Gluconeogenesis + Cori cycle
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
1
New cards
What amino acid becomes pyruvate?
Alanine
2
New cards
Where does gluconeogenesis occur?
Mitochondria + ER
3
New cards
Pyruvate to Oxaloacetate enzyme
Pyruvate carboxylate
4
New cards
Bicarbonate
Adds a carbon onto pyruvate to oxaloacetate
5
New cards
Fructose 1,6-BPase
Takes phosphate off of F16BP into F6P
6
New cards
Glucose-6-phosphatase
Converts G6P into glucose in the smooth ER (requires water and is irreversible)
7
New cards
Glut-1
Transporter in all mammalian cells. Involved in basal glucose uptake
8
New cards
Glut-2
Transporter in the liver and pancreas
9
New cards
T1
Transporter that transports G6P in the smooth ER
10
New cards
T2
Transporter that transports inorganic phosphate in the smooth ER
11
New cards
Biotin
Cofactor used by pyruvate carboxylase to form carboxyphosphate. Carrier for CO2
12
New cards
Oxaloacetate
Traps pyruvate as an enol for the next steps of gluconeogenesis
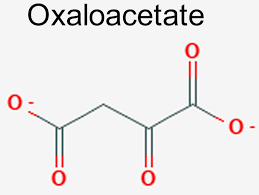
13
New cards
Oxaloacetate to PEP enzyme
PEPCK (uses GTP)
14
New cards
Gluconeogenesis net reaction
2 pyruvate + 4 ATP + 2 GTP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 4 H2O -> Glucose + 4 ADP + 2 GDP + 6 Pi + 2 NAD+
15
New cards
Where can we get pyruvate?
Alanine (starving conditions) or Lactate (anaerobic conditions)
16
New cards
Triose phosphates
DHAP and GAP
17
New cards
G6P to glucose enzyme
G6 phosphotase