Environmental Science for AP - Friedland and Relyea Chapter 9
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Aquifers
Permeable layers of rock and sediment that contain groundwater in many small spaces.
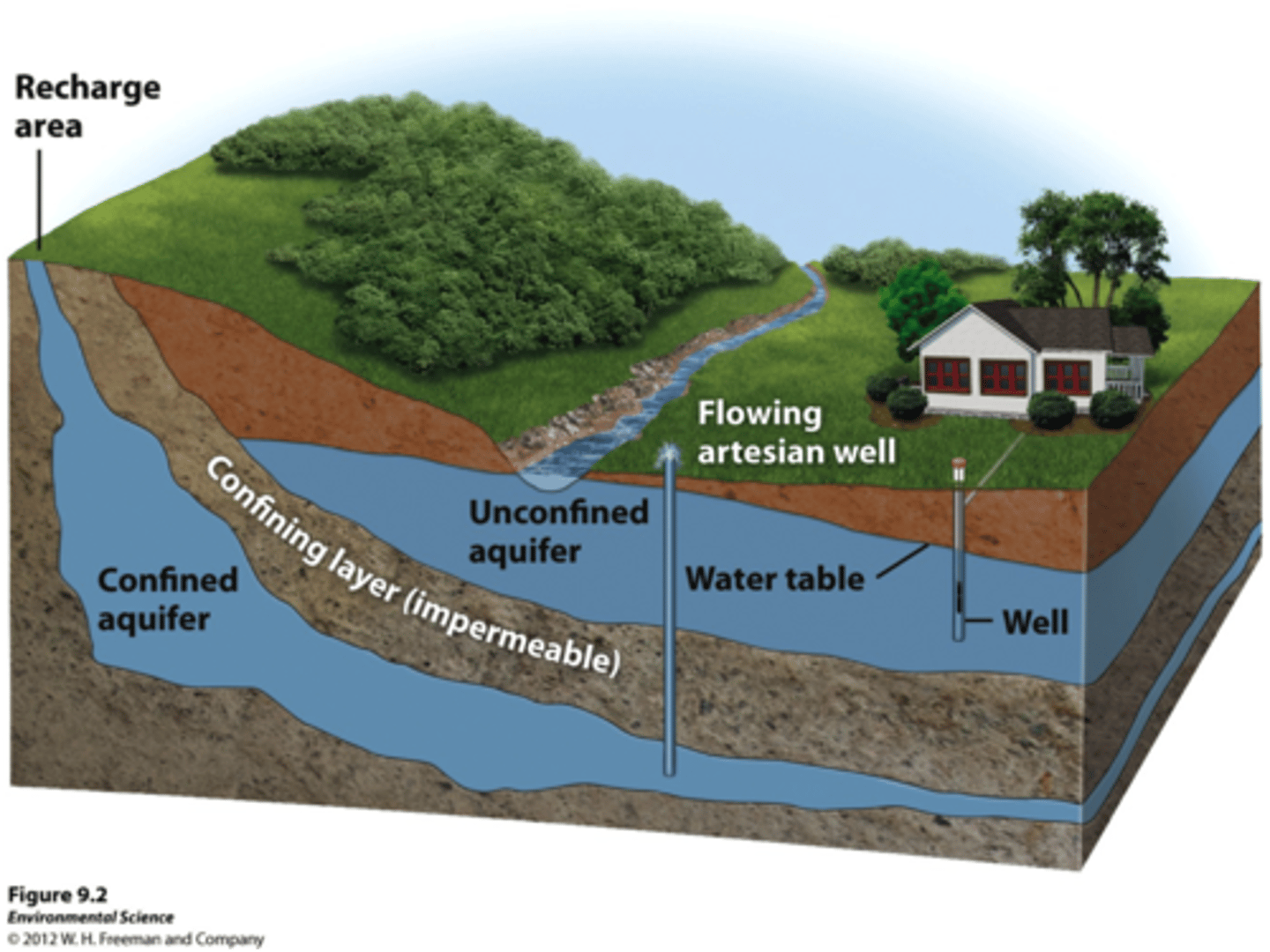
Unconfined Aquifer
Aquifers made of porous rock covered by soil out of which water can easily flow. Rapidly recharges groundwater.
Confined Aquifer
Aquifers surrounded by a layer of impermeable rock or clay that impedes water flow
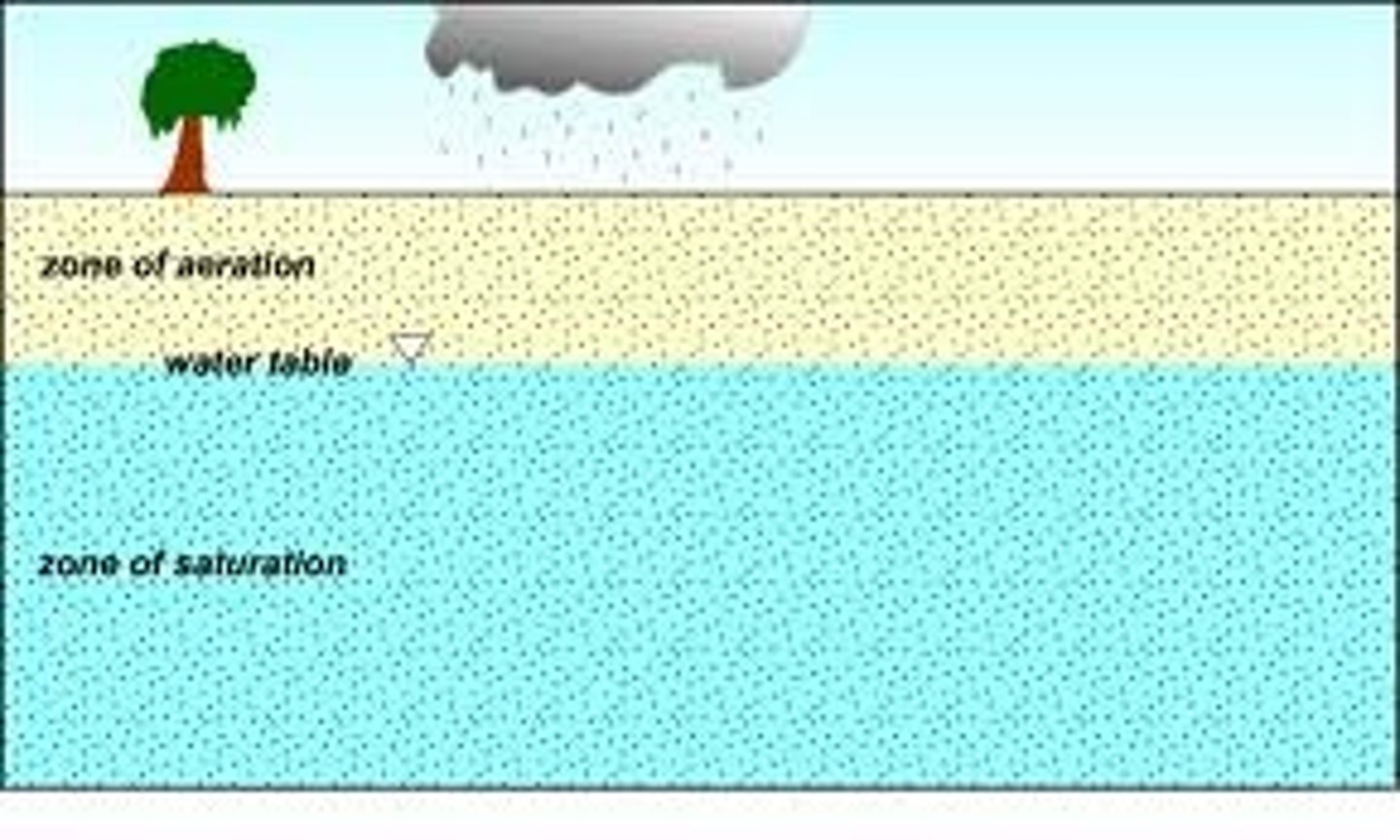
Water Table
Uppermost aquifer layer where water fully saturates the rock or soil.
Groundwater Recharge
Water from precipitation percolates through soil and into aquifer. If confined, can't recharge.
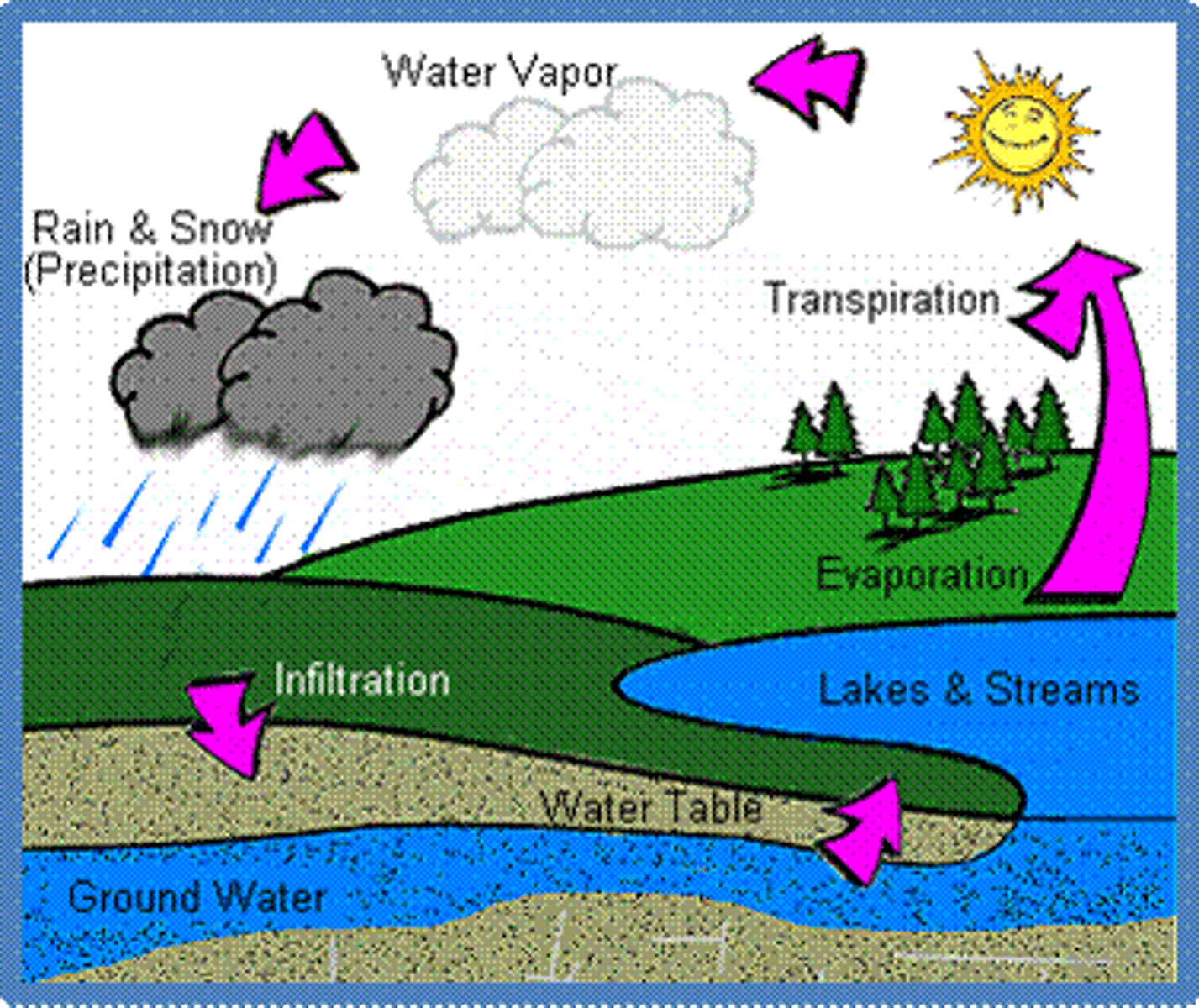
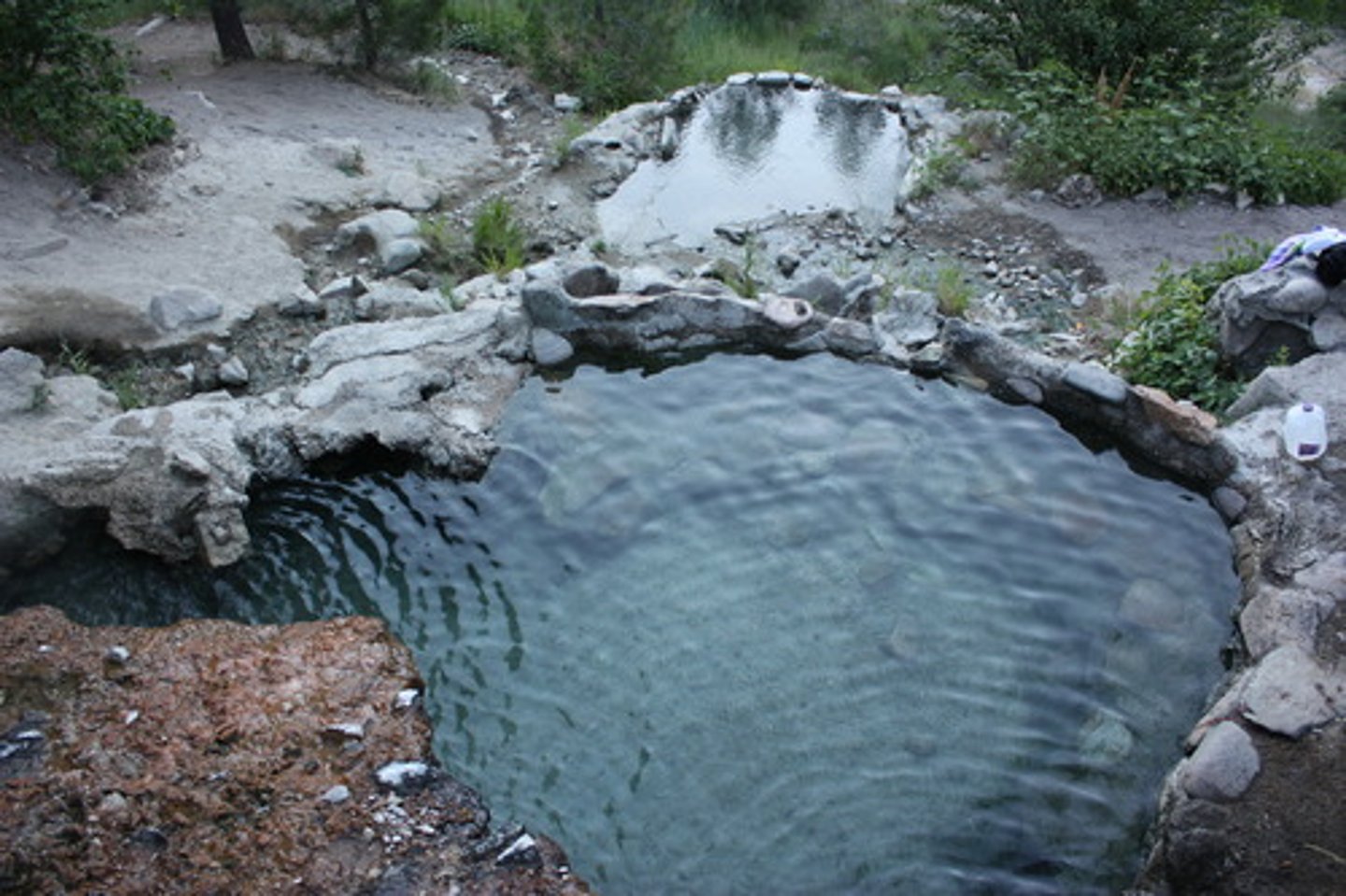
Springs
Water from some aquifers naturally comes up, natural source of freshwater

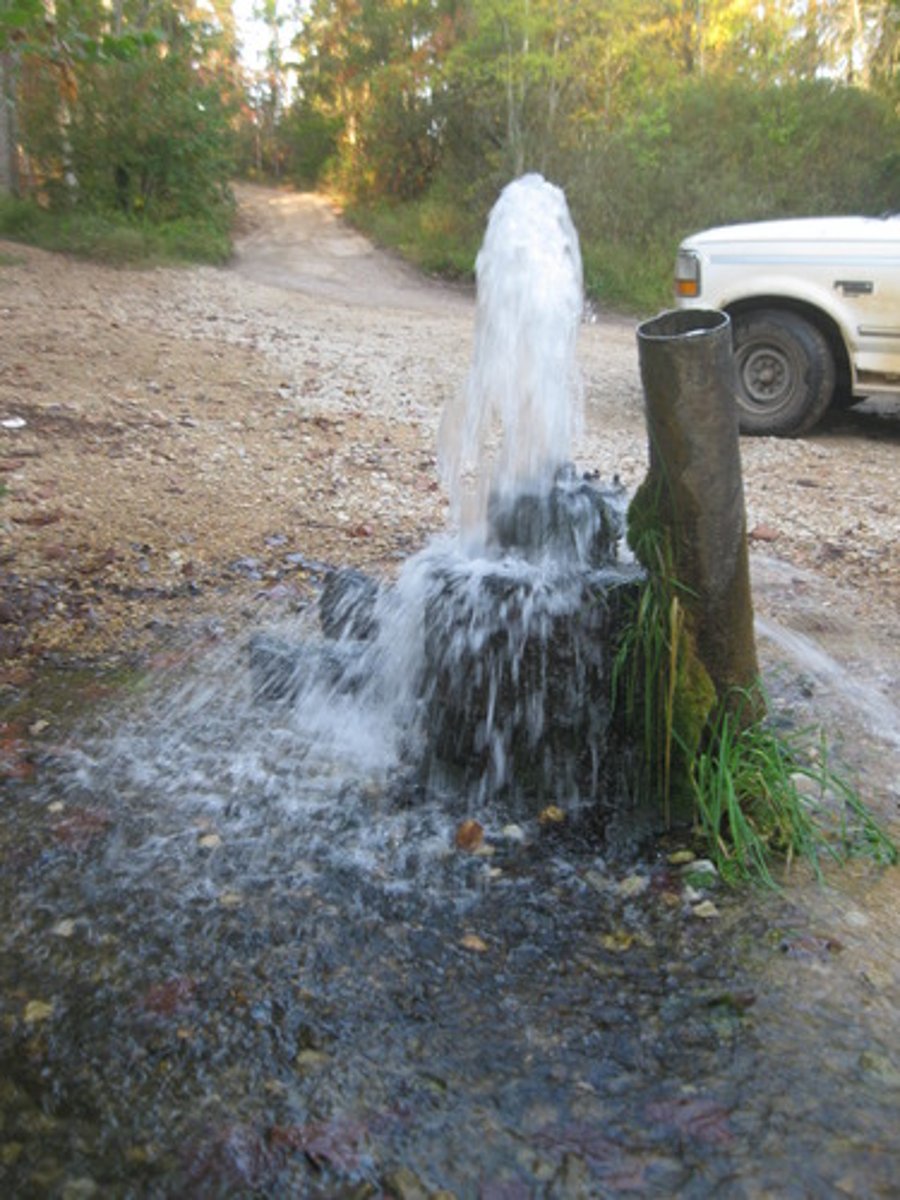
Artesian Wells
Drilled hole in a confined aquifer releases pressure and pushes water up.

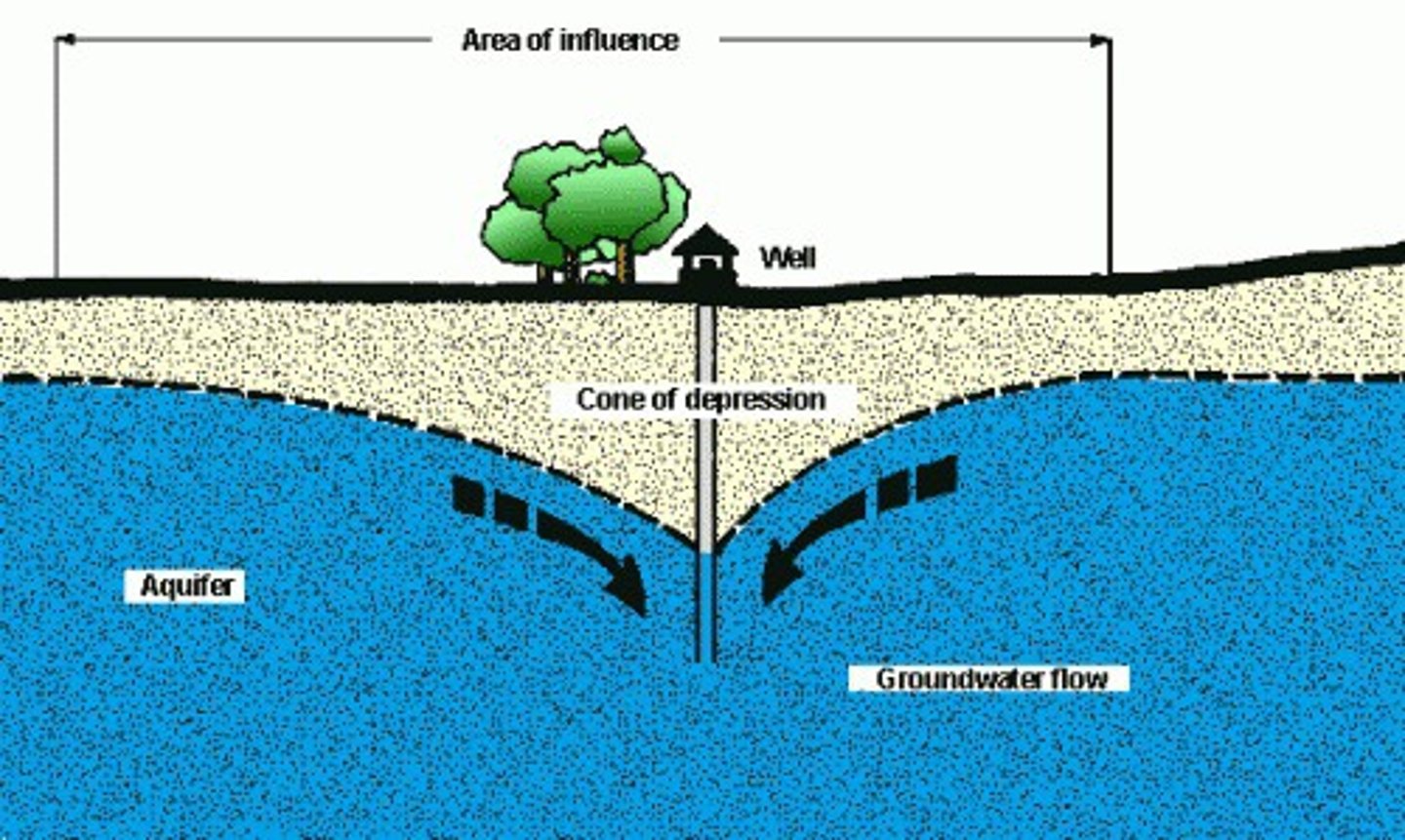
Cone of Depression
Area where there's no longer any groundwater, caused by well overuse, eventually will go dry.
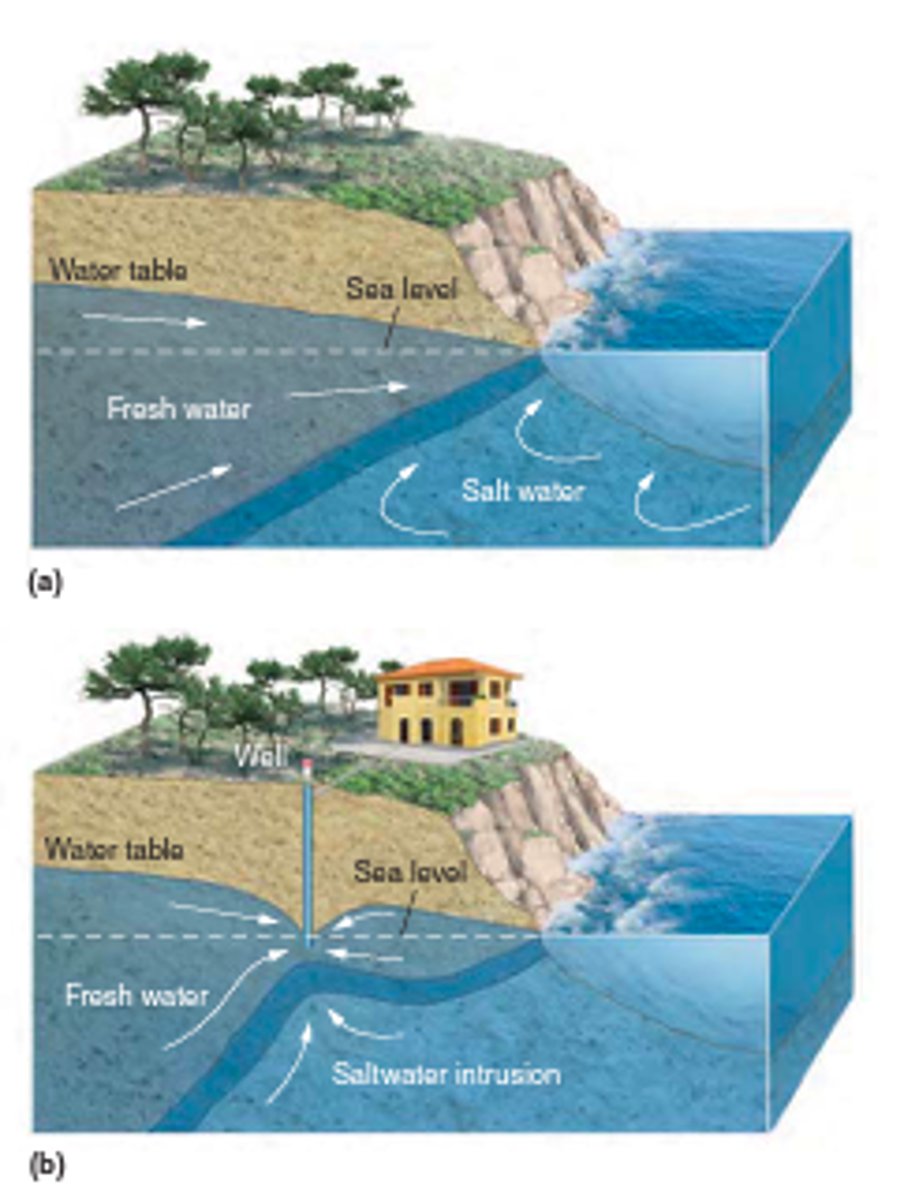
Saltwater intrusion
Lessened pressure from over-pumping so salt water infiltrates and makes well water salty.
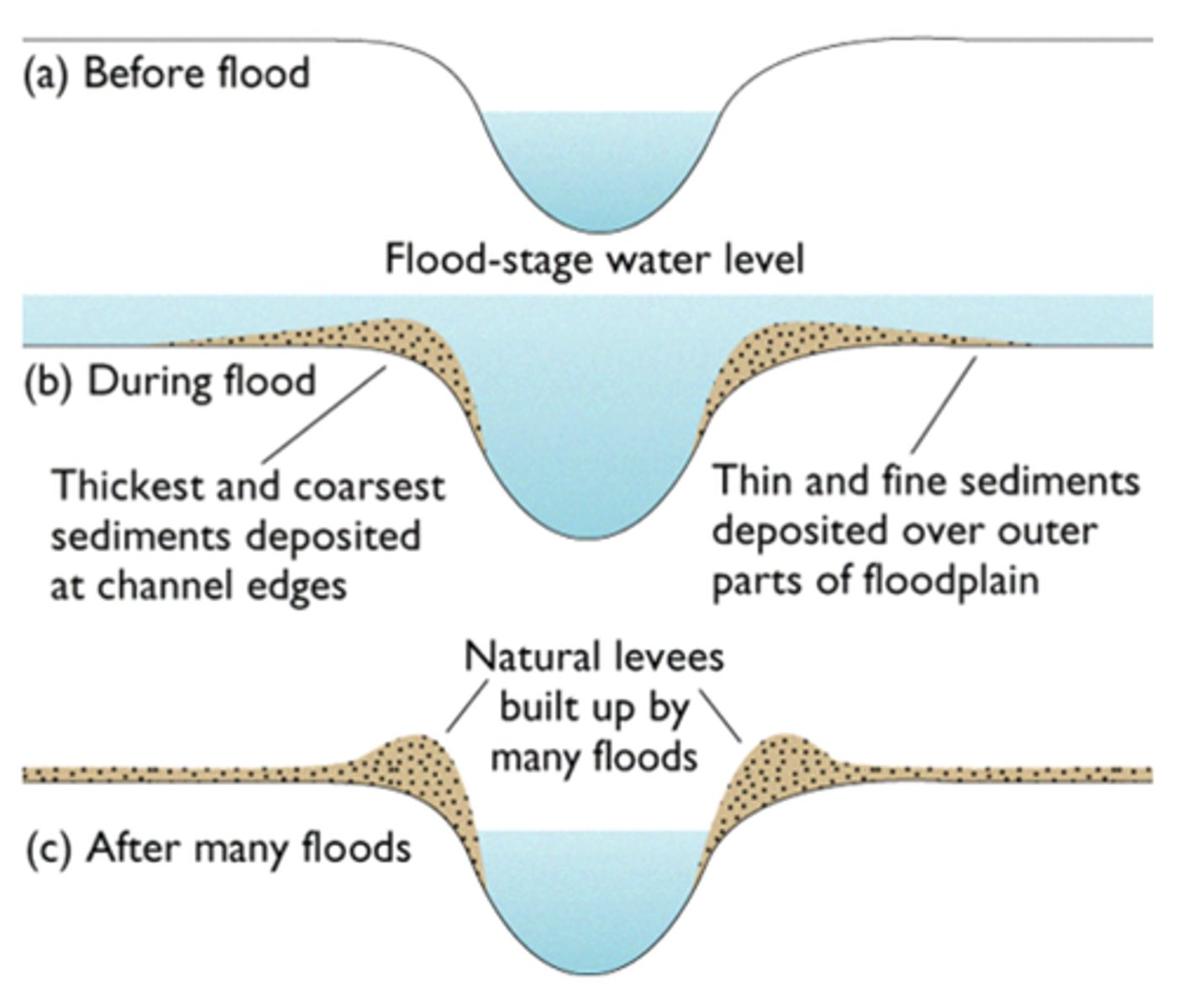
Floodplain
Land adjacent to river where excess water spreads onto.

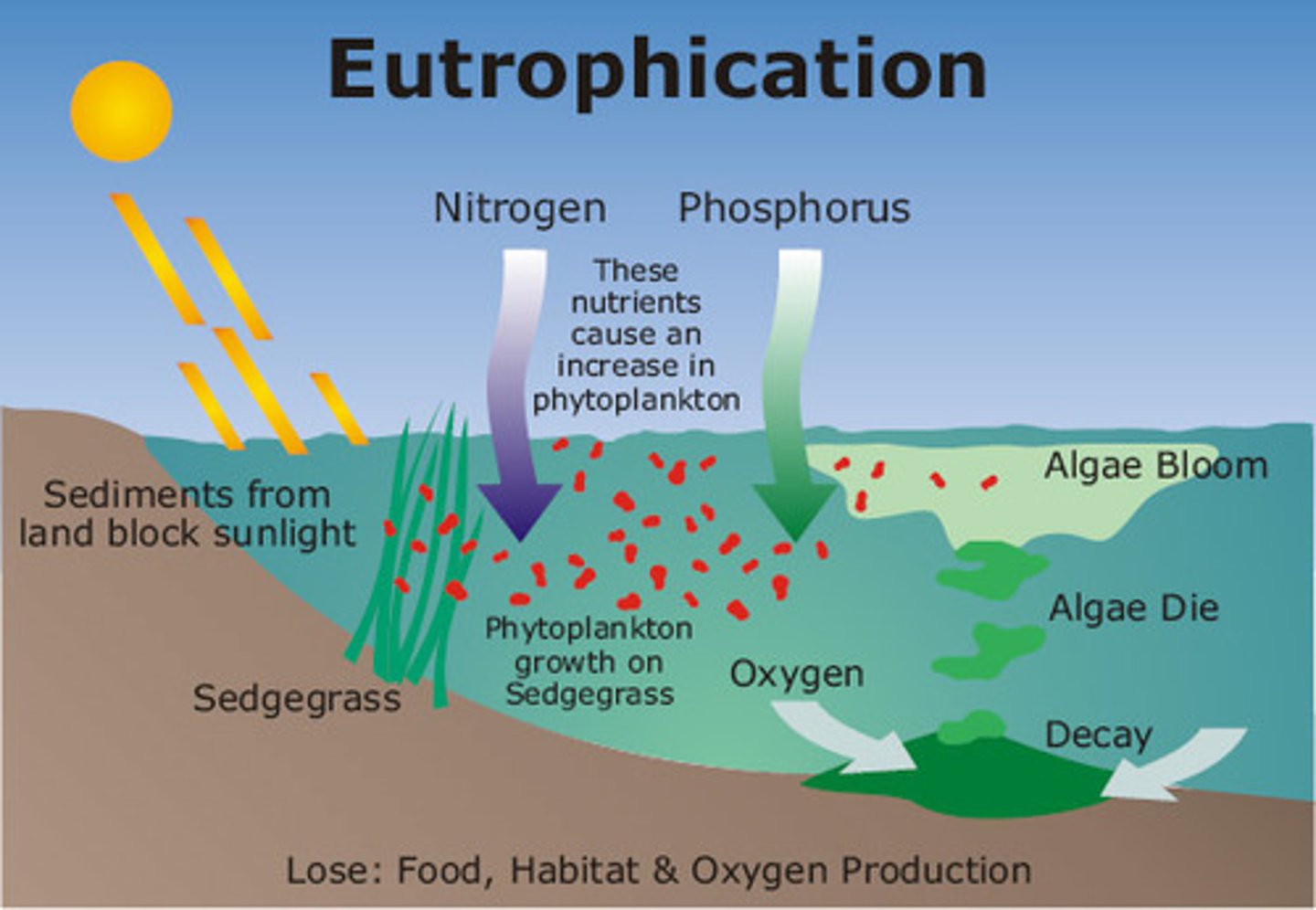
Oligotrophic
Lakes with low productivity because of little nutrients such as phosphorus and nitrogen.
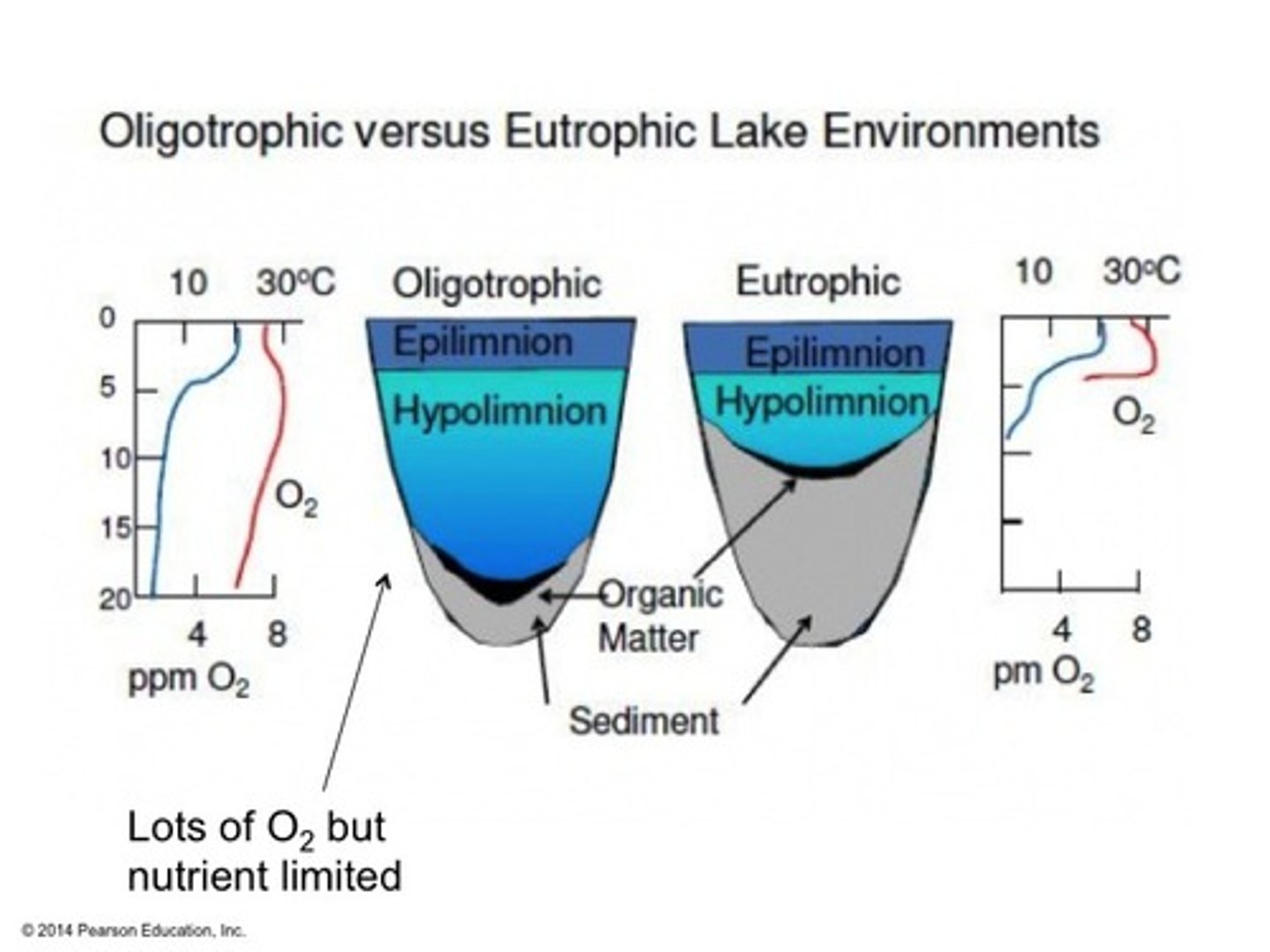
Mesotrophic
Lakes with moderate levels of productivity

Eutrophic
Lakes with high levels of productivity
Impermeable Surfaces
Pavement, buildings, etc. Doesn't allow water penetration, water then runs into sewers and streams. Excess water causes floods.

Levee
Enlarged bank on each side of river to prevent flooding
Dikes
Similar to levees but to prevent ocean waters from flooding coasts that are under sea level.

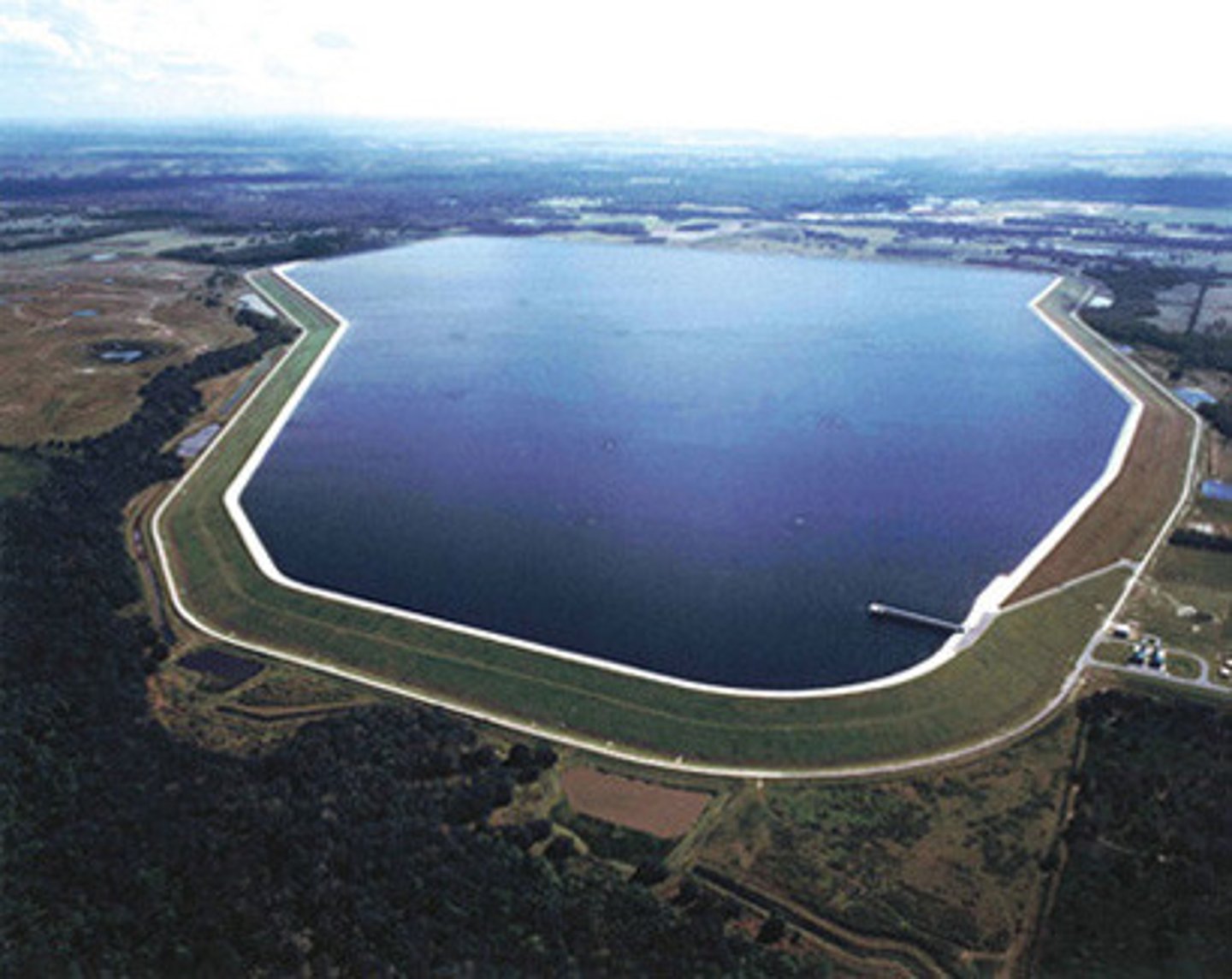
Dam
Barrier that runs across a river/stream to control water flow

Reservoir
Large body of water stored behind a dam. Held for consumption, generating electricity, flood control, or recreation.

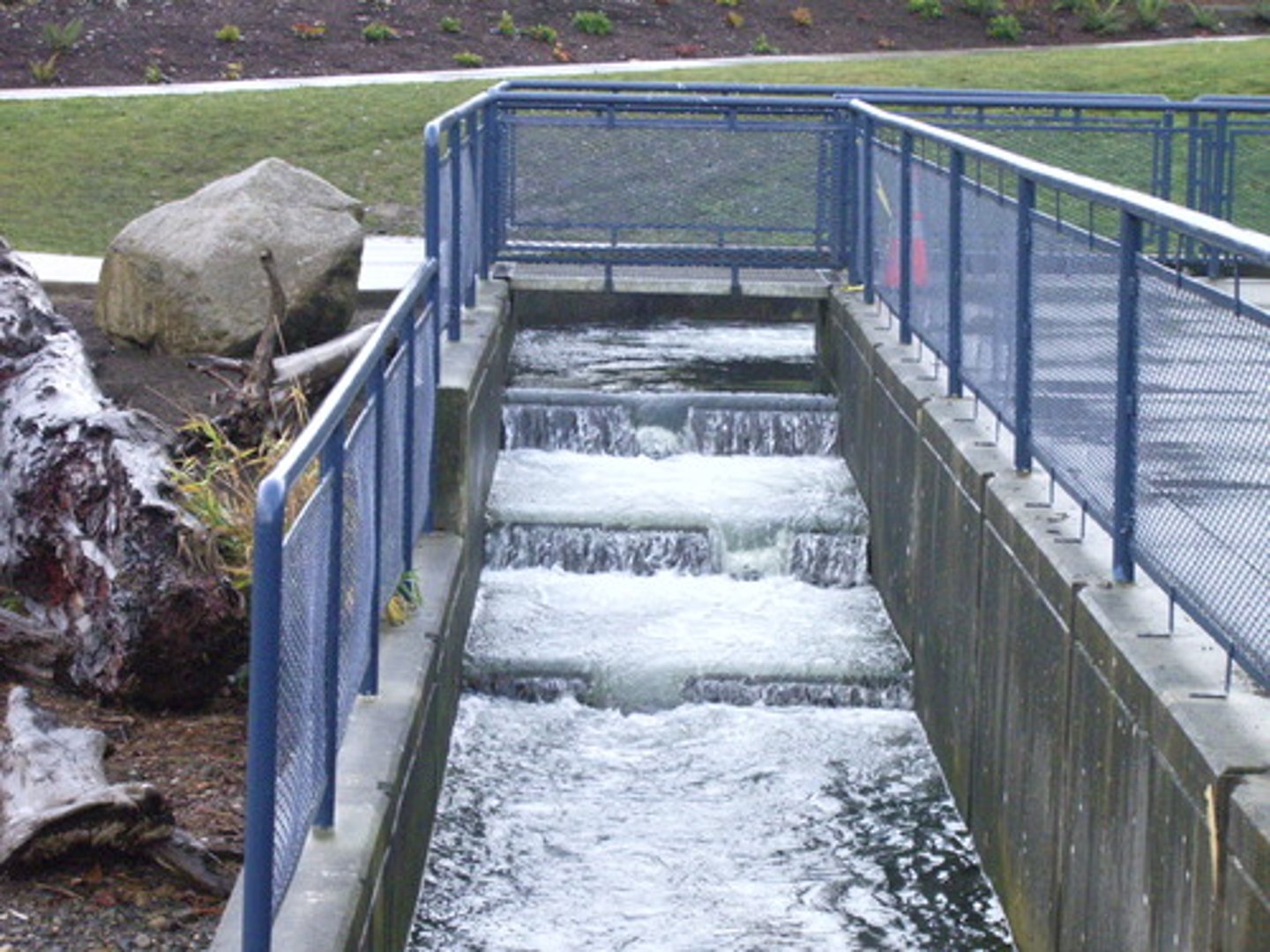
Fish Ladders
Sets of stairs with water flowing over them to have fish migrate despite dams.

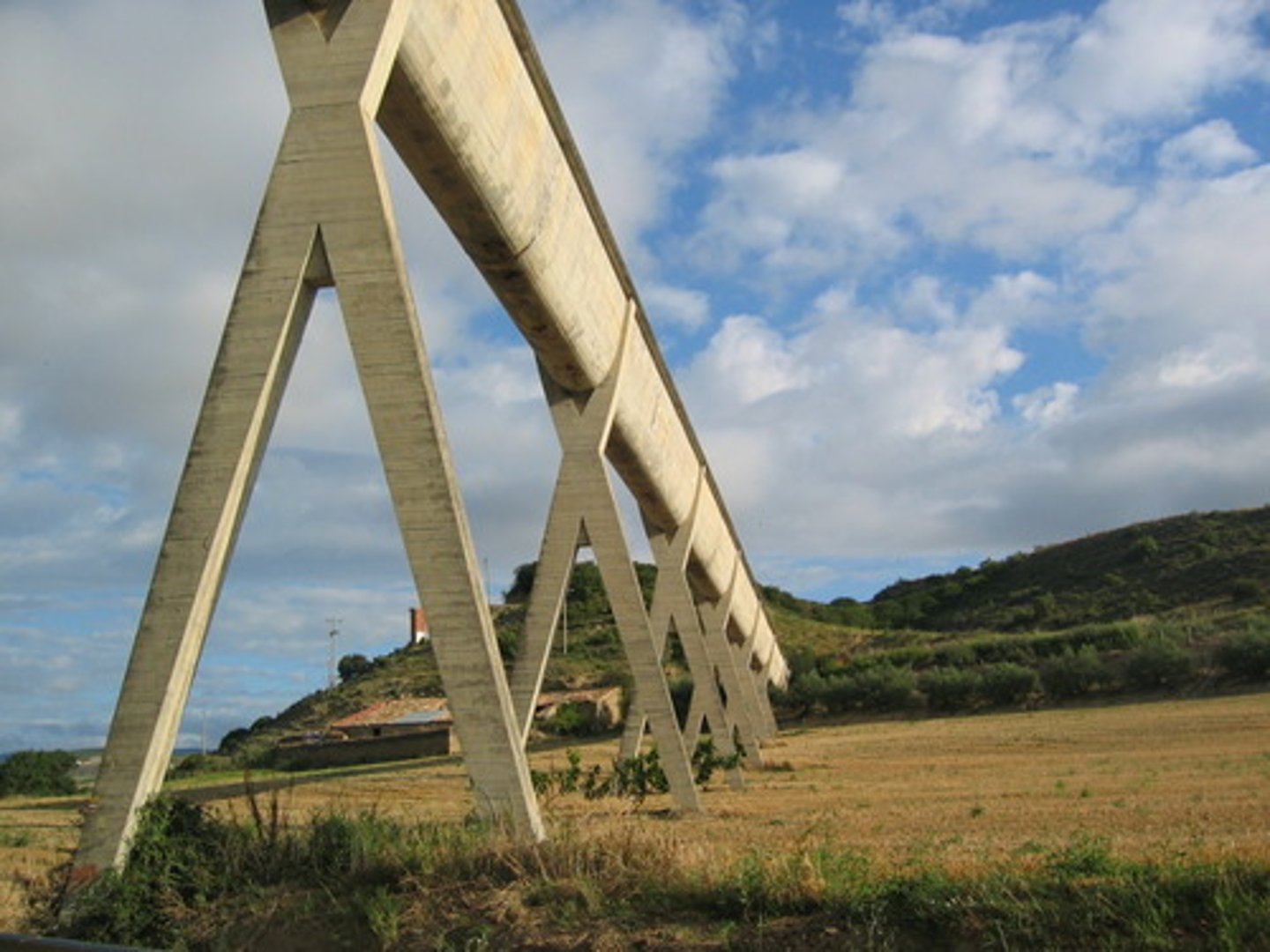
Aqueducts
Canals or ditches used to carry water between locations. Transports water to dry areas. Can alter food webs.

Desalination
Removes salt from salt water to make fresh water.
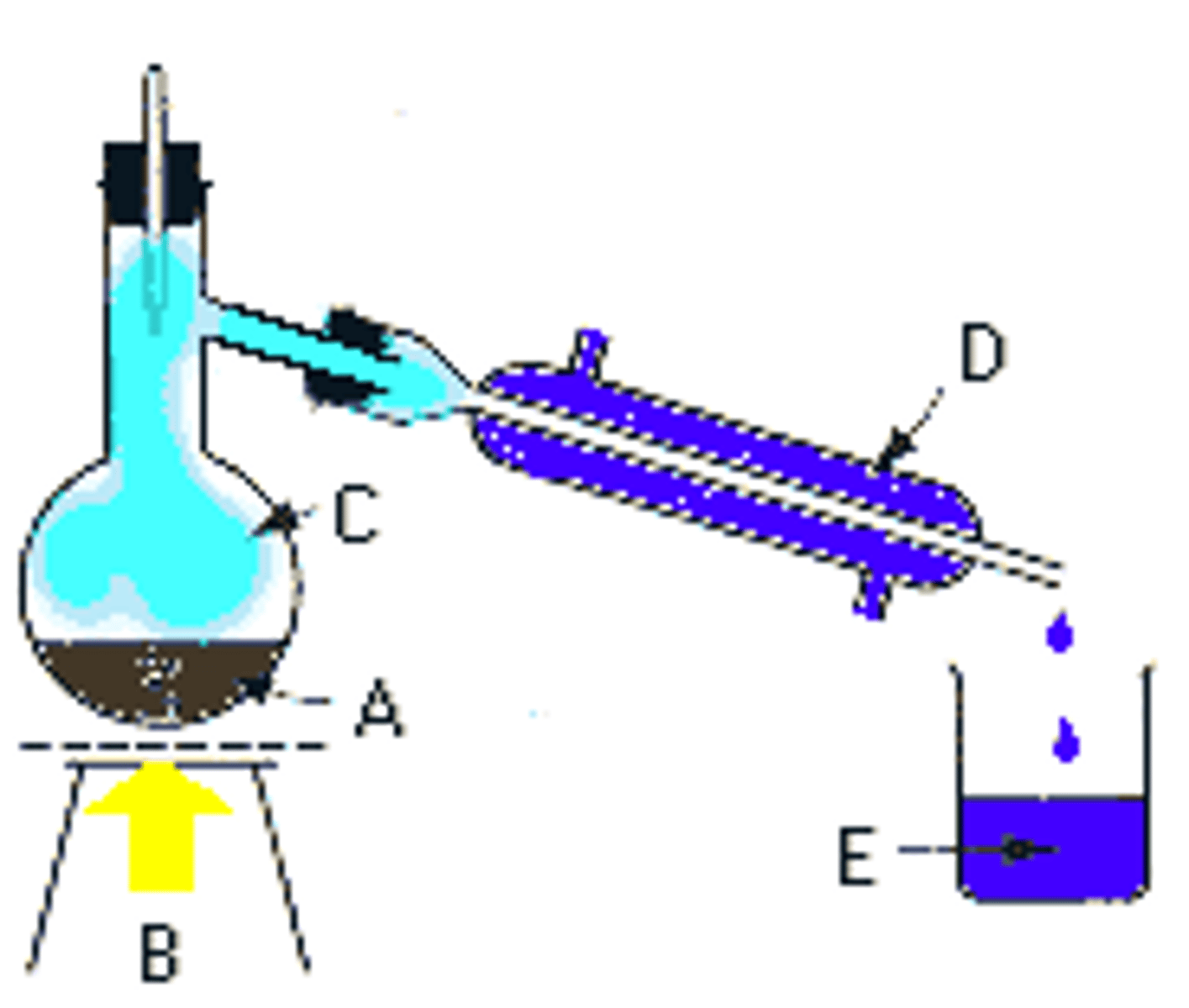
Distillation
Desalination method. Seawater flows in, heated to create steam, cool seawater in condensing coil causes steam to condense. Brine and fresh water then flows out.
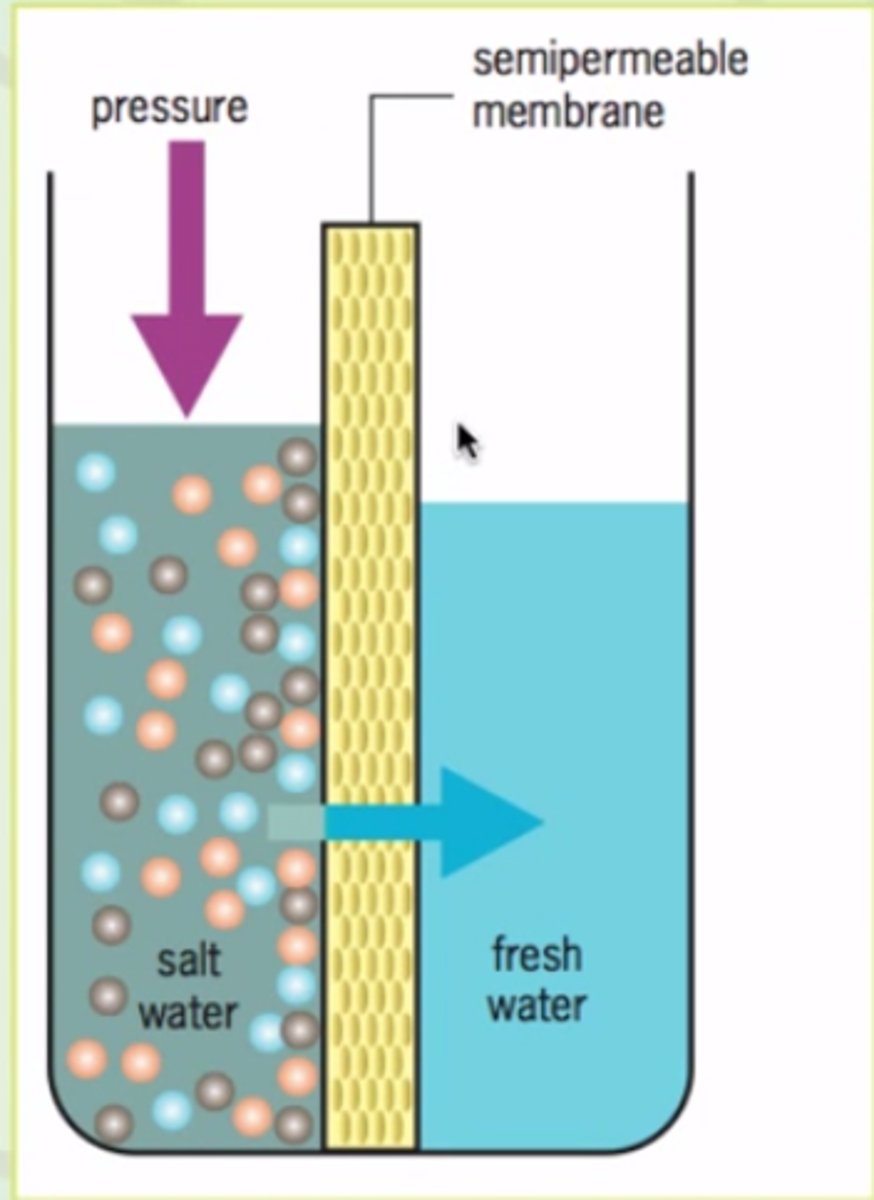
Reverse Osmosis
Desalination method. Seawater flows in, pressure applied, water goes through semipermeable membrane, salt can't. Water and brine flows out.
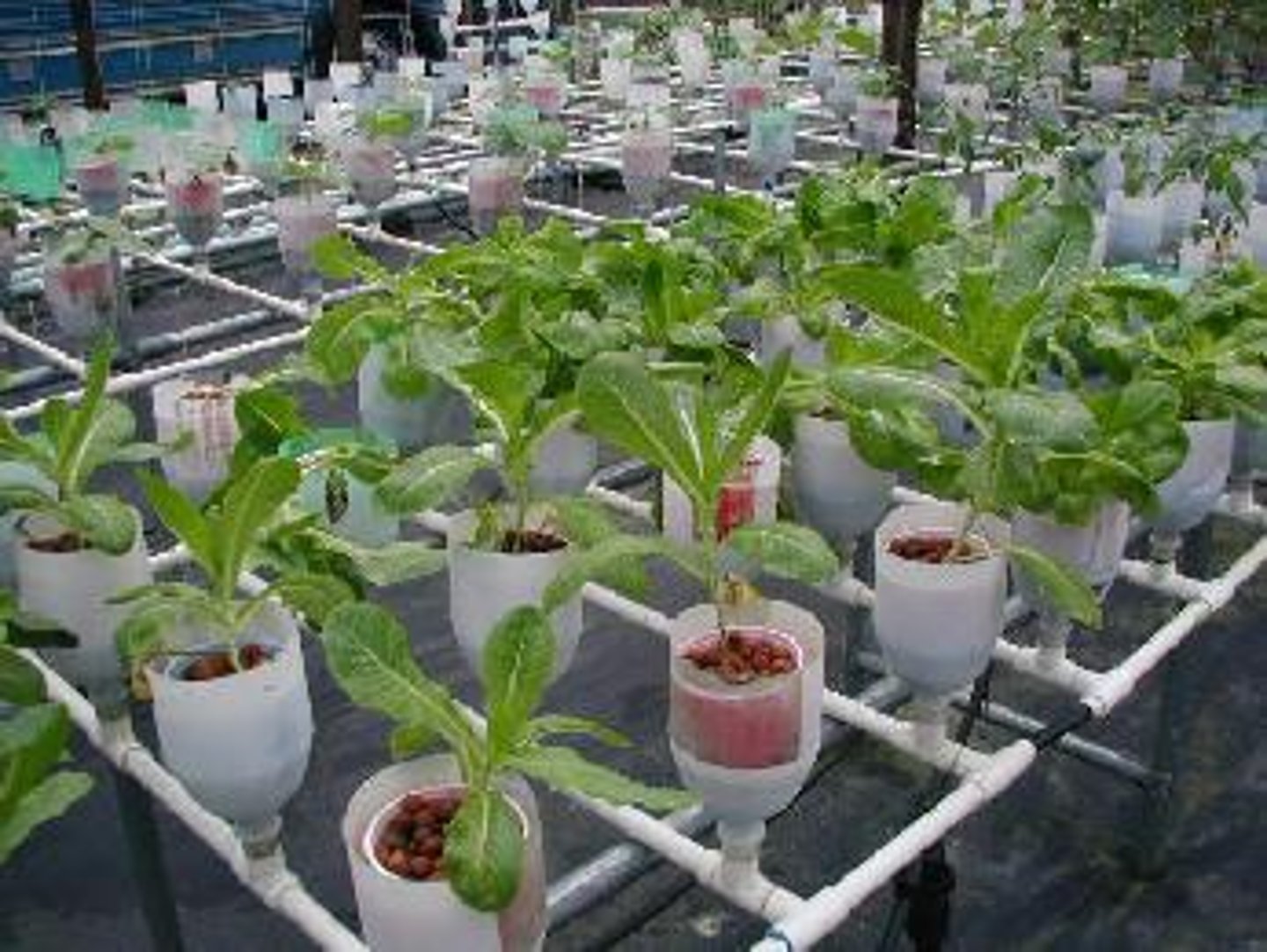
Hydroponic Agriculture
Cultivation under greenhouse conditions with roots in nutrient rich solution, and not soil.

#1 form of usable water on earth
groundwater
Ogallala Aquifer
Largest aquifer in U.S.
North Africa and Middle East
Regions with lowest amounts of available fresh water
Water footprint
Total daily per capita use of fresh water
Furrow
Trench is flooded with water-Least expensive, most wasteful and easiest type of irrigation
Flood
Entire field flooded with water-similar to furrow type of irrigation
Spray
irrigation method that involves an apparatus spraying water across a field-doesn't evaporate as easily
Drip
irrigation type in which a slow dripping hose is laid on or buried beneath the soil-most expensive & efficient, least amount of water loss
Industrial water use purposes
Generating electricity, cooling machinery, refining metals, making paper
Gray water
wastewater from bathtubs, showers, bathrooms, and washing machines
Contaminated water
wastewater from toilets, sinks and dishwashers
Top three uses of water
Agriculture-70%, industrial-20% and household-10%