Biochem 406-lecture 1,2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the purpose of lipid droplets
Lipid droplets are used to store fats and act as an energy reservoir
What are lipid droplets made of
Phospholipid monolayer and periipin proteins on the outside. Cholesterol esters and triacylglycerols on the inside
Why are fats better for long term energy storage than carbohydrates
Triacylglycerols can pack closely together, excluding water.
Fats are more reduced
How do bile salts help in lipid digestion
Bile salts are amphipathic and can emulsify lipids in aqueous environments like the small intestine, forming mixed micelles
what does human pancreatic lipase do and what is its cofactor
works outside of the cell at the lipid/water interface to break down fats
And colipase is the cofactor
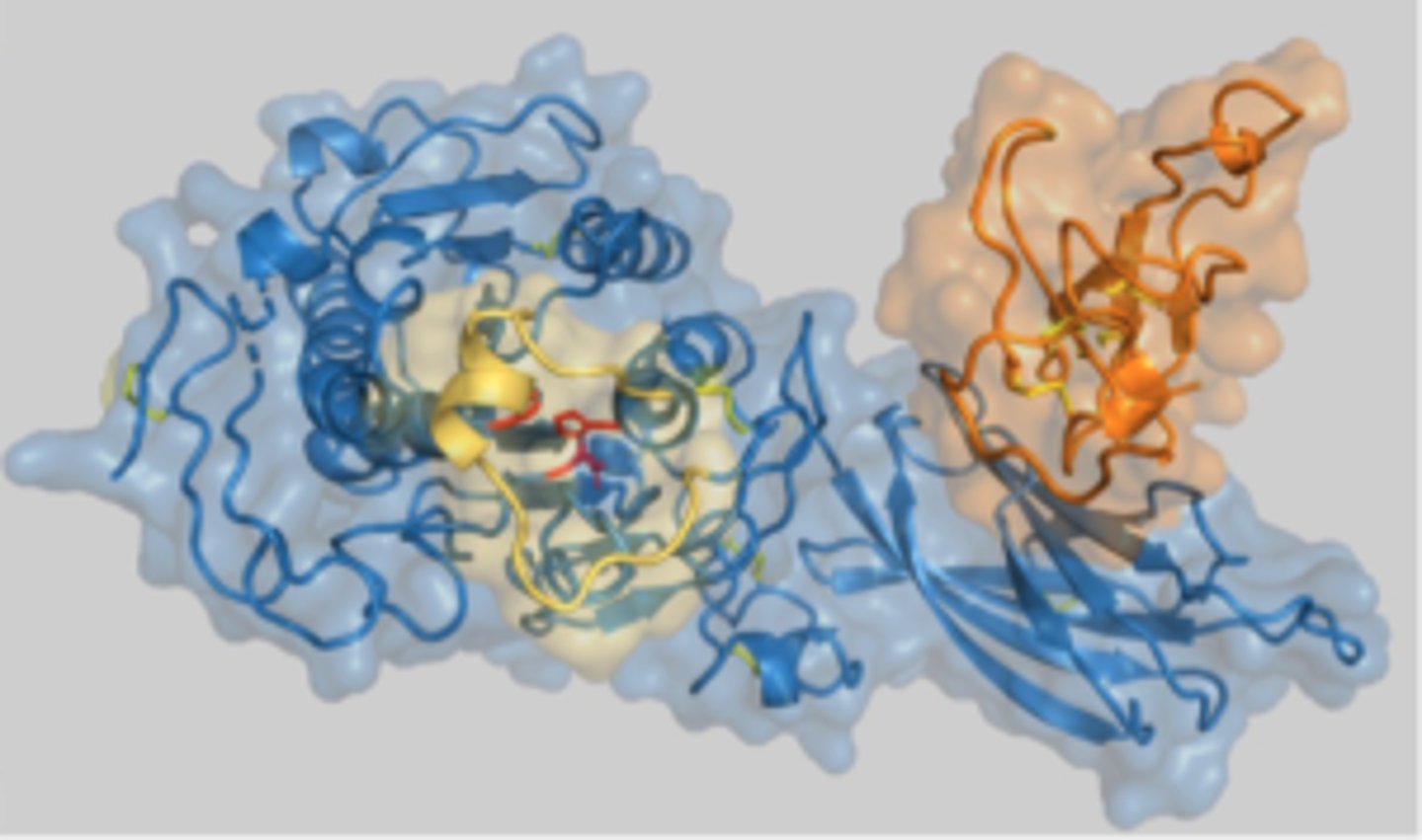
What does colipase do
Co lipase is a cofactor of HPL which binds the lid exposing the active site
What conformation changes occur in the human pancreatic lipase when it shifts from closed to open conformation
In the inactive form the lid region blocks accesses to the active site
In the active form the conformational change creates a large hydrophobic surface on HPL that allows it to insert into to the monolayer of the mixed micelle
What are Fatty Acid Binding Proteins (FABP)
Make fats soluble inside of the cell
How does inhibiting HPL through drugs like Orlistat work?
Orlistat inactivates HPL by forming a covalent bond with a key serine residue in the active site. Inhibiting HPL prevents dietary fats from being broken down so they pass through the digestive system un digested and end up being excreted as waste.
where are fatty acids synthesized in the body
Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the liver and adipose tissue. Fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm
What is the first step of the citrate shuttle which transports acetyl-CoA from the mitochondria matrix to the cytoplasm
Citrate synthase catalyzes the reaction where oxaloacetate and acetyl CoA combine to make citrate
Whats the second step of the citrate shuttle mechanism
Citrate is transported through the mitochondrial membrane via the citrate shuttle
Whats the third step of the citrate shuttle
Citrate lyase catalyzes the break down of citrate into Acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate
what happens to the Acetyl CoA and Oxaloacetate in the cytoplasm
Acetyl-CoA goes on to be used for fatty acid biosynthesis
oxaloacetate is converted into malate (by malate dehydrogenase) which is then converted into pyruvate and sent back to the mitochondria to regenerate oxaloacetate
What are the products and reactants of the citrate shuttle
Uses 2 ATP, 1 NADH
Generates 1 NADPH
what is the reaction catalyzed by Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase
First committed step of Fatty Acid Synthesis -> carboxylation of acetyl CoA to form Malonyl-CoA (highly exergonic reaction and essentially irreversible)
By how much does each of the 6 enzyme activities in Fatty Acid Synthase extend the fatty acyl chain by
Each enzyme extends the chain by 2 Carbon units
How does the ACC enzyme catalyze the reaction of acetyl-CoA to malonyl CoA
1. HCO3- is activated by ATP
2. Biotin cofactor with swinging arm takes the reactive CO2 to Acetyl-CoA
3. Acetyl-CoA with the CO2 attached becomes Malonyl-CoA
What is ACP
ACP = acyl carrier protein.
Intermediates in fatty acid synthesis are attached to an ACP
What is the overall reaction catalyzed by fatty acid synthase
Acetyl-CoA and Malonyl-CoA form Palmitate (16C saturated FA) in the cytosol.
Uses 8 acetyl-CoA, 7ATP, and 14 NADPH
What is the first step of Fatty Acid Synthase
Malonyl/Acetyl-CoA ACP transacylase (MAT) catalyzes the transfer of Acetyl CoA and Malonyl CoA onto ACP (drops off Acetyl-CoA in KS first)
What is the second step of Fatty Acid Synthase
KS catalyzes the condensation of malonylACP and AcetylACP, releasing a CO2
What is the third step of fatty Acid synthase
KR catalyzes the reduction of the fatty acid chain using NADPH which turns a ketone to an alcohol
What is the fourth step of fatty acid synthase
DH catalyzes a dehydration reaction in which a water molecule is released, and the alcohol becomes an alkene
what is the 5th step of fatty acid synthase
Enoyl-ACP reductase (ER) reduces the fatty acid chain using an NADPH turning the alkene into an alkane
what is the 6th step of fatty acid synthase
The cycle repeats (and a new malonyl CoA is added) until the chain reaches 16 carbons long (palmitate)
How is the growing chain released once it reaches 16 carbons
The fatty acid acyl chain can only properly bind in the C16 pocket of thioesterase once the carbon chain is 16 carbons long. Then it will be properly positioned for hydrolysis
How are longer fatty acid chains synthesized
Palmitate is the primary product and longer chain FA are built off of it. Elongation mostly happens in the ER and sometimes in mitochondria and separate enzymes are used
What do desaturases do
add cis double bonds, important for the synthesis of unsaturated fatty acids
why is arachidonate important
Serves as the precursor for important signaling molecules (the eicosanoids powerful hormones that break down quickly)
How does Asprin help with pain
By inhibiting the COX enzymes which are the enzymes responsible for pain/inflammation