Dendrology Terminology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
woody plants
long lived perennials. keep growing year after year
hemipiphytes
germinate in tree canopies
lianas
long stem woody vines
tree
tall, over >20ft. central woody stem(trunk)
shrub
short, less <20ft. multiple woody stems from ground.
conifer
mostly evergreen. don’t drop leaves or cones. soft wood. have needles. many of the late successional species.
broadleaves
monocots and dicots. usually bear flowers and fruits
monocot
parallel veins in leaves. angiosperms. no secondary growth.
dicots
wide broad leaves. evergreen or deciduous. netted veins in leaves. angiosperms
range
where the organism can evolve without human help. natural evolution.
parts of a leaf
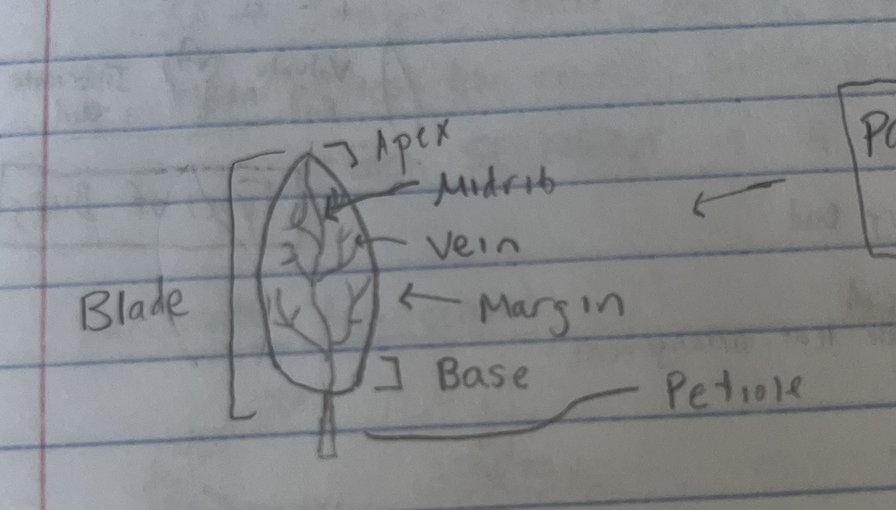
venation
the pattern of veins
serrate margin
rigid outer layer, tooth jagged
entire margin
completely smooth
double serrate margin
large teeth, smaller teeth on larger teeth
pinate venation

palmate venation

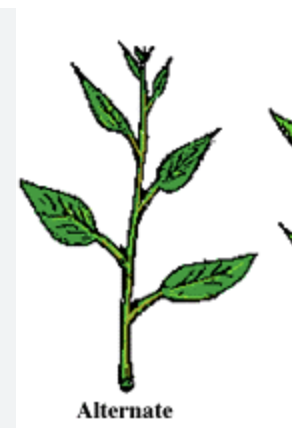
alternate leaf arrangement
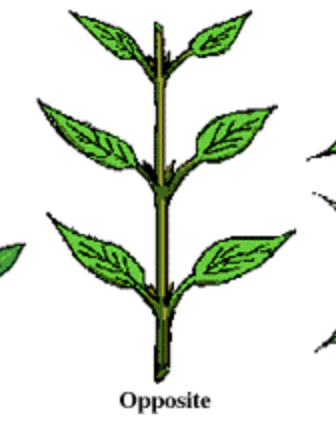
opposite leaf arrangement
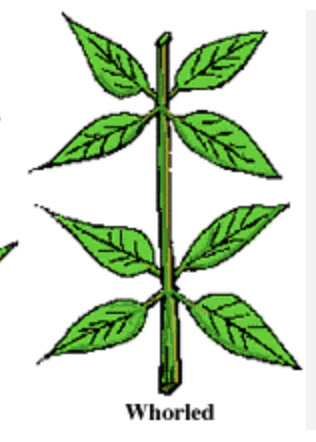
whorled leaf arrangement
pith
very central part of the twig
spur shoots
branches where the inter-node do not grow much. does NOT elongate
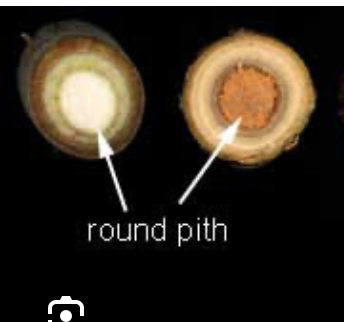
round pith
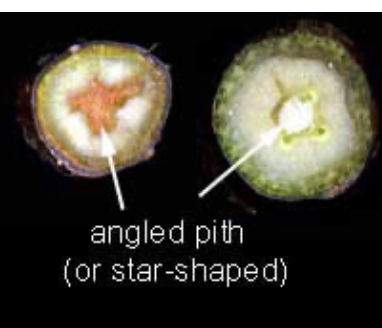
angled pith
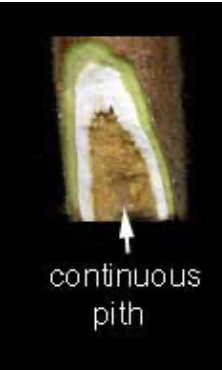
continuous pith
chambered pith

fascicles
only in pines. more than one needle attached to each leaf scar.
ternate arrangement
three needles per node
awl-like arrangement
short and triangular. sharply pointed
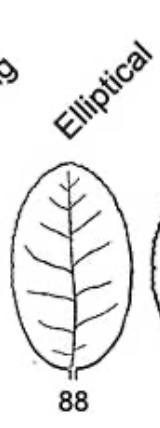
elliptical leaf shape
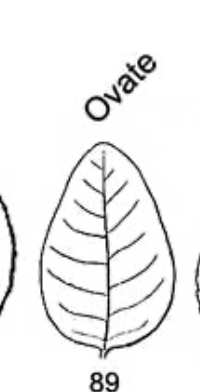
ovate leaf shape
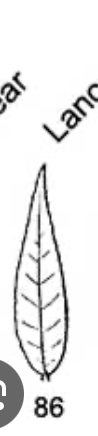
lanceovate leaf shape
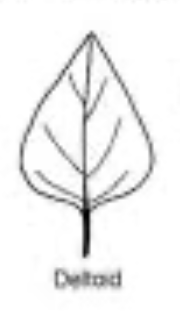
deltoid leaf shape
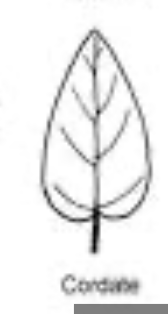
cordate leaf shape
common names
often numerous and in regional language. describes something about the tree.
scientific classification
ordering of things into groups based on shared characteristics
chinuk Wawa
trade language emerged in late 1700s. spoken by confederate tribes.
species
a group of organisms that share a lot of characteristics.
artificial classification
based on a few physical characteristics. arbitrary
natural classification
based on evolutional relationships.
pistil,stamen, sepals, petals
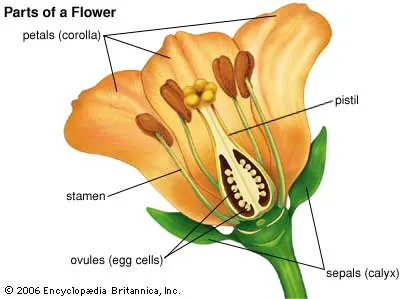
male or female? stamen
male
male or female? pistil
female
complete flower
has all four parts. pistil, stamen, sepals, petals
perfect flower
has all reproductive parts. male AND female
monoecious
individuals bear both staminate and pistillate flowers.
dioecious
two sexes. females bare distillates and males bare staminates
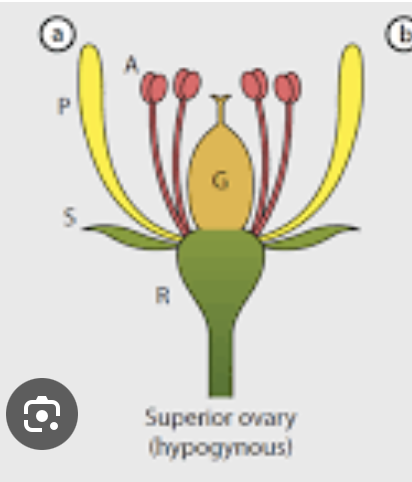
ovary position: superior
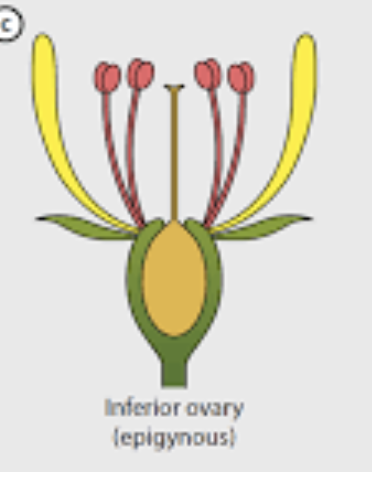
ovary position: inferior
inflorescence
a collection of flowers that share the same stalk
solitary flower
all alone. not inflorescent
catkin
all staminate or all pistillate
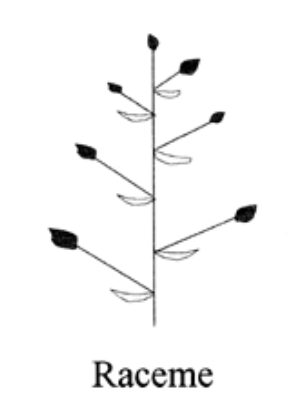
raceme orientation
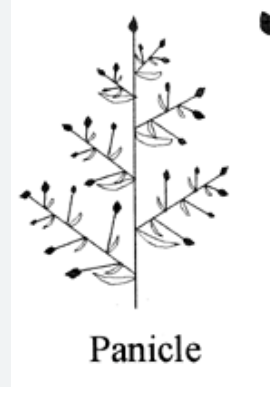
panicle orientation
fruit development
flower parts fall off. ovary develops, becomes the fruit. ovule grows and develops into seed.
dehiscent
breaks open alone pre-determined lines or sutures
idehiscent
fused shut. does not open alone predetermined lines
follicle
one carpel, dehiscent, one line
capsule
multiple carpels, dehiscent, several lines of dehiscence.
legume
one carpel, dehiscent, two lines of dehiscence.
nut
indehiscent, single seed in hard shell
samara
indehiscent, single seed, paper wing, wind dispersal
drupe
fleshy fruit with single hard seed in center
pome
fleshy accessory fruit that develops an inferior ovary. seed embedded in papery to woody core
berry
fleshy fruit with seeds embedded in flesh
valvate arrangement
pendent
cones that hang downward. face ground
erect
cones that face up. perched. upright