Equine Dentistry
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What 3 things are included in the crown area of the tooth?
Enamel, dentin, and a small amount of pulp
What 3 things are included in the root area of the tooth?
Cementum, dentin, and pulp
What are the 3 characteristics of hypsodont teeth?
Large crown reserve below the gingiva, continually erupts throughout the horse’s life, and dentin is laid down to prevent pulp exposure
What does lingual mean?
Relating to the tongue, one the side near the tongue
What does buccal mean?
Relating to the cheek, on the side near the cheek
What does rostral mean?
Toward the front of the mouth
What does caudal mean?
Toward the back of the mouth
What is a horse’s permanent teeth dental formula?
2 x (Incisors 3/3, canines 1/1 or 0/0, premolars 3/3 or 4/4, molars 3/3) = 36-44 teeth, depending on presence of canines and premolar 1
What is a horse’s deciduous teeth formula?
2 x (incisors 3/3, canines 0/0, premolars 3/3) = 24 teeth
What are 3 human risks in equine dentistry?
Kick, strike, or bite injuries, speculum injury, and tooth dust
Where should you never stand when a horse is sedated?
Directly in front of them
What 2 risks comes from tooth dust?
Inhalation an ocular risk
What are 7 risks to equine patients in equine dentistry?
Accidental loosening or extraction of teeth in older horses, over filing, fractured teeth, fracture mandible or maxilla from speculum, lacerated palatine artery, TMJ injury, and thermal injury to tooth
What are 10 clinical signs of equine dental disease?
Anorexia, difficulty eating or slow eating, dropping excessive grain, foul order in mouth, quizzing of hay/pocketing grain in cheeks, nasal discharge, facial or mandibular swelling, draining tracts, undigested grain or long strands of hay, behavioral changes, and sometimes nothing at all.
What 4 things are included in an oral examination of a horse?
Visual inspection, smell oral cavity, move the mandible and maxilla, and palpate the teeth and soft tissues
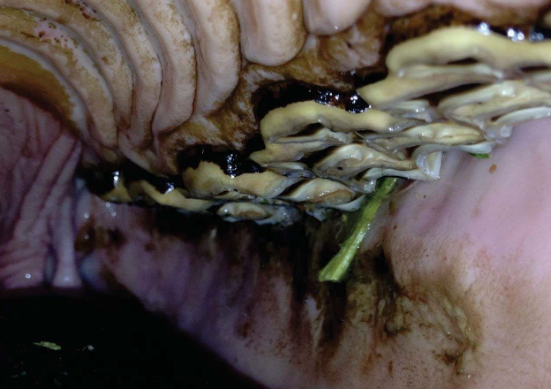
What dental abnormality is this?
Enamel points with buccal ulceration
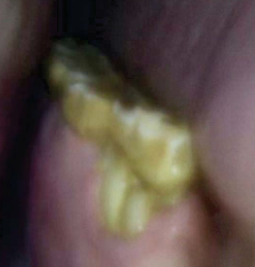
What dental abnormality is this?
Retained deciduous teeth (caps)
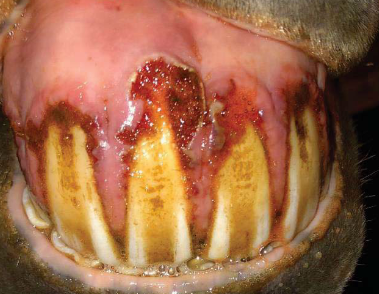
What dental abnormality is this?
Gingivitis
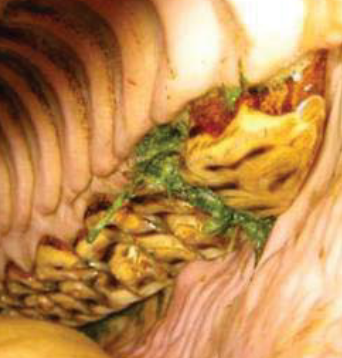
What dental abnormality is this?
Periodontal disease
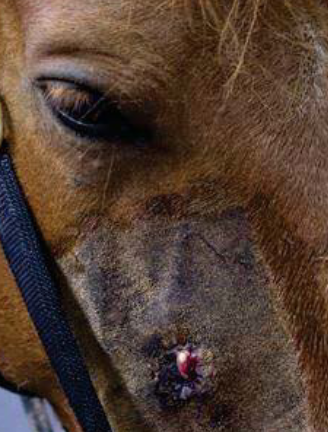
What dental abnormality is this?
Tooth root abscess
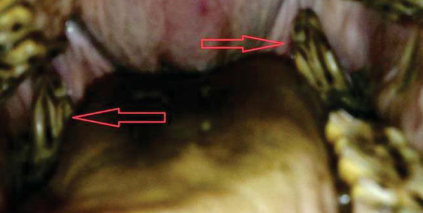
What dental abnormality is this?
Tall or overgrown teeth
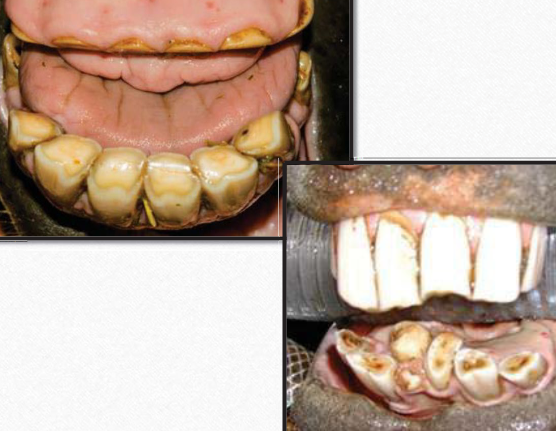
What dental abnormality is this?
Incisor abnormalities
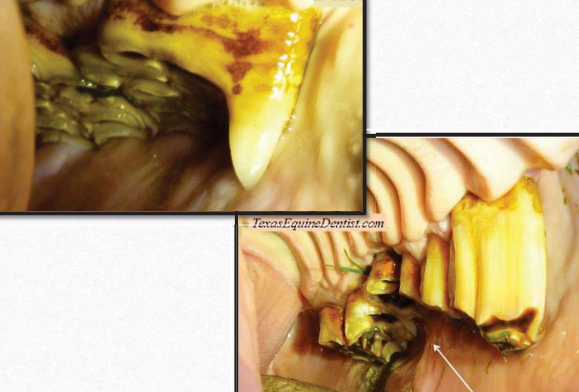
What dental abnormalities are shown?
Hooks, ramps, and wave mouth
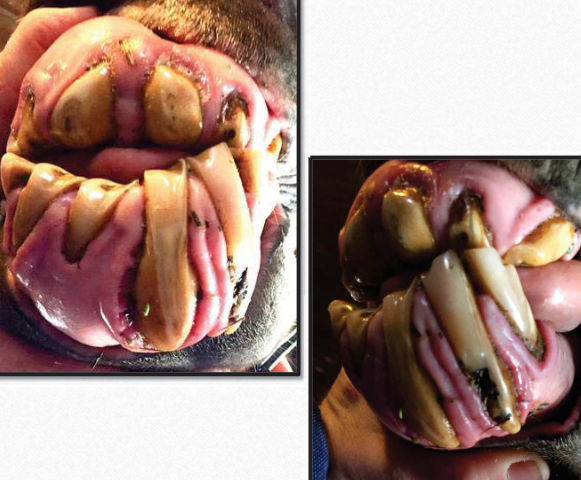
What dental abnormality is this?
Equine Odontoclastic Tooth Resorption and Hypercementosis (EOTRH)
What are the two types of floats?
Hand floats and power floats
What are the 4 characteristics of hand floats?
Relatively inexpensive ($600-$1000 for a good set), physically more exhausting, increased trauma to the oral cavity (bruising of soft tissues, gingival abrasions), and difficult to correct abnormalities
What are 4 characteristics of the power float?
Expensive ($4000-$8000), physically easier on practitioner, excellent for correcting abnormalities, required sedation and a full mouth speculm
What are 2 concerns with the power float?
Over-filing and thermal injury to the tooth
What are the 4 additional dental equipment’s?
Full mouth speculum, specialty speculums, head lamp, speculum lamp
What 6 things are a part of proper preparation and restraint for an equine dental?
Safe location, equipment set-up, sedation, speculum placement, flush oral cavity, stabilize the head