opioids/opiates
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
opioid vs. opiate: opioid
any drug that acts on opioid receptors in the brain/CNS
mainly synthetic drugs
examples: hydrocodone, oxycodone, fentanyl, heroin
opioid vs opiate: opiate
considered a subset of opioids that is naturally derived from the poppy plant
currently, opioid is the common term to describe opiates and opioids
examples: morphine, codeine, opium
endogenous opioid peptides
includes peptide neurotransmitters, opioids, and opioid metabotropic receptors
function is to alleviate stress/pain
targeted by analgesics, some general anesthetics, and drugs of abuse
naturally produced in the CNS and act as neuromodulators
what are the three opioid receptors?
delta, kappa, and mu
all are Gi coupled GPCRs
what are the three classes of the endogenous opioid peptides?
enkephalins
dynorphins
endorphins
pharmacology of endogenous opioids
inhibit glutamate release and inhibit the activation of spinal nociceptive neurons
Gi coupled - includes mu, delta, and kappa
expressed in CNS at sites of pain modulation, and endogenous opioids are released to alleviate pain
endorphins: delta = mu
enkephalins: delta > mu
dynorphins: kappa, sensitize nociceptive signals in dorsal horn
endomorphins: mu (main target for pain meds)
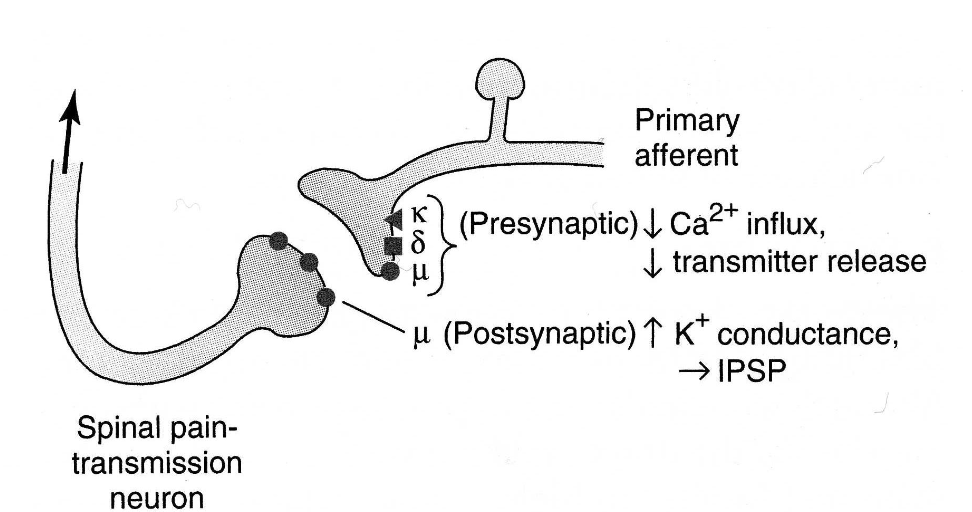
presynaptically, which opioid receptors are expressed?
all 3 are expressed on primary afferent neurons
postsynaptically, which opioid receptors are expressed?
mu, on spinal nociceptive neurons and peripheral terminals of sensory neurons
what are the sites of action of the opioid receptors?
spinal cord (pre and post)
supraspinal effects (pre and post)
peripheral terminals (post only)
understand this diagram well per dr. missaoui!
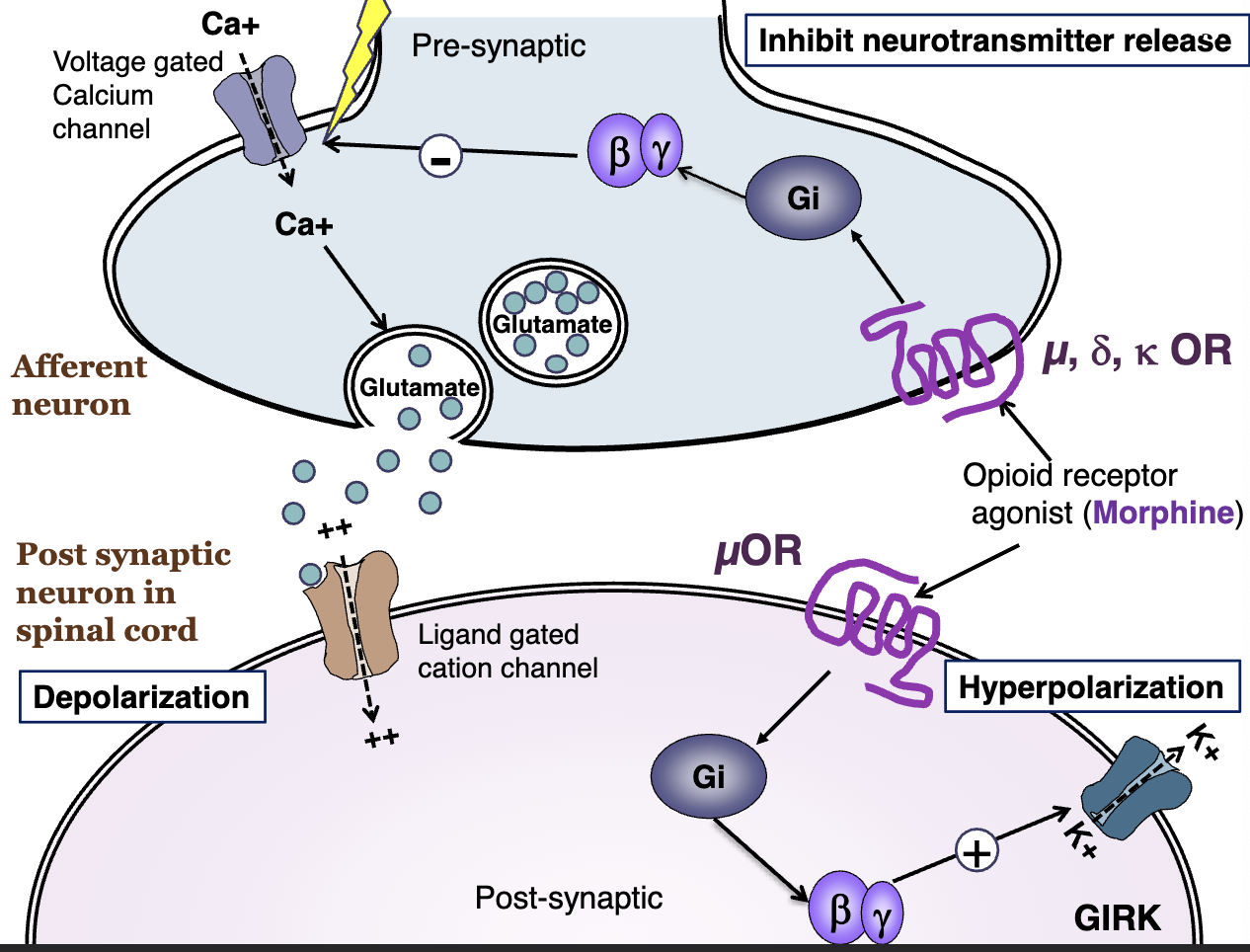
how does the direct inhibition in the ascending pathway work?
see image for more details
activation of postsynaptic mu opioid receptor inhibits the neuronal activation/pain transmission
which receptors are the primary therapeutic target of opioid analgesics?
mu
can cause analgesia, euphoria, respiratory depression, and dependence
kappa selective opioid agonists
effective analgesics, but can cause anxiety, panic, delirium, etc
which receptors likely contribute to tolerance?
delta
which receptors are important in sedative and GI effects of opioid agonists?
kappa
full/strong mu OR agonist list
morphine, hydromorphone, oxymorphone, heroin, methadone, fentanyl and its derivatives, mepiridine, levorphanol, dextromethorphan
partial/mild mu OR agonists list
codeine, oxycodone, hydrocodone, propoxyphene, loperamide, diphenoxylate, difenoxin
mixed mu and kappa OR agonists/antagonists list
nalbuphine, buprenorphine, butorphanol, pentazocine, dezocine
mu OR antagonists list
naloxone, naltrexone
metabolism of opioid agonists
morphine and mepiridine are full agonists that can cause seizures
phenanthrenes are converted to nonactive polar glucuronides in the liver and are excreted by the kidneys (except morphine - see above)
phenylpiperidines are metabolized by 3A4 (except mepiridine - see above)
absorption of opioid agonists
generally well absorbed from multiple routes with signficiant first pass metabolism
the least metabolized: oxycodone, codeine
can include parenteral, rectal, intranasal, transdermal, etc.
CNS effects of opioids
good/desired effects: analgesia, euphoria, cough suppression, sedation sometimes
bad/undesired effects: sedation, respiratory depression, miosis, truncal rigidity, n/v
respiratory depression is especially a problem in asthma, COPD, increased intracranial pressure
peripheral effects of opioids
CV: bradycardia (except mepiridine = tachycardia), hypotension
GI: constipation, no tolerance development
uterus: reduce uterine tone, prolong baby delivery
renal: urinary retention, reduced renal function
neuroendocrine: regulates relese of LH, ADH, prolactin
pruritis triggered mostly by mu agonists
immune: inhibits lymphocytes, NKs
clinical use of opioids - analgesia
used for severe acute pain
must consider:
maximal efficacy
pain is usually self-reported/not quantifiable
duration of action of therapy
route of administration
ADRs
individual opioid history
also used in chronic pain, but tolerance/dependence is possible with limited efficacy
can be used in terminal illness as well for analgesia
other clinical uses of opioids
anesthesia (alone or adjunct) - pre-op and during surgery
acute pulmonary edema can be alleviated by morphine (not sure how)
diarrhea (loperamide, diphenoxylate, difenoxin)
cough suppression (codeine, dextromethorphan)
potencies of the fentanyl derivatives
sufentanil > fentanyl > alfentanil
alfentanil and remifentanil have short half life and rapid action
mepiridine
has antimuscarinic activity
avoid in tachycardia and in decreased renal function
methadone
long acting, used to treat opioid use disorder (OUD)
used for detox and to lessen withdrawal severity by blocking the rewarding effects of heroin and other drugs
potent NMDA receptor blocker and potent mu OR agonist
used as a morphine alternative in “opiate rotation”
true or false: a patient receiving a partial agonist can also receive a full agonist
false
what will partial agonists do if administered with a full agonist?
they will compete and hinder the full agonist from reaching its maximum effect
true or false: you should not give a mixed agonist to pts receiving a full agonist
true
true or false: all mixed agonists have the potential for negative psychotogenic effects, like delusion and hallucination
true
nalbuphine
mixed kappa agonist and mu antagonist
butorphanol
mixed kappa agonist and partial mu agonist
pentazocine
mixed kappa agonist and weak mu antagonist
buprenorphine
mixed long-acting partial mu agonist and delta/kappa antagonist
used for detox
lower risk for respiratory depression than methadone
naloxone-resistant
tramadol
SERT blocker, weak mu agonist
used in chronic neuropathic pain
no respiratory effects
can cause seizures, nausea
tapentadol
NET blocker
weak mu agonist
codeine
cough suppressant and a partial mu agonist
given at sub-analgesic doses
dextromethorphan (DXM)
full mu agonist cough suppressant
non-habit forming and less constipating than codeine
stereoisomer of levorphanol
levopropoxyphene
cough suppressant stereoisomer of dextropropoxyphene
contraindications of opioids
partial agonists can cause withdrawals in pts receiving full aognists
pre-existing intracranial pressure/head injury
pregnancy
pre-existing pulmonary impairments
pre-existing impaired renal or hepatic function
hypothyroidism or low adrenal activity
opioid antagonists
high affinity for mu receptors
used for management of acute opioid overdose to completely reverse morphone effects
includes naloxone (IV, short-acting) and naltrexone (oral long-acting, maintenance)
opioid tolerance
clinically relevant around 2 weeks into treatment
highest tolerance develops toward analgesia, euphoria, sedation, and respiratory depression
limited tolerance develops with mixed-type opiates/opioid rotation
risk varies with opioid efficacy and DOA
likely involves up-regulation of cAMP pathway, down-regulation/internalization of mu ORs, receptor uncoupling, and NMDA receptors
chronic opioid administration may lead to hyperalgesia
opioid dependence
withdrawal/abstinence syndrome can develop upon d/c of the drug
includes rhinorrhea, lacrimation, yawning, chills, goosebumps, hyperthermia, hyperventilation, n/v/d, mydriasis, muscle aches, anxiety, hostility
opiate administration immediately reverses withdrawal
withdrawal intensity is dependent on half life
morphine/heroin: peaks 48hrs in, lasts 5 days
mepiridine/fentanyl: complete within 24hrs
methadone: peaks 3-5 days, lasts 2 weeks, less intense - used for heroin detox
antagonist-precipitated withdrawal can cause immediate symptoms upon administration of naloxone
abrupt d/c of mixed agonist can cause less severe withdrawals