal dura mater?
falx cerebri
between right & left cerebrum
tentorium cerebelli
divides cerebrum from cerebellum
falx cerebelli
divides right & left cerebellar (cerebellum)
Dural sinuses
veins
- run along sheets of dura mater - formed between layers of dura mater & transports venous blood
superior & inferior sagittal sinus
all drain into the jugular vein to leave the skull
CSF
in subarachnoid space and made in ventricles (cavities)
- protects, nourishes, and cushion brain
- circulates in ventricles & around the brain in subarachnoid space
(O2, glucose, electrolyties -> Na+, K+, Ca2+)
choroid plexus
in ventricles -> capillaries (blood) + ependymal cells
creates cerebrospinal fluid
Circulation pattern of CSF
- CSF produced by choroid plexus of each ventricle.
(1st and 2nd ventricles) - > 3rd ventricle -> aqeuduct -> lateral - one on either side
circulate around subarachnoid space
3 primary divisions of embryonic brain neural tube
prosencephalon (forebrain)
mesencephalon (midbrain)
rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
Forebrain (prosencephalon)
telencephalon - cerebrum (higher level)
+
diencephalon (2nd) thalamus & epithalamus, hypothalamus
Midbrain (mesencephalon)
(brainstem) - basic vital functions
- breathing, temp, blood pressure
hind brain (rhombencephalon)
metencephalon - (pons) cerebellum (brainstem)
+
myelencephalon - (medulla oblongata)
shape/expansion changes in brain
week 5 - flexures (bends) - midbrain 1st, cervical 2nd (as the head develops)
week 13 - expansion of telencephalon (envelops diencephalon)
week 26 - surface folds in outer cerebrum & expanded + folded cerebellum
week 39 (birth) - complex cerebral cortex - (gray matter) -> synapses (major)
sulci/sulcus
grooves
gyri/gyrus
bumps
forebrain & hindbrain
adult brain shows mostly?
lateral view
cerebrum (4 lobes)
cerebellum (posterior)
superior view
only cerebrum
R + L hemispheres
all gray matter of cortex
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital lobes
precentral (motor) gyrus
frontal lobe
postcentral gyrus (sensory)
parietal
3 functional areas of cerbral cortex
motor areas - control voluntary movement
sensory areas - conscious awareness of sensation
association areas - integrate diverse information
cerebral cortex
motor control (voluntary, conscious - somatic_
mostly frontal lobe, also temporal lobe
primary motor cortex
precentral gyrus - fine muscle control
-conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements
-depicated as a "motor homunculus"
premotor cortex
pattern/repetitive
-learned, repetitive, patterned, sequential motor skills
Broca's area (left side)
speech production
- motor area for speech production, control of tongue muscles
frontal eye field
voluntary eye movements
prefrontal cortex - frontal lobe
most complex area, coordinates multiple inputs & outputs
- working memory (memories)
- compare experiences to problem - solve, reason, make judgements
- contributes to personality, ability to plan & manage tasks
- planning, decisions, judgement
- object-recall tasks, multitask problems, task management
- spatial tasks
sensory cortex
process info from all receptiors (parietal, occipital, temporal)
special senses
- taste
- smell
- sight
- hearing
visual - occipital lobe
Wernicke's area
understanding and interpreting language (temporal lobe)
sensory homunculus
proportionally more cerbral sensory cortex is devoted to
-hands (finger and thumb)
-mouth (tongue)
-eyes
-genitalia
-internal organs
limbic system
responsible for feeling emotions
- for emotional impact to help establish memories & learn (gratification, aversion, danger, pleasure)
cingulate gryus
emotional impact -> memories and affect behavior decisions
capgras delusion/imposter syndrome
-lesion in limbic system
-recognize a relative as someone u know but believe they are an imposter bc there is no emotional impact associated w the person
white matter tracts of cerebrum
- commissural fibers (corpus callosum)
- myelinated axon paths -> connect cerebral cortex to spinal cord -> body
L hemipshere
language, math, logic, abstract physical tasks
R hemisphere
artistic, visual spatial, intuition
Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
"gateway to cortex" - directs neuron tracts
- central part - THALAMUS
-sorts information from sensory
Epithalamus
pineal gland - melatonin
hypothalamus
autonomic NS
control basic viseral functions
(BP, HR, hunger, body temp, sleep;
endocrine (hormone secretion)
pituitary gland -> "master" endocrine
a) hormones for reproduction
b) fluid balance -> kidneys
- optic chiasma
Thalamus
encloses 3rd ventricle
Mesencephalon
midbrain (least elaborated region of brain & part of brainstem)
-> corpora quadrigemina
a) superior colliculi
-visual reflexes
b) inferior colliculi
-auditory reflexes
(a & b are fast autonomic protective)
cerebral aqueduct
connection between 3rd and 4th ventricles of the brain
pons (brainstem)
breathing & swallowing
some facial expression
breathing rate + rhythm
metencephalon
- cerebellum (elaborate)
- balance, recognizing position in 3D space, agility, motor rhythm, and coordination
-> gray + white matter (folded)
lots of surface area (arbor vitae - tree of life)
cauda equina
collection of nerves at the end of the spinal cord that resembles horse tail
myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
controls autonomic reflexes
-cardiovascular center: blood pressure, heart rate, vascoconstriction
-respiratory center: generate rhythm, coughing, sneezing
spinal cord
beings at foramen magnum in vertebral canal
- gray matter (central) cell bodies, synapses, interneurons, somas of motor neurons
-white matter (peripheral) myelinated axons and dendrities
white matter of spinal cord is vertically oriented
gray matter of spinal cord connects to PNS