Near East Art History
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Apadana
the great audience hall in ancient Persian palaces
bent-axis plan
A plan that incorporates two or more angular changes of direction
capital
top of column

cella
the main room of a temple where the god is housed
cuneiform
A system of writing in which wedge-shaped symbols represented words or syllables. It originated in Mesopotamia and was used initially for Sumerian and Akkadian but later was adapted to represent other languages of western Asia.represent other languages of western Asia.

ground line
a base line upon which figures stand

hierarchy of scale
a system of representation that expresses a person's importance by the size of his or her representation in a work of art

Lamassu
a colossal winged human-headed bull in Assyrian art

lapis lazuli
a semiprecious blue stone

negative space
empty space around an object or a person, such as the cut-out areas between a figure's legs or arms of a sculpture
register
a horizontal band, often on top of another, that tells a narrative story

relief sculpture
Sculpture that projects from a flat background

votive
offered in fulfillment of a vow or a pledge

Ziggurat
a pyramid-like building made of several stories that indent as the building gets taller; thus, ziggurats have terraces at each level
Sumerian Art (Iraq)
c. 3,500-2,340 BCE
Babylonian Art (Iraq)
1,792-1,750 BCE
Assyrian Art (Iraq)
883-612 BCE
Persian Art (Iran)
c. 559-331 BCE
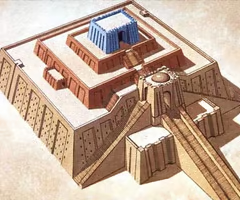
White Temple
-3,200-3,000 BC (Sumerian)
-location: Uruk, Iraq (modern day Warka)
-elements: bent-axis plan, cella
-materials: mud bricks
-purpose: a ziggurat which is a focal point for city-states and religion and government; rituals were conducted

Votive figures of Eshnunna
- c. 2,700 BC (Sumerian)
-location: Eshnunna, Iraq (modern day Tel-Asmar
-elements: cylindrical, geometric, stylized human representation
-materials: Gypsum, shell, black limestone
-purpose: placed in temples before the statues of deities in order to offer constant prayers

Standard of Ur
- c. 2,600-2,400 BC (Sumerian)
-location: Ur, Iraq
-elements: mosaic, registers
-materials: wood, lapis lazuli, shell, red limestone
-purpose: may have been carried into battle on a pole; or a musical instrument

Hammurabi's Code
- ca. 1,780 BC (Babylonian)
-location: Susa, Iran
-elements: stele, composite form, relief sculpture
-materials: Basalt
-purpose: a public monument establishing the law of code of Babylonian leader Hammurabi; show's a ruler needs to establish harmony in society

Lamassu
-ca. 721-705 BC (Assyrian)
-location: Dar Sharrukin, Iraq
-elements: high relief sculpture,
-materials: Gypseous alabaster
-purpose: thought to be protective spirits; meant to ward off enemies both spiritual and physical

Audience Hall or Darius and Xerxes
-ca. 520-465 BC (Persian)
-location: Persepolis, Iran
-elements: apadana, hypostyle hall, relief structure
-materials: limestone
-purpose: a seat of spectacular receptions and festivals; Persian king entertained audiences and received tribute
