1.1.2 - Diagnosing Bacterial Infections Blood Cultures
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
single venipuncture with blood inoculated into blood culture bottles
A. blood culture
B. bacteremia
C. sepsis
D. collection
A. blood culture
presence of microorganism in the blood
A. blood culture
B. bacteremia
C. sepsis
D. collection
B. bacteremia
presence of microorganism AND clinical symptoms of infection
A. blood culture
B. bacteremia
C. sepsis
D. collection
C. sepsis
bacteremia and sepsis are associated with ___________ morbidity and mortality
A. high
B. low
A. high
bloodstream infection without evidence of an infection site
A. primary infection
B. secondary infection
C. transient infection
D. constant infection
A. primary infection
isolation of organisms from blood and another site
A. primary infection
B. secondary infection
C. transient infection
D. constant infection
B. secondary infection
Patient X has the pathogen strep pnuemonia that is located in both the lung and blood. What type of bloodstream infection does patient X have?
A. primary infection
B. secondary infection
C. transient infection
D. constant infection
B. secondary infection
translocation of bacteria with rapid clearance
A. primary infection
B. secondary infection
C. transient infection
D. constant infection
C. transient infection
Name the clinical indications for cultures
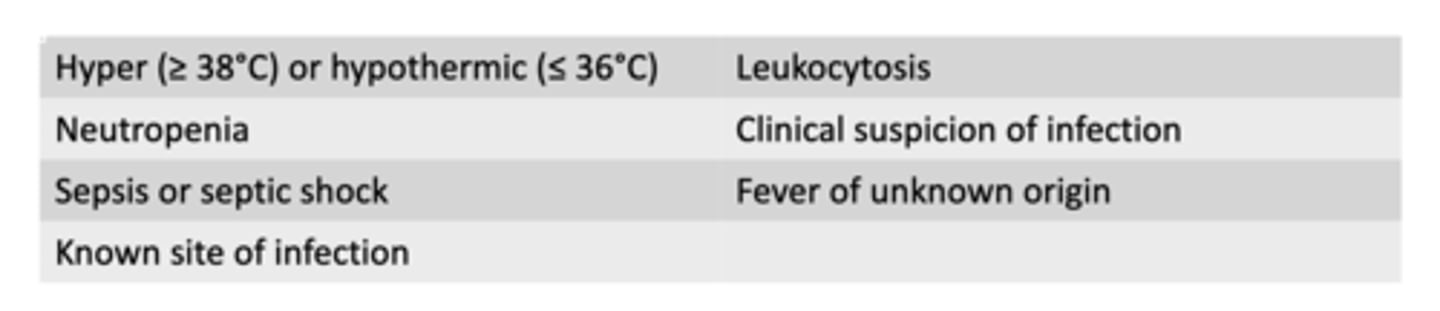
Which of the following are clinical indications for blood cultures: (select all)
A. neutropenia
B. hyperthermia (>=37 C)
C. leukocytosis
D. Fever of known origin
A and C
B is wrong because temperature has to be >=38C
D is wrong because its for a fever of unknown origin
What site do you use to obtain blood cultures?
peripheral venipuncture
Why is it important to carefully assess any blood culture that is taken from a catheter? (select all)
A. catheters can become colonized at site of entry
B. catheters can become colonized in the skin
C. catheters can become colonized in the lumen
A. catheters can become colonized at site of entry
C. catheters can become colonized in the lumen
What does a blood culture set consist of?
A. four bottles (two aerobic two anaerobic)
B. 2 bottles (both anaerobic)
C. 2 bottles (both aerobic)
D. 2 bottles (one aerobic one anaerobic)
D. 2 bottles (one aerobic one anaerobic)
How many sets of cultures are adequate for detection of bacteremia?
A. 2 sets (2 bottles)
B. 1 set (2 bottles)
C. 2 sets (4 bottles)
D. 1 set (1 bottle)
C. 2 sets (4 bottles)
The anaerobic bottle has increased _________ and ___________
A. helium and nitrogen
B. oxygen and helium
C. carbon dioxide and oxygen
D. carbon dioxide and nitrogen
D. carbon dioxide and nitrogen
In what patient population is it difficult to get two sets of cultures?
A. adults
B. pediatric
C. geriatric
D. pregnant
B. pediatric
Why is a single set of cultures at a high risk for being uninterpretable?
higher risk of contamination
When is the best time to collect a blood culture? (select all)
A. Around the time of a fever
B. after antibiotic administration
C. hours after fever onset
D. prior to antibiotic administration
A. Around the time of a fever
D. prior to antibiotic administration
Why is it important to collect blood culture before antibiotic administration?
antibiotics will decrease yield
It is best practice to send two sets ________________ from distinct sites for evaluation
A. within seconds
B. within hours
C. within minutes
D. within years
C. within minutes
What is the ideal volume of blood for identifying bacteremia?
A. one set of 5 mL bottles
B. one set of 10 mL bottles
C. two sets of 5 mL bottles
D. two sets of 10 mL bottles
D. two sets of 10 mL bottles
Overfilling (>10mL/bottle) may result in _________________ results
A. false negative
B. true negative
C. false positive
D. true positive
C. false positive
For children, blood drawn is typically based off of?
weight
For weight based blood drawing of pediatric patients, what is the amount drawn?
A. 1-2% total blood volume
B. 2-4% total blood volume
C. 2-3% total blood volume
D. 1-3% total blood volume
B. 2-4% total blood volume
Rate of false positive results should not exceed _________
A. 1%
B. 2%
C. 3%
D. 4%
C. 3%
Which of the following are variables affecting contamination rates:
A. improper culture bottle preparation
B. collecting 2 sets
C. improper use of skin antiseptic
D. collection from a vascular catheter
A. improper culture bottle preparation
C. improper use of skin antiseptic
D. collection from a vascular catheter
After you collect 2 sets from the patient, what is the next step in the workflow?
A. place in incubator so bacteria can grow
B. streak blood on media
C. set organism for identification and susceptibility
D. PCR
A. place in incubator so bacteria can grow
How long is a blood sample typically incubated for for growth?
A. 12 hours
B. 24 hours
C. 36 hours
D. 48 hours
B. 24 hours
After incubation, what happens to the blood sample?
A. streak on media
B. placed in incubator to grow more
C. set in automated system
D. gram stain
D. gram stain
After the sample is gram stained, what happens?
A. streak blood on media and place in incubator
B. set in automated system
C. get more samples from pt
D. finished
A. streak blood on media and place in incubator
After blood is streaked and placed in incubator, how long is it in the incubator for? How long into the workflow are we?
A. 12 hours; 24 hours into workflow
B. 24 hours; 36 hours into workflow
C. 24 hours; 48 hours into workflow
D. 12 hours; 48 hours into workflow
C. 24 hours; 48 hours into workflow
What is the last step of the workflow?
A. tell pt
B. set organism into automated system for identification and susceptibility at 72 hr
C. PCR
D. obtain more samples
B. set organism into automated system for identification and susceptibility at 72 hr
List the variables predictive of time to (bottle) positivity (TTP)
- intrinsic growth rates of organism
- inoculum size
- presence of antibiotics
- liver failure or neutropenia
most aerobic bacteria grow within ______________
A. 12 hours
B. 24 hours
C. 36 hours
D. 48 hours
B. 24 hours
Stopping or reducing in number and/or narrow spectrum of empiric antibiotic therapy
A. antibiotic resistance
B. Antibiotic mutiny
C. antibiotic escalation
D. antibiotic de-escalation
D. antibiotic de-escalation
What type of media is used: Almost all bacteria; differentiates hemolytic organisms
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
A. blood agar
What type of media is used: Fastidious organisms (neisseria or haemophilus)
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
What type of media is used: gram-negative bacteria
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
C. MacConkey
What type of media is used: contains bile salts to inhibit growth of gram positive bacteria
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
C. MacConkey
What type of media is used: contains antibiotics to maximize growth of desired organism
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
What type of media is used: used for determining antimicrobial susceptibility
A. blood agar
B. Chocolate agar (lysed RBCs)
C. MacConkey
D. Modified thayer martin
E. Regan-Lowe
F. Mueller-Hinton
F. Mueller-Hinton