Integumentary Pathology
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Terminology
Plaque
Scale
Onycholysis
Vesicle
Bulla
Acanthosis
Hyperkeratosis
Parakeratosis
Acantholysis
Erosion
Ulceration
Plaque: raised flat-topped lesion, usually >5mm diameter
Scale: dry flakes that can easily be scraped away due to thickened corneal layer
Onycholysis: separation of nail plate from nail bed
Vesicle: small fluid-filled blister usually <5mm diameter
Bulla: larger fluid-filled blister, usually >5mm diameter
Acanthosis: epidermal thickening due to hyperplasia, stratum spinosum increases
Hyperkeratosis: Increase in thickness of stratum corneum
Parakeratosis: Retention of nuclei in stratum corneum
Acantholysis: loss of intercellular cohesion between keratinocytes
Erosion: Incomplete loss of epidermis
Ulceration: complete loss of epidermis revealing dermis or hypodermis
Psoriasis
Define
Pathogenesis
Macroscopic Morphology aka Clinical Presentation
Microscopic Morphology
Chronic proliferative, non-infectious inflammatory disease
Pathogenesis: arises due to both genetic factor as well as immunological factors (Th1 and Th17 mediated) and environmental factors (local trauma/Koebner phenomenon)
Macroscopic Morphology: well demarcated pink to salmon-colored plaques covered with silvery-white scales
Removal of scales causes petechial bleeding (Auspitz sign)
Onycholysis and oil spots in nails
Skin, elbows, knees
Palliative treatment only
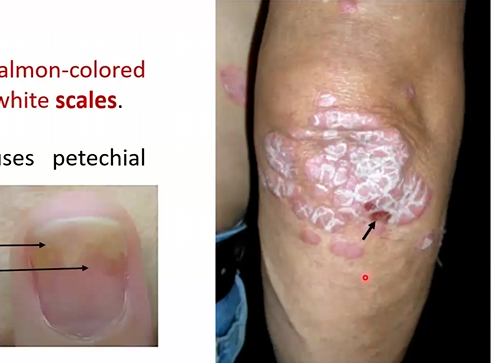
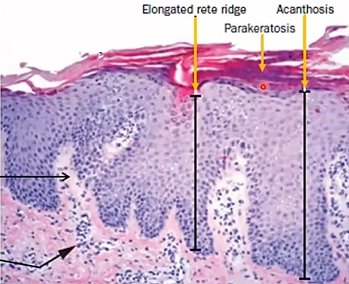
Microscopic Morphology:
Acanthosis with downward elongation of rete ridges
Extensive parakeratosis scaling

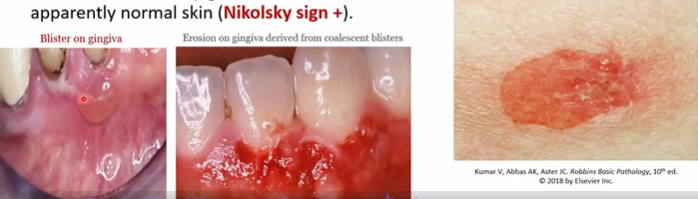
Pemphigus Vulgaris and Foliaceous
Define
Pathogenesis
Micro Morphological features
Macro-Morphological features/Clinical Features
Autoimmune blistering disorder caused by the separation of two layers within the epidermis
Vulgaris: suprabasal separation
Foliaceous: subcorneal separation
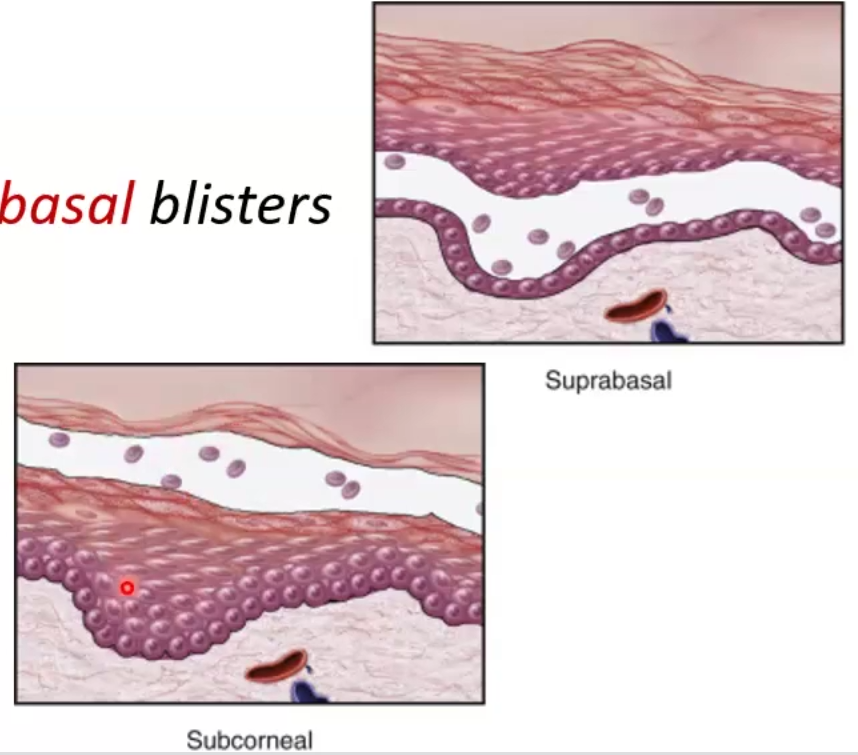
Pathogenesis: causes by antibody-mediated type II hypersensitivity, which causes degradation of desmosomes by plasmin
Vulgaris: antibodies against desmoglein (DSG) 1 and 3
Foliaceous: antibodies against DSG1 only
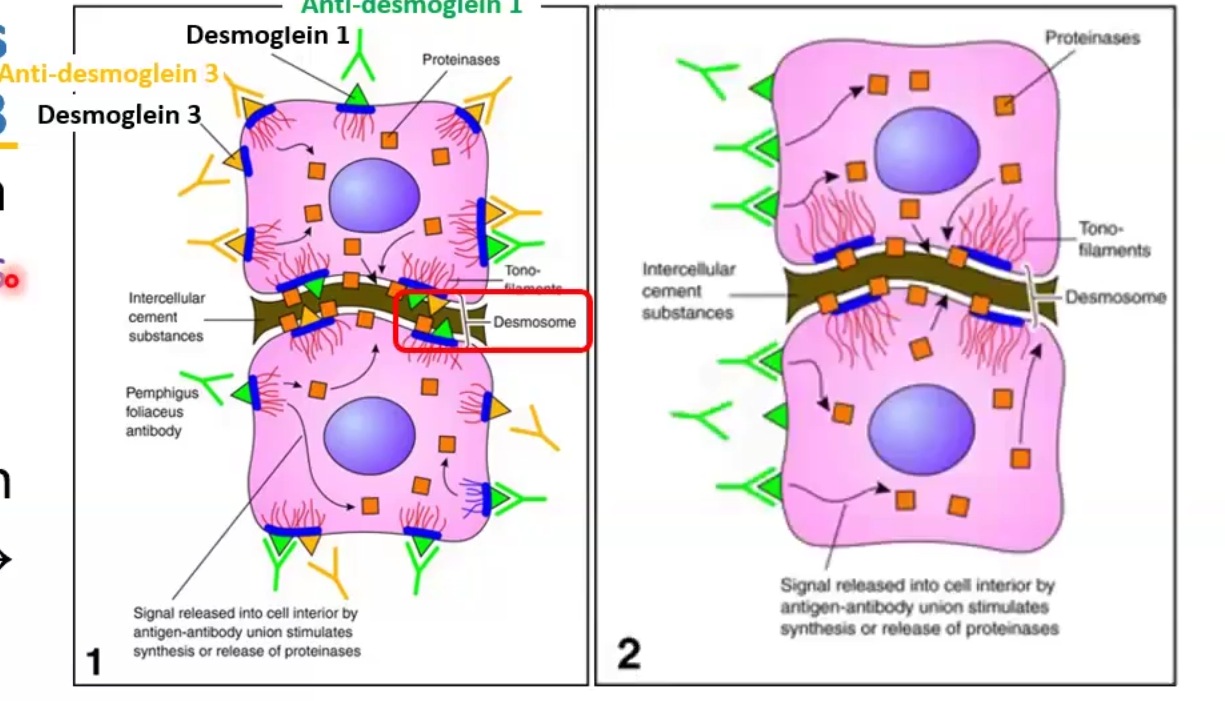
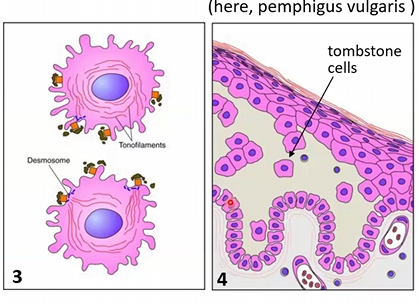
Micro Morphological features:
Vulgaris: Acantholysis leads to tombstone cells in stratum basale
Fishnet pattern caused by IgG deposition upon fluorescence
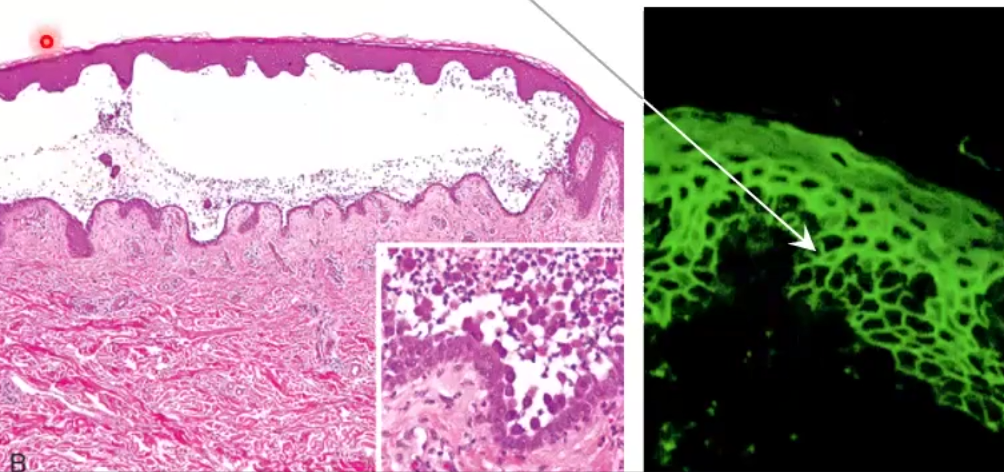
Foliaceus: acantholysis in stratum granulosum, IgG deposits only on superficial layers
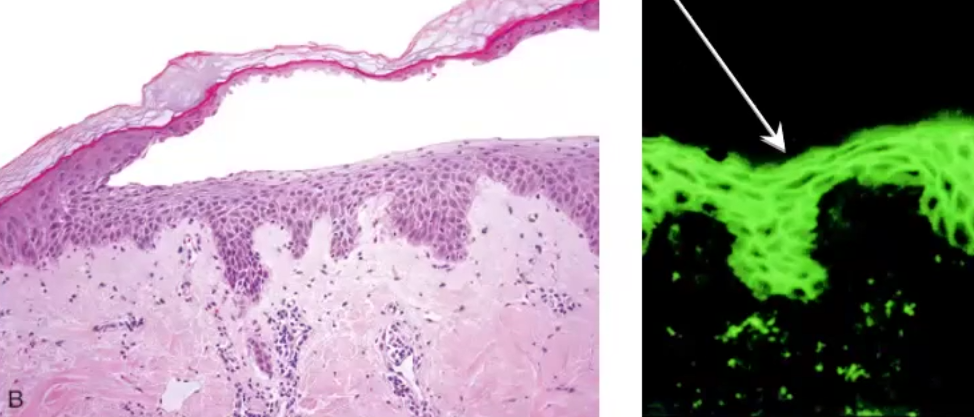
Macro-Morphological features/Clinical Features
Vulgaris: blisters that easily coalesce forming bullae and rupture leaving superficial erosions covered with serum crust; new lesions occurs by gently rubbing (Nikolsky sign+)
Begin as painful blisters in oral mucosa then spread
Foliaceus: more superficial with smaller zones of erythema and crusting
never in oral mucosa
Bullous Pemphigoid
Define
Pathogenesis
Clinical Features
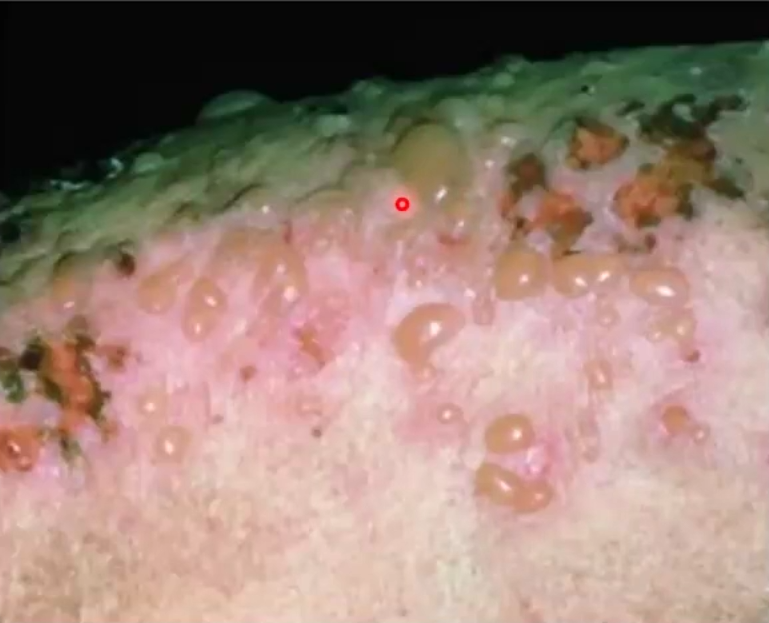
Chronic bullous disorder with an autoimmune basis affecting 60-80 yo
Less severe and more common than pemphigus vulgaris
Pathogenesis: IgG auto-antibodies against basement membrane proteins BPAG1 and BPAG2 through mast cell degranulation
Clinical Features
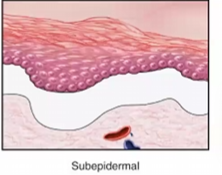
Subepidermal bullae
Unlikely oral involvement 10%
Multiple tense 2cm bullae on erythematous base, do not rupture easily
No acantholysis
Heals w/o scarring
Melanocytic Nevus
Define
Micro-Morphology
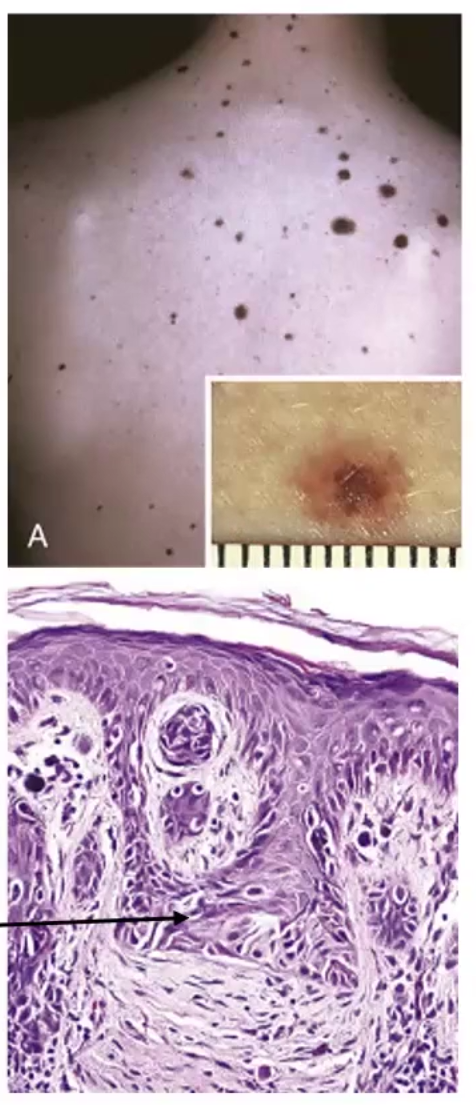
Benign proliferation of nevus cells, a mole
Linked to sun exposure and innate susceptibility
Micro-Morphology: Nests of uniform round cells with inconspicuous nucleoli and few mitotic figures
Dysplastic Nevus
Define
Micro-Morphology
Lesions with variable pigmentation and irregular borders, usually larger than normal nevi
Increases risk for melanoma
Micro-Morphology: irregular nests that bridge
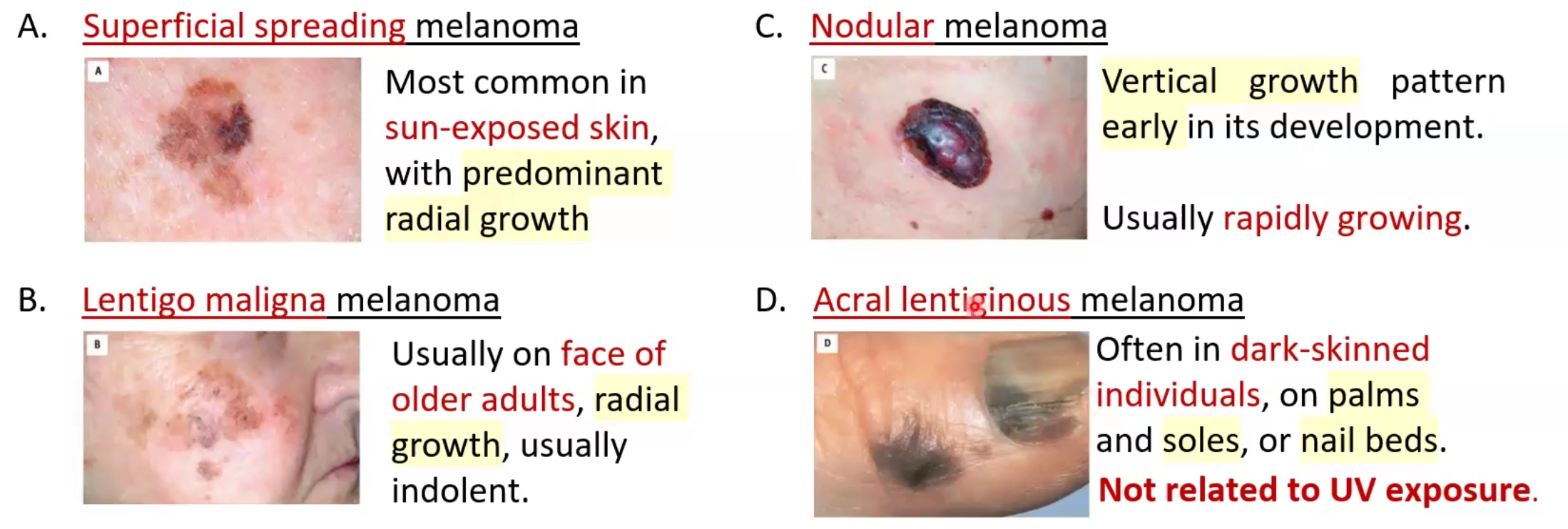
Melanoma
Define
Linked to
Pathogenesis
Morphology
Types of spread
Tumor markers
Malignant neoplasm of melanocytes
Strongly linked to mutations caused by exposure to UV radiation
Leading cause of mortality in young adults
Pathogenesis: caused by UV radiation damaging DNA of melanocytes; hereditary predisposition 5-10%
Mutations in CDKN2A gene disrupt cell cycle oncogenes
Mutations in BRAF and NRAS genes activate MAPK pathway
Morphology: variation in pigmentation, larger size >mm, Irregular notched borders
Types of spread:
Superficial
Lentigo: radial growth on face
Nodular: vertical growth and rapidly growing
Acral lentiginous: palms soles and nail beds get coloration in dark individuals; not related to UV exposure
Tumor markers: S-100 and HMB-45 and use ABCDE guide
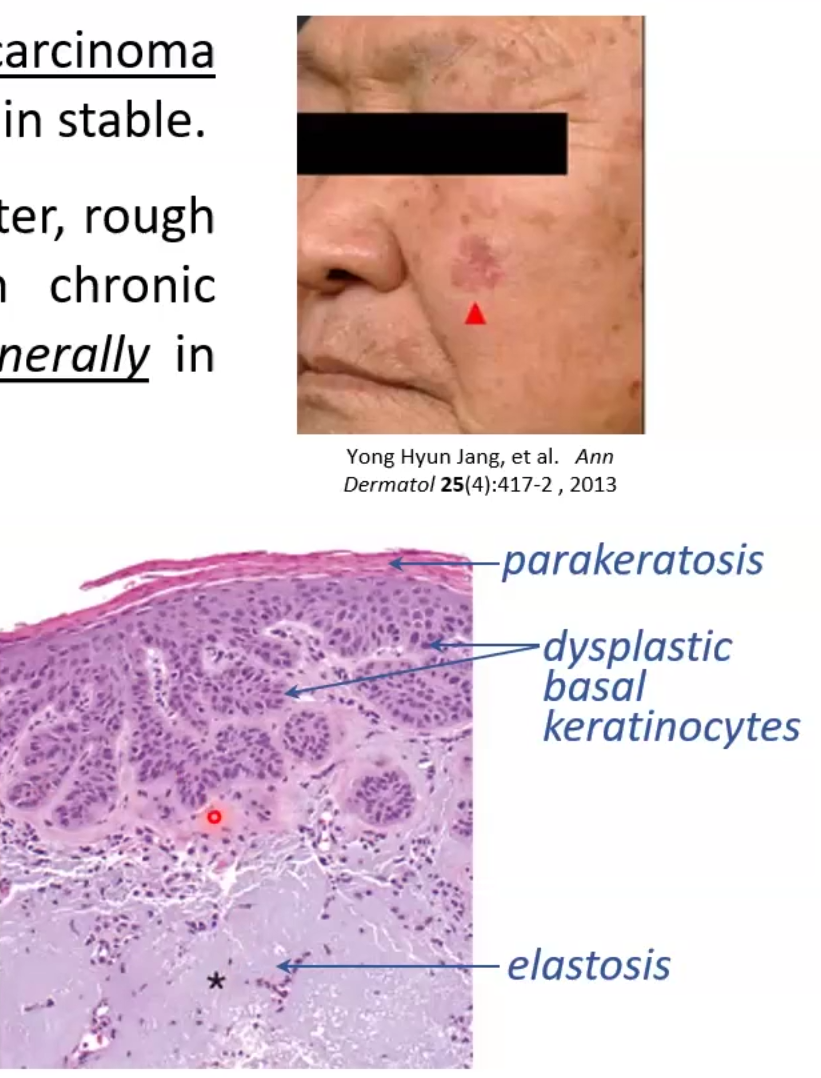
Actinic Keratosis
Define
Pathogenesis
Micro Morphology
Pre-cancerous lesions tht may progress to squamous cell carcinoma
circumscribed tan-brown or red lesions <1cm in diameter that are sand-paper like
Pathogenesis: caused by UV-induced DN damage associated with TP53 mutations
Micro Morphology: basal keratinocytes show dysplasia
Parakeratotic scales and elastosis
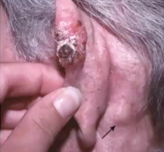
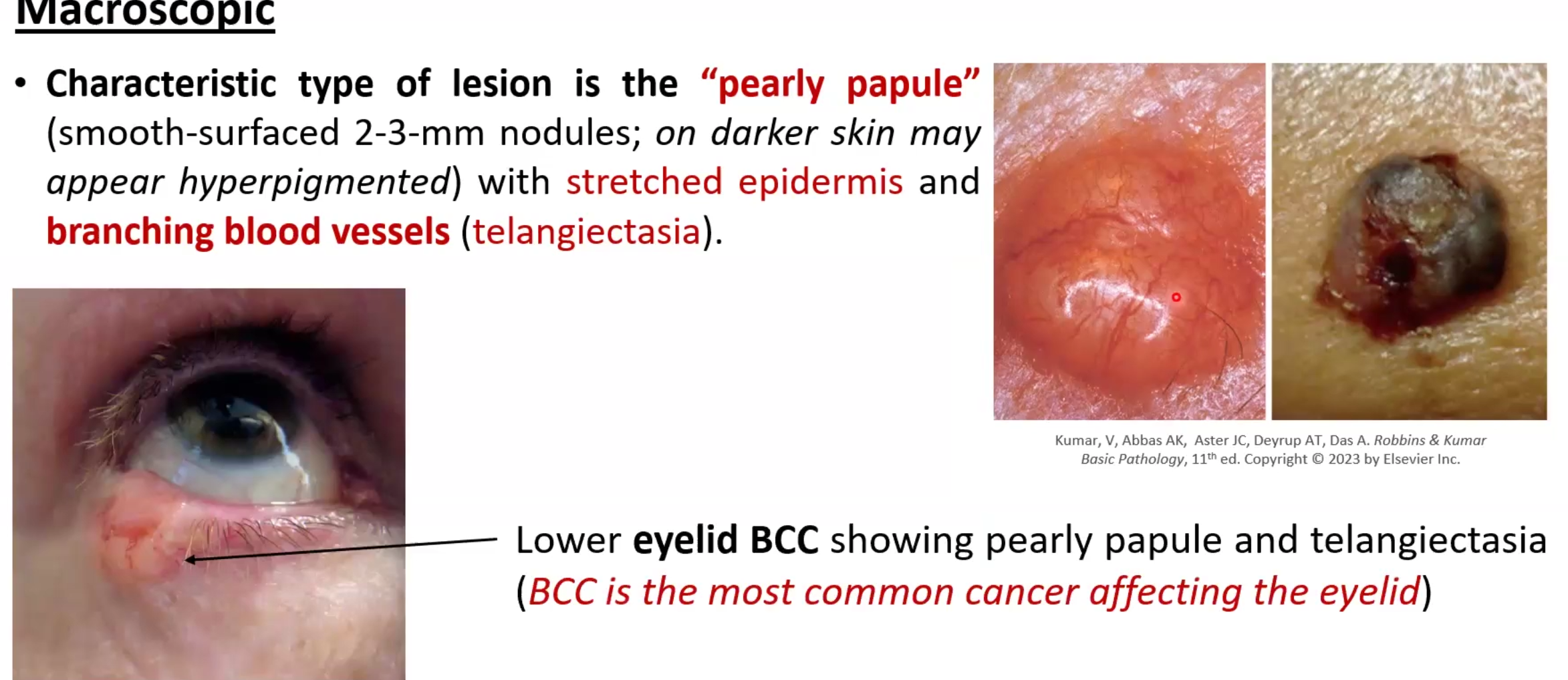
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Define
Pathogenesis
Morphology (macro and micro)
Most common form of skin cancer, may be locally aggressive but metastases is rare
Pathogenesis: caused by mutations (due to UV) in the PTCH1 gene or TP53 for both sporadic and familial
Morphology:
Pearly papule lesion that may be 2-3mm
telangiectasia
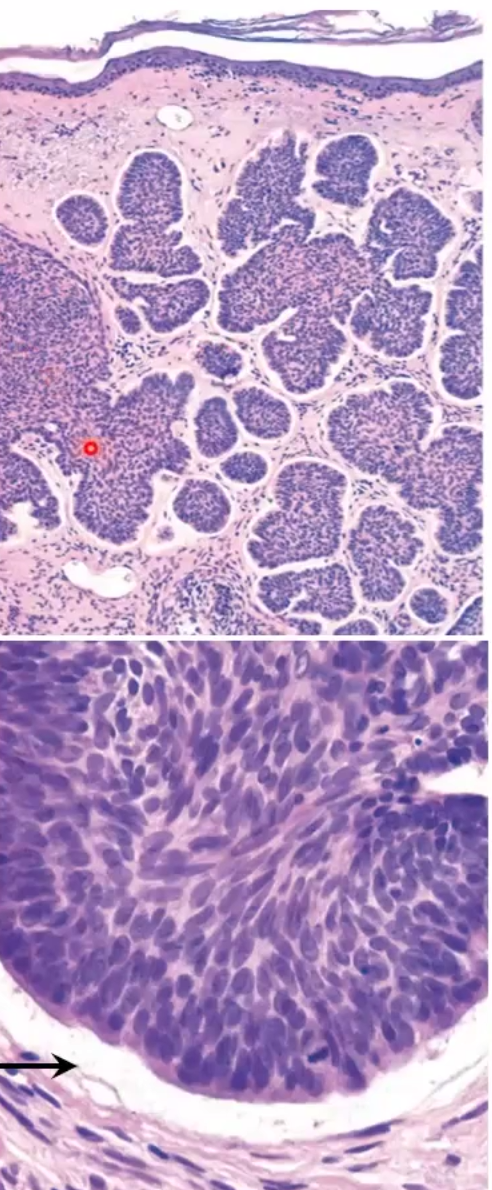
Nests of deeply basophilic epithelial cells, and separation clefts
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Define
Pathogenesis
Morphology (micro and macro)
2nd most common type of skin cancer that typically occurs in sun exposed areas
Pathogenesis: most are mutated TP53 genes
Morphology: red scaling plaques that may ulcerate in ears hands lips and hands
Entire epidermis is replaced by dysplastic keratinocyte
Only metastasize after long periods of time