Lids, Brows, Orbit, Lacrimal
1/195
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
telecanthus
increased distance between the medial canthi of the eyes
poliosis
whitening of lashes
what lies between skin layer and orbicularis layer
subcutaneous areolar layer of connective tissue
what happens when orbicularis muscle is paralyzed
ectropion of lower lid (due to riolan being paralyzed)
where does the superior palpebral levator muscle originate
lesser wing of sphenoid
what innervates the superior palpebral levator muscle
CN III
function of levator aponeurosis
attaches the superior palpebral levator to the upper lid
why does CN III palsy cause severe ptosis of upper lid
lack of CN III innervation to levator stops it from retracting lids
which glands are in the tarsal plate
M, W
meibomian glands, glands of Wolfring
what is found in epithelial layer of palpebral conj & what is their function
goblet cells (inferonasal fornix, bulbar conj)
produce mucin layer of the tear film
which glands are sebaceous glands
MGs & zeis
which glands are apocrine & what does it mean
moll & goblet cells
shed part of cell to be secreted
what type of motor innervation does muller muscle have
involuntary motor innervation (sympathetic system)
function of orbicularis in eyebrow movement
primary lateral depressor of the eyebrows
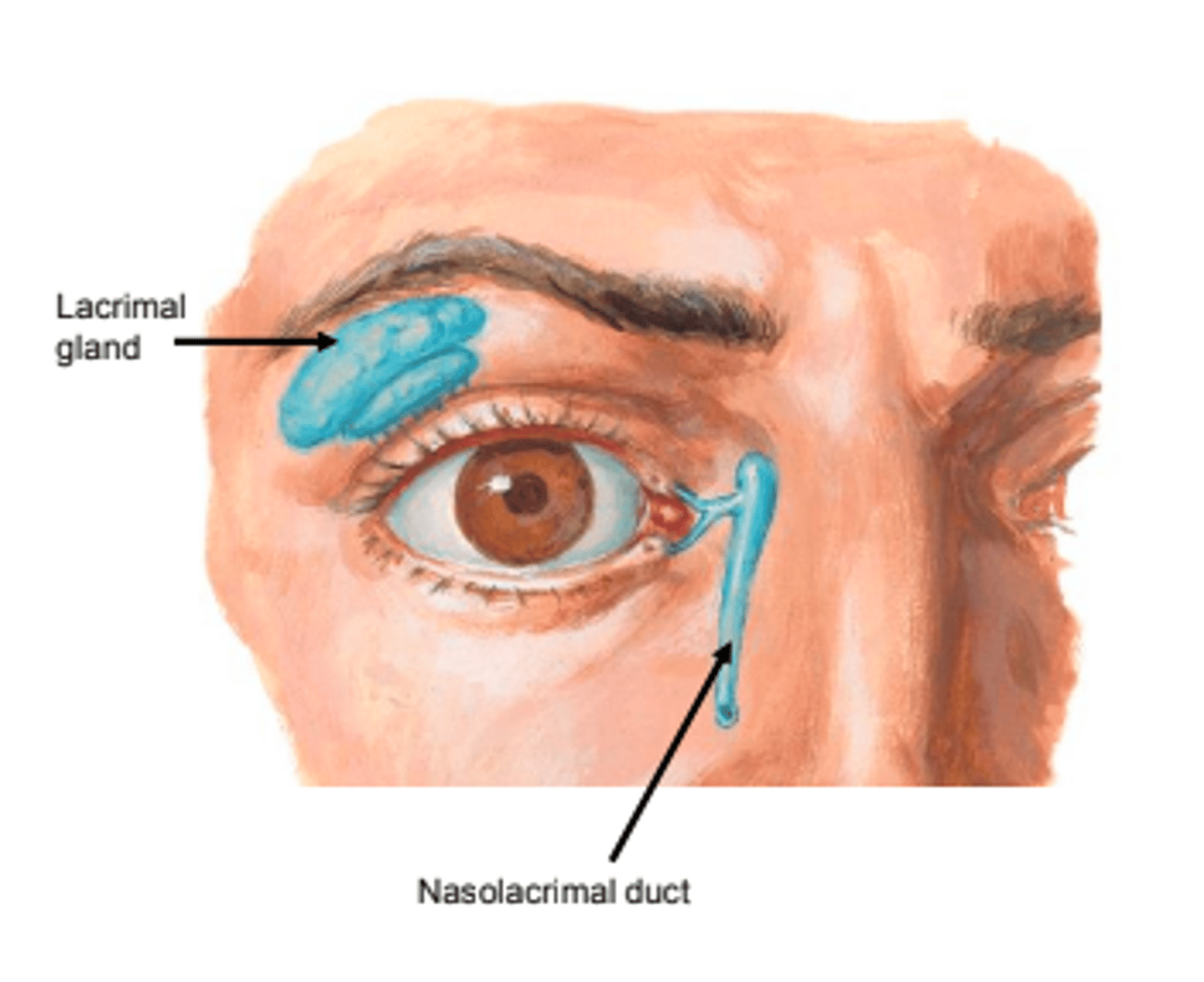
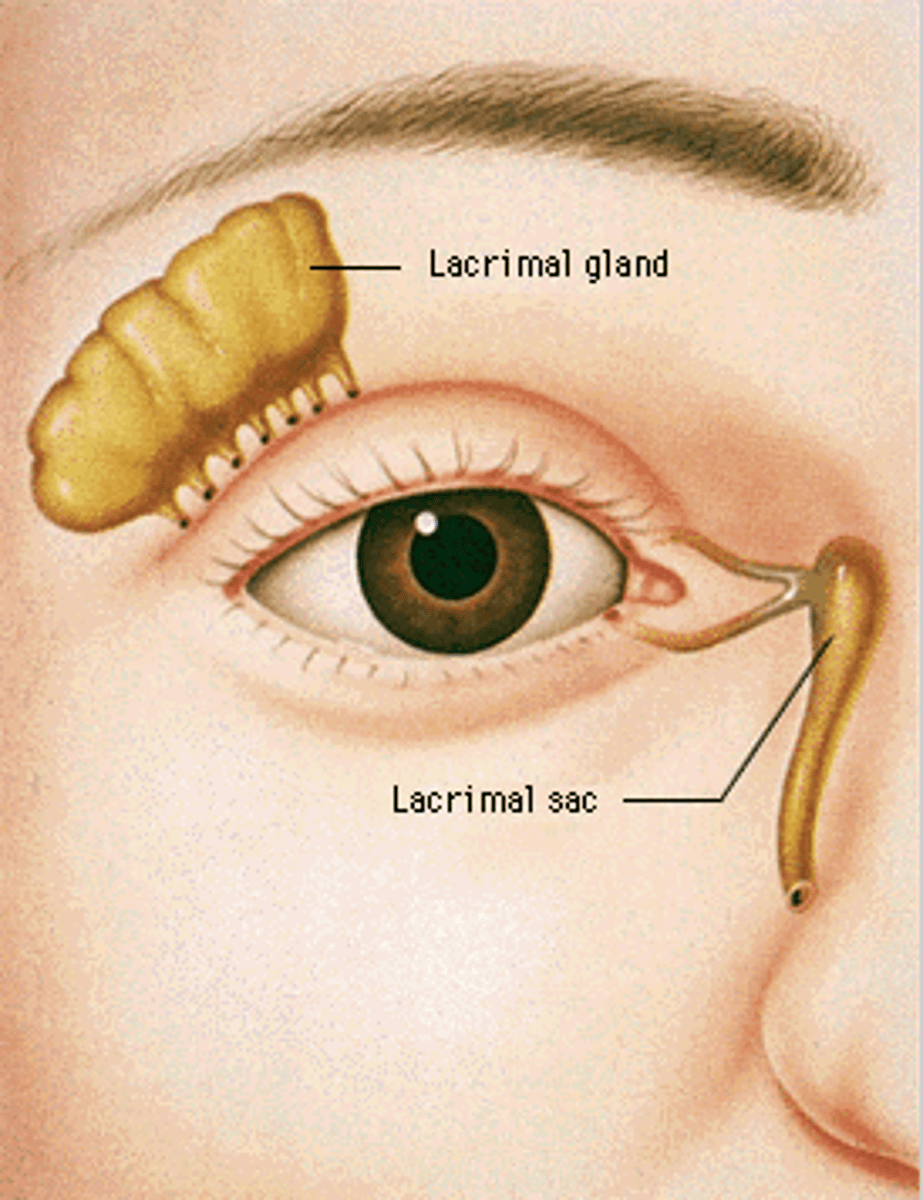
location of the lacrimal gland
lacrimal fossa of on the temporal side of the frontal bone (superior temporal lid)
what artery supplies lacrimal gland
lacrimal artery
what surrounds canaliculi and helps with tear drainage
muscle of horner
what lines the lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct
double epithelium, microvilli, and goblet cells
location and function of valve of hasner
end of nasolacrimal duct
prevents back flow of nasal fluid into lacrimal drainage system
two compartments of adipose tissue within EOMs
intraclonal: within the muscle cone of the recti
extraclonal: outside the muscle cone between EOMs and orbit
where in the eye do the EOMs attach
sclera
3 characteristics that differentiate EOMs from other skeletal muscles
EOMs have: denser blood supply, denser nerve supply, faster & more fatigue resistant movements
what is the LR anchored to
Whitnall's ligament
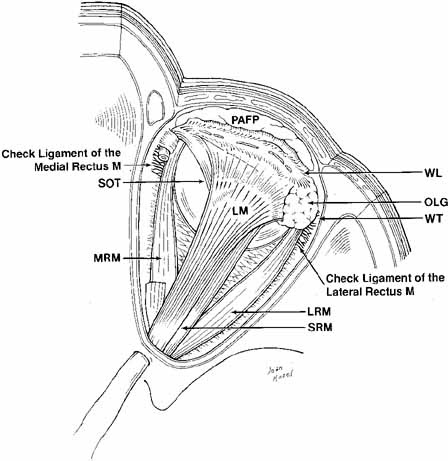
what is the MR anchored to
medial orbital septum
where does SO originate
lesser wing of sphenoid bone, and passes through trochlea
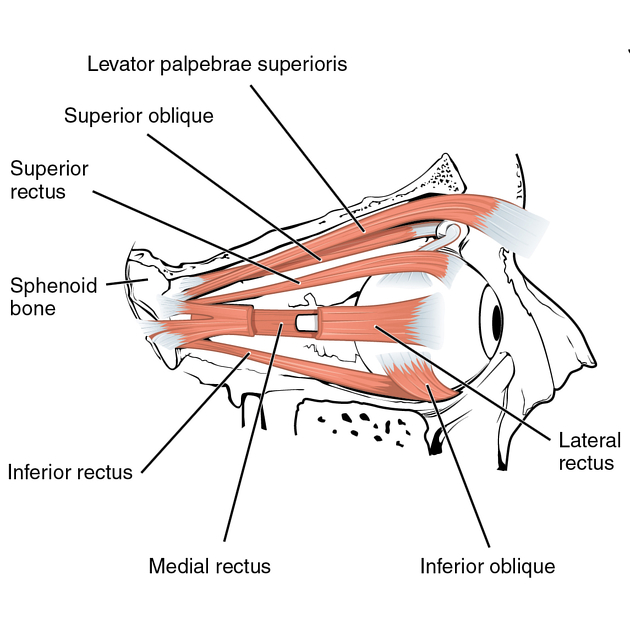
LR actions
primary: abduction
MR actions
primary: adduction
SR actions
primary: elevation
secondary: intorsion
tertiary: adduction
because of angle of insertion, SR & IR are responsible for ___________________ when eye is ________________ @ ______ degrees from the midline
pure depression or elevation, abducted, 23
what does the inferior CN III innervate
IR, IO, MR
functions of orbital fascia
provides support to BVs
serves as a point of attachment for muscles, tendons, and ligaments within the orbit
madarosis
loss of lashes
trichiasis
turning in of the lashes
phthiriasis palpebrarum
infection of lashes caused by Phthirus pubis (pubic lice)
what innervates the palpebral orbicularis oculi
CN VII
zygomatic branch of the facial nerve
what action is the orbital orbicularis oculi responsible for
forced closure of lids
what action is the palpebral orbicularis oculi responsible for
spontaneous actions and reflexive blinking
what 2 muscles are in the palpebral orbicularis oculi
muscle of riolan (pars ciliaris) & muscle of horner (pars lacrimalis)
function of muscle of riolan
riolan rotates ; roll, tide, divide
allows lashes to rotate towards eye during closure
keeps lid margin tightly against globe
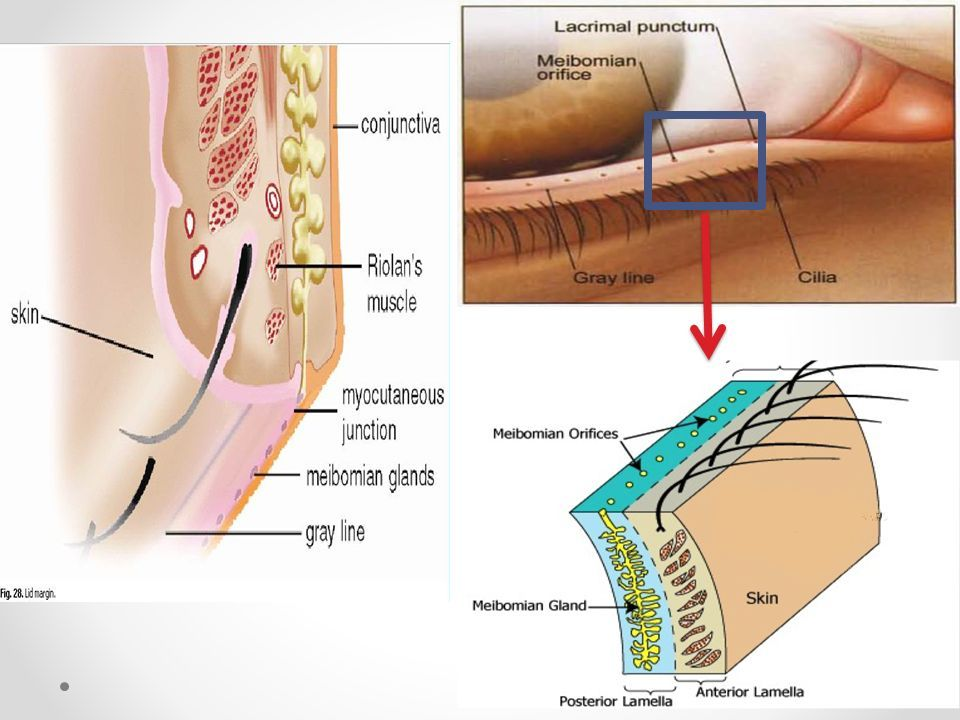
most anterior portion is gray line, which divides lashes & MGs
ectropion
lower lid droops away from globe
function of muscle of horner
has fibers that encircle canaliculi and help drain tears into lacrimal sac
function of orbital septum
barrier of the orbit
prevents orbital fat from falling into lid
keeps infections localized to anterior lid and away from orbit
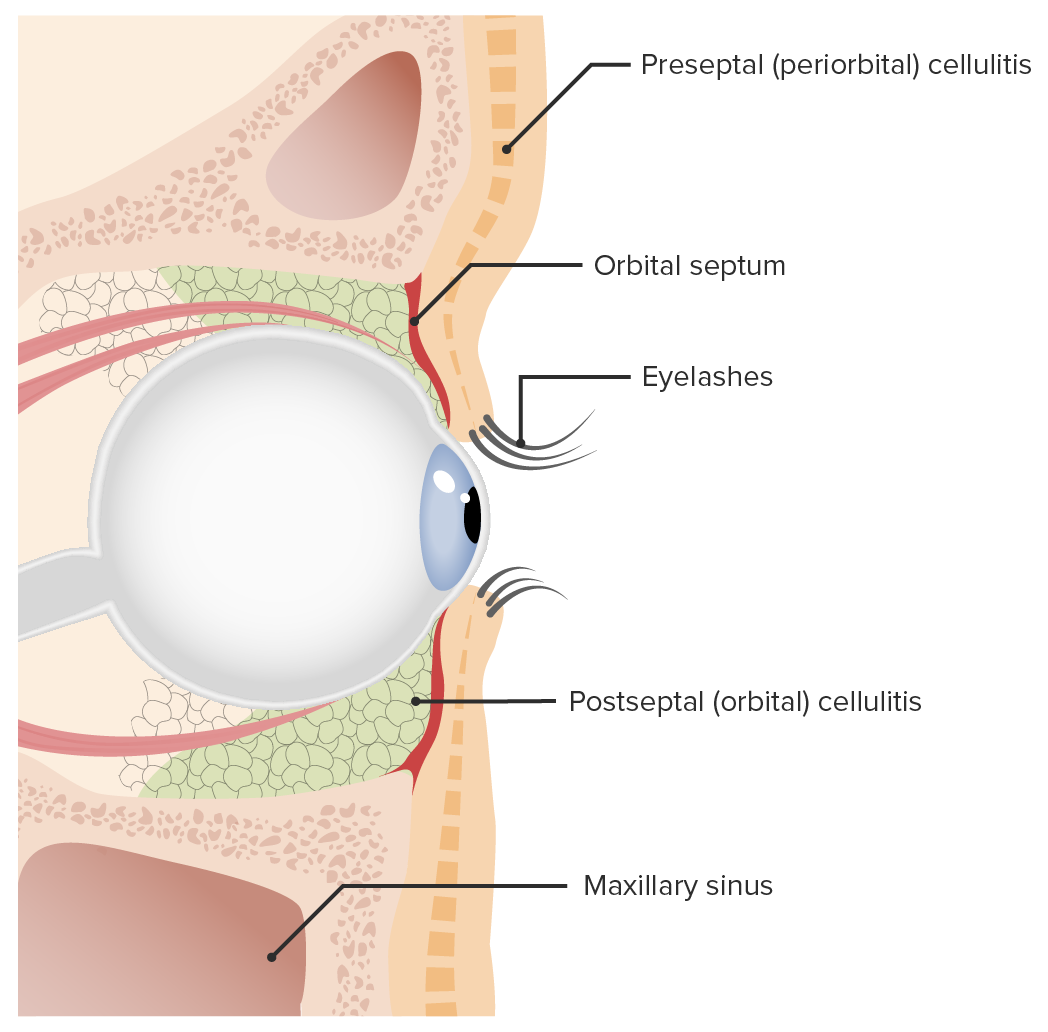
what part of the eye does the orbital septum not protect from infection & why
lacrimal sac
orbital septum attaches medially
lacrimal sac is located in front of attachment of septum
what structure separates preseptal cellulitis from orbital cellulitis
orbital septum
preseptal is in front of septum
orbital is behind septum
function of superior palpebral levator muscle
main retractor of eyelid
what ligament allows superior palpebral levator muscle to move and function
Whitnall's ligament
what does the superior palpebral levator become as it extends into the eyelid
levator aponeurosis tendon
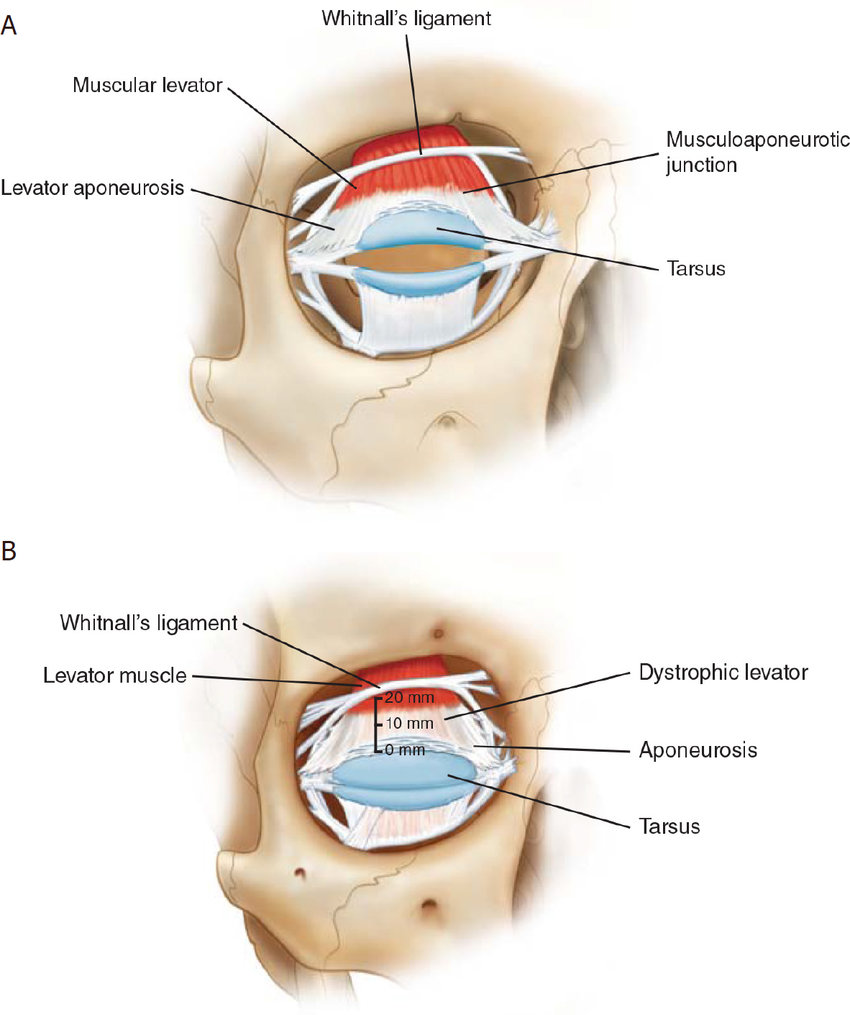
what creates the superior & inferior palpebral furrow
superior: where levator aponeurosis attaches to lid
inferior: where inferior rectus muscle attaches to lid
what kind of muscle is muscle of muller
smooth muscle (a2 receptors)
what innervates muscle of muller
sympathetic nervous system
what is the function of the muscle of muller
minor retractor of lids
why does Horner's syndrome cause ptosis & reverse ptosis
lack of sympathetic innervation to Muller's stops it from retracting the upper and lower lids
(lack of retraction = ptosis)
is ptosis worse in Horner's or CN III palsy
CN III palsy
Horner's stops innervation to Muller, which is a minor retractor
CN III palsy stops innervation to levator, which is the main retraction
why does thyroid eye disease result in signature bulging eyes
TED causes increased sympathetic innervation, causing Muller's to retract lids more than it normally does
average interpalpebral fissure
10-12 mm
what nerve causes eye to open vs close
CN III causes eye to open (levator)
CN VII causes eye to close (orbicularis)
what is the tarsal plate composed of
connective tissue and collagen
function of tarsal plate
gives eyelids rigidity
2 layers of palpebral conj
epithelial & stroma (submucosa, substantia propria) layers
2 layers of stromal palpebral conj
superficial lymphoid layer
deep fibrous layer
function of superficial lymphoid layer of stromal palpebral conj
immunologically active layer with IgA, macrophages, mast cells, PMNs, eosinophils (protects conj from disease)
function & contents of deep fibrous layer of stromal palpebral conj
connects conj to underlying structures
houses accessory lacrimal glands of Krause
meibomian gland function & location
produces anterior lipid layer of tear film
tarsal plate
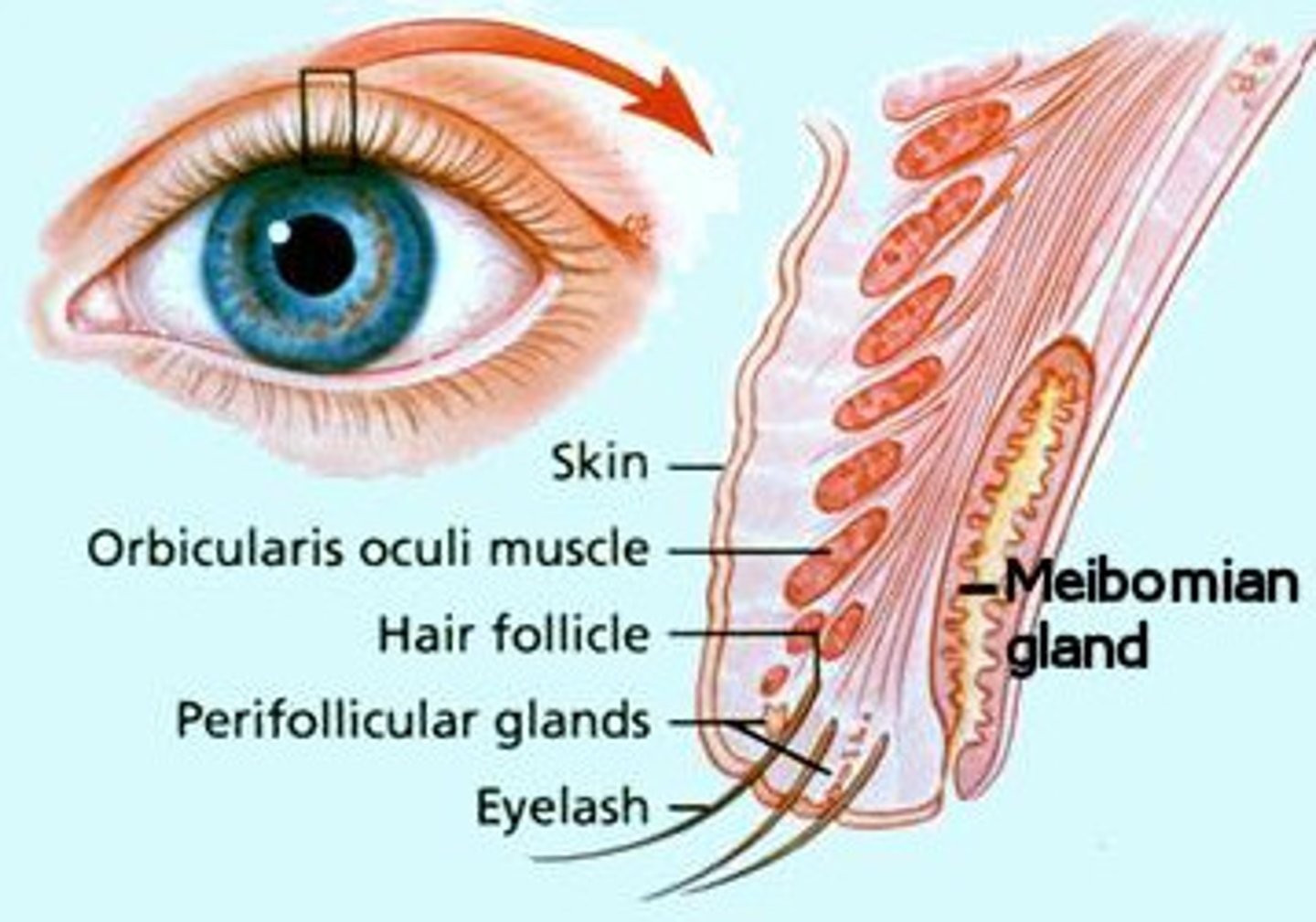
glands of zeis function & location
lubricate eyelashes
located at lash follicles
glands of moll location
near lid margin
glands of krause function and location
accessory lacrimal glands that secrete tears
located at fornices of the conj (fibrous layer of stromal palpebral conj)
glands of wolfring function and location
accessory lacrimal glands (less in # than krause)
located in tarsal conj
which glands are holocrine & what does it mean
MGs & zeis
shed entire cell to be secreted
which glands are merocrine & what does it mean
accessory lacrimal glands
don't shed any part of cell, secrete substances via exocytosis
what type of motor innervation does the orbicularis oculi have
voluntary motor innervation (zygomatic branch of CN VII)
what supplies sensory innervation to the upper and lower lids
CN V (trigeminal nerve)
upper: CN V1 (supraorbital & supratrochlear branches of frontal branch and lacrimal branch of ophthalmic nerve)
lower: CN V2 (infraorbital and zygomaticofacial branches of maxillary nerve)
what does the infratrochlear nerve innervate, and where does it come from
innervates medial aspect of upper and lower lids
comes from the nasociliary nerve that branches off of the ophthalmic nerve (CNV1 > nasociliary nerve > infratrochlear nerve)
path of arterial blood supply to deeper eyelid tissues
internal carotid artery > ophthalmic artery > lateral & medial palpebral arteries > deep eyelid blood supply
(lateral palpebral artery branches off of lacrimal artery)
2 branches of palpebral arcades and what they supply
marginal palpebral arcades: eyelid margin
peripheral palpebral arcades: fornices and posterior conj
what part of the lids do the external carotid branches supply
superficial eyelids
where do the anterior ciliary arteries supply blood
bulbar conj & ciliary body
why does uveitis cause circumlimbal injection and decreased aqueous production
the anterior ciliary arteries supply blood to the bulbar conj and ciliary body (where aqueous production occurs)
where do the eyelid veins drain
palpebral and ophthalmic veins
where are lymphatic vessels of the eyes found
conjunctiva
where do lateral lymphatics of the eye drain
parotid/preauricular lymph nodes (in front of ears)
where do medial lymphatics of the eye drain
submandibular lymph nodes (under jaw)
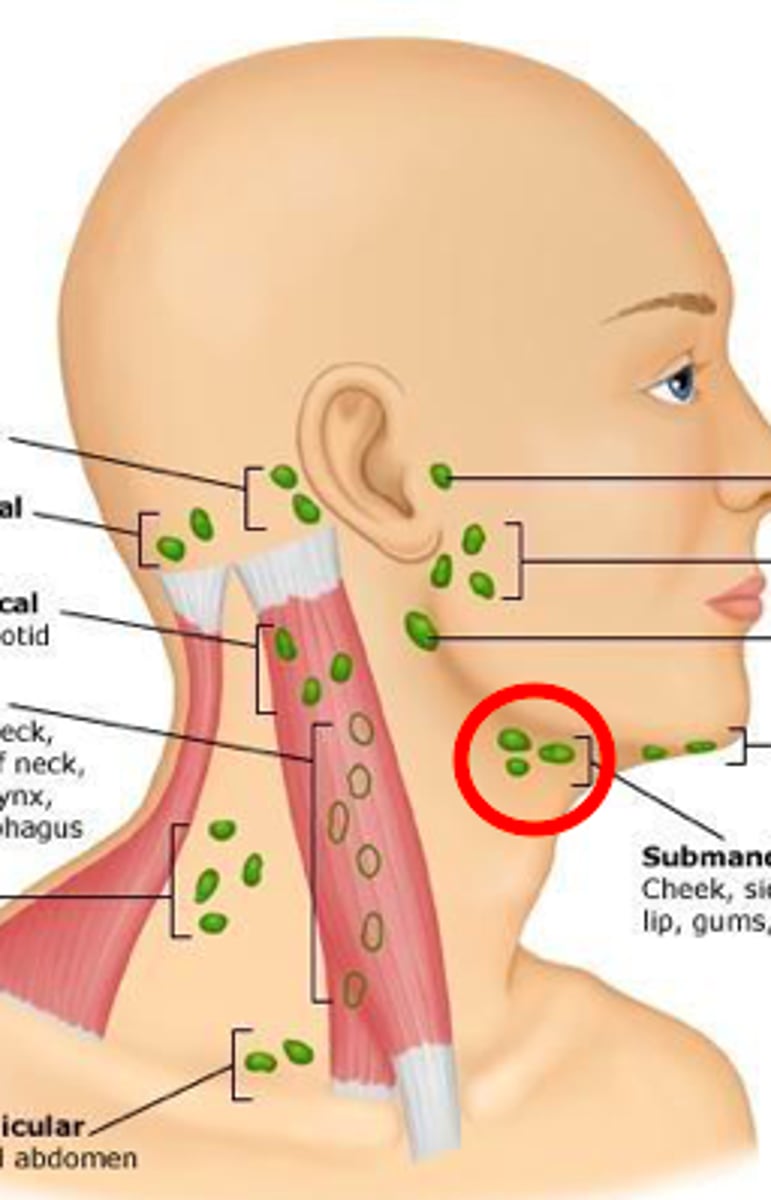
what ocular diseases can cause swollen preauricular lymph nodes
EKC!
chlamydial & gonococcal conjunctivitis, dacryadenitis
what ocular disease causes swelling of preauricular & submandicular lymph nodes
parinaud's oculoglandular syndrome
eyebrow function
protection & facial expression
what innervates the eyebrow muscles
CN VII
4 forehead muscles that create eyebrow movement
frontalis, corrugator, procerus, orbicularis
function & location of frontalis muscle
main eyebrow elevator
fibers run vertically on the scalp and insert into orbital rim
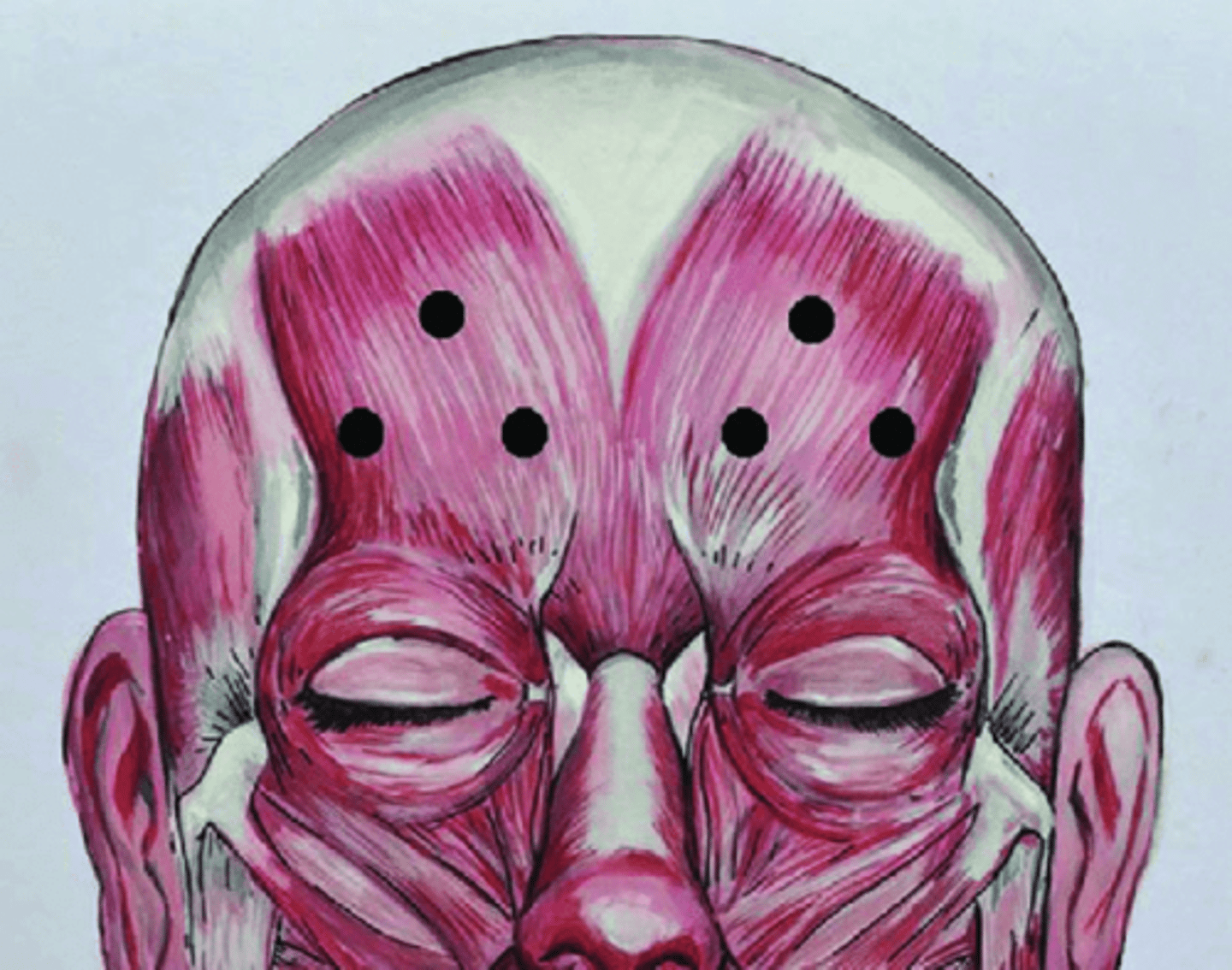
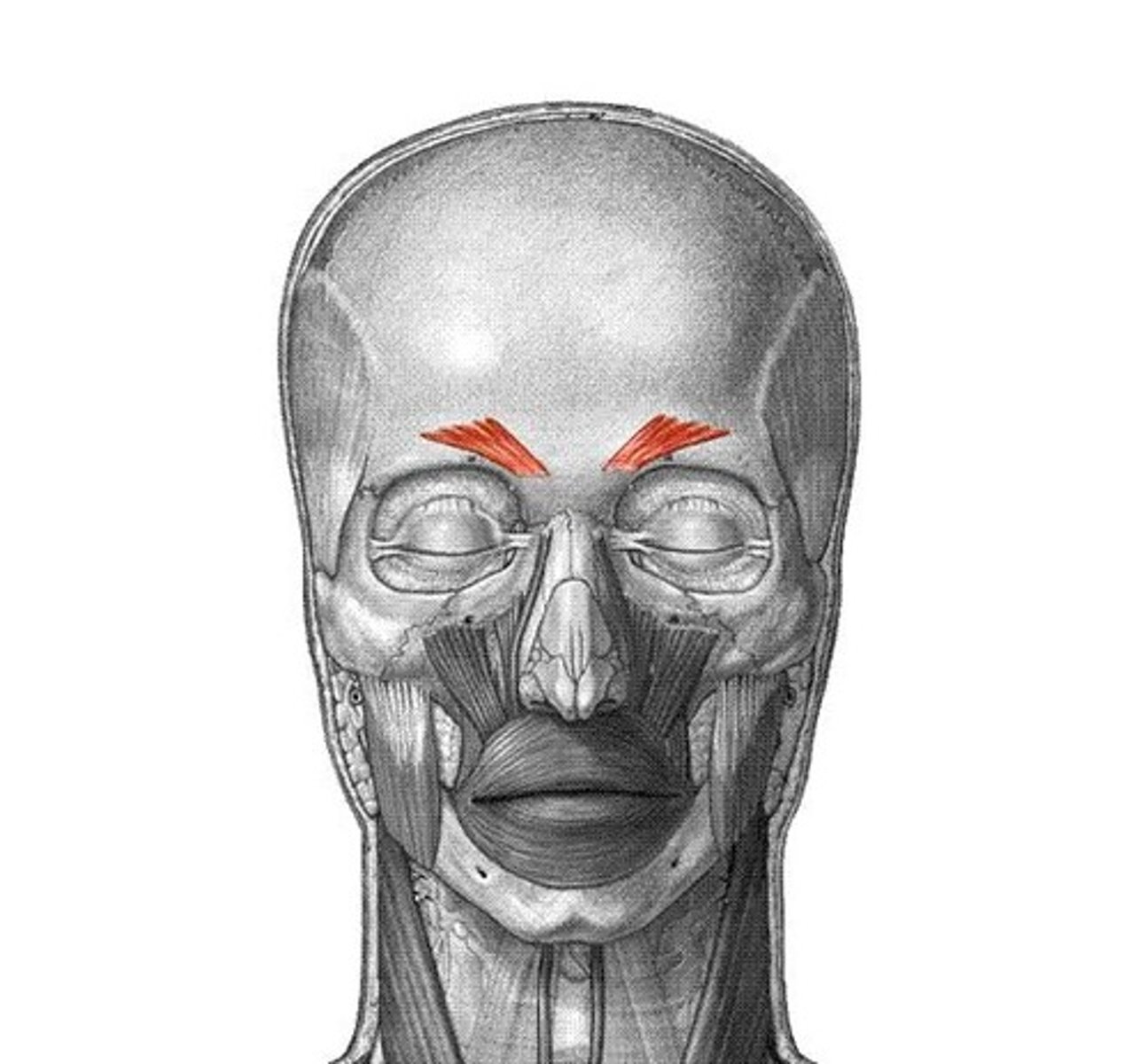
function & location of corrugator muscle
medial depressor of eyebrows
oblique fibers that pull brows down and in and produce vertical wrinkles on forehead, inserting into skin near medial brows
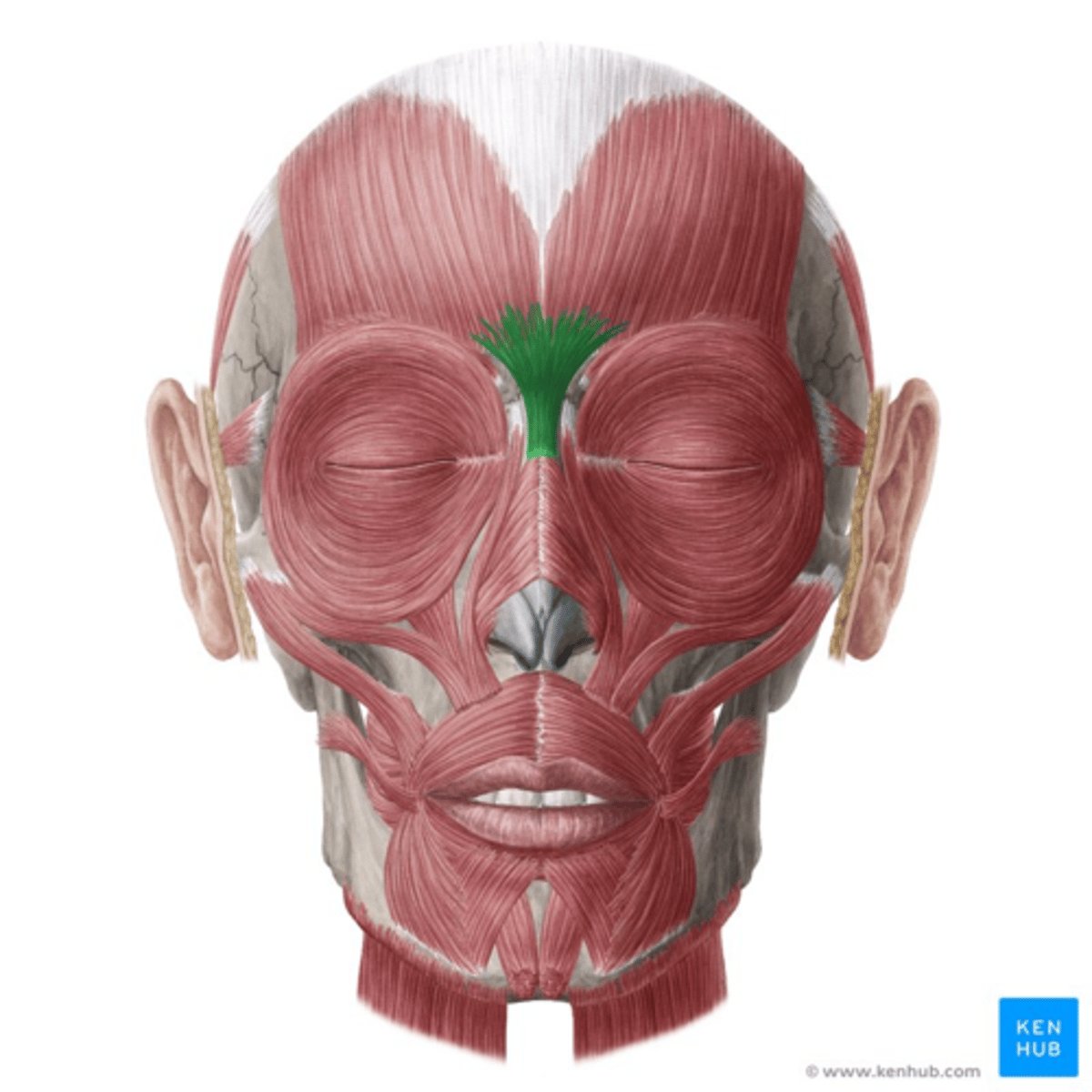
function & location of procerus muscle
medial depressor of eyebrows
pulls skin between the brows down and originates at nasal bone, giving horizontal wrinkes across bridge of nose
what divides the lacrimal gland into orbital and palpebral portion
tendon of levator aponeurosis
what kind of gland is the lacrimal gland & how does it release its products
tubuloalveolar exocrine gland
releases products via merocrine secretion
what vein drains lacrimal gland
lacrimal vein
where are the only lymphatic vessels in the orbit located
lacrimal gland (drain to preauricular nodes)
what type of innervation does the lacrimal gland receive and what does lacrimal innervation result it
parasympathetic innervation
stimulation causes secretion of the aqueous layer of tears
what innervates the lacrimal gland
lacrimal nerve of the pterygopalatine ganglion of CN VII (facial nerve)
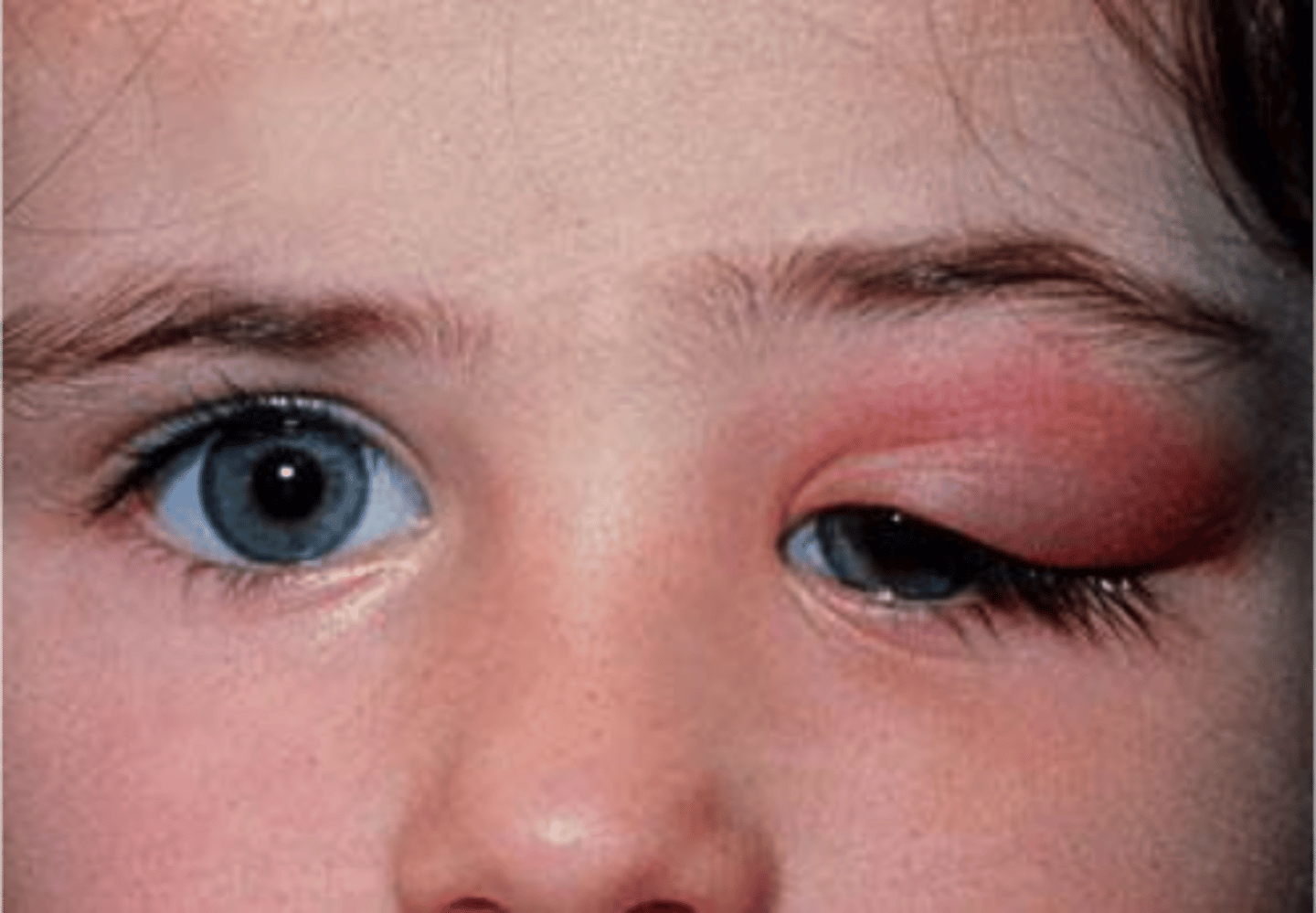
dacryoadenitis
inflammation (due to infection) of the lacrimal gland that can cause swelling in the upper lateral lid

what is the lacrimal papilla and what does it do
ring of connective tissue surrounding the lacrimal puncta that is responsible for keeping the lacrimal puncta open
path of nasolacrimal drainage
sup & inf lacrimal puncta > sup & inf canaliculi > common canaliculus > lacrimal sac > nasolacrimal duct > valve of hasner
what lines the canaliculi
stratified & pseudostratified epithelium
where is the lacrimal sac located
fossa (lacrimal crest) in the medial orbital wall between lacrimal and maxillary bone