Lower Limb - functions, areas, and general (bones)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
what are 3 functions of lower limbs
1. locomotion
2. supporting body weight
3. maintaining balance
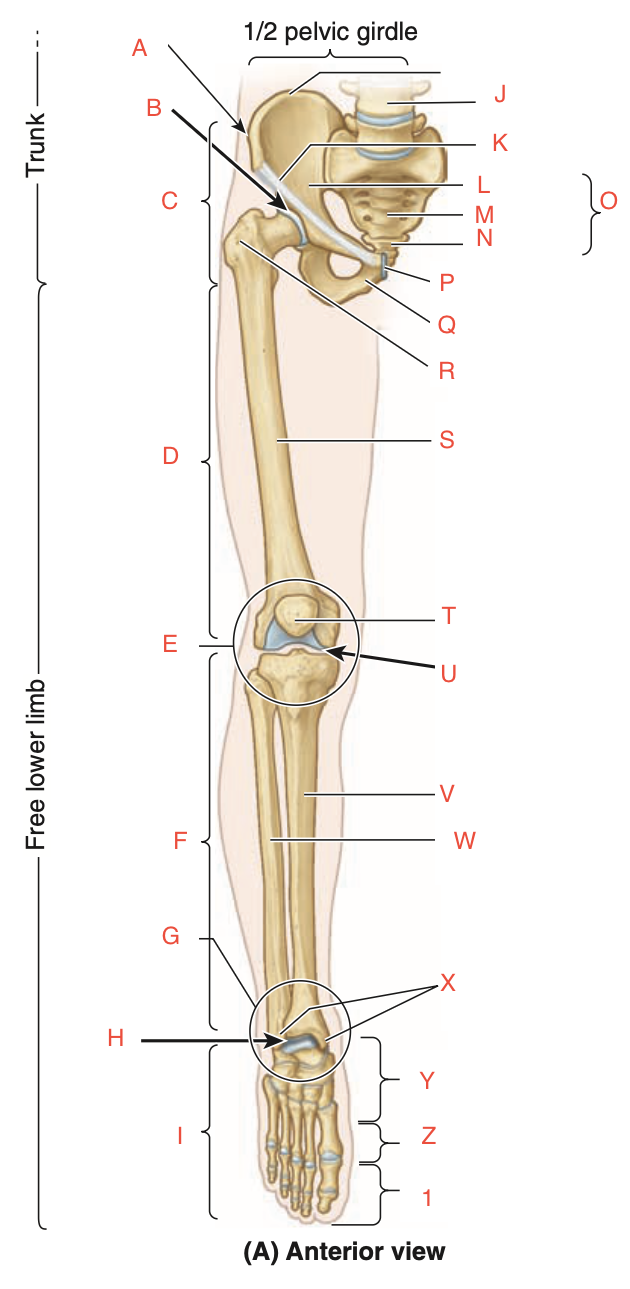
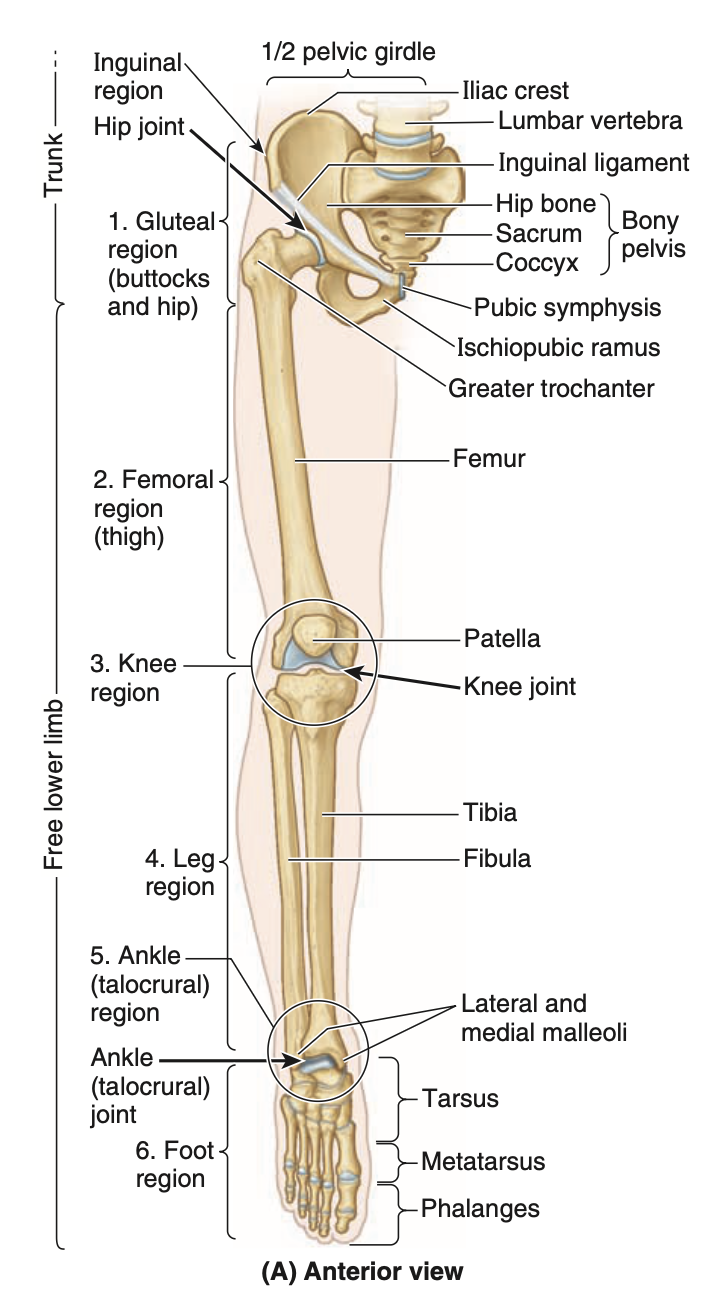
how are lower limbs connected to trunk (explain)
by pelvic girdle (bony ring composed of sacrum, right and left hip bones joined anteriorly at pubic symphysis)
1st region of lower limb
Gluteal: transitional zone between trunk and free lower limbs. includes buttocks and hip region, which overlies hip joint and greater trochanter of femur
2nd region of lower limb
femoral (thigh): includes most of femur, which connects hip and knee joints
3rd region of lower limb
knee: includes distal femur, proximal tibia and fibula, and patella, as well as joints between the bony structures
what is the fat-filled hollow posterior to knee called
popliteal fossa
4th region
leg: connects knee and ankle joints, includes tibia and fibula (calf)
5th region
ankle/talocrural: includes narrow distal leg and ankle (talocrural) joint
6th region
foot: distal part of lower limb. contains tarsus, metatarsus and phalanges
superior vs inferior foot
superior surface: dorsum of foot
inferior, ground-contacting: sole/plantar region
differences between toes
toes are digits of the foot: digit 1 (greater toe) has only 2 phalanges and other digits have 3
body weight transfer (+ explain last part)
vertebral column (then through sacro-iliac joints) --> pelvic girdle (then through hip joints) --> femurs --> knee joints (then through tibia) --> ankle joint --> talus.
Talus is the keystone of the longitudinal arch formed by tarsals and metatarsals, which distribute weight evenly between heel and forefoot when standing
how do femurs help to support erect bipedal posture
femurs are oblique (slanted) within thighs so when standing knee are adjacent and placed directly inferior to trunk, returning centre of gravity to the vertical lines of the supporting legs and feet
female vs male femurs
female femurs are slightly more oblique, reflecting a greater width of pelves