Fluid Compartments, Types, and Routes & Dehydration/Maintenance
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Total body water
60% of body weight
Total body water pediatric patients
70% of body weight
Total body water pediatric patients
Use the lean body mass (70% of body weight) then 60% of that
Blood volume dogs
8-9% BW
Blood volume cats
5-6% BW
Forces between ICF and ECF
-permeable to H2O based on concentration
-impermeable to electrolytes and proteins
-OSMOTIC FORCES
Forces within ECF and between INT/IV
-freely permeable to electrolytes based on concentration and H2O follows
-impermeable to proteins and large molecules
-STARLINGS FORCES
Osmolality is proportion to
The number of non-dissociable ions
What determines movement of fluid between ECF and ICF?
Osmolality
What is the main component of osmolality?
Na
Cat and dogs normal osmolality
300mOsm/L
Osmolality equation & distribution of ions
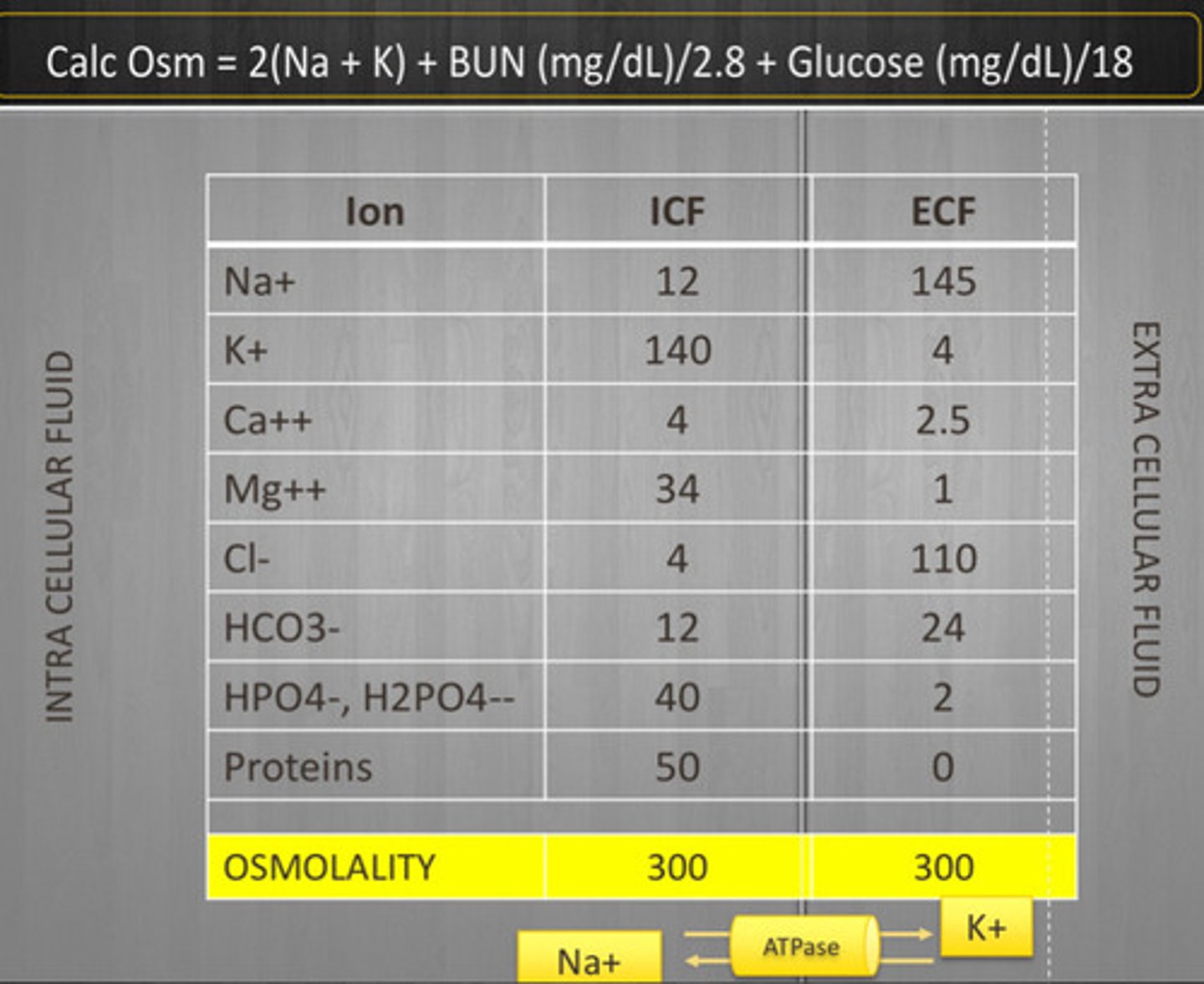
Effective osmoles
-generate osmotic pressure that results in movement of water
-determines tonicity of compartment
-Na, K
Ineffective osmoles
-have osmotic potential but can diffuse!
-no osmotic pressure, no movement of water
-contributes to osmolality but not tonicity
-urea, glucose, D5W acts like H2O
Starling forces equation and diagram
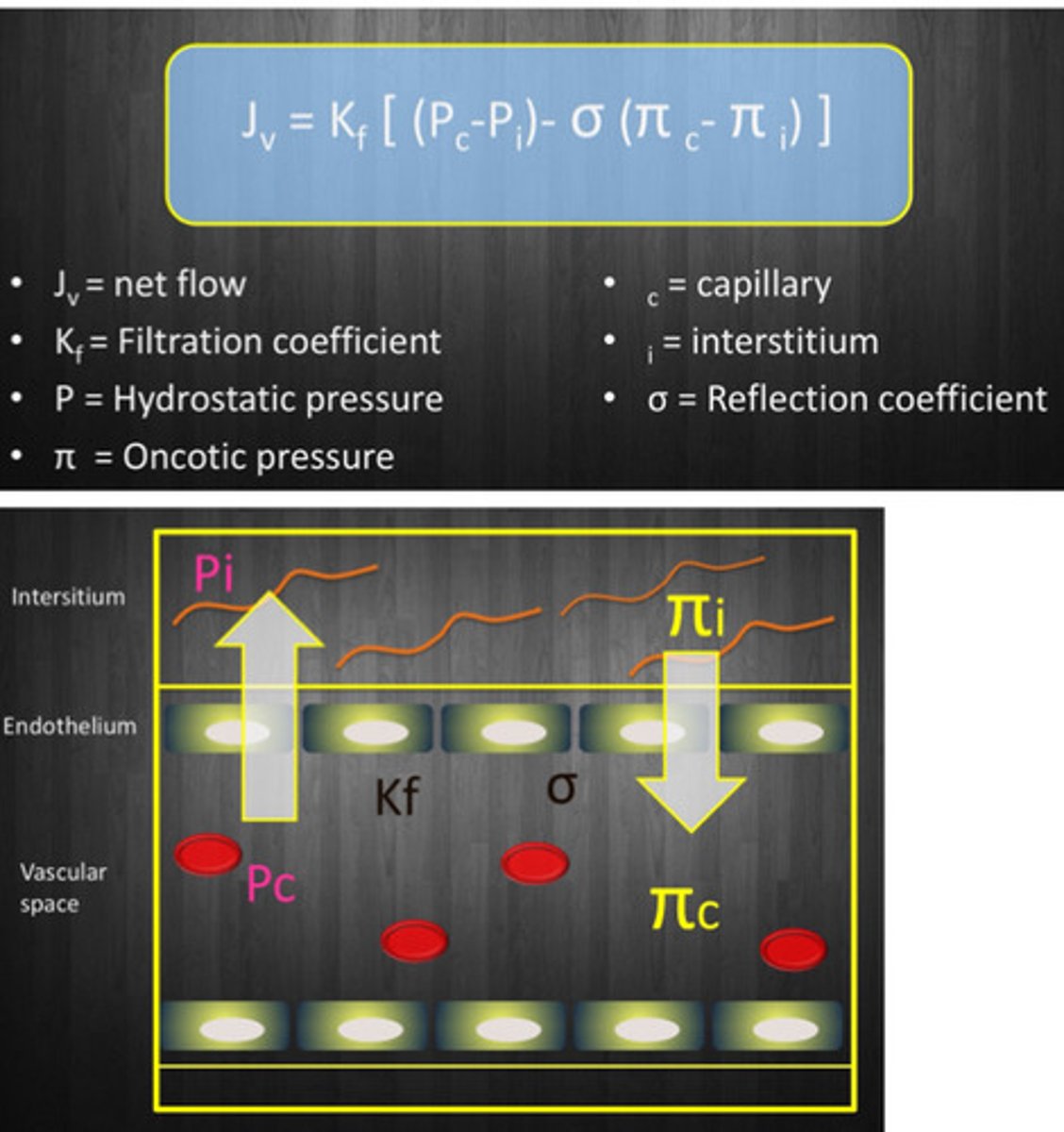
Hydrostatic pressure
-Pc-Pi
-fluid leakage OUT of vessul
-capillary dependent on venous pressure
-venous stasis = increase pressure
Oncotic presure
-fluid to go IN to vessels
-depends on proteins, primarily albumin (# = concentration/molecular wt)
Dog and cat capillary oncotic pressure normals
Dogs = 21-25mmHg
Cats = 23-28mmHg
Filtration coefficient (Kfc)
-will increase as capillary SA increases
-depends on leakiness of vessels
-liver/kidney = leaky
-brain/mm = tight
Reflection coefficient
Permeability of the capillary bed to the protein. Liver low, kidney high
Lungs
Low Kfc & high reflection coefficient = NOT very leaky
Endothelial glycocalyx
Mesh like gel covering the endothelial cells that acts as a barrier to protect the endothelium from things inside of the vessel
Hypotonic osmolality
0.45% NaCl = 154mOsm/L
Isotonic osmolality
0.9% NaCl = 310mOsm/L
Hypertonic osmolality
7.5% NaCl = 1300mOsm/L
Fluid electrolyte divisions
NaCl (LRS) or electrolytes (plasmalyte)
Fluid acid base divisions
-none = acidifying
-lactate (LRS) or gluconate/acetate = alkalinizing
Hypotonic fluid behavior
-distributed in ICF and ECF
-depends on Na in solution
-isotonic portion goes to 100% ECF
-water portion = 67% ICF, 33% ECF
Hypotonic fluids indications
-maintenance
-free water deficit (hypernatremia)
-maintenance when Na restriction is needed (cardiac/renal dz)
Hypotonic fluids contraindications
-shock
-hyponatremia
Hypotonic fluids side effects
-hyponatremia
-rapid admin = acute changes in blood osmolarity/fluid shufts
-neuro sequels and RBC damage
Isotonic fluids behavior
Stays in the ECF (3/4 interstitium, 1/4 intravascular), takes 20-30 min to get to the interstitium
Isotonic fluids indications
-shock
-rehydration
-replacement of loss
Isotonic fluids contraindications
-low oncotic pressure
-severe cardiac/renal dz
-severe, acute bleeding (no large volumes)
-free H2O loss/gain (Na disturbances)
Isotonic fluids side effects
-tissue edema with large volume
-worsening/creation of acid-base disorders
-pro-inflammatory effects
Hypertonic fluids behavior
-fluid from ICF —> IV
-rapidly redistributes across all compartments
-improved cardiac contractility
Hypertonic fluids indications
-shock
-TBI
-hyponatremia
Hypertonic fluids contraindications
-chronic hyponatremia
-severe dehydration
Hypertonic fluids side effects
-cannot be redosed
-transient hypernatremia
-if you give it too fast, can cause vasodilation/bradycardia
Colloids definition
Contains larger molecules that do not readily cross capillary membranes
Colloids behavior
-stays in vascular space
-contributes to oncotic pressure
Synthetic colloids
HES that has prolonged vascular expansion than crystalloids. Used in shock cases and for oncotic support for hypoproteinemia
Side effects of synthetic colloids
-dose dependent coagulopathy >20ml/kg/day! But is less concerning with vetstarch
-renal injury (unclear mechanism, evidence in humans but is poor in animals)
Natural colloids — plasma
-usually use FFP as CRI because canine serum albumin is challenging to buy
-use in acute blood loss, coagulopathy, hypoalbuminemia
Natural colloids — HSA
-stays in the vasculature and pulls fluid from interstitium and ICF
-side effect = type I/III hypersensitivity
-ONE DOSE ONLY!!!
-use in severe sepsis and shock
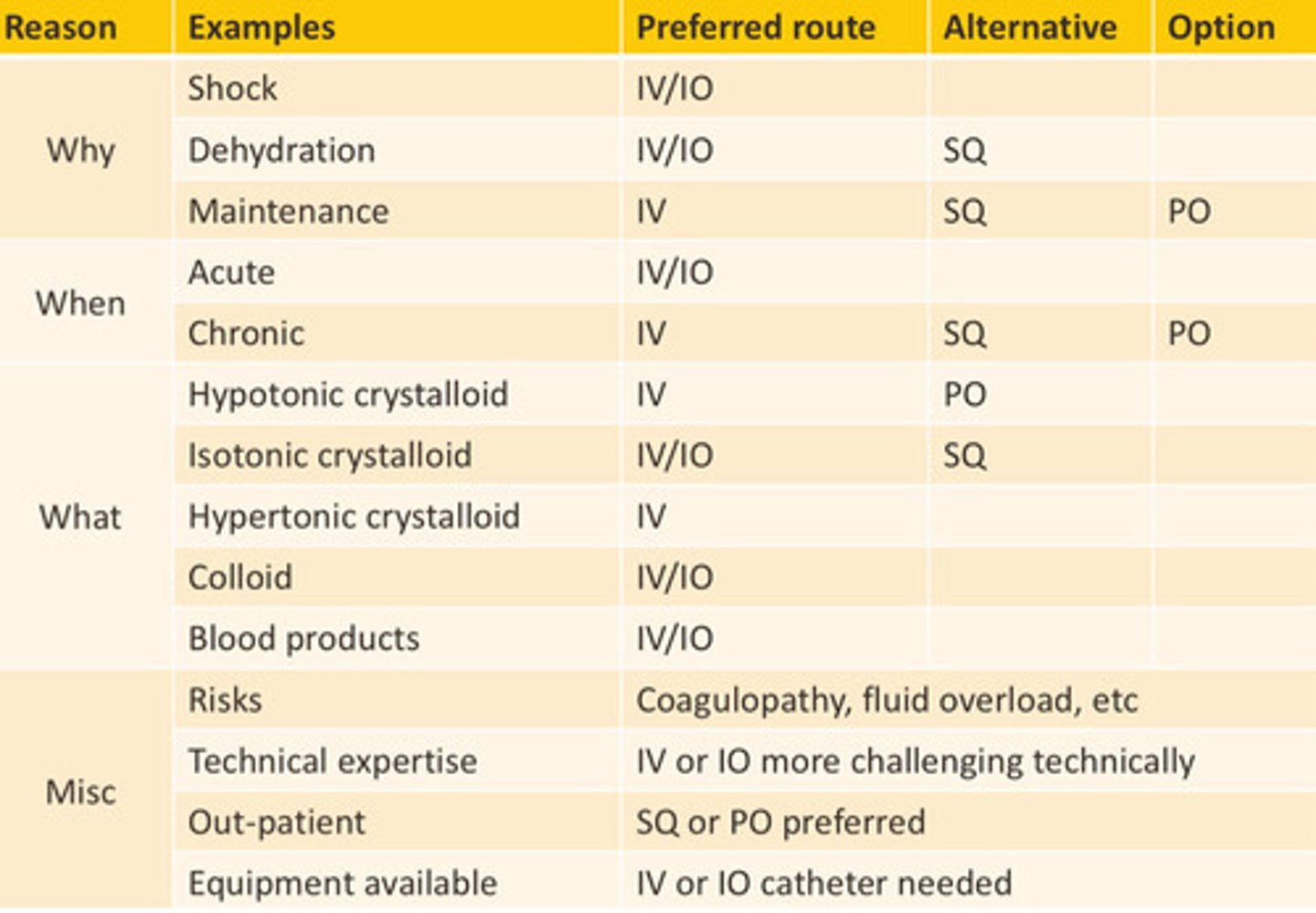
Disadvantages of peripheral IV
Only for relative isotonic samples and usually cannot be used for sampling
Central line
-safer admin of hypo and hypertonic fluids
-serial blood sampling
-more expensive
-do not give for TBI, active bleeding, or high risk of bleeding
Dog/cat IO placement
Proximal humerus, femur, tibia
Bird IO placement
Distal ulnar, proximal tibia
SQ fluids
-isotonic cause hypo/hyper can cause tissue injury
-NOT for severe dehydration or shock
Chart for route
What is dehydration?
Isotonic fluid (salt and water) loss
% dehydration =
% body wt (kg) loss
Dehydration chart
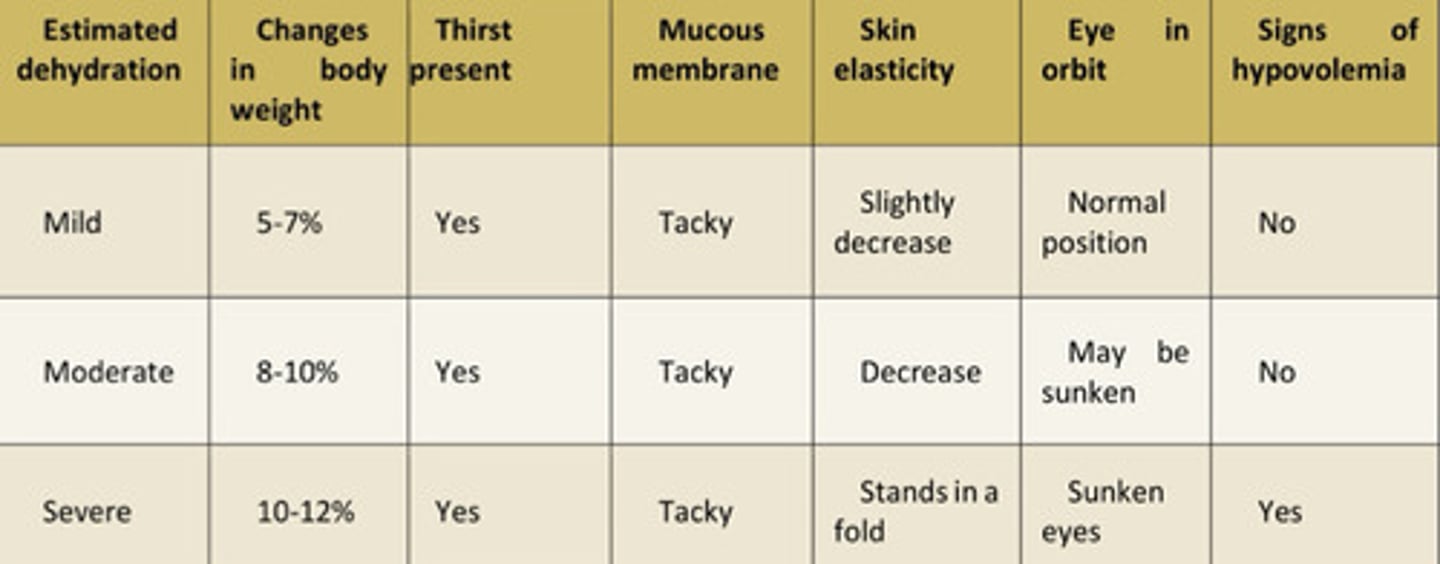
Mucus membrane moistness is influenced by
-evaporation (panting)
-oral ulceration, uremia, etc
-tear production influences (KCS, fan in front of dog, etc)
Skin elasticity influenced by
-youth more elastic than old
-body fat
-breed differences
Eye position
Late finding and is influenced by ocular disease and BCS/nutritional dz
Changes in body weight
Corrected 5% dehydration SHOULD increase patient body weight by 5%
Thirst mechanism
-baroreceptors sense decrease in volume and signals ADH and RAAS
-increase in osmolality of EC space is sensed by osmosreceptors and makes animal seek out water
Hypovolemia
ONLY seen with 10% plus dehydration
Fluid type for dehydration
Isotonic crystalloid
Usual time frame for dehydration
8-12 hours
What impacts how fast?
-severe dehydration = faster
-pt tolerating fluid deficit w/o changes = can be slower
-heart/kidney/lung dz = slower
-cats are less tolerant of larger volumes
More aggressive therapy means
More aggressive monitoring
Maintenance for fluid type
Usually isotonic with K+ or hypotonic is true maintenance and can be good for the renal and heart patients