Historical Antecedents in Science and Technology
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
Science
Systematic study of the natural world through observation.
Technology
Application of scientific knowledge to solve problems.
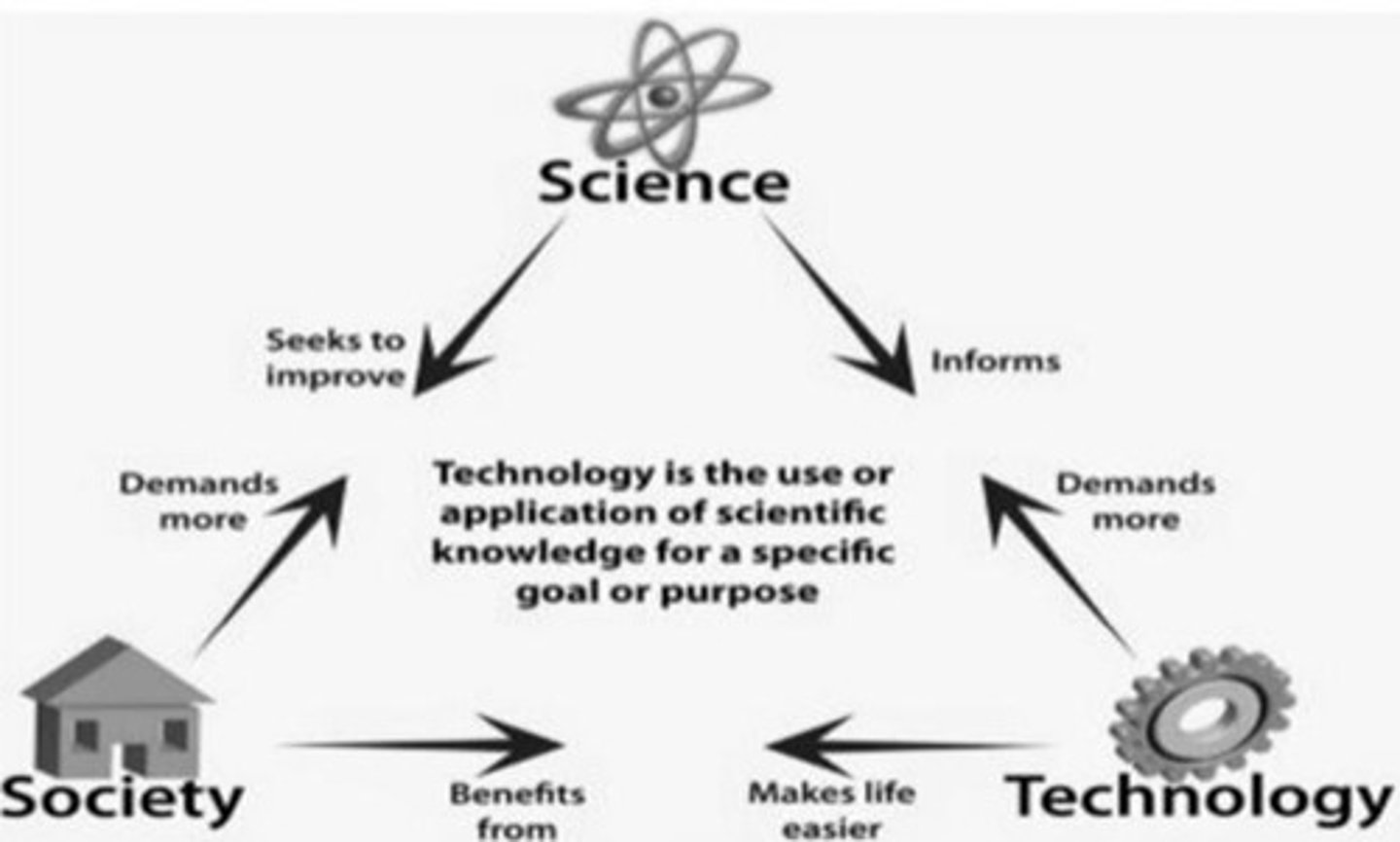
Society
Group of individuals engaged in social interactions.
Scientific Method
Structured approach for conducting scientific experiments.
Invention
Creation of a new device or process.
Innovation
Improvement or modification of existing technologies.
Interdisciplinary Course
Course integrating multiple fields of study.
Empirical Activities
Experiments generating universal truths through observation.
Human Values
Principles guiding human behavior and decision-making.
Social Organization
Structure and arrangement of society's groups.
Environmental Concerns
Issues related to the natural environment's health.
Economic Resources
Assets used to produce goods and services.
Political Decisions
Choices made by authorities affecting society.
Scientific Knowledge
Body of facts and principles derived from science.
Technological Systems
Processes and objects designed for human assistance.
Problem Solving
Finding solutions through inquiry and information collection.
Natural Environment
Physical surroundings influencing human life and activities.
Human Needs
Basic requirements essential for human survival.
Human Wants
Desires that enhance quality of life beyond needs.
Modification of Nature
Changing natural elements to meet human requirements.
Society
Community sharing geographical or social territory.
Persistent Social Interaction
Ongoing exchanges among individuals in society.
Scientific Knowledge Influence
Impact of science on individuals and societal structures.
Technological Change
Transformations in technology affecting daily life.
Global Scenario
Current worldwide conditions affecting science and technology.
Holistic Study
Comprehensive approach considering all aspects of a subject.
Synthesis
Combining knowledge for deeper understanding.
Scientific Methods
Systematic approaches for investigating phenomena.
Engine of Growth
Factors driving economic and technological advancement.
Cognitive Enhancement Interventions
Techniques to improve mental capabilities.
Proton Therapy
Cancer treatment using protons to target tumors.
Genetic Engineering
Modifying organisms' DNA for desired traits.
Historical Antecedents
Earlier influences shaping modern scientific thought.
Old Science
Knowledge based on tradition and authority.
New Science
Knowledge based on empirical evidence and experimentation.
Ancient Egyptians
Pioneers of advanced medical practices and records.
Imhotep
First known physician and architect in history.
Scientific Method
Process involving observation, experimentation, and conclusion.
Papyrus
Ancient writing material made from papyrus plant.
Mesopotamians
Early civilization known for pottery and chariots.
Chinese Compasses
Navigational tools used for travel guidance.
Multidisciplinary Science
Combining various fields for comprehensive problem-solving.
Hellenistic Period
Era marked by significant scientific advancements.
Plato's Academy
First institution for higher learning in Greece.
Aristotle
Philosopher who contributed to scientific methodology.
Eratosthenes
Calculated Earth's circumference using geometry.
Euclid
Father of geometry, authored 'Elements'.
Archimedes
Mathematician known for principles of buoyancy.
Technological Revolutions
Major advancements transforming economies and societies.
Micro-processors
Small computing units driving modern technology.
Nano-technology
Manipulating matter at atomic and molecular levels.
Thales of Miletus
First philosopher-scientist theorized water as fundamental elements.
Plato
Developed the Pythagorean Theorem
Empirical Research
Knowledge gained through observation and experimentation.
Aristotle
Greek philosopher (384-322 BC) influencing science.
Scientific Renaissance
15th-16th centuries focused on ancient knowledge.
Archimedes
Greek mathematician known for buoyancy and levers.
Scientific Revolution
17th century shift from recovery to innovation.
Eratosthenes
Measured Earth's circumference accurately in ancient Egypt.
Islamic Golden Age
Cultural and scientific flourishing from 8th to 14th century.
Renaissance Humanism
Nature viewed as spiritual, not governed by laws.
Copernicus
Proposed heliocentric model of the universe.
Gutenberg
Inventor of the movable-type printing press.
Al-Khwarizmi
Persian mathematician known as the father of algebra.
Ibn Sina
Wrote 'The Canon of Medicine' in Persia.
Alhazen
Pioneer of optics and the scientific method.
Four Great Inventions
Papermaking, printing, gunpowder, and compass from China.
Age of Reason
Emphasized reason over superstition in the Enlightenment.
Chinese Compass
Used lodestone on bronze plate for navigation.
Galileo Galilei
Key figure in the Scientific Revolution, Italian astronomer.
Johannes Kepler
Formulated laws of planetary motion in the 17th century.
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz
Mathematician and philosopher, co-inventor of calculus.
House of Wisdom
Baghdad center for translation of classical works.
Block Printing
Technique that spread from China to the West.
Scientific Inquiry
Exploration in fields like chemistry and botany.
Communications Revolution
Printing's impact compared to invention of writing.
1467 Wooden Press
Introduced printing technology to Italy.
Six Million Books
Total printed by presses in Europe by 1500.
Cultural Flourishing
Period of significant growth in Islamic science.
Papermaking in Spain
Introduced by Arabs from China in the 12th century.
Flemish Technique
Origin of new printer's ink for printing.
Scientific Texts Rediscovery
Accelerated after the Fall of Constantinople in 1453.
Printing
Democratized learning and spread ideas faster.
Isaac Newton
Published 'Principia Mathematica' in 1686.
Scientific Renaissance
Coined by Marie Boas Hall (1450-1630).
John Locke
Authored 'Essay Concerning Human Understanding' in 1689.
Industrial Revolution
Period of industrial growth from 1760 to 1840.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Computers that mimic human thinking and reasoning.
Close Observation
Careful generalization for practical utilization.
James Watt
Improved steam engine in 1769, boosting industry.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Immersive digital experiences using VR headsets.
Augmented Reality (AR)
Merges digital and physical worlds.
Science of Metallurgy
Tailoring alloy steels for industrial specifications.
Biotechnology
Develops new pharmaceuticals and efficient materials.
Science of Chemistry
Creation of new substances like aniline dyes.
Energy Sources
Includes coal, steam, electricity, petroleum.
3D Printing
Manufacturing parts quickly and cost-effectively.
Robotics
Design and use of robots for various applications.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Everyday items connected to the internet.
Energy Capture
Technologies for renewable energy storage and transmission.