AP Biology Unit 5
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
172 Terms
If a horticulturist breeding gardenias succeeds in having a single plant with a particularly desirable set of traits, which of the following would be her most probable and efficient route to establishing a line of such plants?
A) Backtrack through her previous experiments to obtain another plant with the same traits.
B) Breed this plant with another plant with much weaker traits
C) Clone the plant asexually to produce an identical one.
D) Force the plant to self-pollinate to obtain an identical one.
E) Add nitrogen to the soil of the offspring of this plant so the desired traits continue.
C) Clone the plant asexually to produce an identical one.
5) Which of the following defines a genome?
A) representation of a complete set of a cell's polypeptides
B) the complete set of an organism's polypeptides
C) the complete set of a species' polypeptides
D) a karyotype
E) the complete set of an organism's genes
E) the complete set of an organism's genes
Which is the smallest unit containing the entire human genome?
A. all of the DNA of one human
B. one human somatic cell
C. one human chromosome
D. the entire human population
E. one human gene
B
If an organism is diploid and a certain gene found in the organism has 18 known alleles
(variants), then any given organism of that species can/must have which of the following?
A) At most, 2 alleles for that gene
B) Up to 18 chromosomes with that gene
C) Up to 18 genes for that trait
D) A haploid number of 9 chromosomes
E) Up to, but not more than, 18 different traits
A) At most, 2 alleles for that gene
4) Which of the following is a true statement about sexual vs. asexual reproduction?
A) Asexual reproduction, but not sexual reproduction, is characteristic of plants and fungi.
B) In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring.
C) In asexual reproduction, offspring are produced by fertilization without meiosis.
D) Sexual reproduction requires that parents be diploid.
E) Asexual reproduction produces only haploid offspring.
B) In sexual reproduction, individuals transmit 50% of their genes to each of their offspring.
6) At which stage of mitosis are chromosomes usually photographed in the preparation of a karyotype?
A) prophase
B) metaphase
C) anaphase
D) telophase
E) interphase
B) metaphase
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome number of 2n = 16?
A. During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 32 separate chromosomes.
B. The species is diploid with 32 chromosomes per cell.
C. A gamete from this species has four chromosomes.
D. The species has 16 sets of chromosomes per cell.
E. Each cell has eight homologous pairs.
E
Eukaryotic sexual life cycles show tremendous variation. Of the following elements, which do all sexual life cycles have in common?
I. Alternation of generations
II. Meiosis
III. Fertilization
IV. Gametes
V. Spores
A. II, IV, and V
B. I, II, and IV
C. I, IV, and V
D. I, II, III, IV, and V
E. II, III, and IV
E
Which of these statements is false?
A. At sexual maturity, ovaries and testes produce diploid gametes by meiosis.
B. Sexual life cycles differ with respect to the relative timing of meiosis and fertilization.
C. In humans, each of the 22 maternal autosomes has a homologous paternal chromosome.
D. Single, haploid (n) sets of chromosomes in ovum and sperm unite during fertilization, forming a diploid (2n), single-celled zygote.
E. In humans, the 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, determines whether the person is female (XX) or male (XY).
A
Referring to a plant's sexual life cycle, which of the following terms describes the process that leads directly to the formation of gametes?
A. sporophyte meiosis
B. gametophyte mitosis
C. sporophyte mitosis
D. gametophyte meiosis
E. alternation of generations
B
Which of the following is an example of alternation of generations?
A. A grandparent and grandchild each have dark hair, but the parent has blond hair.
B. A diploid animal produces gametes by meiosis, and the gametes undergo fertilization to produce a diploid zygote.
C. A diploid plant (sporophyte) produces, by meiosis, a spore that gives rise to a multicellular, haploid pollen grain (gametophyte).
D. A diploid cell divides by mitosis to produce two diploid daughter cells, which then fuse to produce a tetraploid cell.
E. A haploid mushroom produces gametes by mitosis, and the gametes undergo fertilization, which is immediately followed by meiosis.
C
The human X and Y chromosomes
A. are called autosomes.
B. are almost entirely homologous, despite their different names.
C. are about the same size and have approximately the same number of genes.
D. are both present in every somatic cell of males and females alike.
E. include genes that determine an individual's sex.
E
Which of these is a karyotype?
A. a display of all the cell types in an organism.
B. the appearance of an organism.
C. a display of a cell's mitotic stages.
D. organized images of a cell's chromosomes.
E. a natural cellular arrangement of chromosomes in the nucleus.
D
Mitosis is commonly found in all but one of the following. Select the exception:
A. a diploid animal cell
B. a haploid plant cell
C. a haploid animal cell
D. a diploid plant cell
C
Which of these is a way that the sexual life cycle increases genetic variation in a species?
A. by allowing an increase in cell number
B. by decreasing mutation frequency
C. by allowing crossing over
D. by increasing gene stability
E. by conserving chromosomal gene order
C
A given organism has 46 chromosomes in its karyotype. We can therefore conclude which of the following?
A. It must be sexually reproducing.
B. It must be an animal.
C. Its gametes must have 23 chromosomes.
D. It must be a primate.
E. It must be human.
C
15) A triploid cell contains three sets of chromosomes. If a cell of a usually diploid species with 42 chromosomes per cell is triploid, this cell would be expected to have which of the following?
A) 63 chromosomes in 31 1/2 pairs
B) 63 chromosomes in 21 sets of 3
C) 63 chromosomes, each with three chromatids
D) 21 chromosome pairs and 21 unique chromosomes
B) 63 chromosomes in 21 sets of 3
Which of the following best describes a karyotype?
A. a display of each of the chromosomes of a single cell
B. a photograph of all the cells with missing or extra chromosomes
C. a pictorial representation of all the genes for a species
D. the combination of all the maternal and paternal chromosomes of a species
E. the collection of all the chromosomes in an individual organism
A
Which of the following can utilize both mitosis and meiosis in the correct circumstances?
A. any diploid animal cell
B. a haploid animal cell
C. a diploid cell from a plant stem
D. an archaebacterium
E. a plantlike protist
E
The somatic cells of a privet shrub each contain 46 chromosomes. To be as different as they are from human cells, which have the same number of chromosomes, which of the following must be true?
A. Genes on a particular privet chromosome, such as the X, must be on a different human chromosome, such as number 18.
B. Privet sex cells have chromosomes that can synapse with human chromosomes in the laboratory.
C. Genes of privet chromosomes are significantly different than those in humans.
D. Privet shrubs must be metabolically more like animals than like other shrubs.
E. Privet cells cannot reproduce sexually.
C
In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If we choose one of these pairs, such as pair 14, which of the following do the two chromosomes of the pair have in common?
A. Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes.
B. Length and position of the centromere only.
C. Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and DNA sequences.
D. Length, centromere position, and staining pattern only.
E. They have nothing in common except they are X-shaped.
A
To view and analyze human chromosomes in a dividing cell, which of the following is/are required?
A. a stain particular to human cells
B. a scanning electron microscope
C. radioactive staining
D. DNA staining and a light microscope
E. fluorescent staining and a transmission electron microscope
D
The karyotype of one species of primate has 48 chromosomes. In a particular female, cell division goes awry and she produces one of her eggs with an extra chromosome (25). The most probable source of this error would be a mistake in which of the following?
A. mitosis in her ovary
B. telophase II of one meiotic event
C. metaphase I of one meiotic event
D. telophase I of one meiotic event
E. either anaphase I or II
E
If a cell has completed the first meiotic division and is just beginning meiosis II, which of the following is an appropriate description of its contents?
A. It has one-fourth the DNA and one-half the chromosomes as the originating cell.
B. It has the same number of chromosomes but each of them has different alleles than another cell from the same meiosis.
C. It has half the amount of DNA as the cell that began meiosis.
D. It has half the chromosomes but twice the DNA of the originating cell.
E. It is identical in content to another cell from the same meiosis.
C
Which of the following might result in a human zygote with 45 chromosomes?
A. lack of chiasmata in prophase I
B. failure of the egg nucleus to be fertilized by the sperm
C. an error in either egg or sperm meiotic anaphase
D. an error in the alignment of chromosomes on the metaphase plate
E. fertilization of a 23 chromosome human egg by a 22 chromosome sperm of a closely related species
C
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter cell is
A. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
B. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
C. tetraploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
D. diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
E. haploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a single chromatid.
B
How do cells at the completion of meiosis compare with cells that have replicated their DNA and are just about to begin meiosis?
A. They have half the number of chromosomes and one-fourth the amount of DNA.
B. They have twice the amount of cytoplasm and half the amount of DNA.
C. They have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
D. They have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA.
E. They have half the amount of cytoplasm and twice the amount of DNA.
A
When does the synaptonemal complex disappear?
A.mid-prophase of meiosis I
B. during fertilization or fusion of gametes
C. late prophase of meiosis I
D. early anaphase of meiosis I
E. late metaphase of meiosis II
C
Which of the following happens at the conclusion of meiosis I?
A. Cohesins are cleaved at the centromeres.
B. Sister chromatids are separated.
C. Homologous chromosomes of a pair are separated from each other.
D. The chromosome number per cell is conserved.
E. Four daughter cells are formed.
c
Chromatids are separated from each other.
A. The statement is true for meiosis II only.
B. The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
D. The statement is true for mitosis only.
E. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
E
Which of the following occurs in meiosis but not in mitosis?
A. synapsis of chromosomes
B. production of daughter cells
C. chromosome replication
D. condensation of chromatin
E. alignment of chromosomes at the equator
A
Whether during mitosis or meiosis, sister chromatids are held together by proteins referred to as cohesins. Such molecules must have which of the following properties?
A.They must be removed before meiosis can begin.
B. They must reattach to chromosomes during G1.
C. They must persist throughout the cell cycle.
D. They must be intact for nuclear envelope re-formation.
E. They must be removed before sister chromatids or homologous chromosomes can separate.
E
Experiments with cohesins have found that
A. cohesins are protected from destruction throughout meiosis I and II.
B. cohesins are protected from cleavage at the centromere during meiosis I.
C. cohesins are cleaved from chromosomes at the centromere before anaphase I.
D. a protein cleaves cohesins before metaphase I.
E. a protein that cleaves cohesins would cause cellular death.
B
A pair of homologous chromosomes includes which of the following sets of DNA strands?
A. four sister chromatids
B. eight sister chromatids
C. two single-stranded chromosomes that have synapsed
D. two sister chromatids that have synapsed
E. four unique chromosomes
A
When we see chiasmata under a microscope, that lets us know which of the following has occurred?
A. prophase I
B. asexual reproduction
C. meiosis II
D. anaphase II
E. separation of homologs
A
To visualize and identify meiotic cells at metaphase with a microscope, what would you look for?
A. individual chromosomes all at the cell's center
B. the synaptonemal complex
C. pairs of homologous chromosomes all aligned at the cell's center
D. an uninterrupted spindle array
E. sister chromatids of a replicated chromosome grouped at the poles
C
Homologous chromosomes are aligned at...
...
For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below.
I. Prophase I V. Prophase II
II. Metaphase I VI. Metaphase II
III. Anaphase I VII. Anaphase II
IV. Telophase I VIII. Telophase II
Synaptonemal complexes form or are still present.
A. II and VI only
B. I and IV only
C. I, II, III, and IV only
D. I and VIII only
E. I only
E
For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below.
I. Prophase I V. Prophase II
II. Metaphase I VI. Metaphase II
III. Anaphase I VII. Anaphase II
IV. Telophase I VIII. Telophase II
Centromeres of sister chromatids disjoin and chromatids separate.
A. II
B. III
C. IV
D. V
E. VII
E
Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs.
A. The statement is true for meiosis II only.
B. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
C. The statement is true for meiosis I only.
D. The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E. The statement is true for mitosis only.
C
Which of the following best describes the frequency of crossing over in mammals?
A. ~50 per chromosome pair
B. at least 1-2 per chromosome pair
C. ~2 per meiotic cell
D. a very rare event among hundreds of cells
E. ~1 per pair of sister chromatids
B
When homologous chromosomes cross over, what occurs?
A. Two chromatids get tangled, resulting in one re-sequencing its DNA.
B. Each of the four DNA strands of a homologous pair is broken, and the pieces are mixed.
C. Specific proteins break the two strands of nonsister chromatids and re-join them.
D. Two sister chromatids exchange identical pieces of DNA.
E. Maternal alleles are "corrected" to be like paternal alleles and vice versa.
C
Which of the life cycles is typical for animals?
I only
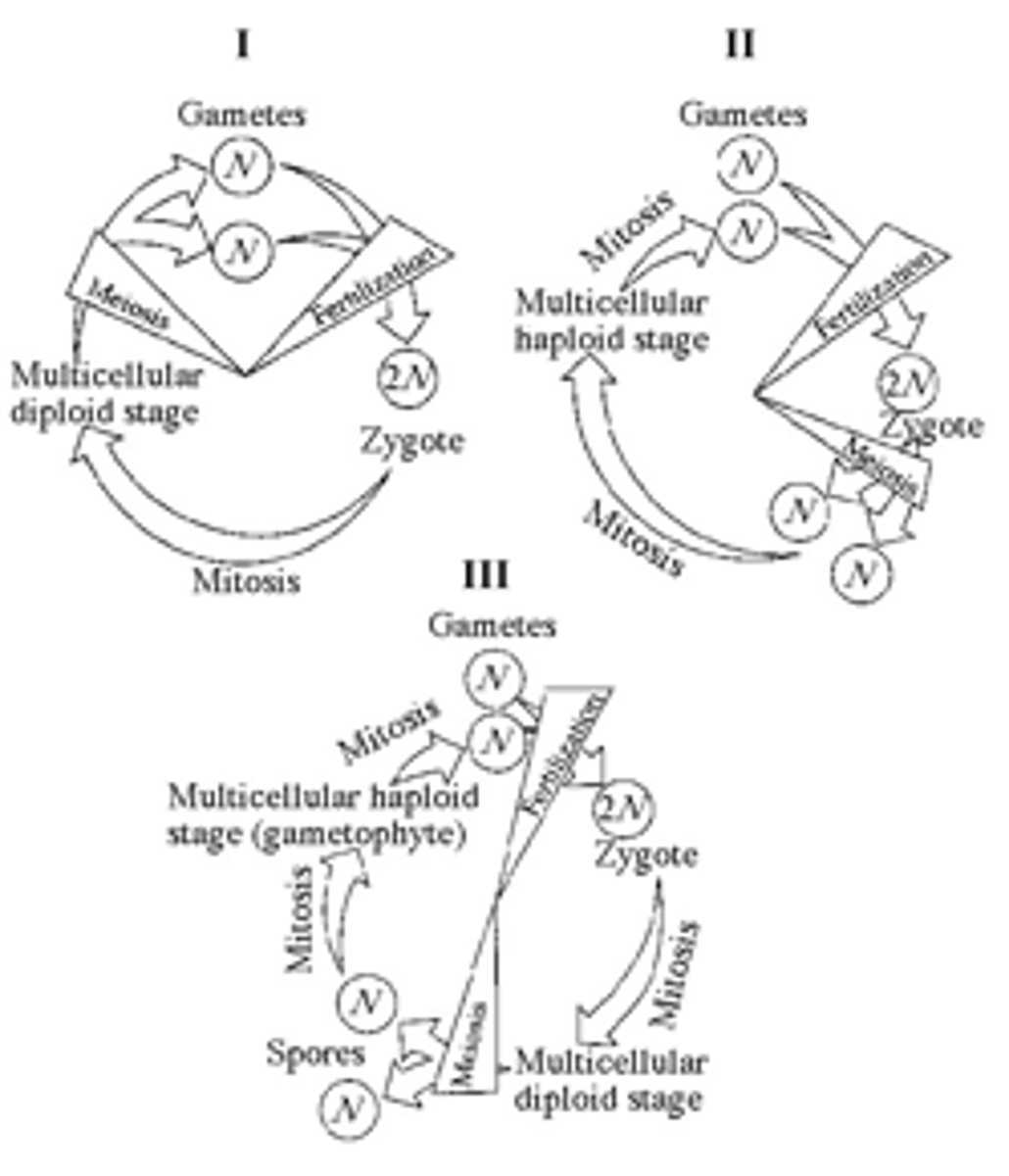
48) Which of the life cycles is typical for plants and some algae?
III only
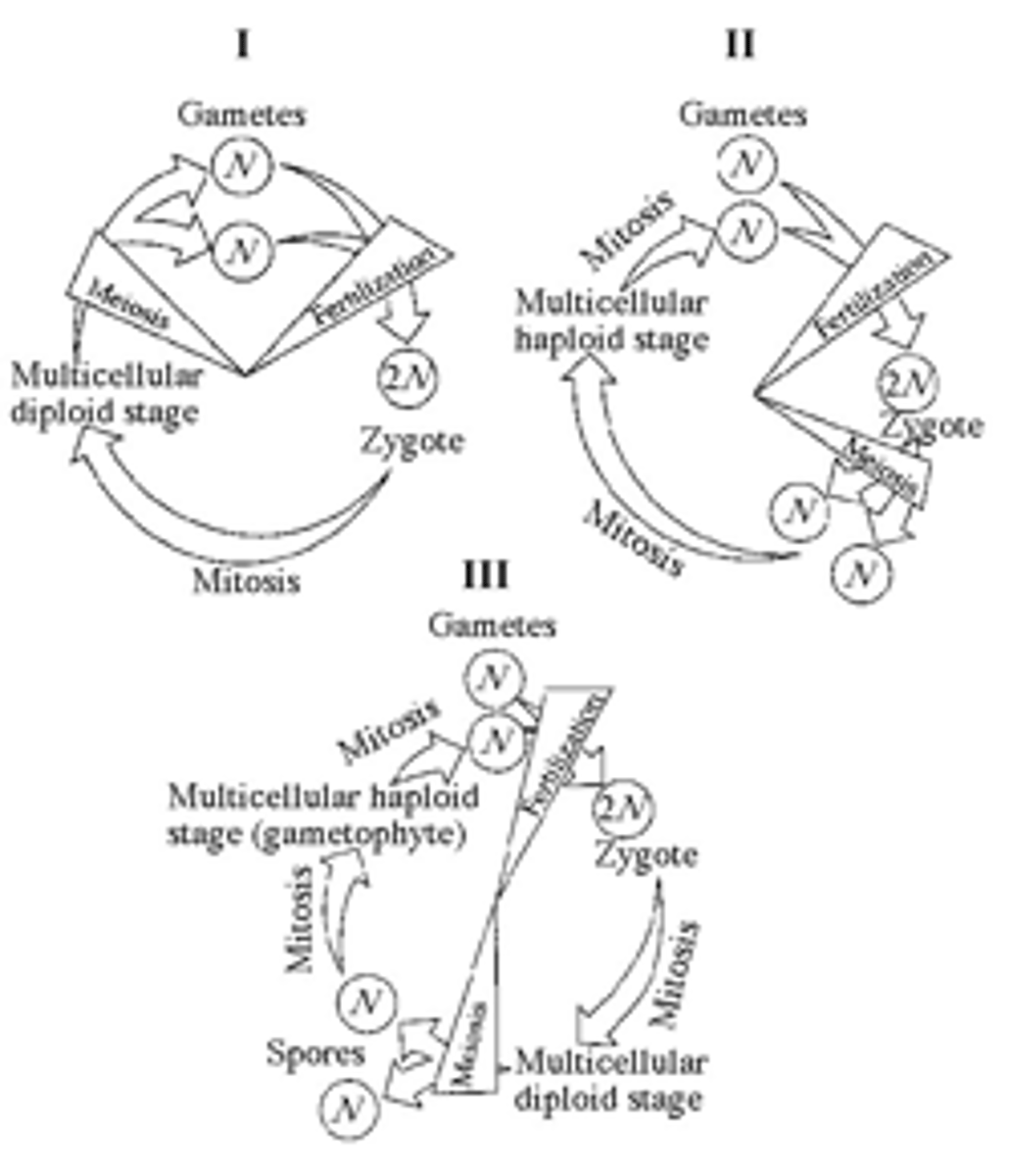
49) Which of the life cycles is typical for most fungi and some protists?
II only
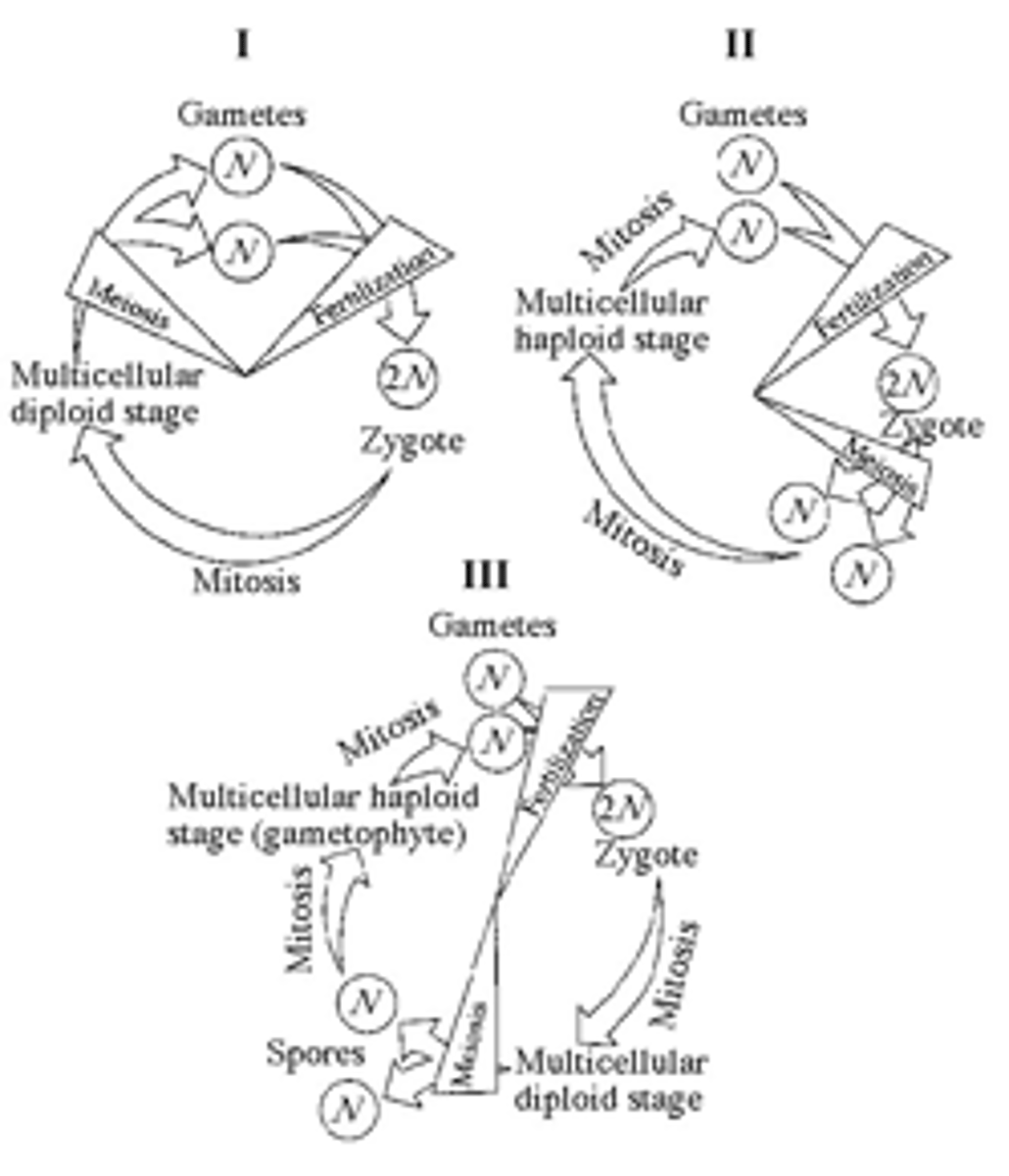
50) In part III of Figure 10.1, the progression of events corresponds to which of the following series?
A) zygote, mitosis, gametophyte, mitosis, fertilization, zygote, mitosis
B) sporophyte, meiosis, spore, mitosis, gametophyte, mitosis, gametes, fertilization
C) fertilization, mitosis, multicellular haploid, mitosis, spores, sporophyte
D) gametophyte, meiosis, zygote, spores, sporophyte, zygote
E) meiosis, fertilization, zygote, mitosis, adult, meiosis
B) sporophyte, meiosis, spore, mitosis, gametophyte, mitosis, gametes, fertilization
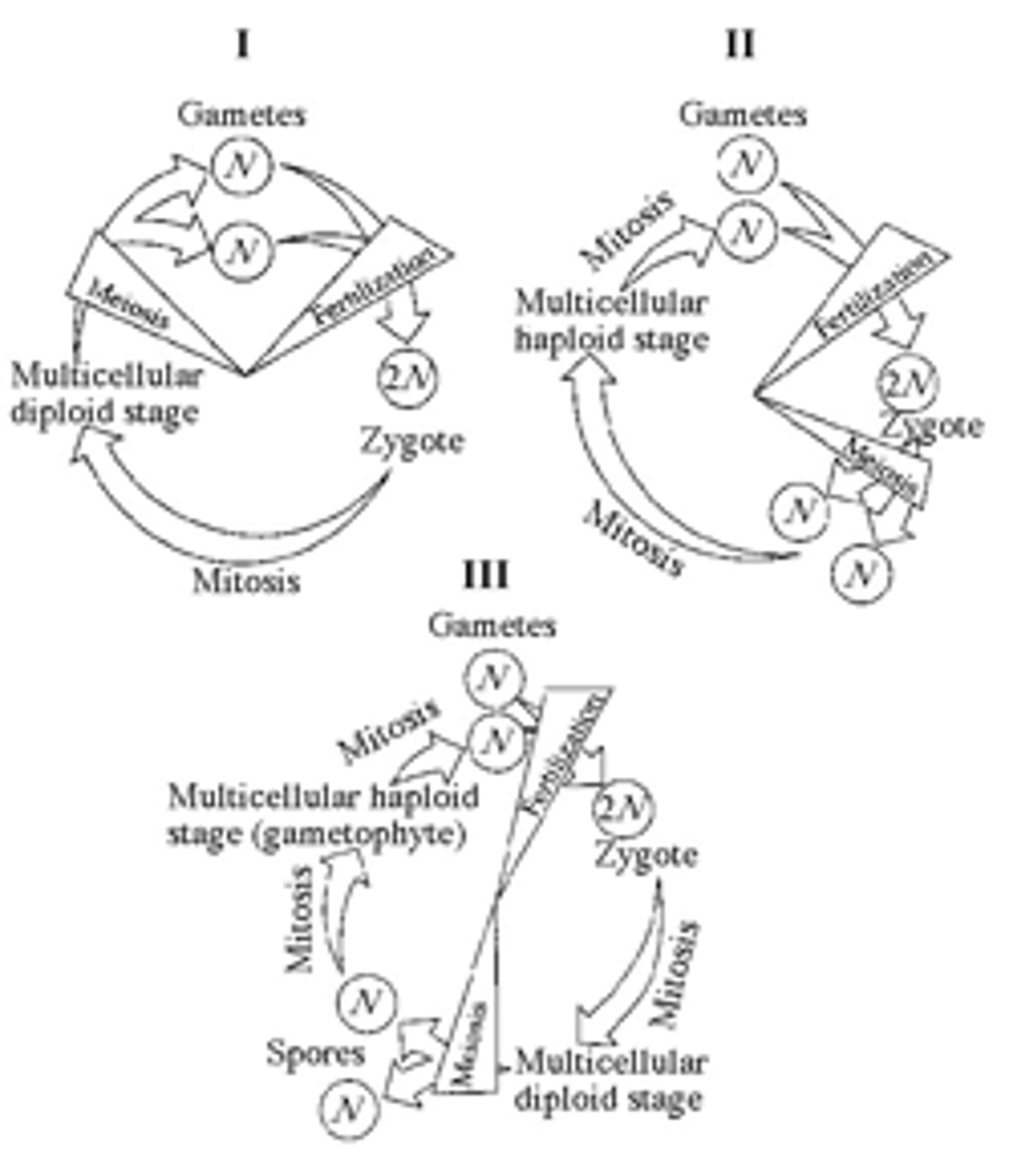
51) In a life cycle such as that shown in part III of Figure 10.1, if the zygote's chromosome number is 10, which of the following will be true?
A) The sporophyte's chromosome number per cell is 10 and the gametophyte's is 5.
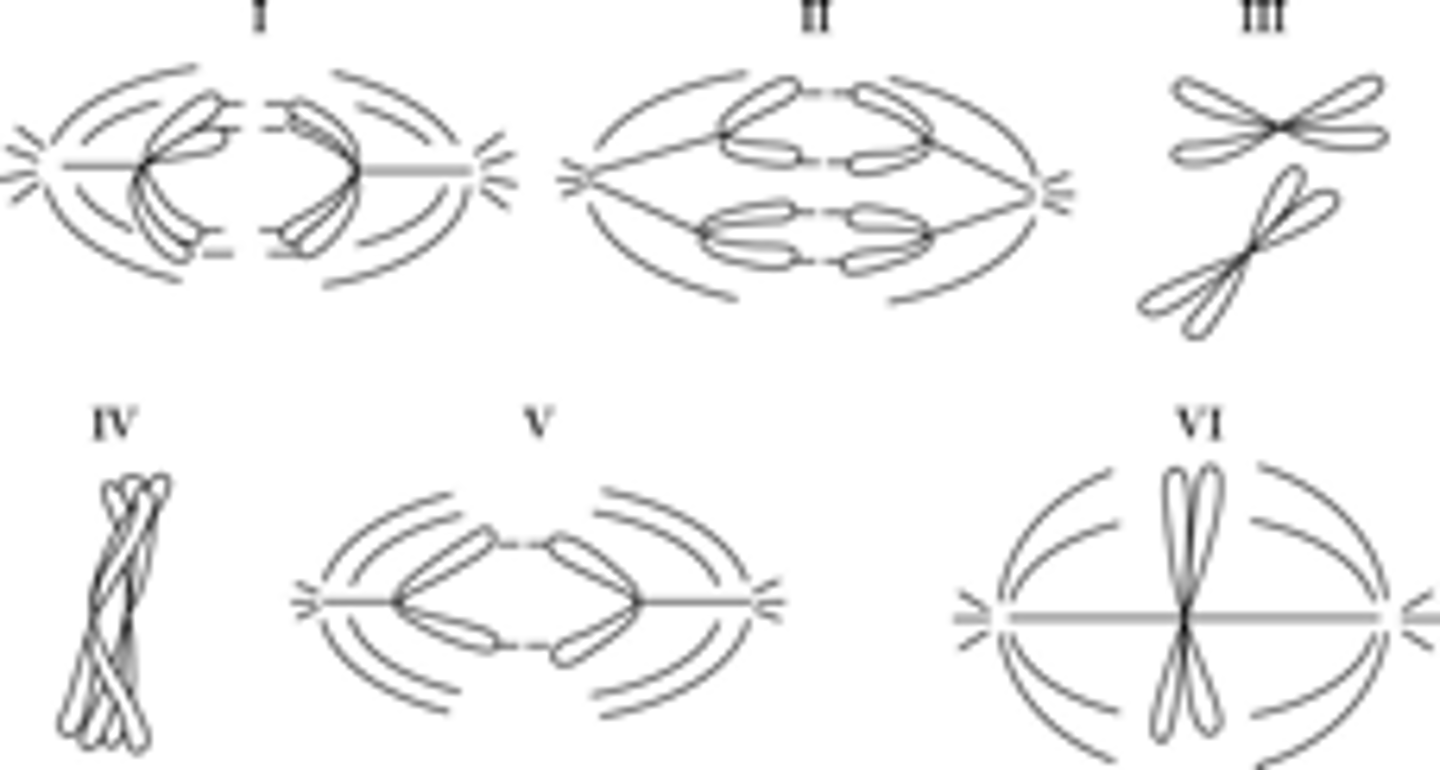
52) Which diagram represents anaphase I of meiosis?
I
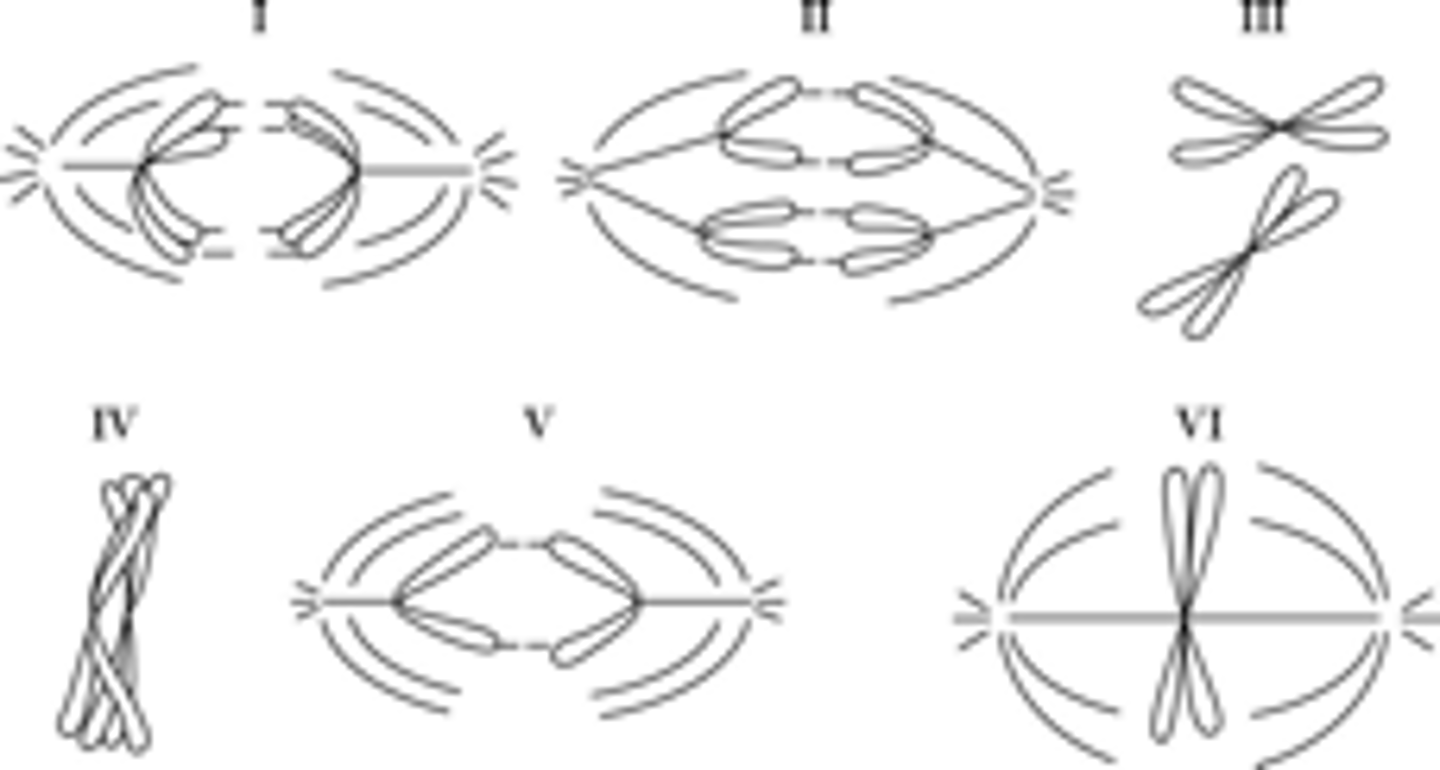
53) Which diagram(s) represent anaphase II of meiosis?
V only
54) Which sample of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle?
I
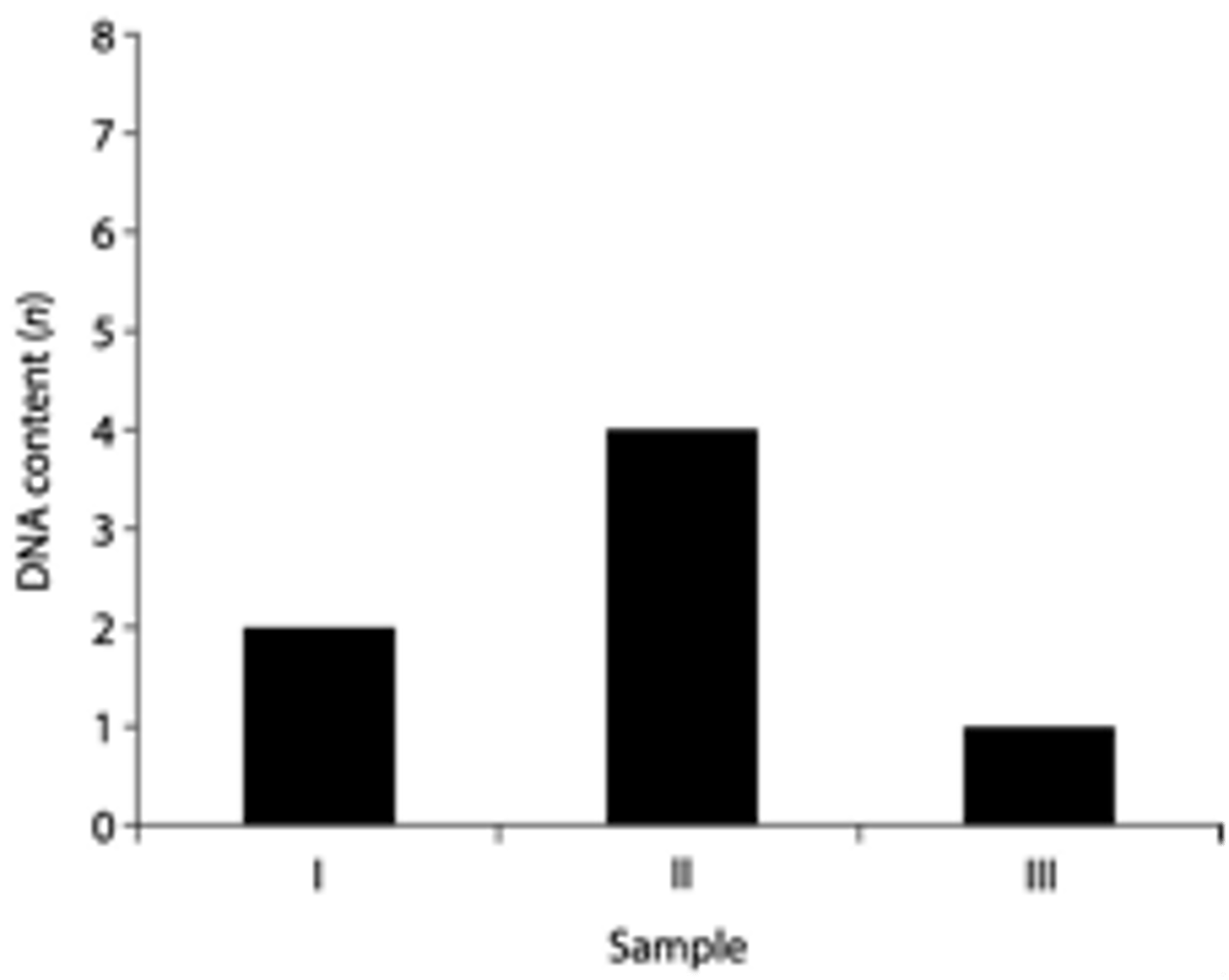
55) Which sample might represent an animal cell in the G2 phase of the cell cycle?
II
56) Which sample might represent a zygote?
I
Refer to the following information and the figure to answer the following question.
A certain (hypothetical) organism is diploid, has either blue or orange wings as the consequence of one of its genes on chromosome 12, and has either long or short antennae as the result of a second gene on chromosome 19, as shown in the figure.
A certain female's number 12 chromosomes both have the blue gene and number 19 chromosomes both have the long gene. As cells in her ovaries undergo meiosis, her resulting eggs (ova) may have which of the following?
A. one chromosome 12 with one blue gene and one chromosome 19 with one long gene
B. either two number 12 chromosomes with blue genes or two with orange genes
C. either one blue or one orange gene in addition to either one long or one short gene
D. either two number 19 chromosomes with long genes or two with short genes
A
Refer to the following information and the figure to answer the following question.
A certain (hypothetical) organism is diploid, has either blue or orange wings as the consequence of one of its genes on chromosome 12, and has either long or short antennae as the result of a second gene on chromosome 19, as shown in the figure.
If a female of this species has one chromosome 12 with a blue gene and another chromosome 12 with an orange gene, and has both number 19 chromosomes with short genes, she will produce which of the following egg types?
A. only blue short gene eggs
B. three-fourths blue short and one-fourth orange short gene eggs
C. three-fourths blue long and one-fourth orange short gene eggs
D. one-half blue short and one-half orange short gene eggs
E. only orange short gene eggs
D
Refer to the following information and the figure to answer the following question.
A certain (hypothetical) organism is diploid, has either blue or orange wings as the consequence of one of its genes on chromosome 12, and has either long or short antennae as the result of a second gene on chromosome 19, as shown in the figure.
A female with a paternal set of one orange and one long gene chromosome and a maternal set comprised of one blue and one short gene chromosome is expected to produce which of the following types of eggs after meiosis?
A. All eggs will have maternal types of gene combinations.
B. All eggs will have paternal types of gene combinations.
C. Half the eggs will have maternal and half will have paternal combinations.
D. Each egg has a three-fourths chance of having blue long, one-fourth blue short, three-fourths orange long, or one-fourth orange short combinations.
E. Each egg has a one-fourth chance of having either blue long, blue short, orange long, or orange short combinations.
E
Use the following information to answer the next question.
There is a group of invertebrate animals called rotifers, among which a particular group of species reproduces, as far as is known, only asexually. These rotifers, however, have survived a long evolutionary history without evidence of having been overcome by excessive mutations.
Since the rotifers develop from eggs, but asexually, what can you predict?
A. All males can produce eggs.
B. The eggs and the zygotes are all haploid.
C. While asexual, both males and females are found in nature.
D. The animals are all hermaphrodites.
E. No males can be found.
E
There is a group of invertebrate animals called rotifers, among which a particular group of species reproduces, as far as is known, only asexually. These rotifers, however, have survived a long evolutionary history without evidence of having been overcome by excessive mutations.How is natural selection related to sexual reproduction as opposed to asexual reproduction?
A. Sexual reproduction results in the most appropriate and healthiest balance of two sexes in the population.
B. Sexual reproduction allows the greatest number of offspring to be produced.
C. Sexual reproduction results in the greatest number of new mutations.
D. Sexual reproduction utilizes far less energy than asexual reproduction.
E. Sexual reproduction results in many new gene combinations, some of which will lead to differential reproduction.
E
A human cell containing 22 autosomes and a Y chromosome is
A. a sperm.
B. a zygote.
C. a somatic cell of a male.
D. a somatic cell of a female.
E. an egg.
A
Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles of a dividing cell during
A. binary fission.
B. fertilization.
C. meiosis I.
D. meiosis II.
E. mitosis.
C
If the DNA content of a diploid cell in the G1 phase of the cell cycle is x, then the DNA content of the same cell at metaphase of meiosis I would be
A. 4x.
B. 0.5x.
C. x.
D. 0.25x.
E. 2x.
E
If we continued to follow the cell lineage from question 3, then the DNA content of a single cell at metaphase of meiosis II would be
A. 0.5x.
B. 4x.
C. x.
D. 0.25x.
E. 2x.
C
How many different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes can be packaged in gametes made by an organism with a diploid number of 8 (2n = 8)?
A. 8
B. 16
C. 2
D. 4
E. 32
B
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
A) The gene involved is on the Y chromosome.
B) The gene involved is on the X chromosome.
C) The gene involved is on an autosome, but only in males.
D) Other male-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
E) Other female-specific factors influence eye color in flies.
The gene involved is on the X chromosome
3) Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century?
A) Individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes.
B) Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and in turn segregate during meiosis.
C) Homologous chromosomes give rise to some genes and crossover chromosomes to other genes.
D) No more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy normal cell.
E) Natural selection acts on certain chromosome arrays rather than on genes.
Answer: B
6) Males are more often affected by sex-linked traits than females because
A) male hormones such as testosterone often alter the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
B) female hormones such as estrogen often compensate for the effects of mutations on the X chromosome.
C) X chromosomes in males generally have more mutations than X chromosomes in females.
D) males are hemizygous for the X chromosome.
E) mutations on the Y chromosome often worsen the effects of X-linked mutations.
Answer: D
8) In cats, black fur color is caused by an X-linked allele; the other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross of a black female and an orange male?
A) tortoiseshell females; tortoiseshell males
B) black females; orange males
C) orange females; orange males
D) tortoiseshell females; black males
E) orange females; black males
Answer: D
9) Red-green color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait in humans. Two people with normal color vision have a color-blind son. What are the genotypes of the parents?
A) XcXc and XcY
B) XcXc and XCY
C) XCXC and XcY
D) XCXC and XCY
E) XCXc and XCY
Answer: E
10) Cinnabar eyes is a sex-linked recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F₁ males will have cinnabar eyes?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Answer: E
Normally, only female cats have the tortoiseshell phenotype because
a male inherits only one allele of the X-linked gene controlling hair color.
13) Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY region of the Y chromosome. An abnormality of this region could allow which of the following to have a male phenotype?
A) Turner syndrome, 45, X
B) translocation of SRY to an autosome of a 46, XX individual
C) a person with an extra X chromosome
D) a person with one normal and one shortened (deleted) X
E) Down syndrome, 46, XX
Answer: B
14) In humans, clear gender differentiation occurs, not at fertilization, but after the second month of gestation. What is the first event of this differentiation?
A) formation of testosterone in male embryos
B) formation of estrogens in female embryos
C) anatomical differentiation of a penis in male embryos
D) activation of SRY in male embryos and masculinization of the gonads
E) activation of SRY in females and feminization of the gonads
Answer: D
15) Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their 20s. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition?
A) Women can never have this condition.
B) One-half of the daughters of an affected man could have this condition.
C) One-fourth of the children of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
D) Very rarely would a woman have this condition; the condition would be due to a chromosome error.
E) Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition.
Answer: D
16) Women (and all female mammals) have one active X chromosome per cell instead of two. What causes this?
A) modification of the XIST gene so that it is active only on one X chromosome, which then becomes inactive
B) activation of the Barr gene on one of the two X chromosomes that then inactivates
C) crossover between the XIST gene on one X chromosome and a related gene on an autosome
D) inactivation of the XIST gene on the X chromosome derived from the male parent
E) the removal of methyl (CH3) groups from the X chromosome that will remain active
Answer: A
17) Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
A) The closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a crossover will occur between them.
B) The observed frequency of recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a maximum value of 100%.
C) All of the traits that Mendel studied-seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others-are due to genes linked on the same chromosome.
D) Linked genes are found on different chromosomes.
E) Crossing over occurs during prophase II of meiosis.
Answer: A
18) How would one explain a testcross involving F₁ dihybrid flies in which more parental-type offspring than recombinant-type offspring are produced?
A) The two genes are closely linked on the same chromosome.
B) The two genes are linked but on different chromosomes.
C) Recombination did not occur in the cell during meiosis.
D) The testcross was improperly performed.
E) Both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene.
Answer: A
19) What does a frequency of recombination of 50% indicate?
A) The two genes are likely to be located on different chromosomes.
B) All of the offspring have combinations of traits that match one of the two parents.
C) The genes are located on sex chromosomes.
D) Abnormal meiosis has occurred.
E) Independent assortment is hindered.
Answer: A
Three genes (A, B, and C) at three loci are being mapped in a particular species. Each gene has two alleles, one of which results in a phenotype that is markedly different from the wild type. The unusual allele of gene A is inherited with the unusual allele of gene B or C about 50% of the time. However, the unusual alleles of genes B and C are inherited together 14.4% of the time. Which of the following describes what is happening?
Gene A is assorting independently of genes B and C, which are linked.
23) Recombination between linked genes comes about for what reason?
A) Mutation on one homolog is different from that on the other homolog.
B) Independent assortment sometimes fails because Mendel had not calculated appropriately.
C) When genes are linked they always "travel" together at anaphase.
D) Crossovers between these genes result in chromosomal exchange.
E) Nonrecombinant chromosomes break and then re-join with one another.
Answer: D
24) Why does recombination between linked genes continue to occur?
A) Recombination is a requirement for independent assortment.
B) Recombination must occur or genes will not assort independently.
C) New allele combinations are acted upon by natural selection.
D) The forces on the cell during meiosis II always result in recombination.
E) Without recombination there would be an insufficient
Answer: C
25) Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons?
A) The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of the chromosome.
B) The relationship between recombination frequency and map units is different in every individual.
C) Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell cycle.
D) The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly different in every individual.
E) Linkage map distances are identical between males and females.
Answer: A
20) What is the reason that linked genes are inherited together?
A) They are located close together on the same chromosome.
B) The number of genes in a cell is greater than the number of chromosomes.
C) Chromosomes are unbreakable.
D) Alleles are paired together during meiosis.
E) Genes align that way during metaphase I of meiosis.
Answer: A
2) Sturtevant provided genetic evidence for the existence of four pairs of chromosomes in Drosophila in which of these ways?
A) There are four major functional classes of genes in Drosophila.
B) Drosophila genes cluster into four distinct groups of linked genes.
C) The overall number of genes in Drosophila is a multiple of four.
D) The entire Drosophila genome has approximately 400 map units.
E) Drosophila genes have, on average, four different alleles.
Answer: B
If cell X enters meiosis, and nondisjunction of one chromosome occurs in one of its daughter cells during meiosis II, what will be the result at the completion of meiosis?
A. Two of the four gametes descended from cell X will be haploid, and two will be diploid.
B. All the gametes descended from cell X will be diploid.
C. 1/4 of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, 1/4 will be n - 1, and 1/2 will be n.
D. There will be three extra gametes.
E. Half of the gametes descended from cell X will be n + 1, and half will be n - 1.
C
28) One possible result of chromosomal breakage is for a fragment to join a nonhomologous chromosome. What is this alteration called?
A) deletion
B) transversion
C) inversion
D) translocation
E) duplication
Answer: D
29) A nonreciprocal crossover causes which of the following products?
A) deletion only
B) duplication only
C) nondisjunction
D) deletion and duplication
E) duplication and nondisjunction
Answer: D
31) Of the following human aneuploidies, which is the one that generally has the most severe impact on the health of the individual?
A) 47, +21
B) 47, XXY
C) 47, XXX
D) 47, XYY
E) 45, X
Answer: A
32) A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counseling because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his chromosome 4 that has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome 12. Although he is normal because his translocation is balanced, he and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm?
A) 1/4 will be normal, 1/4 will have the translocation, and 1/2 will have duplications and deletions.
B) All will carry the same translocation as the father.
C) None will carry the translocation since abnormal sperm will die.
D) His sperm will be sterile and the couple might consider adoption.
E) 1/2 will be normal and the rest will have the father's translocation.
Answer: A
33) Abnormal chromosomes are frequently found in malignant tumors. Errors such as translocations may place a gene in close proximity to different control regions. Which of the following might then occur to make the cancer worse?
A) an increase in nondisjunction
B) expression of inappropriate gene products
C) a decrease in mitotic frequency
D) death of the cancer cells in the tumor
E) sensitivity of the immune system
Answer: B
34) An inversion in a human chromosome often results in no demonstrable phenotypic effect in the individual. What else may occur?
A) There may be deletions later in life.
B) Some abnormal gametes may be formed.
C) There is an increased frequency of mutation.
D) All inverted chromosomes are deleted.
E) The individual is more likely to get cancer.
Answer: B
35) What is the source of the extra chromosome 21 in an individual with Down syndrome?
A) nondisjunction in the mother only
B) nondisjunction in the father only
C) duplication of the chromosome
D) nondisjunction or translocation in either parent
E) It is impossible to detect with current technology.
Answer: D
36) Down syndrome has a frequency in the U.S. population of ~1/700 live births. In which of the following groups would you expect this frequency to be significantly higher?
A) people in Latin or South America
B) the Inuit and other peoples in very cold habitats
C) people living in equatorial areas of the world
D) very small population groups
E) No groups have such higher frequency.
Answer: E
37) A couple has a child with Down syndrome. The mother is 39 years old at the time of delivery. Which of the following is the most probable cause of the child's condition?
A) The woman inherited this tendency from her parents.
B) One member of the couple carried a translocation.
C) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in somatic cell production.
D) One member of the couple underwent nondisjunction in gamete production.
E) The mother had a chromosomal duplication.
Answer: D
40) What is a syndrome?
A) a characteristic facial appearance
B) a group of traits, all of which must be present if an aneuploidy is to be diagnosed
C) a group of traits typically found in conjunction with a particular chromosomal aberration or gene mutation
D) a characteristic trait usually given the discoverer's name
E) a characteristic that only appears in conjunction with one specific aneuploidy
Answer: C
41) Which of the following is known as a Philadelphia chromosome?
A) a human chromosome 22 that has had a specific translocation
B) a human chromosome 9 that is found only in one type of cancer
C) an animal chromosome found primarily in the mid-Atlantic area of the United States
D) an imprinted chromosome that always comes from the mother
Answer: A
At what point in cell division is a chromosome lost so that, after fertilization with a normal gamete, the result is an embryo with 45, X?
I. an error in anaphase I
II. an error in anaphase II
III. an error of the first postfertilization mitosis
IV. an error in pairing
I, II, III, or IV
43) Which of the following is true of aneuploidies in general?
A) A monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy.
B) 45 X is the only known human live-born monosomy.
C) Some human aneuploidies have selective advantage in some environments.
D) Of all human aneuploidies, only Down syndrome is associated with mental retardation.
E) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion of a chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication.
Answer: B
5) A woman is found to have 47 chromosomes, including three X chromosomes. Which of the following describes her expected phenotype?
A) masculine characteristics such as facial hair
B) enlarged genital structures
C) excessive emotional instability
D) normal female
E) sterile female
Answer: D
) Between which two genes would you expect the highest frequency of recombination?
A) A and W
B) W and E
C) E and G
D) A and E
E) A and G
Answer: E
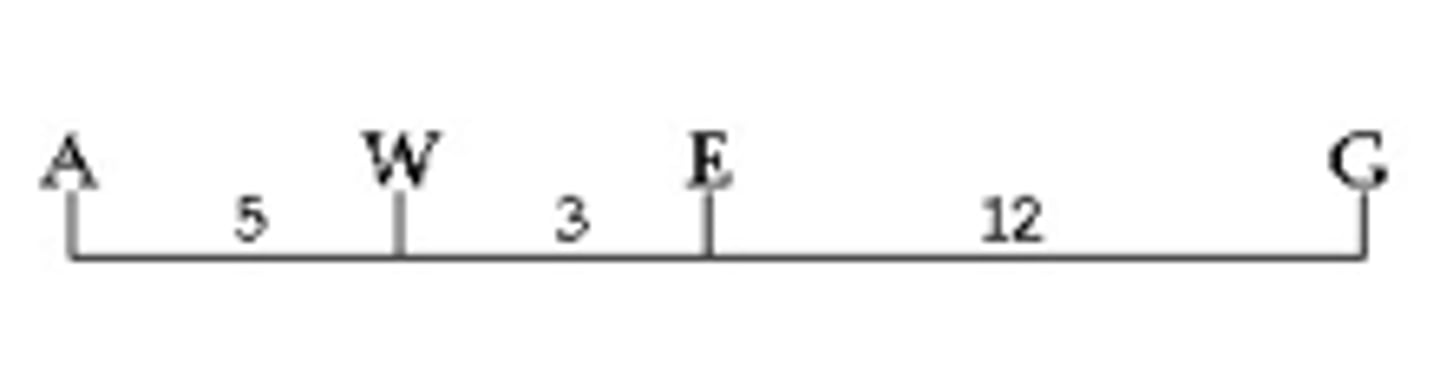
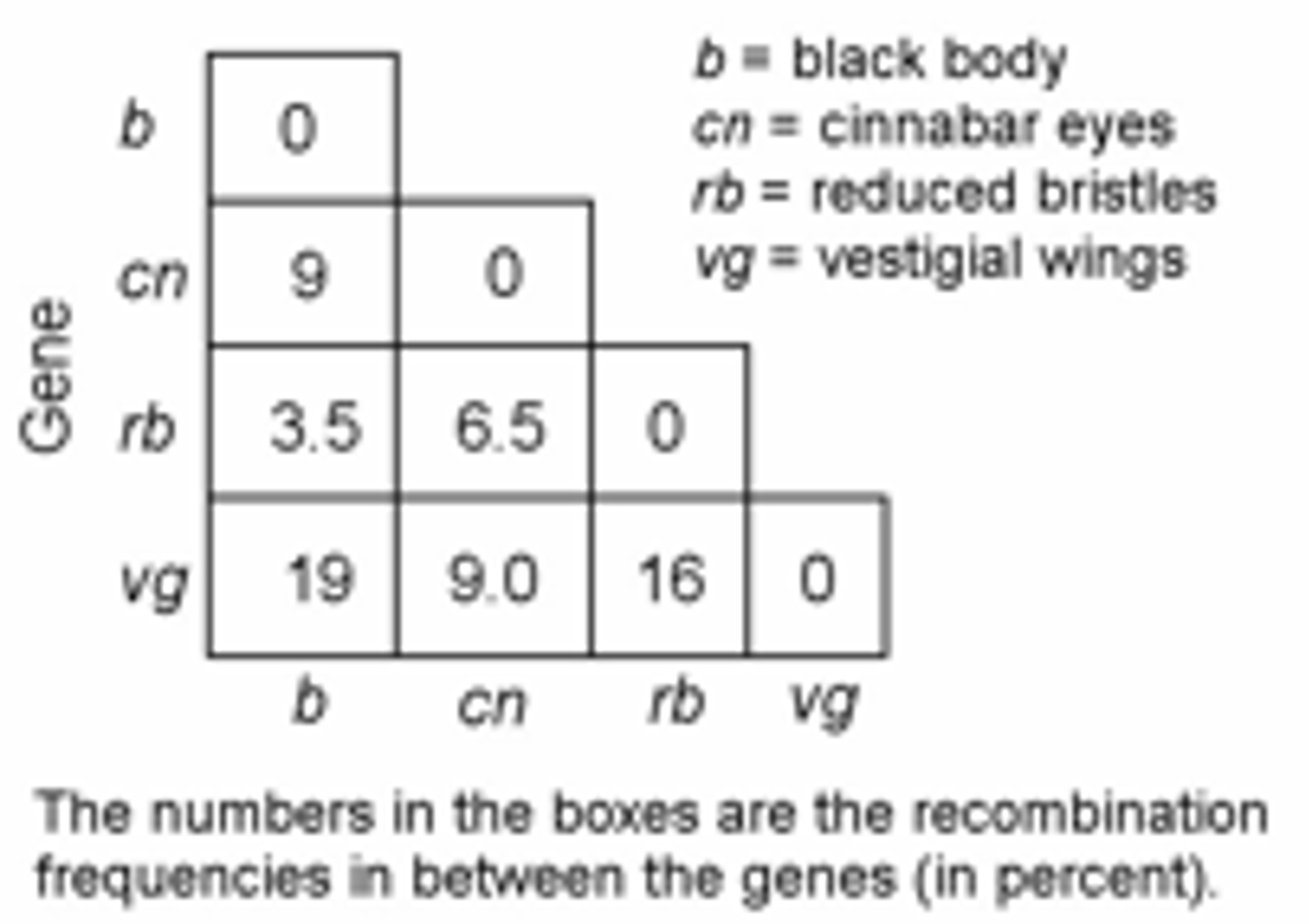
52) In a series of mapping experiments, the recombination frequencies for four different linked genes of Drosophila were determined as shown in Figure 15.2. What is the order of these genes on a chromosome map?
A) rb-cn-vg-b
B) vg-b-rb-cn
C) cn-rb-b-vg
D) b-rb-cn-vg
E) vg-cn-b-rb
Answer: D
A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine as follows: A geneticist did a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type): Phenotypes Leaves Stems Roots Number 1 a + + 14 2 a + c 0 3 a b + 32 4 a b c 440 5 + b + 0 6 + b c 16 7 + + c 28 8 + + + 470 Total 1,000 Which of the following are the phenotypes of the parents in this cross?
A) 2 and 5
B) 1 and 6
C) 4 and 8
D) 3 and 7
E) 1 and 2
c