Year 9 Chemistry & Physics 2023
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:18 AM on 5/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
1
New cards
What are all three of the subatomic particles?
Protons (+) Neutrons, Electrons (-)
2
New cards
Which subatomic particles make up the nucleus of an atom?
Protons and Neutrons
3
New cards
True or false: Electrons are much bigger and heavier than protons/ neutrons.
False: Electrons are much smaller and lighter than protons/ neutrons.
4
New cards
What is the definition of mass number?
The total number of neutrons and protons (mass number is always the bigger number)
5
New cards
What is the definition of atomic number?
The number of protons (identifies the element)
6
New cards
True or false: In an element, the number of electrons are the same number of protons.
True
7
New cards
How do you find the number of neutrons?
Mass number- atomic number
8
New cards
\
Elements
Elements
A substance made from the same kind of atom.
9
New cards
Molecules
A substance made up of two or more of the same atom chemically bonded.
10
New cards
Compounds
A substance made up of two or more different atoms chemically bonded. Eg. H2O
11
New cards
Groups
↓Number of valence electrons (electrons in the outermost shell)
12
New cards
Groups tell us the reactivity of the element. Which groups in the periodic table are the most unstable?
Group 1 and Group 17 are the most unstable.
13
New cards
Periods
→Number of shells
14
New cards
Characteristics of noble gases
\
* They are in Group 18
* Unreactive
* Stable
* They are in Group 18
* Unreactive
* Stable
15
New cards
How many electrons are in each shell of an atom (electronic configuration)?
\
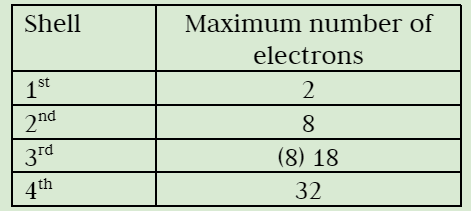
16
New cards
How does a flame test identify metallic elements?
If we give energy to some metallic atoms, by heating them, their electrons jump from one electron shell to another. As they fall back to their normal state they release the excess energy in the form of light. Each atom emits a unique colour of light and thus the flame test can be used to identify different metals.
17
New cards
Anions
If an atom gains an electron (overall negative charge) eg. Oxygen gains two electron it becomes 02-
18
New cards
Cations
If an atom loses an electron, (overall positive charge) eg. Oxygen loses 2 it becomes O2+
19
New cards
Elements in group 1, with a valence electron of 1, will always want to __****__ that electron as fast as possible.
Lose
20
New cards
Elements in group 7, with a valency of 7, will always want to _____ an electron, making it reactive as well.
Gain
21
New cards
Elements in group 8, with a full outer shell, will always be very ______ and ______.
Stable and unreactive
22
New cards
Isotopes
Has the same atomic number as the original atom but a different number of neutrons.
23
New cards
The more neutrons, the more _____ the isotope becomes.
Unstable
24
New cards
True or false: Carbon 12 is more stable than Carbon 14 as it has an equal number of protons and neutrons.
True
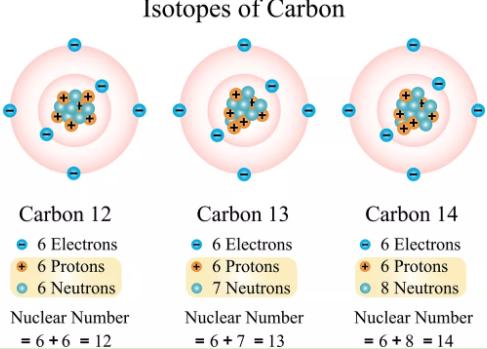
25
New cards
What is the difference between radioactive and radiation?
An unstable isotope is **radioactive**, whilst the energy emitted from nuclear decay is **radiation**.
26
New cards
Half-life
The time it takes for half (50%) of the isotope to decay. Something stable decays really slowly, whilst something unstable decays really quickly.
27
New cards
Law of Conservation of Mass
Atoms cannot be broken down or destroyed, they can only be reshuffled to form new substances. What is on one side of the equation must be on the other side.
28
New cards
Acids
A substance that releases hydrogen ions (H+) into an aqueous solution (containing water).
29
New cards
What are characteristics and an example of acids?
* Sour taste
* PH Less than 7
* Corrosive
* Hydrochloric acid (HCI)
* PH Less than 7
* Corrosive
* Hydrochloric acid (HCI)
30
New cards
Bases
A substance that releases hydroxide ions (OH-) into an aqueous solution.
31
New cards
What are characteristics and an example of bases?
* Taste bitter and soapy
* PH Above 7
* Corrosive
* Ammonia (NH3) Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
* PH Above 7
* Corrosive
* Ammonia (NH3) Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
32
New cards
What does a pH scale measure?
The concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution. In an acidic solution, there are more **hydrogen ions** than hydroxide ions. In an alkaline solution, there are more **hydroxide ions** than hydrogen ions.
33
New cards
Indicators
They help you find whether a solution is acidic, basic or neutral. They change colours in solutions of different pH.
34
New cards
Neutralisation reaction
When an acid and a base are mixed.
35
New cards
The products of a neutralisation reaction
Salt + Water
36
New cards
Independent variables
The variable that is changed.
37
New cards
Dependent variables
The variable that is measured.
38
New cards
Controlled variables
The variable that stays the same.
39
New cards
Accuracy
It is close to the ‘true’ value of the quantity being measured.
40
New cards
Precision
How closely two or more measurements are. (The smaller the range the more precise.)
41
New cards
Energy
Energy is the ability to do work.
42
New cards
The two main types of energy are:
Potential (Stored)
Kinetic (Moving)
Kinetic (Moving)
43
New cards
Which energies are kinetic?
* Heat
* Light
* Sound
* Mechanical
* Electrical
* Light
* Sound
* Mechanical
* Electrical
44
New cards
Which energies are potential?
* Nuclear
* Gravitational
* Elastic
* Chemical
* Gravitational
* Elastic
* Chemical
45
New cards
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another.
46
New cards
In energy flow charts, the first starting energy is always…
potential
47
New cards
Energy Efficiency
Remember to use units!

48
New cards
Power
The rate at which energy is transformed from one type to another.
49
New cards
Series circuit
Electrons can only take one path
50
New cards
Series circuit characteristics
* All globes glow with the same brightness
* Globes share the battery voltage, so the more globes the dimmer
* If one globe burns out, all the other ones burn out as well
* Globes share the battery voltage, so the more globes the dimmer
* If one globe burns out, all the other ones burn out as well
51
New cards
Parallel circuit
Electrons can take more than one path
52
New cards
Parallel circuit characteristics
* All globes glow with the same brightness, but individual globes are brighter than those connected in series
* Use more energy so the battery runs out faster
* If one globe dies, the others will still glow
* Use more energy so the battery runs out faster
* If one globe dies, the others will still glow
53
New cards
Current
A measure of the flow of electrons through a circuit every second.
54
New cards
Current is measured in:
Amps (A) Milliamps (mA)
55
New cards
Voltage
A measure of how much energy the power source (eg. battery) gives the electrons to move around the circuit.
56
New cards
Voltage is measured in:
Volts (V)
57
New cards
Resistance
How a device or material reduces the electric current flow through it.
58
New cards
Resistance is measured in:
ohms (Ω)
59
New cards
The equation for resistance is:
__**Resistance (Ω) = Voltage- Volts (V)/Current- Amps (I)**__
60
New cards
Conductors
Allow a current to pass through easily, and have low resistance.
61
New cards
Examples of Conductors
* Silver
* Aluminium
* Copper
* Iron
* Aluminium
* Copper
* Iron
62
New cards
Insulators
Have a high resistance where the current does not flow as easily.
63
New cards
Examples of Insulators
Paper, wood, rubber
64
New cards
\
Whenever current flows through a resistor a **…….** effect occurs, this factor can be used in heating elements, such as in a …….
Whenever current flows through a resistor a **…….** effect occurs, this factor can be used in heating elements, such as in a …….
Heating, kettle
65
New cards
What natural substance is a good conductor and why?
*Saltwater is a good conductor as it contains many ions.*
66
New cards
Repeatability
When you can obtain the same results in an experiment multiple times under the same conditions (people, equipment, laboratory.)
67
New cards
Reproducibility
When you can obtain the same results as another group’s experiment under different conditions (different people, equipment, laboratory.)
68
New cards
The characteristics of a fair experiment:
* All the variables in an experiment must be considered and controlled
* Only one variable may be altered at a time
* Only one variable may be altered at a time