BMS exam 2 meds
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
antihypertensives
diuretics, ACE/ARB, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, vasodilators, alpha 2 adrenergic agonist
check BP, BP trends, parameters, hold if BP low, hold if HR too low
statins
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors. used for high total cholesterol, high LDL, high triglycerides, low HDL, high cardiovascular disease risk
monitor liver function9 every 3-6 months, give in evening, avoid grapefruit.
AE: myopathy, hepatotoxicity
coronary artery disease (CAD) meds
prevent MI and death. statins and antiplatelets.
prevent myocardial ischemia and anginal pain via beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates
anticoagulants
used for venous thrombus, large veins, areas with slower bloodflow.
used short term for DVT/PE prevention and treatment
used long term for prosthetic heart valve and afib
REVERSIBLE
antiplatelets
prevent arterial thrombus (MI, ischemic stroke), peripheral artery disease (PAD). in smaller arteries to prevent acute processes
IRREVERSIBLE
aspirin
antiplatelet
check vital signs and antagonists
AE: bleeding, GI upset, nephrotoxicity
clopidogrel
antiplatelet
for CAD, PAD, and ischemic stroke (CVA). used for dual antiplatelet therapy (2 at once)
check vital signs and antagonists
AE: bleeding
heparin
anticoagulant
IV: prevents and treats DVT/PE.
SQ: treats VTE prophylaxis, no aPTT monitoring
AE: bleeding, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
labs: PLT, aPTT
antagonist (reversal agent): protamine sulfate
enoxaparin
aka Lovenox. a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)
same as normal heparin but no aPTT monitoring
has a little air bubble that goes INSIDE patient
home use: stable DVT/PE, reliable,
low bleeding risk, adequate renal function, normal VS, monitorable
never give concurrently with heparin
warfarin
AKA Coumadin
long-term for anticoagulation. treats and prevents DVT/PE
PO. get PT/INR labs (normal INR 0.8-1.1, therapeutic 2-3). 48-72 hr onset. ensure stable vitamin K diet consumption. avoid NSAIDS, salicylates, and OTC drugs.
antagonist: vitamin K
AE: bleeding
factor Xa inhibitor
fondaparinux (Arixtra) SQ. rivaroxaban (Xarelto) and apixaban (Eliquis) both PO
treat and prevent DVT/PE. long-term for anticoagulation.
no reversal agent.
AE: bleeding
direct thrombin inhibitors
dabigatran (Pradaxa)
treat and prevent DVT/PE. long-term anticoagulation. PO.
no reversal agent
AE: bleeding
skeletal muscle relaxant
dantrolene
for malignant hyperthermia. assess liver function.
AE: hepatotoxicity
antiemetics
promethazine, metoclopramide, prochlorperazine, ondansetron
for N/V
monitor I/Os, emesis quantity. working if decrease in what and increase in activity and intake
AE: excessive sedation, respiratory depression
surfactant laxative
docusate sodium
allows water and oil into stool to make it slipperier
stimulant laxative
bisacodyl
activate colon nerves to move it along
osmotic laxative
polyethylene glycol
brings water into colon to soften stool
laxatives
for surgery + procedure prep and constipation
assess for abd pain, bowel sounds, allergies. encourage fluid intake. do not give if bowel obstruction or fecal impaction. med is working if bowels are prepped for procedure and there is no constipation.
AE: electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, diarrhea
pain meds
assess pain and med effectiveness. working if increased activity, decreased pain indicators
strong opioid agonists
morphine, hydromorphone
for severe pain
monitor VS, sedation level, I/Os, bowels, LOC, swallowing pills
AE: resp depress, change in sedation/LOC, constipation, urinary retention
moderate to strong opioid agonists
oxycodone/acetaminophen, hydrocodone.acetaminophen
for moderate pain
assess pain 60 min after PO, VS, what, bowels, GI upset, sedation, LOC, education, give with food
AE: resp depress, constipation, urinary retention, cough suppression, change in LOC/sedation
opioid antagonist
naloxone
reverses opioid agonists (+ resp depress)
given IV, IM, or SQ. immediate effects, 30-90 duration, given several times due to short half-life. working if patient is less sedated and their pain status improves. monitor VS and LOC
AE: withdrawal symptoms in dependent patients
analgesic/antipyretic
acetaminophen
for mild pain
no more than 4g/day, give with food.
AE: hepatotoxicity (high liver function tests, jaundice)
mild pain NSAID
ibuprofen
GI upset, give with food, bleeding
AE: gastric ulcer, bleeding, renal impairment
moderate to severe NSAID
ketorolac
monitor for bleeding
AE: gastric ulcer, bleeding, renal impairment
NSAIDs
monitor VS and hemoglobin + hematocrit
AE: gastric ulcer, bleeding, renal impairment (elevated what)
glucocorticoids
prednisone, methylprednisolone
used for rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune disorders, IBS, lupus, COPD, resp distress syndrome, transplant recipients, cancer, dermatologic disorders
AE: thromboembolism, hyperglycemia, decreased wound healing, infection, fluid electrolyte imbalance, osteoporosis
diuretics
for hypertension and edema
monitor fluid volume, VS, I/Os, weight, labs, nutrition
AE: dehydration, electrolyte imbalance
loop diuretics
-ide. furosemide, bumetanide
for hypertension, edema, and heart failure. tells loop of henle to not reabsorb water and Na into blood
AE: dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, hypokalemia
potassium sparing diuretics
AKA aldosterone receptor blockers
spironolactone
counters K loss, as opposed to other diuretics. do not give K supplements since med is already making K reabsorb
AE: electrolyte imbalance, dehydration, hyperkalemia
ACE inhibitors and ARBs
angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs)
used for hypertension, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy, myocardial infarction
monitor BP, labs, K, BUN/Cr
AE: angioedema, hypotension
ACE inhibitors
-pril. captopril, enalapril, lisinopril
used for hypertension, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy, myocardial infarction
monitor BP, labs, K, BUN/Cr. decreased mortality for cardiovascular disease patients
SE: cough
AE: angioedema, hypotension, first dose effect (allergy)
ARBs
angiotensin 2 receptor blockers
-sartan. losartan, candesartan, valsartan
used for hypertension, heart failure, diabetic nephropathy, myocardial infarction
monitor BP, labs, K, BUN/Cr. decreased mortality for cardiovascular disease patients
SE: cough, hyperkalemia
AE: angioedema
beta blockers
adrenaline/epinephrine binds to beta receptors, causing fight or flight (high HR, high BP). blocks this to reduce stress on heart
-lol
cardioselective: atenolol, metoprolol (less chance to cause bronchoconstriction)
noncardioselective: carvedilol, labetolol, propanolol (hurts ppl with asthma or COPD)
used for angina, hypertension, heart failure, MI/CAD
monitor BP, HR, lung sounds
SE: fatigue, erectile dysfunction (ED)
AE: hypotension, bradycardia, bronchoconstriction (non-cardio)
topical beta blockers
betaxolol (Betoptic S) and timolol (Timoptic). for glaucomas
SE: blurred vision, photophobia (light sensitivity), dry eyes
AE: hypotension, bradycardia, bronchoconstriction (non-cardio)
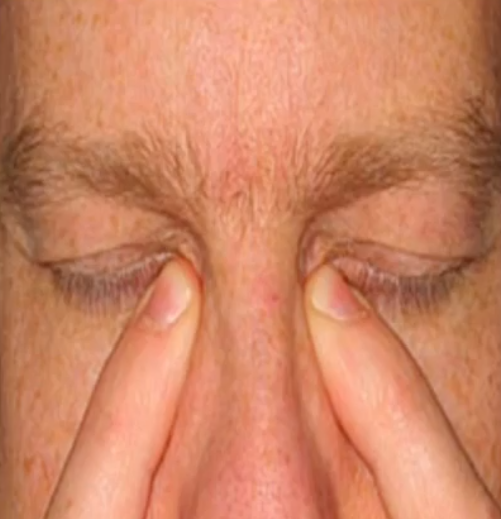
use punctal occlusion (block puncta so drops in eye do not drain into nasal cavity for 30-60 seconds)
smooth muscle calcium channel blockers
-dipine.
amlodipine, nifedipine, nicardipine.
monitor BP, HR, bowels
AE: hypotension
smooth and heart muscle calcium channel blockers
verapamil, diltiazem
monitor BP, HR, bowels
AE: hypotension, bradycardia
vasodilators
isosorbide, hydralazine, nitroglycerin
for hypertension, angina, heart failure
monitor BP, use of ED drugs (sildenafil/Viagra). can be sublingual, IV drip, IV push, paste, and PO
AE: hypotension
alpha 2 adrenergic agonist
methyldopa, clonidine
for hypertension. can be transdermal or PO
monitor BP, sedation
SE: drowsiness (give at night).
AE: hypotension, rebound hypertension if not tapered off