Organic Chemistry Exam Style Qs
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is meant by the term catalyst? (2)
m1: a substance which increases the rate of reaction m2: and is chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction
Explain how a catalyst works (2)
m1: provides an alternative pathway m2: alternative path has a lower activation energy
Give three reasons why cracking is carried out (3)
m1: over/greater supply of long-chain hydrocarbons m2: high demand for short-chain hydrocarbons m3: alkenes used to make polymers
One of the compounds sometimes present in crude oil has the formula
C6H12S
Explain why it is important to remove this compound from a fuel (2)
m1: forms sulfur dioxide when burned m2: which causes specified problem for the environment
Two reactions that can occur when hydrocarbon A is burned in air are represented by these equations.
Equation for reaction 1 CH4 + 2O4 → CO2 + 2H2O
Equation for reaction 2 CH2 + 1½O2 → CO + 2H2O
Explain why a different product is formed in reaction 2 and why this product is dangerous.
m1: incomplete combustion m2: carbon monoxide is a toxic/poisonous gas m3: reduces capacity in the blood to carry oxygen
Explain what is meant by the term isomerism (2)
m1: compounds with the same molecular formula but a m2: different displayed formula
When heptene is added to bromine water, and the mixture is shaken, a reaction occurs.
State the type of reaction and give the colour of the bromine water before and after the reaction with hepten (3)
m1: type of reaction → addition m2: colour before → orange m3: colour after → colourless
Compare the hydrocarbons in fractions D and F in terms of
boiling point
size of molecules
viscosity
(3)
m1: D have a higher boiling point m2: larger molecules m3: more viscious
The alkanes are a homologous series of hydrocarbons obtained from the fractions in crude oil.
Describe how crude oil is separated into fractions in industry. (4)
m1: fractional distillation m2: crude oil vaporised m3: fractions condense m4: fractions have different boiling points
Explain why some compounds are described as hydrocarbons. (2)
m1: they all contain hydrogen and carbon m2: only
All alkanes in a homologous series have the same general formula
State two other features of a homologous series (2)
m1: similar chemical properties m2: gradual change m3: same functional group
Describe how the boiling point, colour and viscosity of the fuel oil fraction differ from those of the gasoline fraction. (3)
m1: have higher boiling points m2: have higher viscosities m3: darker in colour
Compare the hydrocarbons in fractions D and F in terms of
boiling point
size of molecules
viscosity
(3)
m1: higher boiling point m2: larger molecules m3: more viscious
Explain why cracking is an important process in the oil industry. (4)
m1: produces smaller, shorter chain molecules m2: which have greater demand m3: smaller chain molecules burn more cleanly m4: crude oil has a surplus of long-chain molecules m5: alkenes used to make alcohols/polymers/etc
The alkanes are a homologous series of hydrocarbons obtained from the fractions in crude oil.
Describe how crude oil is separated into fractions in industry. (4)
m1: fractional distillation m2: crude oil vaporised m3: fractions condense m4: fractions have different boiling points
State the meaning of the term biodegrade (2)
m1: polymer breaks down m2: by bacteria
What is the meaning of the term polymer? (2)
m1: long chain molecule m2: formed when many small molecules join together
Explain why addition polymers that are buried in landfill sites remain chemically unchanged for many years (2)
m1: they do not biodegrade m2: because they are inert/unreactive
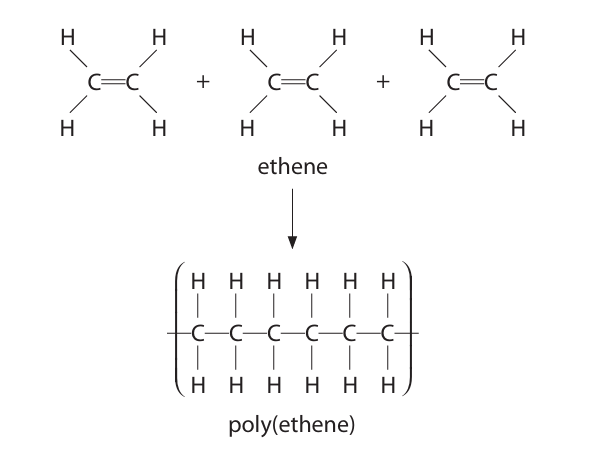
Use the diagram to state two changes that occur during the formation of poly(ethene). (2)
m1: one of the bonds in the double bonds break m2: many molecules join together
These are two methods used to dispose of the polymer
burying in landfill sites
burning
Discuss the environmental problems caused by these two methods of disposal.
m1: polymers will remain in landfill indefinitely m2: as they are inert and do not biodegrade m3: burning produces greenhouse gases m4: and causes global warming as greenhouses gases trap warm air in the atmosphere m5: combustion produces toxic gases