19. Coagulation disorders
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
31/12/2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Name 2 inherited platelet disorders
Glanzmann’s Thrombasthenia
Bernard-Soulier syndrome
Name 3 acquired platelet disorders
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Aetiology of glanzmann’s thrombasthenia
Autosomal recessive
Caused by mutations in ITGA2B, ITGB3
Causing reduced function of the fibrinogen receptor
So platelets fail to bind to each other and the platelet plug cannot be stabilised by fibrinogen
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia platelet count
Normal
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia Lumi aggregometry test result
No visible platelet aggregation
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia flow cytometry test result
Absence of the fibrinogen receptor
Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia genetic test result
Mutations in these genes:
ITGA2B
ITGB3
Treatment for Glanzmann’s thrombasthenia
Platelet transfusion
Novoseven- synthetic factor VII which reduces bleeding
For women- brith control to stop period and iron to support blood loss
Aetiology of Bernard-Soulier syndrome
Autosomal recessive disease
Caused by mutations in GPIBA, GPIBB and GP9
Severe reduction/ reduced function of vWF and thrombin receptor
Leads to thrombocytopenia and giant platelets
Mutations in which genes are associated with Bernard-Soulier syndrome?
GPIBA
GPIBB
GP9
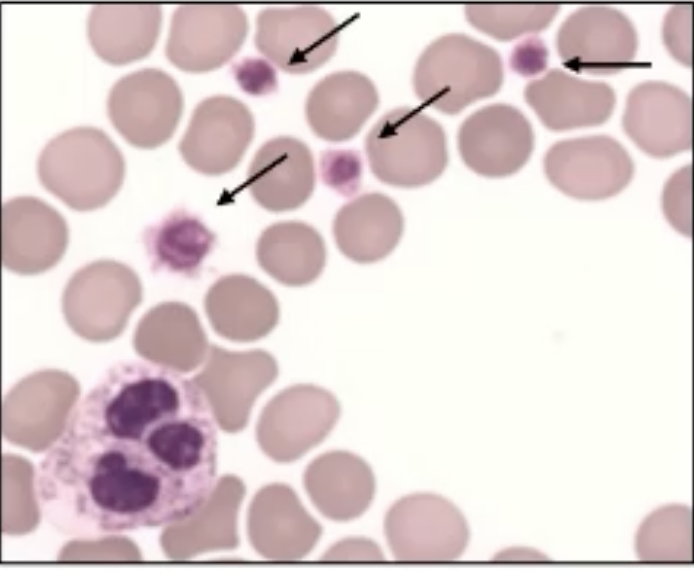
What are the arrows pointing at in this image?
Bernard-Soulier platelets
Bernard-Soulier syndrome Platelet count
Low
Bernard-Soulier Lumi aggregometry test result
Low response to ristocetin
Sometimes a low response to thrombin
Bernard-Soulier syndrome flow cytometry test result
Decreased levels of receptors in the vWF and thrombin receptor complex
Bernard-soulier syndrome genetic test result
Mutations in these genes:
GPIBA
GPIBB
GP9
Treatment fot Bernard-Soulier syndrome
Platelet transfusion
Aetiology of Immune thrombocytopenia
Platelets are destroyed by the body’s immune system
Primary: atuo-immune anti-platelet antibodies
Secondary: other auto-immune disease/ infection by bacteria or virus
Low platelet count resulting in bleeding
Symptoms of immune thrombocytopenia
Petechiae
Platelet count for immune thrombocytopenia
Low
Treatment for immune thrombocytopenia
Steroids: to reduce antibody production which slows down platelet destruction
Intravenous gamma globulin: Antibodies that neutralise the antibodies destroying platelets
Aetiology of thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura
Haemolytic condition
Platelets clump together in small vessels leading to a low platelet count
Low levels/ decreased function of ADAMTS13:because antibodies have formed against ADAMTS13
What does ADAMTS13 do?
Cleaves multimeric vWF into monomeric fragments to inactivate vWF
Symptoms of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Petechiae
Purpura
Treatment for thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura
Plasma exhange: healthy plasma containing ADAMTS13 and removal of antibodies
Aetiology of disseminated intravascular coagulation
Severe thrombotic condition leading to blood clots
Caused by the release of tissue factor from endothelial cells, activating the extrinsic pathway
Can occur with severe sepsis or cancer
Platelets and coagulation factors are used up which can lead to uncontrollable bleeding
Symptoms of disseminated intravascular coagulation
Petechiae
Purpura
Ecchomyosis
Treatment for disseminated intravascular coagulation- bleeding/ low platelet count
Platelet concentrate
Blood transfusion
Treatment for disseminated intravascular coagulation- thrombosis/risk of thrombosis
Use low molecular weigh heparin as prophylaxis
What is thrombophilia?
An abnormal tendency to form clots
When is thrombophilia often identified?
After deep vein thrombosis
What are 3 key types of inherited thrombophilia
Protein C deficiency
Protein S deficiency
Factor V leiden
How does deep vein thrombosis for?
Enhanced coagulation
Change in blood flow
Damage to vessel wall starts coagulation
Aetiology of protein C deficiency
Autosomal dominant
Deficiency makes it difficult to prevent coagulation, so clotting is promoted
What is the role of protein C
Natural anticoagulant
Activated by thrombin
Cleaves factor Va and VIIIa to prevent thrombin formation
Aetiology of protein S deficiency
Autosomal dominant
Deficiency leads to purpura fulminans
Skin bleeds and dies rapidly
Where is protein S synthesised and which vitamin is it dependent on?
In the liver
Vitamin K
What is protein S?
A non-enzyme co-factor for protein C
Factor V leiden aetiology
Autosomal dominant
Point mutation in the gene that encodes for factor V
Mutation makes protein C inable to inactivate factor Va
What does factor V leiden increase the risk of?
blood clots in legs and lungs
Venous thromboembolism (VTE)