Neuroscience: Brain Plasticity, Functions, and Disorders
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Plasticity
Refers to the brain's ability to reorganize and adapt throughout life in response to experiences, learning, and environmental changes.
Corpus callosotomy
A surgical procedure that disconnects the two hemispheres of the brain, primarily done as a treatment for severe epilepsy.
Split Brain Research
Studies individuals who have undergone corpus callosotomy, examining how each hemisphere functions independently.
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
The phenomenon where each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body.
Hemispheric Specialization
The concept that each hemisphere of the brain has specialized functions and abilities.
Epilepsy
A neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, which can sometimes originate from abnormal electrical activity spreading between the two hemispheres of the brain.
Left hemisphere
The hemisphere of the brain that typically controls language and verbal processing in right-handed individuals.
Right hemisphere
The hemisphere of the brain that is often associated with non-verbal and spatial processing.
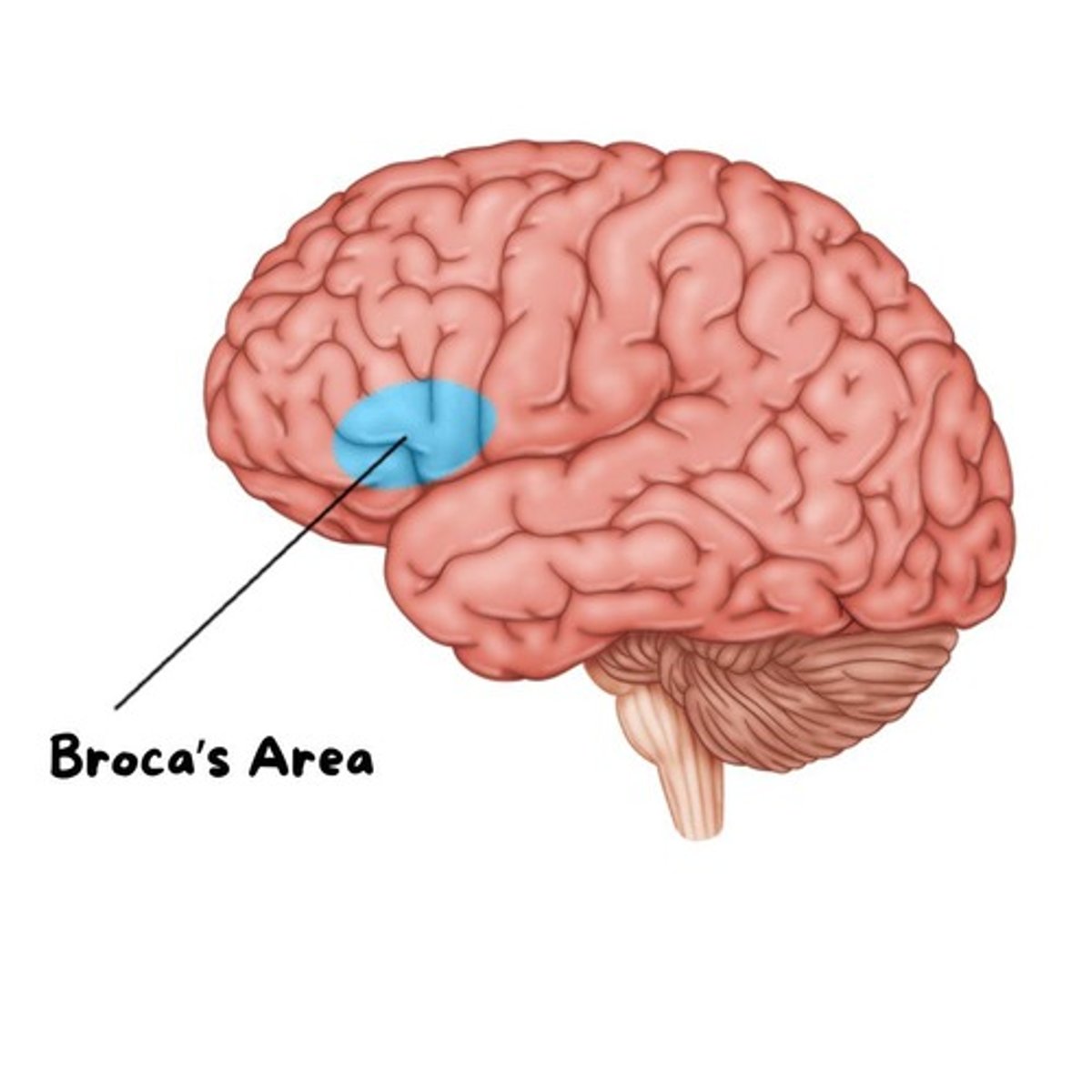
Broca's Area
Located in the left hemisphere of the brain, specifically in the frontal lobe, that is responsible for speech production and language processing.
Wernicke's Area
Region located in the left hemisphere of the brain, specifically in the temporal lobe, that is involved in language comprehension and understanding spoken and written language.
Broca's Aphasia
Language disorder caused by damage to Broca's area in the left hemisphere of the brain, often resulting from stroke or brain injury.
Wernicke's Aphasia
Language disorder caused by damage to Wernicke's area in the left hemisphere of the brain, typically resulting from stroke or brain injury.
Exhibit fluent speech but have difficulty understanding spoken and written language, as well as producing meaningful and coherent speech.
Telegraphic Speech
Patients speak in short, fragmented phrases lacking grammatical structure. Example: 'Want water' instead of 'I want a glass of water.'
Agrammatism
Difficulty forming grammatically correct sentences. Example: 'Go store' instead of 'I am going to the store.'
Difficulty with Articulation
Patients struggle to produce speech sounds accurately. Example: 'I w-w-walk' instead of 'I walk.'
Impaired Naming
Difficulty recalling or finding words. Example: Unable to name common objects like 'pen' or 'table.'
Frustration
Patients may become frustrated or agitated due to communication difficulties.
Word Salad
Grammatically correct but nonsensical speech. Example: 'The purple elephant danced on the piano.'
Neologisms
Creating new or inappropriate words. Example: Referring to a dog as a 'flibbertigibbet.'
Paraphasia
Substituting words, leading to jumbled sentences. Example: Saying 'I hike dice beam' instead of 'I like ice cream.'
Impaired Comprehension
Difficulty understanding spoken or written language.
Lack of Awareness
Unawareness of language deficits or nonsensical speech.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Non-invasive neuroimaging technique used to record the electrical activity of the brain.
EEG Procedure
Involves placing electrodes on the scalp to detect and measure the electrical signals produced by neurons in the brain.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
Neuroimaging technique used to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels.
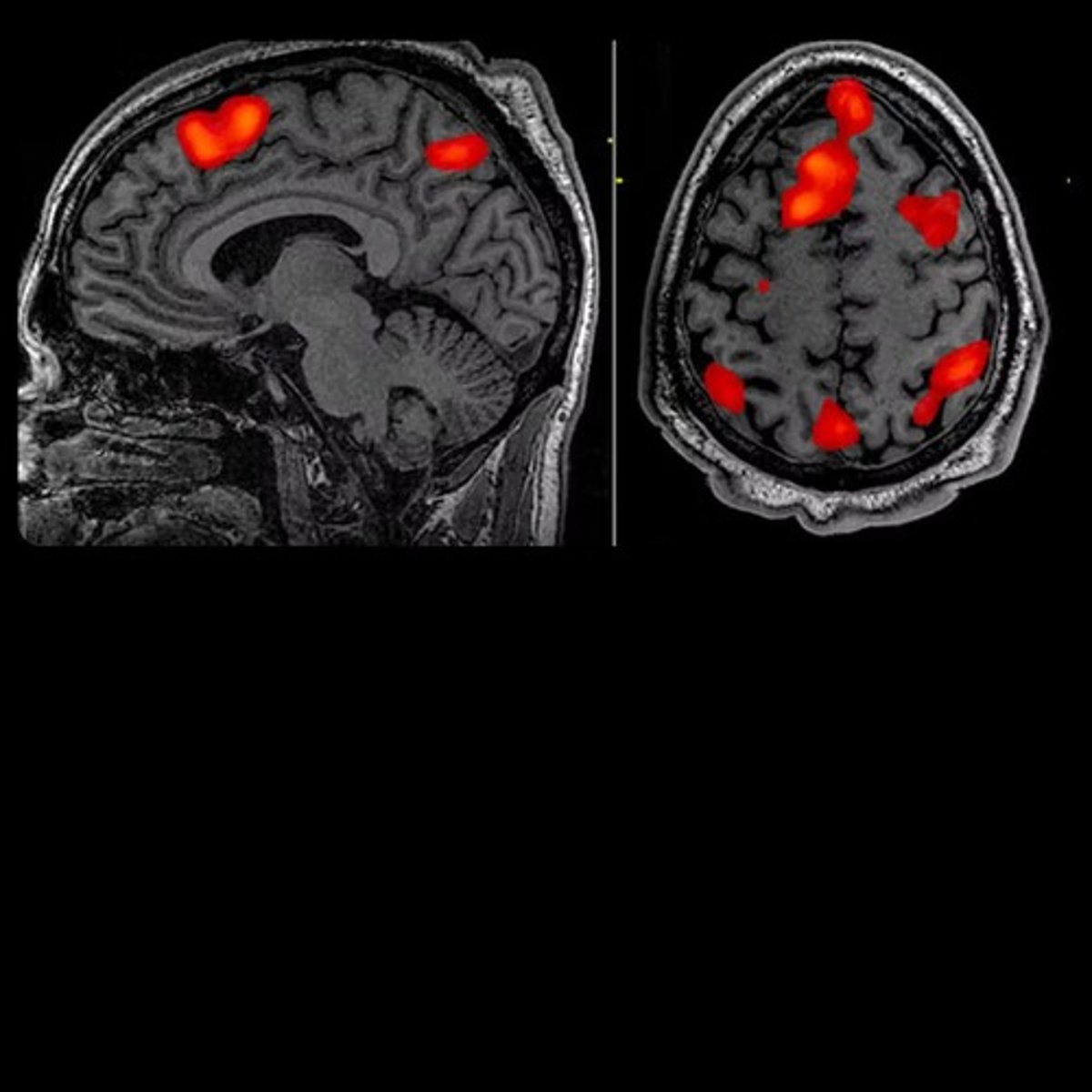
fMRI Functionality
Provides detailed images of the brain's structure and function, allowing observation of active brain areas during specific tasks.
Lesioning
Research technique used to study brain function by intentionally damaging or destroying specific areas of the brain in experimental animals.
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the brain, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions, including thinking, perceiving, and decision-making.
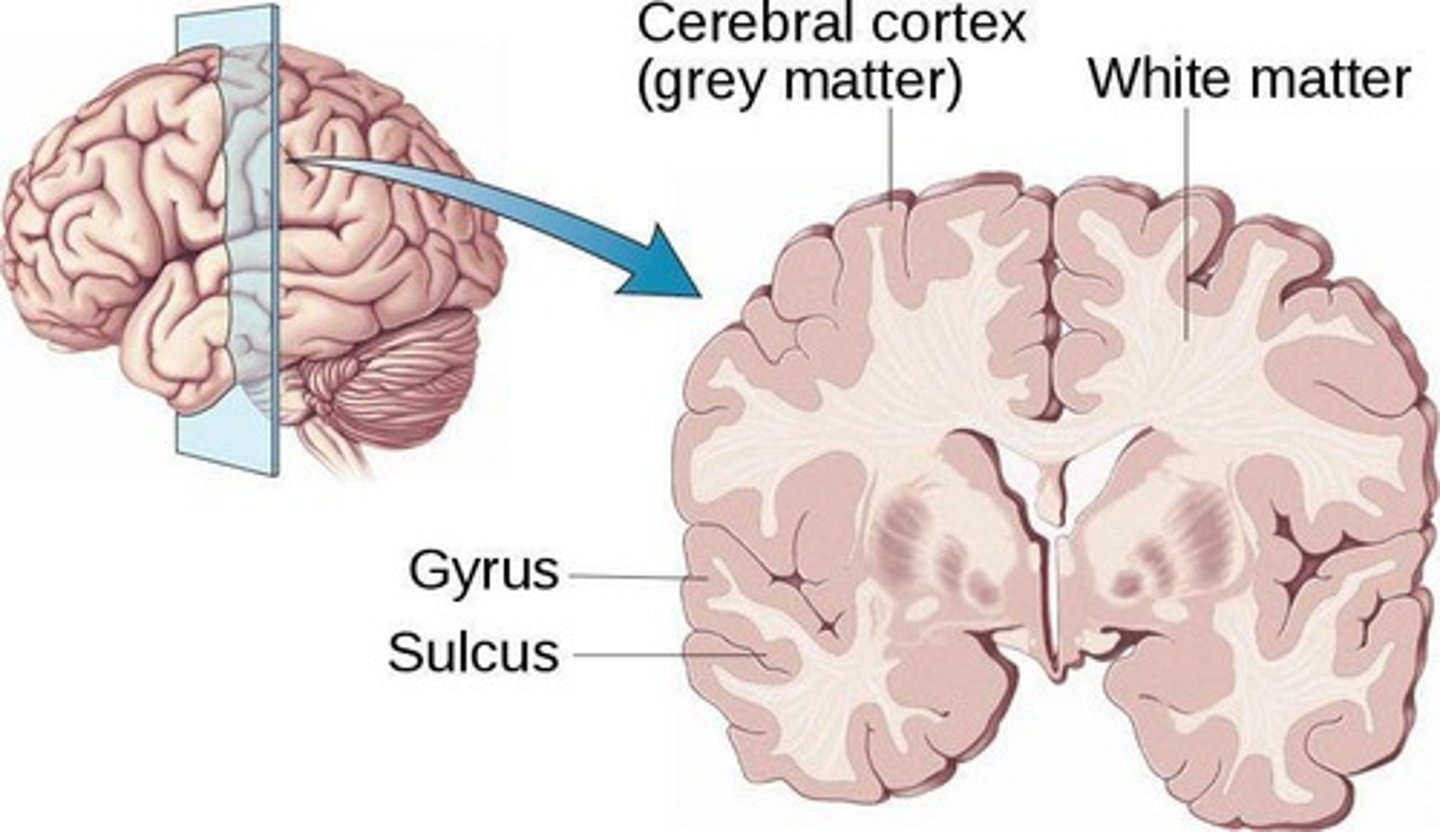
Grey Matter
Where the brain's 'thinking' happens, containing the cell bodies of neurons.
White Matter
Acts as the brain's 'wiring,' consisting of myelinated axons that help transmit signals between different brain regions.
Lobes of the Brain
The four main regions or sections into which the cerebral cortex is divided.
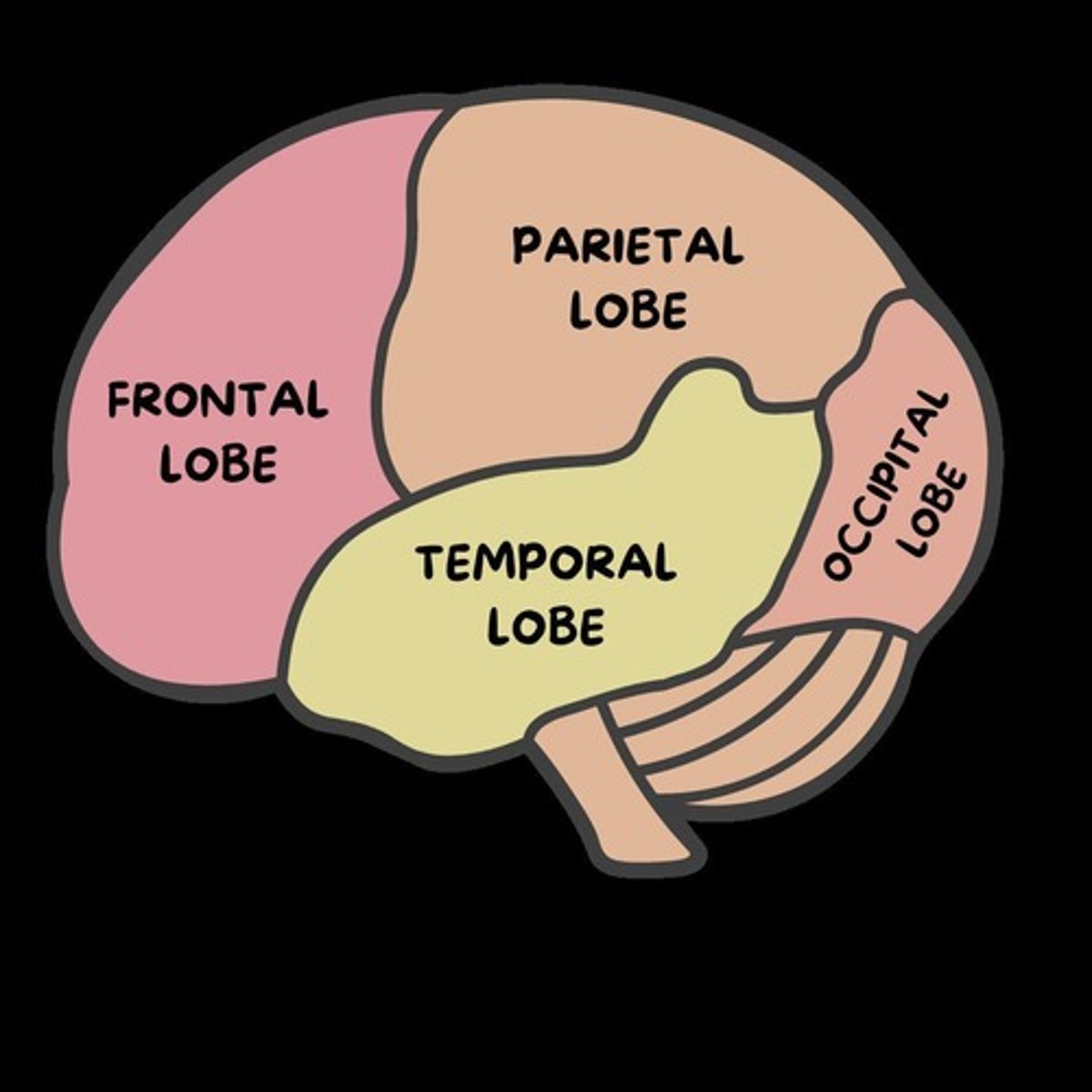
Association Areas
Parts of the brain that take information from all over the place and put it together to help us understand the world around us.
Frontal Lobes
Located at the front of the brain and are involved in higher-level cognitive functions, including decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and personality expression.
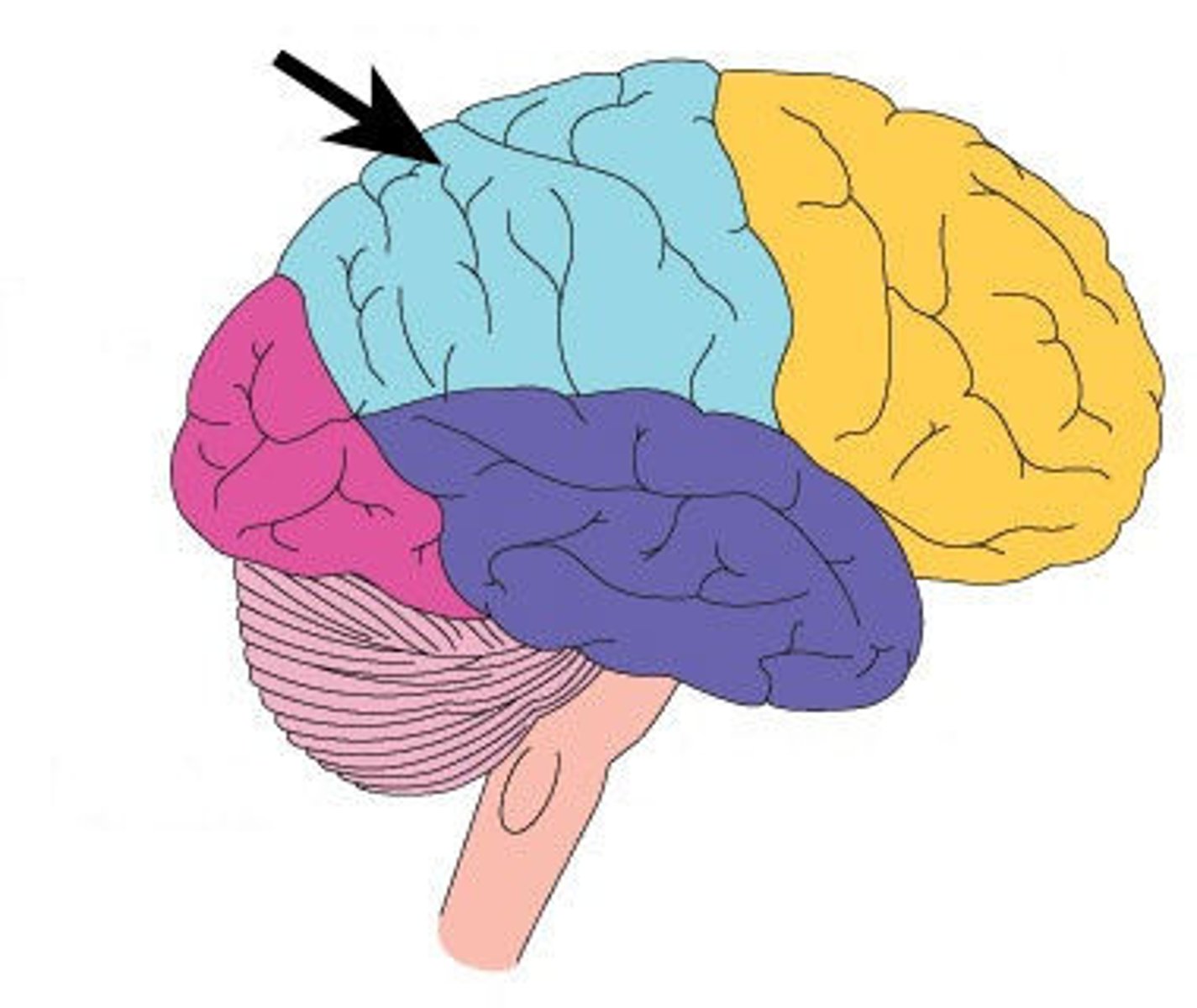
Parietal Lobes
Located at the top of the brain and are primarily responsible for processing sensory information from the body, such as touch, temperature, and spatial awareness.
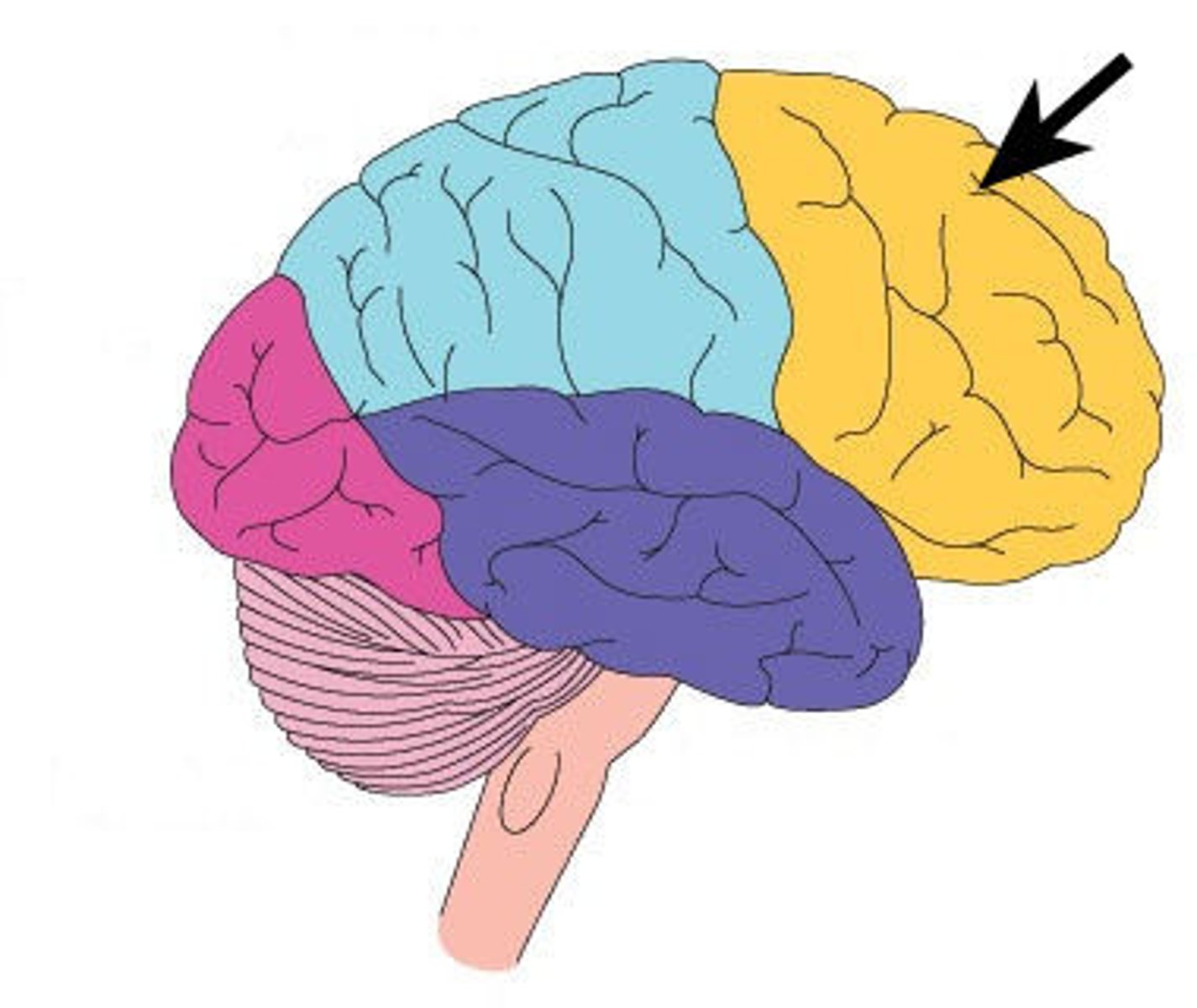
Occipital Lobes
Located at the back of the brain and is primarily responsible for processing visual information received from the eyes.
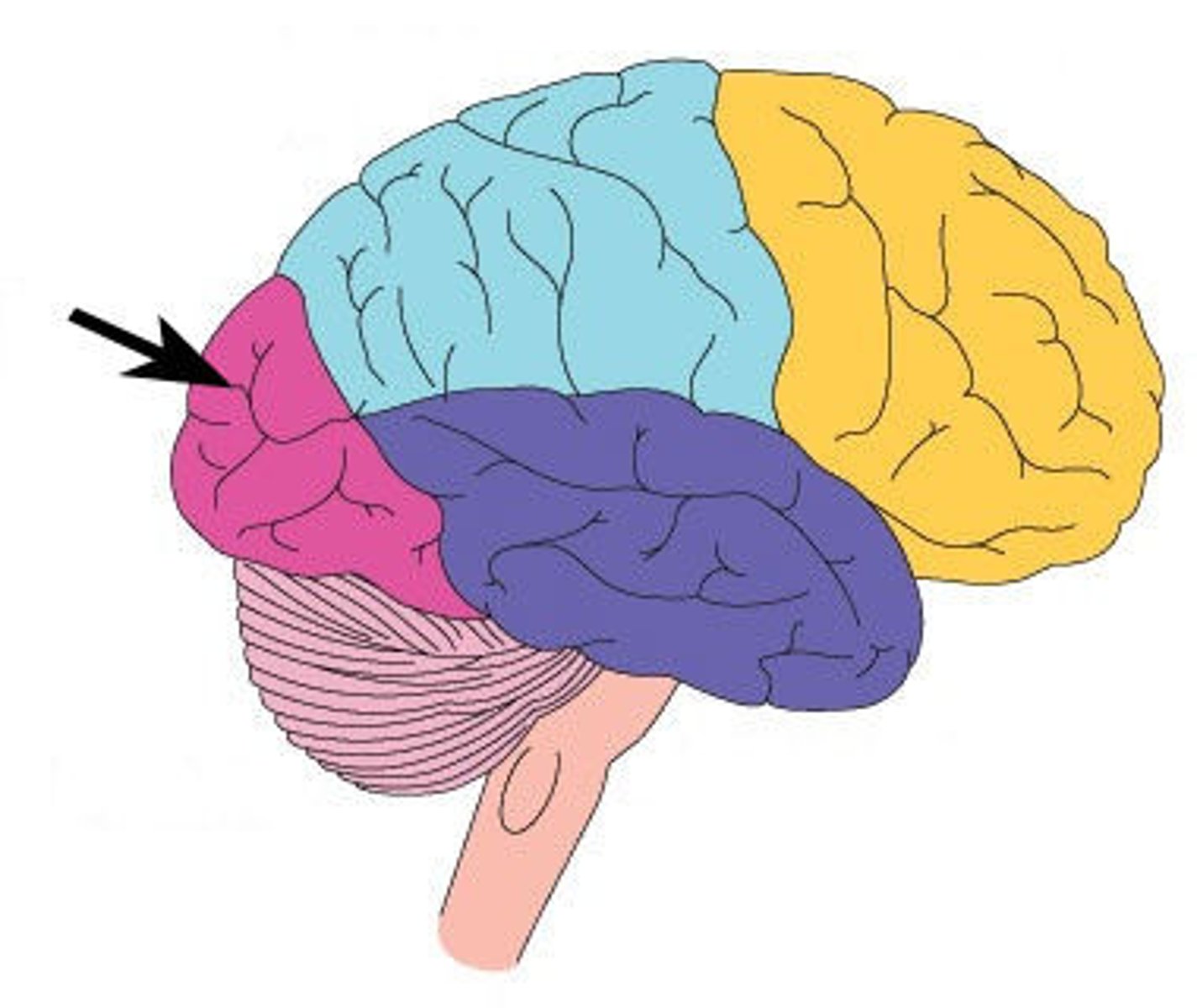
Temporal Lobes
Located on the sides of the brain and are involved in processing auditory information, language comprehension, and memory formation.
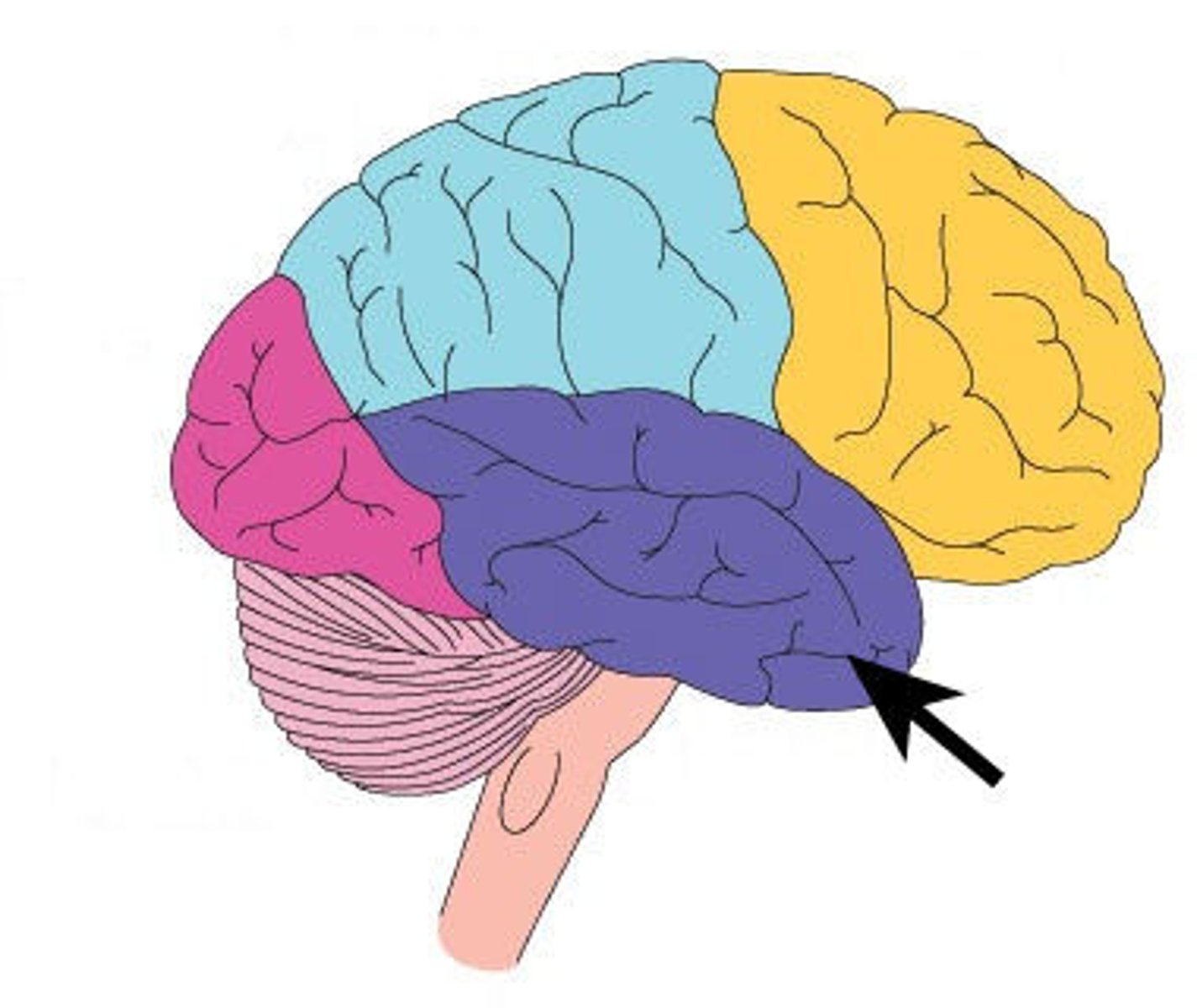
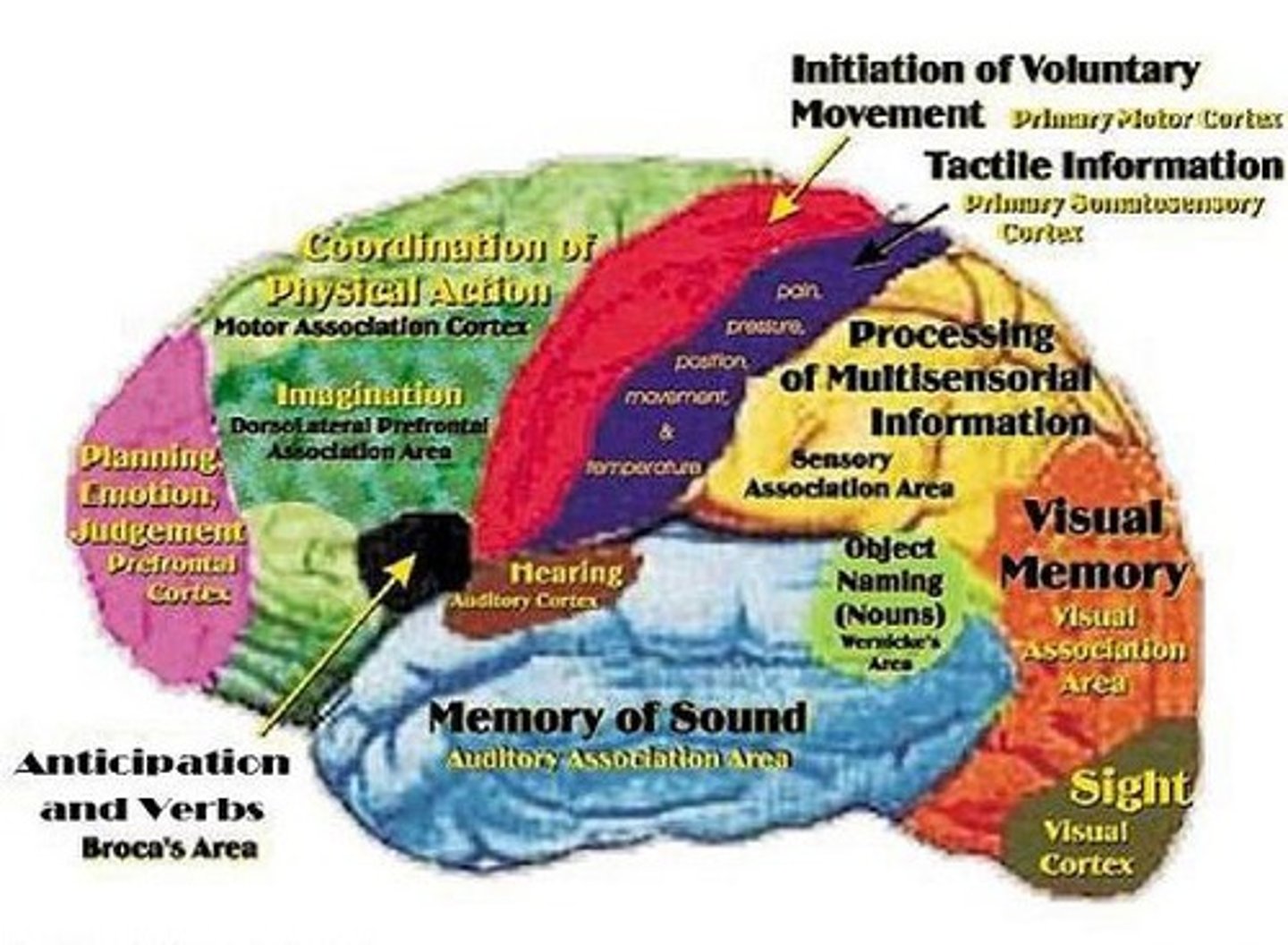
Prefrontal Cortex
A region of the brain located in the frontal lobe, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions and executive functioning.
Executive Functioning
A set of cognitive processes that enable individuals to plan, organize, strategize, focus attention, regulate emotions, and manage time effectively.
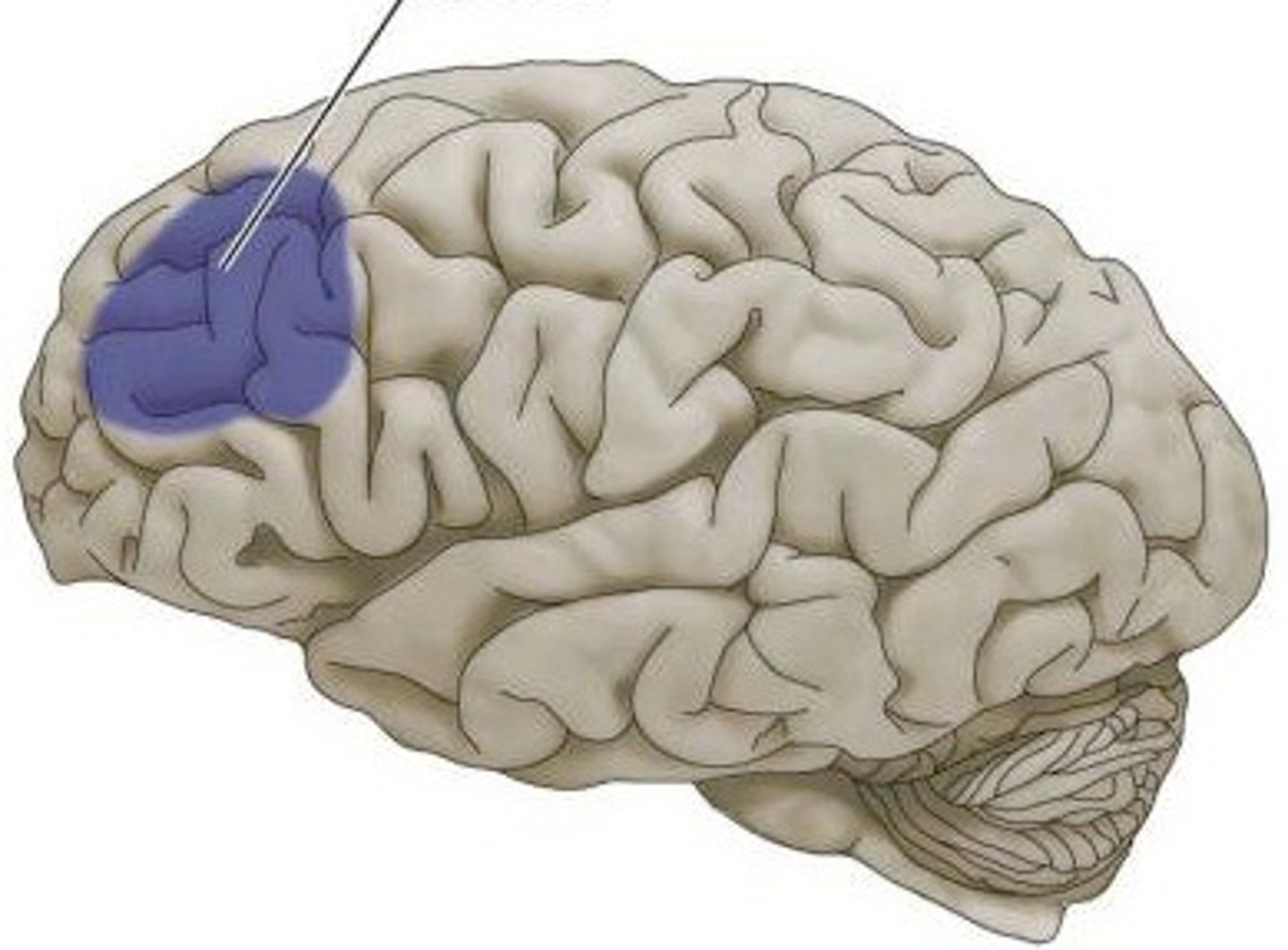
Motor Cortex
Region of the brain located in the frontal lobe, responsible for planning, executing, and controlling voluntary movements of the body.
Motor Cortex Function
Sends signals to the muscles, enabling actions such as walking, talking, and grasping objects.
Somatosensory Cortex
Region of the brain located in the parietal lobe, responsible for processing sensations from the skin, muscles, and joints.
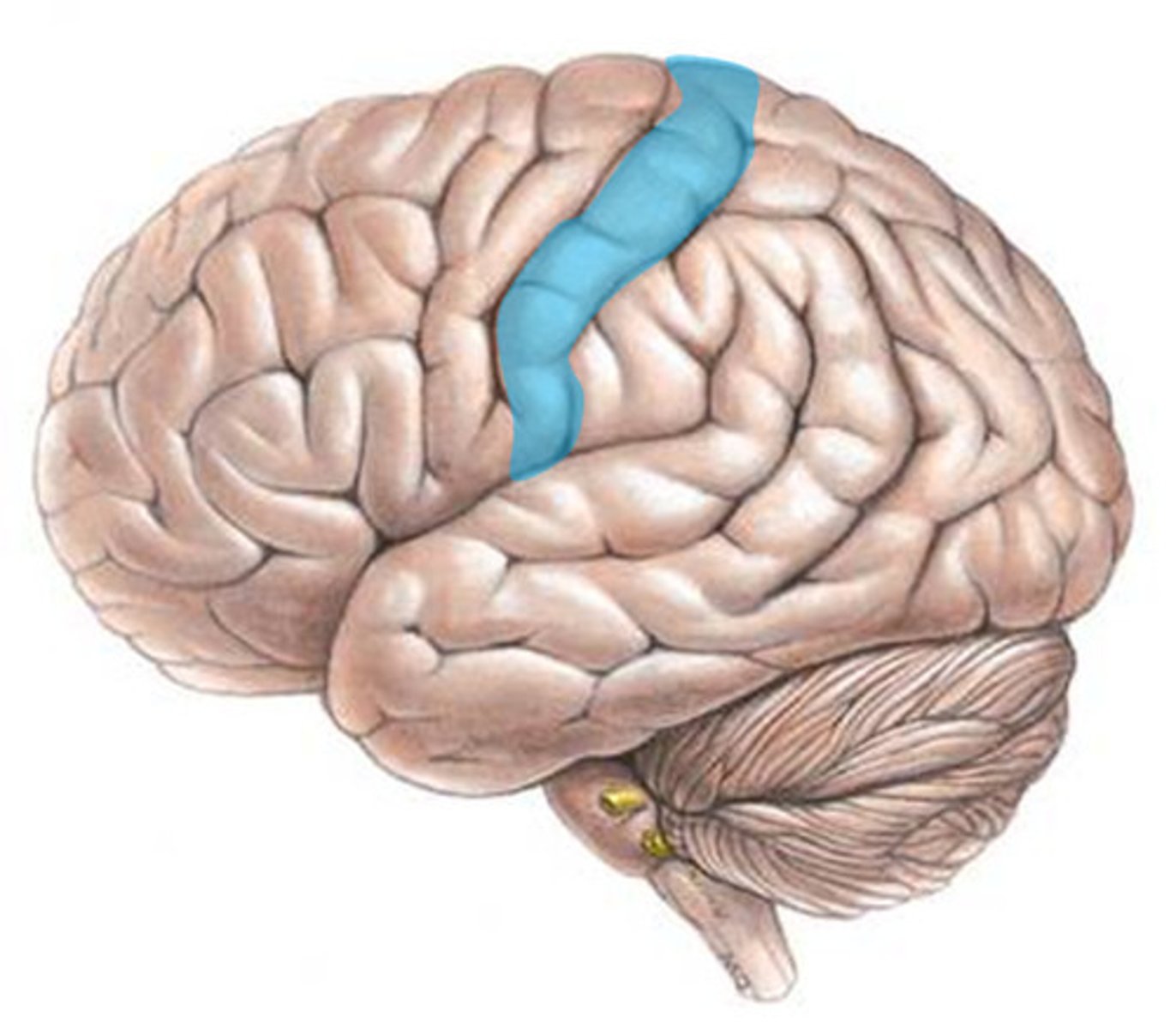
Somatosensory Cortex Function
Interprets touch, pressure, temperature, and pain signals from different parts of the body.
Occipital Lobes Function
Contains the primary visual cortex, which interprets visual stimuli and helps us perceive shapes, colors, and motion.
Temporal Lobes Function
Contain the auditory cortex, which interprets sound signals from the ears.
Corpus Callosum
Thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication and information sharing between the two hemispheres.
Brainstem
The oldest and most primitive part of the brain, responsible for basic life-sustaining functions such as breathing, heart rate, and sleep-wake cycles.
It serves as a pathway for neural signals
traveling between the brain and the
rest of the body, connecting the
cerebral cortex to the spinal cord
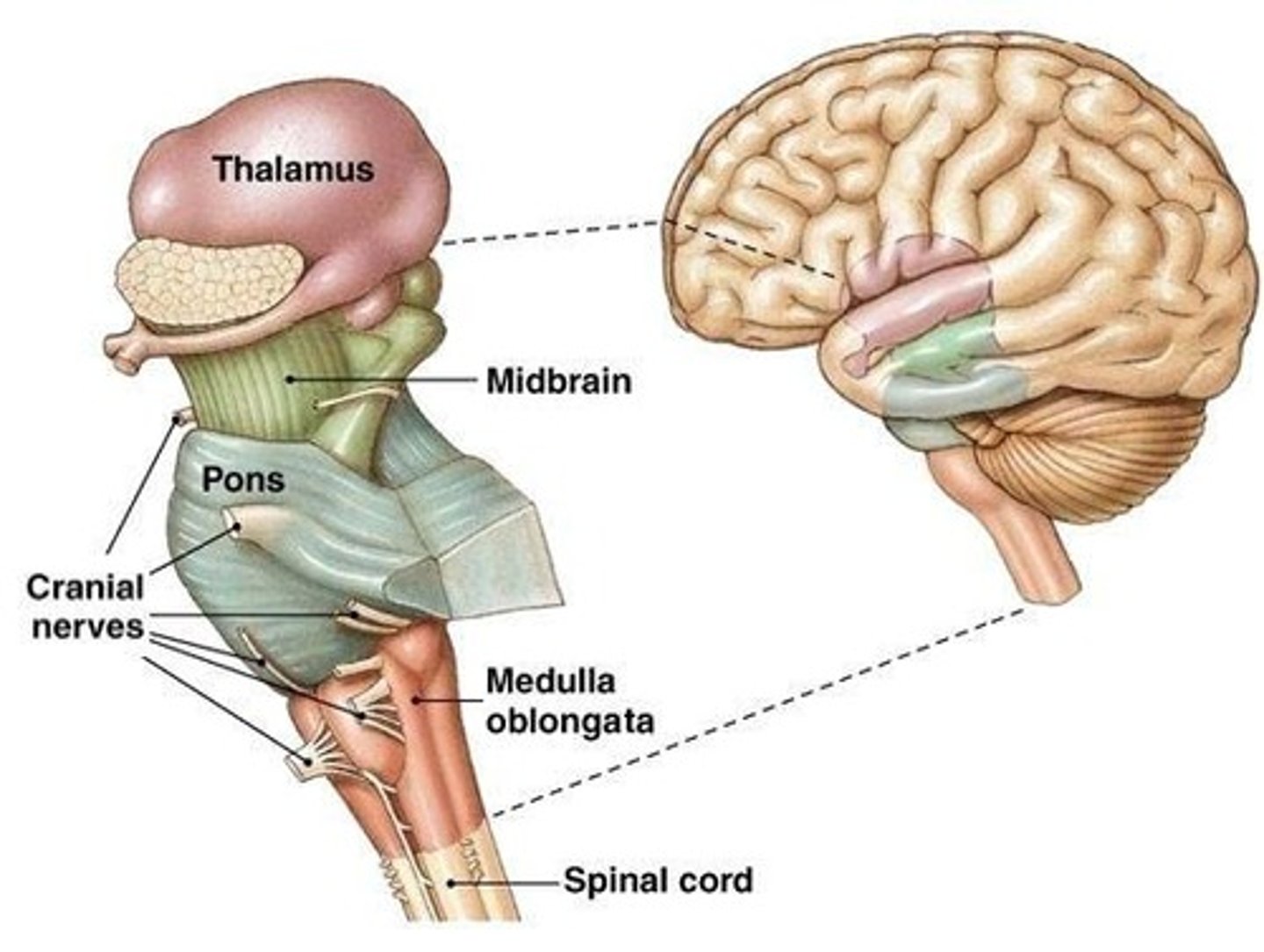
Medulla
Vital structure located at the base of the brainstem, regulating essential autonomic functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure.
Reticular Activating System
A network of neurons located in the brainstem that plays a critical role in regulating arousal, attention, and consciousness.
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, below the cerebral hemispheres, responsible for coordinating movement, balance, and posture.
Limbic System
A set of brain structures located beneath the cerebral cortex, involved in emotions, memory, and motivation.
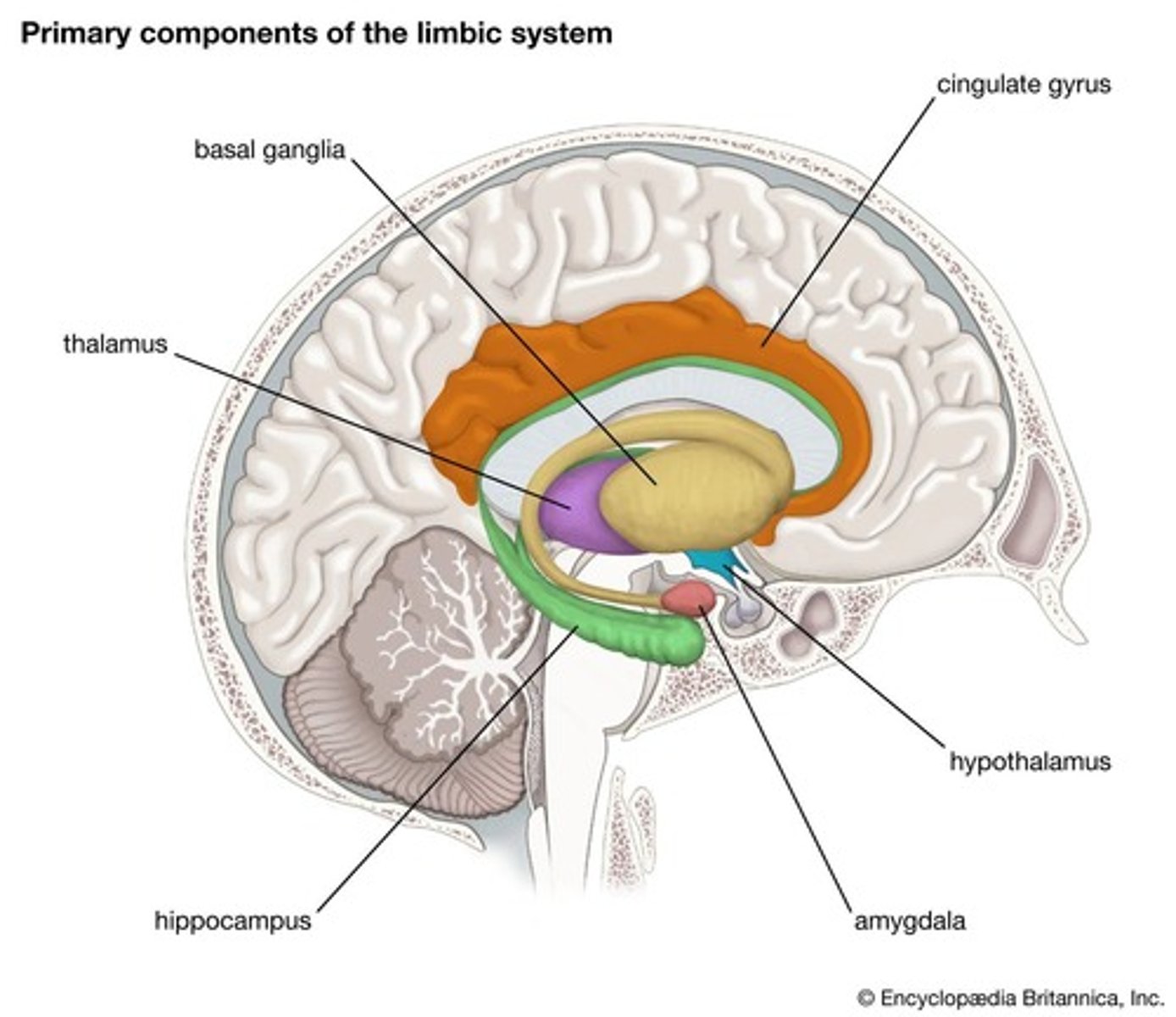
Reward Center
Network of brain structures, primarily located in the limbic system, that processes pleasurable experiences and reinforces behaviors associated with them.
Thalamus
A relay station in the brain that processes and relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex.
Pituitary Gland
A small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, often referred to as the 'master gland' due to its central role in regulating hormone production and secretion throughout the body.
Hippocampus
A curved structure within the brain's temporal lobes, primarily responsible for forming and consolidating new memories.
Amygdala
A small, almond-shaped structure involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and aggression.
Hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
Pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
helps coordinate movements and control sleep.
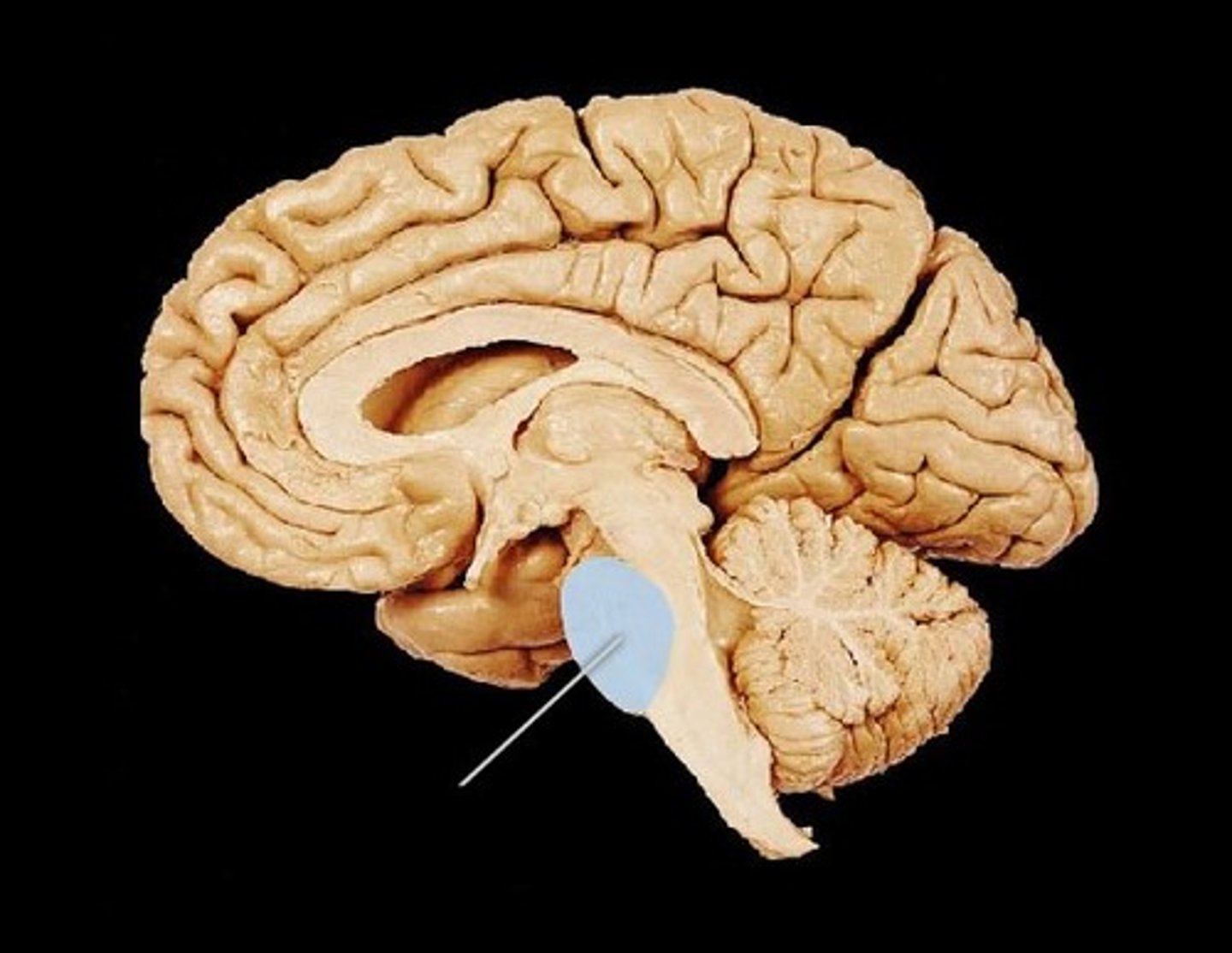
reticular formation
1. filters incoming stimuli and relays important information to other brain areas.
2. controls arousal
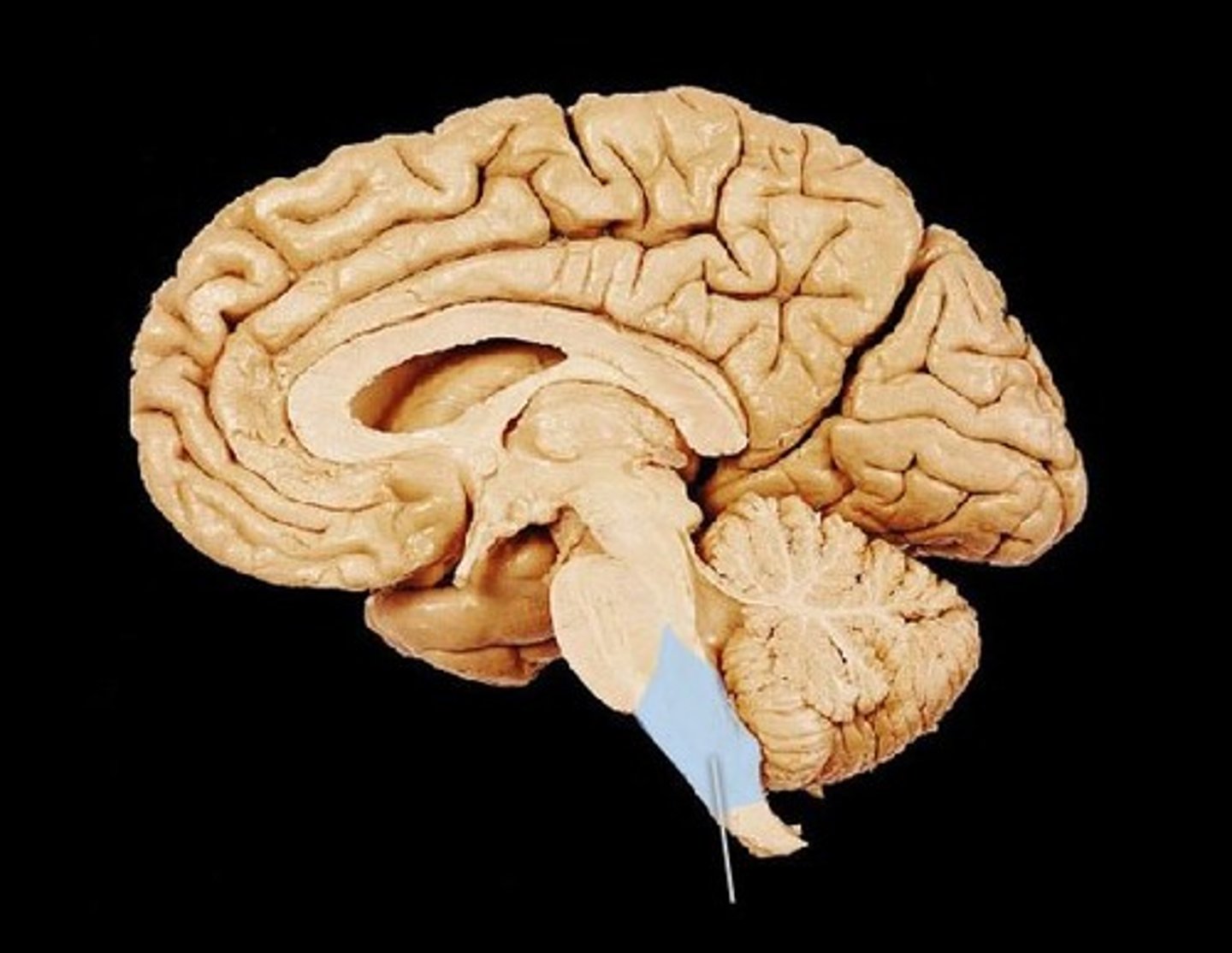
midbrain
connects the hindbrain with the forebrain, controls some motor movement, and transmits auditory and visual information.
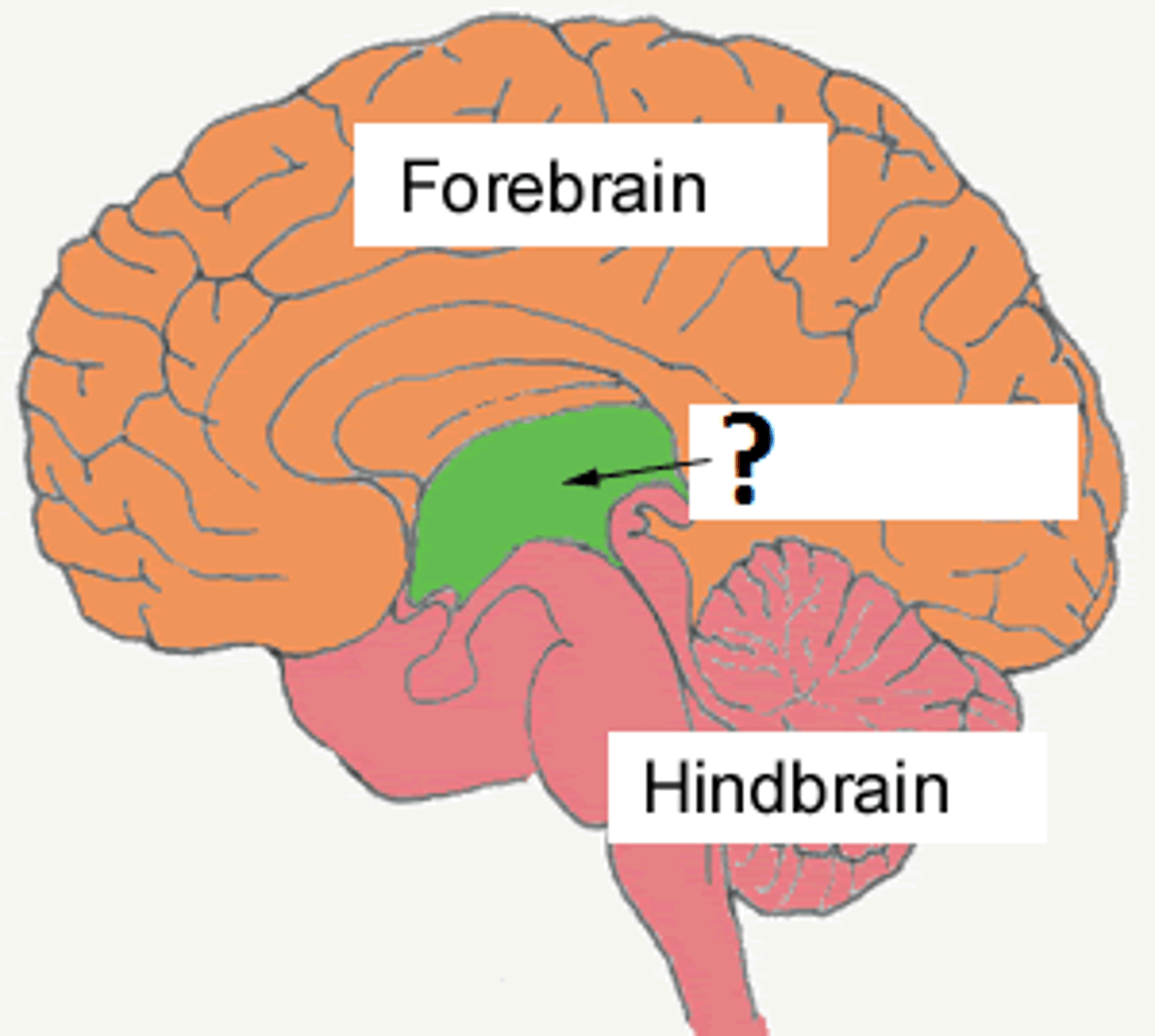
brainstem
the controls for your heartbeat and breathing
The brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions.
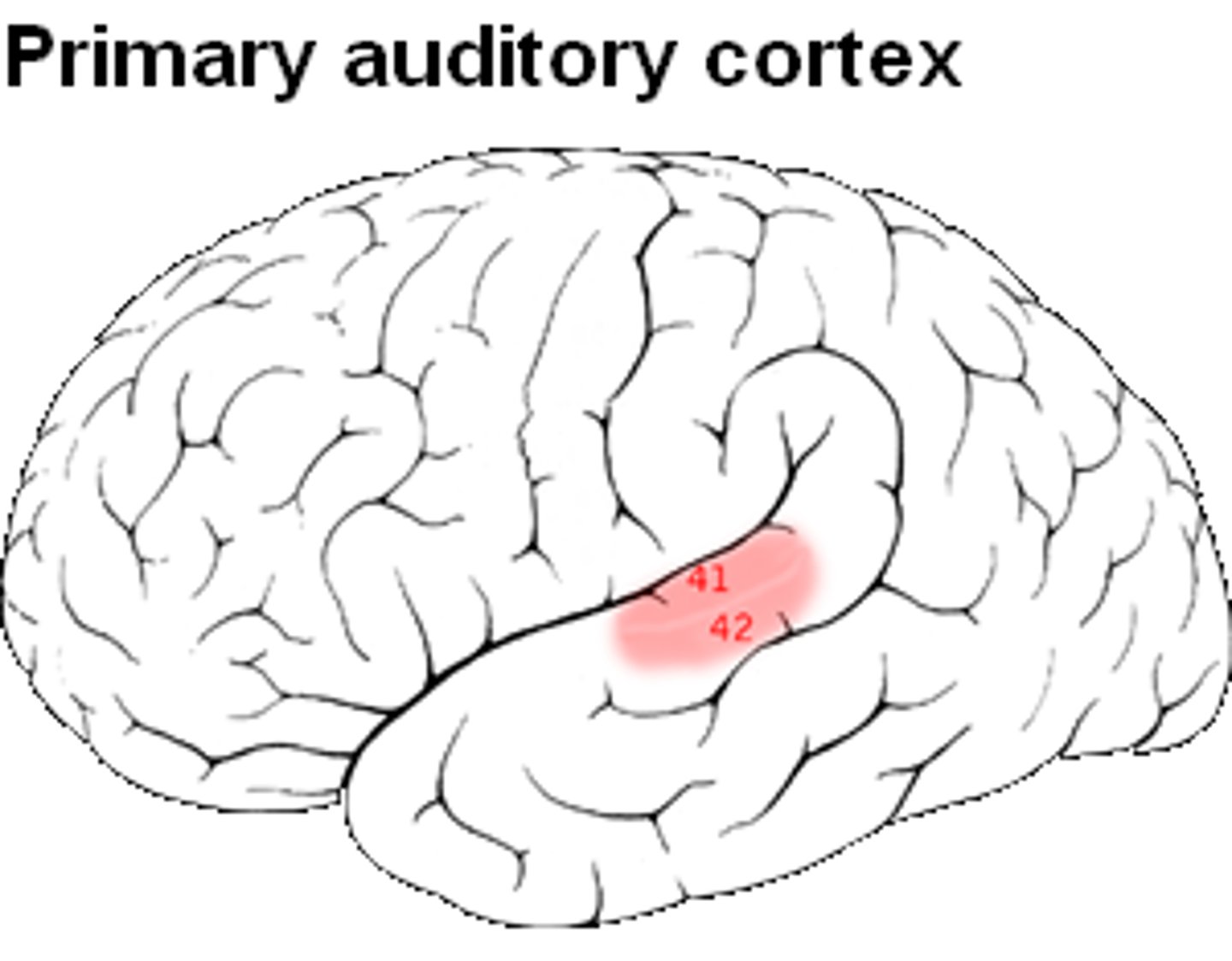
auditory cortex
the area of the temporal lobe responsible for processing sound information
visual cortex
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
left hemisphere
controls the right side of the body; analytical, language, math
right hemisphere
controls the left side of the body; creative, intuitive, spacial
Neuroplasticity
the ability within the brain to constantly change both the structure and function of many cells in response to experience or trauma
neurogenesis
the formation of new neurons
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural levels of analysis
localization of function
specialization of particular brain areas for particular functions
Lateralization
cognitive function that relies more on one side of the brain than the other
Contralateral Control
each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body
split brain
a condition resulting from surgery that isolates the brain's two hemispheres by cutting the fibers (mainly those of the corpus callosum) connecting them
hemispherectomy
surgical procedure where one cerebral hemisphere is removed
sensory rewriting
the brain's ability to change and reorganize its neural connections in response to new sensory input or experience