Hon. Biology - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Quiz
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
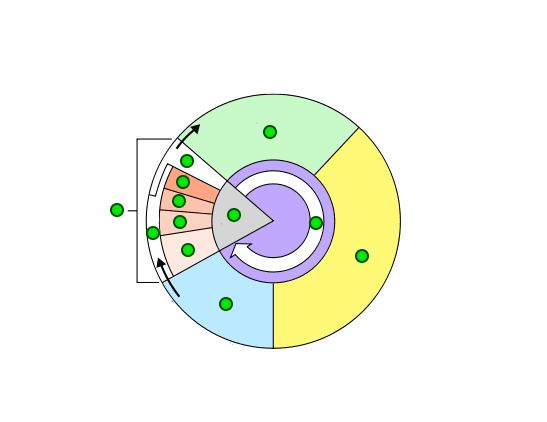
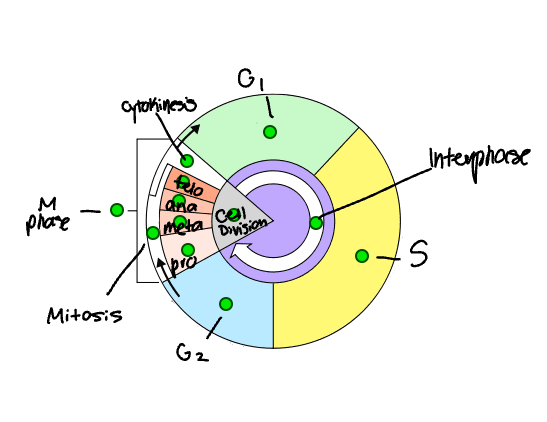
Label the stages of the Cell Cycle
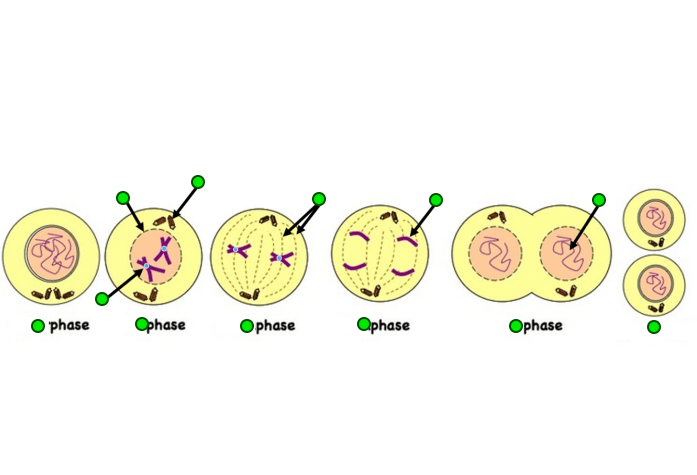
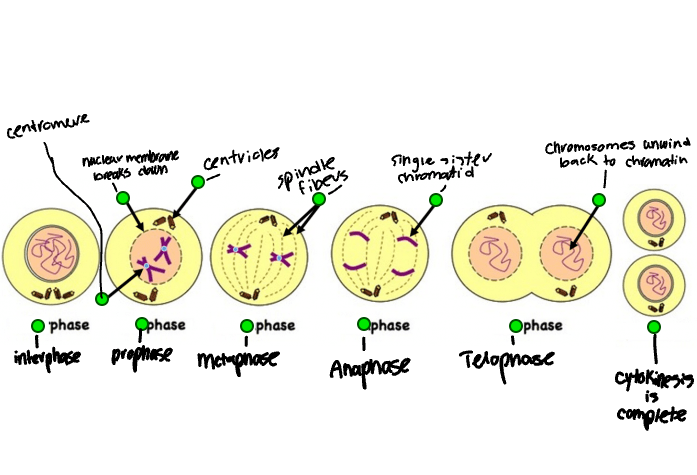
Label the phases of Mitosis
What is one of two identical ¨sister¨ parts of a copied chromosome?
A chromatid
The final phase of Mitosis in which the nuclear envelope re-forms.
Telophase
Division of the cytoplasm of the cell.
Cytokinesis
Disorder in which some of the body’s cells grow uncontrollably.
Cancer
First phase of Mitosis.
Prophase
Part of the cell cycle in which cell grows and replicates it's DNA.
Interphase
Third stage of Mitosis during which the sister chromatids separate and become individual chromosomes.
Anaphase
Division of the cell nucleus.
Mitosis
A tiny structure located in the cytoplasm near the nuclear envelope.
Centriole
During what phase of Mitosis do the chromosomes line up across the center of the cell?
Metaphase
Chromatic coils and condenses to dorm deeply staining bodies (which phase?)
Prophase
Centromeres break, and chromosomes begin migration toward the opposite poles of the cell (which phase?)
Anaphase
The nuclear membrane and nucleoli reappear (which phase?)
Telophase
When chromosomes cease their poleward movement, this phase begins (which phase?)
Telophase
Chromosomes align on the equator of the spindle (which phase?)
Metaphase
The nucleoli and nuclear membrane disappear (which phase?)
Prophase
The spindle forms through the migration of the centrioles (which phase?)
Prophase
Chromosomal material replicates (which phase?)
None (occurs during the S stage in the cell cycle)
Chromosomes first appear to be duplex structures (which phase?)
Prophase
Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers (which phase?)
Metaphase
A cleavage furrow forms during this phase (which phase?)
Telophase
The nuclear membrane is absent during the entire phase (which phase?)
Metaphase and Anaphase
Period during which a cell carries out it's usual metabolic activities (which phase?)
None
Division of the ________ is referred to as mitosis.
Nucleus
Cytokinesis is division of the _________.
Cytoplasm
The major structural difference between chromatin and chromosomes is that the latter (chromosomes) are _______.
Coiled and Condensed
Chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers bu undivided structures called _______.
Centromeres
If a cell undergoes nuclear division but not cytoplasmic division, the product is a __________.
Binuclear Cell
The structure that acts as a scaffolding for chromosomal attachment and movement is called the ________.
Spindle Fibers and/or Centriole
______ is the period of cell life when the cell is not involved in division.
Interphase
What are the stages of Interphase?
G1, S, G2
What happens during Interphase?
Cells are making cell specific proteins
DNA Synthesis (DNA doubles)
Growth
What happens during Prophase?
Chromosomes condense and become visible
Spindle Fibers emerge from the centrosomes
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Nucleolus disappears
What happens during Metaphase?
Mitotic spindle is fully developed; centrosomes are at opposite poles of the cell
Chromosomes are lined up at the metaphase plate
Each sister chromatid is attached to a spindle fiber originating from opposite poles
What happens during Anaphase?
Cohesin proteins binding the sister chromatids together break down
Sister chromatids (now called chromosomes) are pulled towards opposite poles
Non-kinetochore spindle fibers lengthen, elongating the cell
What happens during Telophase?
Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles and begin to decondense
Nuclear envelope material surrounds each set of chromosomes
The miotic spindle breaks down
What happens during Cytokinesis?
Animal Cells: a cleavage furrow separates the daughter cells
Plant Cells: a cell plate separates the daughter cells
The M phase is also known as ______.
Mitosis
Each pair of chromatids is attached at an area called the _______.
Centromere
The _______ is a series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide.
Cell Cycle
The _______ is a fan like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes.
Spindle
What are the four stages of Mitosis (and their order)?
Prophase
Metapase
Anaphase
Telophase
Proteins known as _______ regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells.
CDKs and Cyclins
What process ensure that each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information and that each daughter cell also has increased surface area?
Mitosis
Before cell division, each chromosome consists of two identical “sister” ________.
Chromatids
What phase of Mitosis takes the longest period of time?
Prophase
What part of the cell separates and takes up positions on opposite sides of the Nucleus during Prophase?
Centrioles
What phase of Mitosis usually occurs at the same time as Cytokinesis?
Telophase (begins to pinch at this point)
Why do cells replicate their DNA before Mitosis?
Mitosis divides the Nucleus. The “mother” cell must have two copies of DNA.
During what phase does the nuclear membrane disappear?
Prophase
During what stage does the DNA replicated?
S Stage (Synthesis)
What is the purpose of Mitosis?
Divides up the DNA equally so each new daughter cell has the same DNA.
If a cell has 6 chromosomes goes through Mitosis, how many chromosomes will each new daughter cell have?
6