Chemistry Concepts Flashcards
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key chemistry concepts such as definitions of matter, types of mixtures, atomic structure, and bonding.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Matter
Anything made up of atoms.
Three states of matter
Gas, Liquids, Solids.
Pure Substance
Made up of only one type of particle, including elements and compounds.
Element
Atoms of only one element, e.g., Hydrogen (H).
Compound
Atoms of two or more different elements bonded together, e.g., Water (H2O).
Mixture
Consists of two or more substances physically combined.
Homogeneous Mixture
One or more substances dissolved in another; looks uniform throughout.
Heterogeneous Mixture
Different parts are easily seen and picked out.
Solvent
The substance that does the dissolving in a solution.
Solutes
The substances that get dissolved in a solution.
Physical Properties
Characteristics used to describe how substances behave, e.g., color.
Chemical Properties
Determine when a substance changes to produce a new substance, e.g., flammability.
Qualitative Physical Properties
Described using observations like color or texture.
Quantitative Physical Properties
Measured and expressed with numbers, like density.
Physical Change
A change in physical properties, which is reversible.
Chemical Change
A transformation of a substance into one or more different substances.
Atomic Structure
Made up of protons, neutrons (in the nucleus), and electrons (move around nucleus).
Alkali Metals
Group 1 elements, e.g., Lithium (Li), Sodium (Na).
Alkaline Earth Metals
Group 2 elements, e.g., Beryllium (Be), Magnesium (Mg).
Halogens
Group 17 elements, e.g., Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl).
Noble Gases
Group 18 elements, e.g., Helium (He), Neon (Ne).
Atomic Number
The number of protons in an atom.
Mass Number
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus.
Stable Octet
Having a complete valence shell, usually with 8 electrons.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Ionic Compounds
Formed by transfer of electrons, usually solid at room temperature.
Molecular (Covalent) Compounds
Formed by sharing electrons, usually between nonmetals.
Remember to study Lewis dot diagrams and Bohr Rutherford diagrams
OK
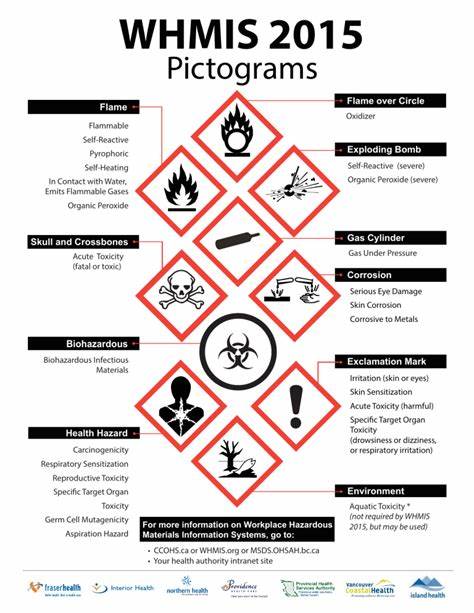
WHMIS Symbols
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System symbols used to communicate hazards.